Ototoxizität - Klinik für Strahlentherapie und Radioonkologie
Werbung

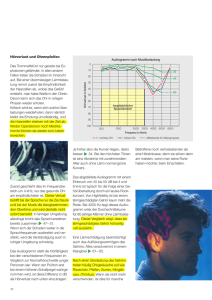
Ototoxizität Aspekte Chemotherapieinduzierter Hörverlust (Cisplatin) Strahlentherapieinduzierter Hörverlust Kategorisierung (Grading) Hörverlust bei Kombination Radiotherapie – Chx. Zeitpunkt (Radiotherapie, Chemotherapie) Protektion Ototoxizität Spektrum des Hörens (Frequenz und Lautstärke) Hall et al., 1997 Ototoxizität Mechanismus des Hörverlustes Zielstrukturen Haarzellen (akut ?) Spiralganglion Stria vasacularis (spät ?) Cisplatin und RT ähnliche Effekte RT : Entzündung und Atrophie (Hoistad et al, 1998) Dosisgrenzwerte RT Kinder : ab 30-35 Gy (Hua, et al., 2009) Erwachsene ab 48-60 Gy (Chen et al., 2006, Bhandare et al., 2007 Ototoxizität Hörverlust nach Cisplatin Ototoxizität Cisplatin Typisch : Hochtonverlust / zeitnah zur Applikation Vor Therapie Nach 1 Kurs Cisplatin (200mg / qm) Nach 2 Kursen (400mg / qm) rechts Grad 0 Grad 1 Grad 2 links Brock et al., 1991 Ototoxizität Cisplatin Hörverlust / Zahl der Kurse (4000 Hz) Schell et al., 1989 Ototoxizität Cisplatin Longitudinaler Verlauf des Hörverlustes Median 135 Tage bis zum Hörverlust Knight et al., 1989 Ototoxizität Hörverlust nach alleiniger Bestrahlung Ototoxizität Hörverlust nach alleiniger Radiotherapie 155 „Ohren“ / Hochtonber. : Schwellendosis ca 32-35 Gy (Epend, LGG, Kranioph / keine Chx.) Hua et al., 2008 Ototoxizität Hörverlust nach alleiniger Radiotherapie 78 Kinder / 155 „Ohren“ / Mittl. Tonber. : Schwellendosis ca 50 Gy (Epend, LGG, Kranioph / keine Chx.) Hua et al., 2008 Ototoxizität Intervall RT - Hörverlust nach alleiniger Radiotherapie 78 Kinder / 155 „Ohren“ (Epend, LGG, Kranioph / keine Chx.) Medianes Intervall : 3,4 Jahre Hua et al., 2008 Ototoxizität Niedriggradige Gliome / Hörverlust nach RT / Memphis Serie Verzögerter Eintritt / progredienter Verlust ? Armstrong et al., 2010 Ototoxizität Hörverlust nach Kombination Cisplatin / Bestrahlung A. Erwachsene (Radio-chx. mit Cisplatin) B. Cisplatin nach RT 1. Medulloblastom standard risk 8 x CCNU / Cisplat. (75 mg / qm) / VCR RT CSA / boost HSG / Tu-bett C. Cisplatin vor RT 2. Nichtsem. KZT (4 x 100 mg / qm Cisplat.) RT lokal (M0) / CSA / boost pinealis (M1-3) Ototoxizität Nasopharynx-Ca / Erwachsene (med. Alter 50 J.) 87 Pat. / simultan Cispl. 2-3 x 100 mg / qm, med. Dosis 57,4 Gy Einfluß Kategorisierung Chan et al, 2009 Ototoxizität Nasopharynx-Ca / Erwachsene (med. Alter 50 J.) 87 Pat. / simultan Cispl. 2-3 x 100 mg / qm, med. Dosis 57,4 Gy Einfluß Cisplatindosis / RT Dosis Chan et al, 2009 Ototoxizität Nasopharynx-Ca / Erwachsene (med. Alter 50 J.) 87 Pat. / simultan Cispl. 2-3 x 100 mg / qm, med. Dosis 57,4 Gy Einfluß Dosisgradient / geom. Präzision Chan et al, 2009 Ototoxizität Kombination Radiotherapie - Cisplatin Hörverlust nach alleinig Cisplatin versus RT + Cisplatin in Abhängigkeit von der Cisplatindosis Nur Cisplatin Cisplatin - RT Schell et al., 1989 Ototoxizität Medulloblastom Radiotherapie CSA – Cisplatin (Dosis – Wirkungsbeziehung ? Additiver Effekt ? Unklare Datenlage) Autor Pat Technik /Dosis (Gy) CochleaDosis (Gy) Nachbeob. Grad 3-4 Ototox. Huang 2002 15 CSA : 23.4 PF : 36 Tumor : 55.8 (IMRT) 36.4 med. 18 Mon. 13% Packer 2006 379 CSA : 23.4 PF : 55.8 Tumor : - n.m. (55.8 Gy ? n.m. Arm A : 28% Arm B : 23% Fouladi 2008 97 CSA : 23.4 PF : 36 Tumor : 55.8 (3 D konf.) 49 Gy med. 19 Mon. 22,7% (4 x 75 mg/qm Cispl. +-Amifost.) Ototoxizität Erwachsene : 325 Pat. mit Kopf-Hals Tumoren (alleinige RT, Radio-chx. / Cisplatin 2-3 x 100mg / qm) (Schwellendosis / Einfluß der Akzelerierung- Fraktionierung) Bhandare et al., 2007 Ototoxizität SIOP PNET IV / Fraktionierung ? Ototoxicity- 3 years after therapy Standard RT versus HFRT n= 82 n= 75 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% Unterschied erst nach mehr als 3 J. Nachbeob. erkennbar ? 20% 10% 0% Standard RT HFRT <=grade1 grade=2 >= grade 3 Ototoxizität - HIT 2000 Radiotherapie Medulloblastome / Hörverlust (Zeitschiene) Grad HIT Audiogramme am Ende der CHX Audiogramme 3-5 Jahren nach Ende der Therapie Alle RT- Hfx RT Pat. n = 83 Pat. n =176 Konv. RT n = 85 Pat. HIT 91 Pat n =8 Alle RT-Pat n =176 Hfx Konv. RT n = RT n = 83 85 Pat. Pat. HIT 91 Pat n = 8 36/176 20% 15/83 18% 20/85 24% 1/8 13% 0/176 0% (-20%) 0/83 0% 0/85 0% 0/8 0% Grad 1 25/176 14% 16/83 19% 9/85 11% 0/8 0% 30/176 17% (+3%) 13/83 15% 13/85 15% 4/8 50% Grad 2 42/176 24% 18/83 22% 20/85 24% 4/8 50% 49/176 29% (+5%) 25/83 30% 23/85 27% 1/8 13% Grad 3 12/176 7% 5/83 6% 7/85 8% 0/8 0% 18/176 10% (+3%) 8/83 10% 10/85 12% 0/8 0% Grad 4 5/176 3% 1/83 1% 3/85 4% 1/8 13% 0 (-3%) 0 0 0 Keine Angaben: n = 56 n =28 n = 26 n=2 n =79 n =37 n =39 n =3 Grad 0 (kein Hörverlust) Ototoxizität - HIT 2000 Radiotherapie Medulloblastome, nach CHX-Ende, n =54/81 Pat. (66%) Hörverlust (Audiogramm + Innenohrdosis : 81 Pat.) Hörverlust bei Innenohrdosis von: HIT Grad 0 HIT Grad 1 HIT Grad 2 HIT HIT Grad 3 Grad 4 (kein Hörverlust) (15dB) (16-30 dB) (31-60 dB) > 55Gy n = 14 n =2 14% n =18 38% n=7 50% n =6 13% n=4 28% n = 14 30% n =1 7% n =7 15% n =0 0% n =2 4% n=7 35% n=5 25% n =6 30% n =1 5% n =1 5% 40-54 Gy n = 47 < 40 Gy n = 20 Ototoxizität - HIT 2000 Radiotherapie Medulloblastome, 3-5 Jahre nach Therapieende, n = 66 / 66 (100%) Hörverlust (Audiogramm + Innenohrdosis : 66 Pat.) Hörverlust bei Innenohrdosis von: HIT Grad 0 > 55Gy n = 12 n=0 40-54 Gy n = 39 n=0 < 40 Gy n = 15 n=0 HIT Grad 1 (15dB) HIT Grad 2 HIT (16-30 dB) Grad 3 (31-60 dB) n=2 16 % n =14 36% n=7 58 % n = 16 41% n =3 25 % n =9 23% n=4 26 % n =8 53% n =3 20% HIT 2000 Radiotherapie (Deutschland) HIT 2000 / Hörverlust + / - Chx (Medulloblastom stand. risk / Ependymom) Hörverlust bei Innenohrdosen <40 Gy bis > 55 Gy 120 % Hörverlust 100 80 Hörverlust bei MB hfx 60 Hörverlust bei MB konv Hörverlust bei EP 40 20 0 < 40 Gy 40-54 Gy Innenohrdosis > 55 Gy Ototoxizität Kombination Radiotherapie – Cisplatin Simultane Applikation / Fallberichte n = 4 Pat. Neuroblastom 4 x 90 mg / qm Cispl. Schwelle Kritische Perzeptionszone n = 3 Pat. 30-54 Gy (unklare Cochleadosis) 200 – 300 mg/qm Cispl. Walker et al., 1989 Ototoxizität Radiotherapie / zusätzliche Faktoren Tumorlokalisation, Shunt, Chx. vor RT (Dosis > 32 Gy, mittlere Freq.) Longitudinale Änderung des Schwellenwertes Merchant et al., 2004 Ototoxizität Hörverlust nach Carboplatin / Bestrahlung Ototoxizität Hörverlust Cisplatin / Carboplatin (99 Kinder / unterschiedl. Tu-Erkrankungen) Dean et al., 2008 Otototoxizität Hörverlust Cisplatin / Carboplatin (Neuroblastom) A : vor Therapie B : nach Cisplatin 400mg/qm C : nach zusätzlich Carboplatin 1700mg/qm Knight et al., 2005 Ototoxizität Hörverlust Protektion Ototoxizität Protektion durch RT Technik / CSA bei Medulloblastom (8 x Packer) 11 Pat. konv. : 23,4 Gy CSA / 54 Gy PF 15 Pat. IMRT : 23,4 Gy CSA / 36 Gy PF / 55.8 Gy Tumorbett Tumorbett / IMRT HSG / konv. Tumorbett HSG Huang et al., 2002 Ototoxizität Protonentherapie Medulloblastom / Aufsättigung d. HSG / Kinder Protonen IMRT Tarbell et al., 2003 Ototoxizität Protektion durch RT Technik Photonen versus Protonen bei RT Tumorregion 10 Fälle mit Ependymom integrale Dosisverteilung linkes Innenohr Photonen Protonen Merchant et al., 2008 Ototoxizität Protektion durch Amifostin / CSA bei MB (4 x 75mg / qm Cispl.) A : 75 Pat. : 23,4 Gy CSA / 36 Gy PF (3-d-konf) 55,8 Gy Tumorbett (3-d) B : 22 Pat. : 23,4 Gy CSA / 55.8 Gy Tumorbett (3-d-konf) Amifostin signifikant protektiv (p = 0.047, multivar. Analyse) Einfluß der RT Dosis unklar (p = n.s in uni- und multivar. Analyse) 82 Pat : Nachbeob. nur 2 Jahre / Cisplat.-dosis 299-301 mg/qm median Grad A Kein Amifostin A Amifostin B Amifostin Cochleadosis Grad 3-4 13 (37,1%) 6 (15%) 3 (13,6) Mean 49.4 Gy Keine Grad 3-4 22 (62,9%) 34 (85%) 34 (86,4%) Mean 49 Gy Gesamt 35 40 22 56 Fouladi et al., 2008 Ototoxizität Protektion / COG-ACCL0431 Phase III Randomized Study of Sodium Thiosulfate in Preventing Ototoxicity in Young Patients Receiving Cisplatin Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Germ Cell Tumor, Hepatoblastoma, Medulloblastoma, Neuroblastoma, Osteosarcoma, or Other Malignancy Primary To compare the efficacy of sodium thiosulfate vs observation in preventing hearing loss Secondary To compare the mean change in hearing thresholds for key frequencies in these patients. To compare the incidences of cisplatin-related grade 3 and 4 nephrotoxicity and grade 3 and 4 cytopenia in these patients. To compare the event-free survival and overall survival of these patients. To evaluate the association of two key gene mutations (TPMT and COMT) with the development of cisplatin-induced hearing loss in these patients. Ototoxizität Kategorisierung (Grading) Ototoxizität Zusammenfassung I Radiotherapie verursacht Hörverlust Hoher Frequenzbereich (wie Cisplatin) Verzögertes Auftreten (Nachb. > 3-5 Jahre notwendig) Schwellendosis (Kinder empfindl. als Erwachsene ?) ca 30-35 Gy (hoher Frequenzbereich) ca 50 Gy (mittlerer Frequenzbereich) (COG Empfehlung, 2010 : Innenohrdosis med < 30-35Gy) Fraktionierung ? Interaktion mit Ko-Faktoren Cisplatin (Carboplatin ?) Tumorlokalisation infratent., (Surrogat für OP ?) Shunt Chx. vor RT Ototoxizität Zusammenfassung II Protektion Amifostin ? (Cisplatin) RT ? Natrium Thiosulfat ? (Cisplatin) RT ? Bestrahlungstechnik (IMRT , Protonen) Probleme Dokumentation der Dosis (Dosisgradient) ? Hetereogene, individuelle Verläufe Ausmaß der Interaktion RT-Dosis-Cisplatin ? RT Dosis wichtiger als medikamentöse Protektion Simultane Interaktion Carboplatin RT-Dosis unbekannt (Radio (CSA)-Chx- mit Carboplatin) Longitudinales Monitoring der Hörfunktion (mind. 5 Jahre) Implementierung von Dose constraints Danke für Ihre Aufmerksamkeit Vielen Dank für Ihre Mitarbeit Wir stehen für Auskünfte / Beratungen jederzeit zur Verfügung Reference Centre for Radiotherapy, Dept. for Radiation Oncology University of Leipzig Johannisallee 34, 04107 Leipzig/Germany Phone: 0049-341-9718542 Co-Workers: A. Klein; A. Lehmann, Dr.rer.nat. S. Klagges, Dr. med. M. Hindemith