Combivis 5 und IP
Werbung

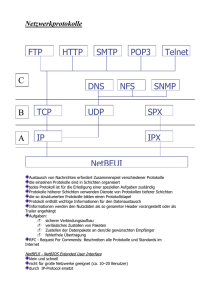
Entwicklungsinformation Development Information COMBICOM IP Dienste COMBICOM IP Services C0.F5.01I-K003 KEB Info 01/2001 COMBICOM IP Service Deutsch COMBIVIS 5 UND IP ...........................................................................................................................................3 BESCHREIBUNG KEB PROTOCOL IP SERVER ..........................................................................................4 DATENPORT ..........................................................................................................................................................5 KONFIGURATION ÜBER BROWSER.........................................................................................................................6 KONFIGURATION ÜBER TELNET ............................................................................................................................7 EINSTELLUNGEN IN COMBIVIS ....................................................................................................................8 English COMBIVIS 5 AND IP ...........................................................................................................................................9 DESCRIPTION KEB PROTOCOL IP SERVER.............................................................................................10 DATA PORT .........................................................................................................................................................11 CONFIGURATION BY BROWSER ...........................................................................................................................12 CONFIGURATION WITH TELNET ..........................................................................................................................13 SETTINGS IN COMBIVIS.................................................................................................................................14 2 COMBICOM IP Service ANTRIEBSTECHNIK Combivis 5 und IP Erstmals in COMBIVIS 5 steht auch ein IP-Treiber zur Kommunikation über schnelle Netzwerke (Ethernet, Token-Ring usw.) zur Verfügung. Der COMBIVIS IP-Protokolltreiber versendet Telegramme über die IP-Dienste TCP oder UDP an einen einstellbaren Host. Dieser Host ist z.B. ein Gatewayprogramm wie der KEB Protocol IP Server, der COM-Server der Firma W&T oder eine beliebige andere Vorrichtung zur Datenübermittlung an die Frequenzumrichter mittels geeignetem Protokoll. Innerhalb der IP-Telegramme werden DIN66019-II-Frames gekapselt, die auch eine Adressierung einzelner Umrichter auf dem Zielgateway ermöglichen. Damit ist z.B. folgende Kommunikation über Netzwerke möglich: COMBIVIS 5 IP Server PC2 PC1 232/485 RS 485 (DIN66019II) Ethernet (IP) Router Ethernet (IP) FU FU FU Die beiden PC's sind über ein normales Netzwerk (Intranet/Internet) verbunden, wobei die Topologie eine untergeordnete Rolle spielt. So kann z.B. die Verbindung auch über eine ISDN-Leitung weitergeführt werden, wichtig ist nur dass das IP-Protokoll die Daten von PC1 zu PC2 und zurück überträgt. Auf PC1 läuft COMBIVIS 5, PC2 beherbergt den KEB-IP-Server, der die IP-Telegramme wieder über DIN66019II, HSP5 oder InterBus auf die Umricher gibt. Weitere mögliche Feldbusprotokolle werden folgen. Es ist auch eine Umsetzung über externe Gateways möglich. Als Beispiel dient der COM-Server Industrie, Fa. W&T (Wiesemann & Theis GmbH, www.WuT.de). Dieser COM-Server ist eine kleine Box mit den Abmessungen 105*75*22 mm, externem Steckernetzteil und passt in jeden Schaltschrank. Empfehlenswert ist die Ausführung mit RS485-Schnittstelle (Störsicherheit, Multi-Inverterbetrieb). COMBIVIS 5 Ethernet (IP) COMServer RS 485 PC Ethernet (IP) Router FU FU FU Auch hier sind der PC und der COM-Server über ein normales Netzwerk verbunden. Auf dem PC läuft COMBIVIS 5, der COM-Server gibt die empfangenen IP-Daten direkt über seine RS485-Schnittstelle als DIN66019II-Telegramme aus und die Antwort über IP zurück an COMBIVIS. Da auf dem COM-Server keine lokalen Protokolle verfügbar sind, kann hier nur über DIN66019 oder DIN66019II mit den Umrichtern kommuniziert werden. 3 COMBICOM IP Service Beschreibung KEB Protocol IP Server Die Software KEB Protocol IP Server dient zur Umsetzung von IP-Telegrammen, die über den IP-Treiber von COMBIVIS 5 versendet werden, auf serielle Bussysteme wie HSP5, DIN66019 oder Feldbussystemen wie Interbus, CAN oder Profibus. Das Programm läuft unter WIN95/98/NT auf Rechnern mit aktiviertem IP-Protokoll. Bei Verwendung von Feldbussystemen ist zusätzlich eine passende Anschaltkarte erforderlich. Das Programm wird auf dem Zielrechner gestartet und zeigt ein kleines Statusfenster, in dem die verbundenen Benutzer mit ihren Adressen und Diensten gezeigt werden. KEB Protocol IP Server Ethernet Network Interface Card IP Protocol stack DATA TELNET HTTP Inverter access Configuration Configuration Monitoring TCP/UDP Port 8000 TCP Port 23 TCP Port 80 WriteData Read Data Set Properties Set Properties Read Data Protocol Drivers DIN66019II HSP5 Interbus PC Hardware COM1..4 COM1..4 RS232 RS232 RS485 F4 4 F5 G4 ISA F4 RS485 TTL F0 F5 Loop2 Profibus PCI-Can PCMCIA-Can ProfiBoard F4 F4 GW F5 F4 CAN BK F5 F5 COMBICOM IP Service ANTRIEBSTECHNIK Datenport Die Übertragung der Datenframes erfolgt über IP-Port 8000 mit dem Diensten TCP oder UDP.(Siehe Abschnitt 'Einstellungen in COMBIVIS'). Dabei werden den Umrichteradressen (0..239) lokal bestimmte Protokolle zugewiesen, d.h. in COMBIVIS 5 sind z.B. die Umrichter 0 bis 3 auf IP-Protokoll gestellt, im IP-Server ist Umrichter 0 auf HSP5, der Rest auf DIN66019 konfiguriert. Das HSP5-Protokoll wird z.B. auf COM1 abgewickelt, DIN66019 über COM2 des IP-Servers versendet. Ausserdem können mehrere COMBIVIS 5 Benutzer gleichzeitig die Umrichter eines IP-Servers benutzen: FU0 : IP FU1 : IP FU2 : IP FU3 : IP COMBIVIS 5 PC FU0 : IP FU2 : IP FU0 : HSP5 FU1 : DIN66019 FU2 : DIN66019 FU3 : DIN66019 COMBIVIS 5 PC HSP5 : COM1 38400 BD DIN66019 : COM2 9600 BD KEB Protocol IP Server Ethernet (IP) COM1 COM2 232/485 RS232 (HSP5) RS 485 (DIN66019) Adapterkabel HSP5 FU0 FU1 FU2 FU3 5 COMBICOM IP Service Konfiguration über Browser Die Einstellung des KEB Protocol IP Servers erfolgt mittels eines Standard-Browsers über HTTP-Port 80. Hier können menügeführt alle Einstellungen verändert sowie alle Umrichterparameter ausgelesen und dargestellt werden. Nach Eingabe des Hostnamens (hier 192.168.2.110) wird die Startseite sichtbar, von der aus alle weiteren Funktionen erreichbar sind: 6 COMBICOM IP Service ANTRIEBSTECHNIK Konfiguration über Telnet Zusätzlich ist auch ein Konfigurationsport (TCP/IP Port 23) verfügbar, über den mittels dem Telnet-Programm von Windows die Einstellungen gesetzt werden können. Nach Eingabe des Hostnamens (hier 192.168.2.110) baut Telnet eine TCP-Verbindung auf und das Hauptmenü erscheint: KEB Protocol IP-Server V2.0 Telnet configuration port Running on Host:Kaiser.dns-keb-domain [192.168.2.110] This is the KEB IP Server (1) Status display (2) Protocol assignments (3) HSP5 setting (4) DIN66019 setting (5) CAN setting (6) Profibus setting (7) Change location text (8) IP client list (9) Set password Menüpunkte werden durch Eingabe der Zahl und der ENTER-Taste ausgewählt. (1) Status display : Zeigt die aktuell verwendeten lokalen Protokolle sowie alle Benutzer mit ihren Diensteinstellungen und IP-Adressen/Ports an. (2) Protocol assignments : Hier wird die aktuelle Zuordnung Umricher<->Protokoll gezeigt: LOCAL PROTOCOL ASSIGNMENTS: Inv 0 HSP5 Inv 1 DIN66019 Inv 2 DIN66019 Inv 3 DIN66019 Danach kann sofort eine Einstellung durch Eingabe der Umrichteradresse geändert werden: Enter inverter address (0..239)4 (Umrichter 4 ändern) (0) = Offline (1) = DIN66019 (2) = HSP5 (3) = InterBus (4) = CAN (5) = Profibus 1 (Auf DIN66019 stellen) Soll keine Änderung erfolgen, ist nur ENTER zu drücken. Um eine Zuordnung aufzuheben wird für den gewünschten Umrichter OFFLINE ausgewählt. (3) HSP5 setting : Anzeige und Einstellung der Schnittstellenparameter für HSP5. (4) DIN66019 setting : Anzeige und Einstellung der Schnittstellenparameter für DIN66019. Achtung: Der selbe COM-Port darf natürlich nicht zwei Protokollen zugewiesen werden, da das 2.Protokoll dann nicht arbeiten kann. (5) CAN setting : Anzeige und Einstellung der CAN-Parameter. (6) Profibus setting : Anzeige und Einstellung der Profibus-Parameter. (7) Change location text : Eingabe der Hauptmenü-Überschrift zur Identifikation des Standorts dieses IPServers. 7 COMBICOM IP Service (8) IP client list : Eingabe und Änderung der zugelassenen IP-Client Adressen. Hier werden freigegebene Adressen von Benutzern des IP-Servers eingetragen. Nur diese Adressen sind auf dem Datenport zugelassen, andere Verbindungen werden nicht beantwortet. Ist diese Liste leer, so kann dieser IP-Server von jeder Station benutzt werden. Eine bestehende Adresse wird durch nochmalige Eingabe aus der Liste gelöscht. (7) Set password : Eingabe oder löschen des Passwortes. Der Konfigurationsport des IP-Servers kann durch Passwort geschützt werden. Ein gesetztes Passwort wird beim Verbindungsaufbau abgefragt. Ist das Passwort nicht korrekt, wird die Verbindung sofort wieder getrennt. Durch Eingabe eines Leerzeichens, gefolgt von ENTER, wird das Passwort gelöscht (Kein Passwortschutz des Konfigurationsports). Einstellungen in COMBIVIS Im Menü Bearbeiten->Konfiguration->IP sind folgende Einstellungen erforderlich: Host: Hier wird die IP-Adresse des IP-Servers oder des COM-Servers eingetragen. Wenn im IP-Netzwerk auch ein DNS-Server verfügbar ist, kann auch der Stationsname des Rechners, auf dem der KEB-IP-Server läuft, eingetragen werden (nicht möglich mit dem W&T COM-Server). Port: Der KEB-IP-Server und der COM-Server antworten auf Port 8000. Andere Systeme haben eventuell andere Portnummern. Time-Out-Zeit : Dies ist die Zeit in millisekunden, in der auf eine Antwort über das IP-Protokoll gewartet wird. Diese Zeit sollte nicht zu kurz eingestellt sein, da je nach Verbindungsweg über Router oder Internet-Server eine längere Zeitspanne vergehen kann. In lokalen Netzen ist ein Wert von 500ms geeignet. TCP oder UDP: Diese Einstellung legt den Dienst, der über IP benutzt wird, fest. TCP ist verbindungsorientiert, d.H. zunächst wird eine logische Verbindung aufgebaut, alle Telegramme werden auf IP-Ebene überwacht und bei Verlust automatisch wiederholt. Dies kann zu längeren Laufzeiten führen und ist für COMBIVIS nicht nötig, da die Telegrammwiederholung bereits vom COMBIVIS erledigt wird. UDP verwendet keine logische Verbindung, die Telegramme werden ohne Verbindungsüberwachung gesendet. Der KEB-IP-Server kann beide Dienste bedienen, beim COM-Server müssen für den UDP-Dienst zunächst im COM-Server einige Einstellungen geändert werden. Weiterhin kann der COM-Server nur eine Verbindung zu einer COMBIVIS-Station haben, der KEB-IP-Server kann mehrere Verbindungen gleichzeitig bearbeiten. 8 COMBICOM IP Service ANTRIEBSTECHNIK Combivis 5 and IP For the first time in COMBIVIS 5 an IP-driver is also available for communication over fast networks (Ethernet, Token Ring etc.). The COMBIVIS IP-protocol driver sends telegrams over the IP-services TCP or UDP to an selectable host. This host is for example a gateway program like the KEB Protocol IP Server, the COM-server of company W&T or any other device for data transfer to the frequency inverters by means of a suitable protocol. Within the IP-telegrams DIN66019-II-frames are enclosed, which also permit the addressing of individual inverters on the target gateway. Thus the e.g. following communication is possible over networks: COMBIVIS 5 IP Server PC2 PC1 232/485 RS 485 (DIN66019II) Ethernet (IP) Router Ethernet (IP) FU FU FU The two PC’s are connected over a standard network (Intranet/Internet), at that the topology plays only a subordinate role. Thus the connection can e.g. also be maintained via an ISDN line, it is only important that the IP-protocol transmits the data from PC1 to PC2 and back. On PC1 runs COMBIVIS 5, PC2 accomodates the KEB-IP-server, which gives the IP-telegrams again over DIN66019II, HSP5 or InterBus onto the inverters. Further possible fieldbus protocols will follow. A conversion is also possible via external gateways. The COM-server industry, company W&T (Wieseman & Theis GmbH, www.WuT.de) serves as example. This COM-server is a small box with the dimensions 105*75*22 mm, external plug-in power supply unit and fits into every control cabinet. Recommended is the design with RS485 interface (interference immunity, multi-inverter operation). COMBIVIS 5 Ethernet (IP) COMServer RS 485 PC Ethernet (IP) Router FU FU FU In this case the PC and the COM-server are also connected over a standard network. COMBIVIS 5 runs on the PC, the COM-server outputs the received IP-data directly via its RS485 interface as DIN66019II-telegrams and gives the response back to COMBIVIS via IP. Since no local protocols are available on the COM-server, the communication with the inverters can take place only over DIN66019 or DIN66019II. 9 COMBICOM IP Service Description KEB Protocol IP Server The software KEB Protocol IP Server serves for the conversion of IP-telegrams, which are sent over the IP-driver of COMBIVIS 5, to serial bus systems such as HSP5, DIN66019 or field bus systems like Interbus, CAN or Profibus. The program runs under WIN95/98/NT on computers with activated IP-protocol. When using fieldbus systems a suitable interface card is required in addition to it. The program is started on the target computer and shows a small status window which displays the connected users with their addresses and services. KEB Protocol IP Server Ethernet Network Interface Card IP Protocol stack DATA TELNET HTTP Inverter access Configuration Configuration Monitoring TCP/UDP Port 8000 TCP Port 23 TCP Port 80 WriteData Read Data Set Properties Set Properties Read Data Protocol Drivers DIN66019II HSP5 Interbus PC Hardware COM1..4 COM1..4 RS232 RS232 RS485 F4 10 F5 G4 ISA F4 RS485 TTL F0 F5 Loop2 Profibus PCI-Can PCMCIA-Can ProfiBoard F4 F4 GW F5 F4 CAN BK F5 F5 COMBICOM IP Service ANTRIEBSTECHNIK Data port The transfer of the data frames is done via IP-port 8000 with the services TCP or UDP. (See section 'Settings in COMBIVIS'). At that certain protocols are assigned locally to the inverter addresses (0..239), i.e. in COMBIVIS 5 are for example the inverters 0 to 3 adjusted to IP-protocols, in the IP-server inverter 0 is adjusted to HSP5, the rest is configurated to DIN66019. The HSP5-protocol is for example processed on COM1, DIN66019 is sent via COM2 of the IP-server. Furthermore, several users of COMBIVIS 5 can use the inverters of an IP-server simultaneously: FU0 : IP FU1 : IP FU2 : IP FU3 : IP COMBIVIS 5 PC FU0 : IP FU2 : IP FU0 : HSP5 FU1 : DIN66019 FU2 : DIN66019 FU3 : DIN66019 COMBIVIS 5 PC HSP5 : COM1 38400 BD DIN66019 : COM2 9600 BD KEB Protocol IP Server Ethernet (IP) COM1 COM2 232/485 RS232 (HSP5) RS 485 (DIN66019) Adapterkabel HSP5 FU0 FU1 FU2 FU3 11 COMBICOM IP Service Configuration by browser The setting of the KEB Protocol IP Server takes place with a standard browsers by HTTP-Port 80. Here all settings can be changed menu driven as well as all inverter parameter can be read out and be displayed. After entering the host name (here 192.168.2.110) the start page becomes visible, from where all further functions are accessible : 12 COMBICOM IP Service ANTRIEBSTECHNIK Configuration with Telnet Additionally a configuration port (TCP/IP port 23) is available, over which by means of the Telnet program of Windows all adjustments can be set. After entering the host name(here 192.168.2.110) Telnet establishes a TCP connection and the main menu appears: KEB Protocol IP-Server V2.0 Telnet configuration port Running on Host:Kaiser.dns-keb-domain [192.168.2.110] This is the KEB IP Server (1) Status display (2) Protocol assignments (3) HSP5 setting (4) DIN66019 setting (5) CAN setting (6) Profibus setting (7) Change location text (8) IP client list (9) Set password Menu items are selected by entering the number and pressing the ENTER key. (1) Status display : Shows the currently used local protocols as well as all users with their service settings and IP-addresses/ports: (2) Protocol assignments : The current assignment inverter<->protocol is displayed here: LOCAL PROTOCOL ASSIGNMENTS: Inv 0 HSP5 Inv 1 DIN66019 Inv 2 DIN66019 Inv 3 DIN66019 After that a setting can be changed immediately by input of the inverter address: Enter inverter address (0..239)4 (Change inverter 4) (0) = Offline (1) = DIN66019 (2) = HSP5 (3) = InterBus (4) = CAN (5) = Profibus 1 (Adjust to DIN66019) Just press ENTER, if no modification is to take place. In order to cancel an assignment select OFFLINE for the desired inverter. (3) HSP5 setting : Display and adjustment of the interface parameters for HSP5. (4) DIN66019 setting : Display and adjustment of the interface parameters for DIN66019, see (3) HSP5 setting. Attention: The same COM port may not be assigned to two protocols, since then the 2. protocol cannot work. (5) CAN setting : Display and adjustment of the CAN parameters. (6) Profibus setting : Display and adjustment of the Profibus-Parameters. (7) Change location text : Input of main menu heading for the identification of the location of this IP-server. 13 COMBICOM IP Service (8) IP client list : Input and change of the allowed IP-client addresses. Here the addresses of released users are entered. Only these addresses are permitted on the data port, other connections will not be answered. If this list is empty, then this IP-server can be used by every station. An existing address is deleted from the list by repeated entry. (9) Set password : Input or deletion of the password. The configuration port of the IP-server can be protected through password. A set password is queried on establishment of the connection. If the password is incorrect, the connection is terminated immediately. Through input of a blank followed by ENTER the password is deleted (no password protection of the configuration port). Settings in COMBIVIS Following settings are necessary in the menu edit->configuration->IP: Host: Here the IP-address of the IP-server or the COM-server is entered. If a DNS-server is also available in the IP-network, the station name of the computer, on which the KEB-IP-server runs, can be entered (not possible with the W&T COM-server). Port: The KEB-IP-server and the COM-server answer on port 8000. Other systems may possibly have different port numbers. Time-Out value: This is the time in milliseconds in which one waits for a response via the IP-protocol. This time should not be adjusted too short, since a longer time period may elapse depending on the connecting path via router or Internet server. In local networks a value of 500ms is suitable. TCP or UDP: This setting determines the service that is used via IP. TCP is connection-oriented, i.e. first a logical connection is established, all telegrams are monitored on the IP-level and are repeated automatically in case of loss. This can lead to longer run times and is not necessary for COMBIVIS, as COMBIVIS already takes care of the telegram repetition. UDP does not use a logical connection, the telegrams are transmitted without monitoring. The KEB-IP-server can process both services, in the case of the COM-server some settings must first be changed in the COM-server for the UDP-service. Moreover, the COM server can have only one connection to a COMBIVIS station, the KEB-IP-server can process several connections simultaneously. 14