Vortrag downloaden
Werbung

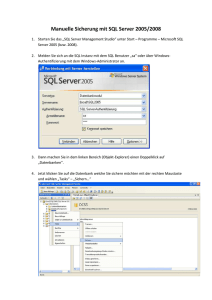
SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton & CSI Version 2 unter der Lupe Sascha Götz Karlsruhe, 03. Dezember 2013 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables “Most of today’s database managers are built on the assumption that data lives on a disk, with little bits of data at a time loaded into memory for manipulation. There’s a whole lot of infrastructure involved in paging those subsets of data in and out[…]” - Kevin Farlee, SQL Server program manager, Microsoft - 2 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables Hekaton 3 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables Query SQL Server Cache Disk-Based File group Memory-Optimized Memory Index Synchronisation Disk Disk Index (Memory Dump) Locking Paging 4 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables ‣ Filegroup hinzufügen ALTER DATABASE [AdventureWorksDW2012] ADD FILEGROUP [Hekaton_FG] CONTAINS MEMORY_OPTIMIZED_DATA GO ‣ Datafile hinzufügen ALTER DATABASE [AdventureWorksDW2012] ADD FILE ( NAME = N'Hekaton', FILENAME = N'C:\Hekaton.ndf') TO FILEGROUP [Hekaton_FG] GO 5 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables CREATE TABLE [dbo].[FactInternetSales_Hekaton] ( [ProductKey] [int] NOT NULL, [OrderDateKey] [int] NOT NULL, [...], ) WITH (MEMORY_OPTIMIZED = ON, DURABILITY = SCHEMA_AND_DATA) ‣ DURABILITY: ‣ SCHEMA_AND_DATA ‣ Schema und Daten werden mit Disk synchronisiert ‣ Speicherplatz wird im RAM und auf Disk benötigt ‣ SCHEMA_ONLY ‣ Nur Schema wird mit Disk synchronisiert 6 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables ‣ Natively Compiled Stored Procedure CREATE PROCEDURE <Schema_Name, sysname, dbo>.<Procedure_Name, sysname, Procedure_Name> -- Add the parameters for the stored procedure here […] WITH NATIVE_COMPILATION, SCHEMABINDING, EXECUTE AS OWNER AS BEGIN ATOMIC WITH --Insert statements for the stored procedure here […] END ‣ Nur Abfrage auf In-Memory Tabellen 7 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables ‣ Index ‣ Memory Optimized tables müssen mindestens einen Index haben (auf PK) ‣ Keine Clustered Indizes ‣ Indexe werden nur im Speicher gehalten ‣ Kein Index Drop, Rebuild ‣ Max. 8 Index pro Tabelle CI Date Date Non-CI I1 I2 1 11.11.13 13.11.13 1 3 2 12.11.13 16.11.13 2 3 13.11.13 14.11.13 4 14.11.13 5 … I8 Date Order# 6 13.11.13 98165 6 2 16.11.13 98121 3 4 1 14.11.13 98474 17.11.13 4 7 3 17.11.13 98521 15.11.13 15.11.13 5 5 4 15.11.13 98451 6 16.11.13 11.11.13 6 1 5 11.11.13 98514 7 17.11.13 12.11.13 7 2 7 12.11.13 98563 … 8 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables ‣ Limitations ‣ Keine Trigger ‣ Keine Foreign Key & Constraints ‣ Keine Identity columns ‣ Keine Schema changes (ALTER TABLE…) 9 Demo SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables Aggregierung (SUM & Group BY) über 2 Mio Datensätze 45 40 40 35 Dauer in Sekunden 30 25 20 20 15 10 4 5 1 0 Ohne Index Non-Clustered Index On-Disk In-Memory 11 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables Update 2 Mio Datensätze 70 60 60 52 Dauer in Sekunden 50 40 32 30 20 10 0 1 On-Disk In-Memory In-Mermory + Natively Compiled 12 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables 1 Mio. Datensätze Load 18 17 16 14 13 Dauer in Sekunden 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 On-Disk In-Memory 13 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables ‣ ‣ Vorteile ‣ Performance ‣ Performance ‣ Performance Kritik ‣ Stabilität ‣ Speichermanagement ‣ Auslagerungs-Falle ‣ Fehlende Features (FKs, Identity Columns, Constraints) ‣ Bestehende Tabellen können nicht in die Hekaton Filegroup verschoben werden 14 SQL 2014 CTP1 Hekaton – Memory optimized tables ‣ Einsatzzweck ‣ DURABILITY: SCHEMA_ONLY ‣ ETL Load Tabelle ‣ Temp Tabellen ‣ DURABILITY: SCHEMA_AND_DATA ‣ Log-Tabellen 15 SQL 2014 CTP1 Columnstore Index Columnstore Index 2 16 SQL 2014 CTP1 Columnstore Index Non-Clustered Columnstore Index (SQL Server 2012) • (+) Performance • (+) Easy-To-Use • (-) Read-Only Clustered Columnstore Index (SQL Server 2014 CTP 1) • • • • • (+) Performance (+) Easy-To-Use (+) Updateable (-) Keine PK & FK (-) Keine Constraints 17 SQL 2014 CTP1 Columnstore Index Aggregierung (SUM & Group BY) über 25 Mio Datensätze 120 106 100 Dauer in Sekunden 80 71 60 40 20 9 1 0 Ohne Index Non-Clustered Index 1 Non-Clustered Columnstore Index Clustered Columnstore Index 18 SQL 2014 CTP1 Columnstore Index 1 Mio. Datensätze Load 30 27 25 23 20 15 Nicht möglich Dauer in Sekunden 20 10 5 0 Ohne Index Non-Clustered Index Non-Clustered Columnstore Index Clustered Columnstore Index 19 SQL 2014 CTP1 Columnstore Index ‣ Daten doch Laden bei Non-Clustered Columnstore Index? ‣ Drop, Load and Rebuild Drop Load Build 103 20 4 ‣ Partition Swap Split Load Build Swap 1 5 20 1 Szenario: 25 Mio Datensätze, Non-Clustered CSI, 1 Mio Datensätze Load 20 SQL 2014 CTP1 Columnstore Index ‣ HowTo: Partition Swapping ‣ Tabelle partitionieren ‣ Leere Partitionen ‣ Load in Temp laden ‣ Partition Split ‣ CSI Index erstellen ‣ Switch <2011 CSI 2011 Facts 2011-2013 2012 2013 >2013 2014 2014 >2014 21 SQL 2014 CTP1 Columnstore Index 1 Mio. Datensätze Load 140 127 120 80 60 40 20 20 23 Drop & Rebuild Dauer in Sekunden 100 27 27 Partition Swap 0 Ohne Index Non-Clustered Index Non-Clustered CSI2 Clustered Columnstore Index Non-Clustered CSI 22 SQL 2014 CTP1 Columnstore Index ‣ ‣ Fazit ‣ Query-Performance: Gigantisch ‣ Load-Performance: Mäßig bis Schlecht ‣ Nachteile: Vorhanden Einsatzzweck: ‣ Non-Clustered CSI ‣ BI Fact tables mit daily/nightly Loads ‣ Partition Swap oder Index Rebuild ‣ Clustered CSI ‣ Log Tabellen ‣ ‚Solo‘-Tabellen (ohne PK /FK) 23 SQL 2014 CTP1 Fragen? 24 SQL 2014 CTP1 Ressources ‣ SQL Server Hekaton CTP1 White Paper http://download.microsoft.com/download/F/5/0/F5096A71-3C31-4E9F-864EA6D097A64805/SQL_Server_Hekaton_CTP1_White_Paper.pdf ‣ http://blogs.msdn.com/b/arvindsh/archive/2013/07/03/sql-2014-in-memory-oltphekaton-training-videos-and-white-papers.aspx ‣ http://www.databasejournal.com/features/mssql/new-enhanced-column-storeindex-in-sql-server-2014-part-1.html ‣ http://rusanu.com/2011/07/13/how-to-update-a-table-with-a-columnstore-index/ 25