Infektionen in der Geburtshilfe und Gynäkologie
Werbung
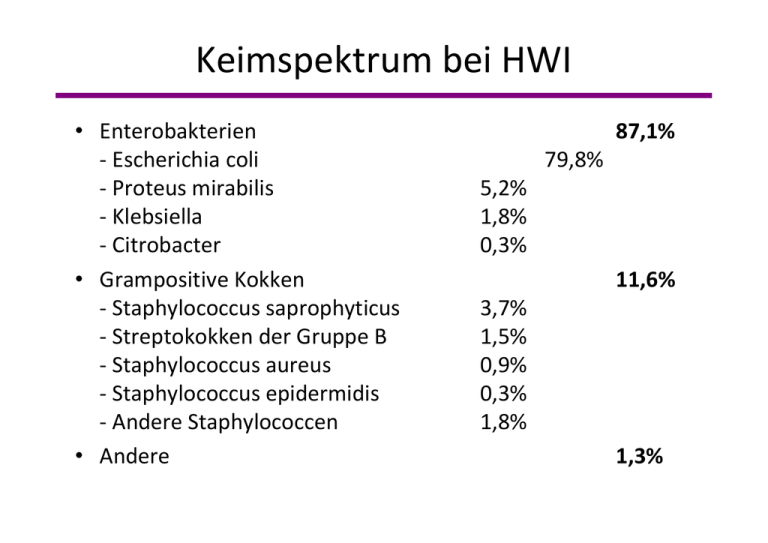
Keimspektrum bei HWI • Enterobakterien ‐ Escherichia coli ‐ Proteus mirabilis ‐ Klebsiella ‐ Citrobacter • Grampositive Kokken ‐ Staphylococcus saprophyticus ‐ Streptokokken der Gruppe B ‐ Staphylococcus aureus ‐ Staphylococcus epidermidis ‐ Andere Staphylococcen • Andere 87,1% 79,8% 5,2% 1,8% 0,3% 11,6% 3,7% 1,5% 0,9% 0,3% 1,8% 1,3% J.P. Arzouni et al.: Harnwegsinfekte bei Frauen von 15 bis 65 Jahren in der Arztpraxis; Med Mal Infect 2000; 30: 699‐702 Erreger von Harnwegsinfektionen (%) Zystitis Pyelonephritis Kompl. HWI E. coli 79 89 32 S. saproph. 11 0 1 Proteus 2 4 4 Klebsiella 3 4 5 Enterokokken 2 0 22 Pseudomonas 0 0 20 Pilze 3 5 10 S. epid. 0 0 15 Kath. 24 0 6 8 7 9 11 8 ESBL ‐ extended spectrum betalactamases Folge der Therapie mit Amoxi/Clav Cefotaxim Ceftriaxon Ceftazidim Ð Therapie der Wahl Penem Chinolon Kasuistik: Sepsis durch ESBL ‐ E. coli Patientin mit Pyeloniephritis | Initiale Therapie mit Amoxi/Clav | Weiterhin septisch, BK: E. coli R Cefotaxim R Ciprofloxacin Ð Ertapenem E. coli resistance in Europe Data from the ECO∙SENS study % resistance 35 16-54% 30 25 20 6-27% 15 5-27% 10 5 0-2% 0-2% 0-5% 0-6% 0-15% ox yc ill in X Am -S M im im Tr im et ho pr et ho pr im Tr qu in o lo ne s n or i Fl uo ro ha lo sp ur an to in Ce p N it r of ec ill in am M Fo sf o m yc in 0 Pivmecillinam • Prodrug Æ aktive Substanz Mecillinam • Absorption > 75 % • Kein Einfluß auf Darmflora • Über die Niere ausgeschieden • Keine NW – Schwangerschaft Die postcoitale Zystitis (Honeymoon) • Trimethoprim 400 mg • Ciprofloxacin 500 mg • Nitrofurantoin 100 mg • Fosfomycin 3000 mg Staphylococcus saprophyticus • Zweithäufigster Erreger bei jungen Frauen • Symptome wie bei E. coli Infektionen • Reservoir: Darm (Fleisch) • Am häufigsten im Sommer • Cefalexin, Pivmecillinam (nein: Chinolone) Empirische Therapie des Harnwegsinfektes Amoxicillin Trimethoprim Amoxi/Clav Fosfomycin Cefalexin Aminoglykoside Mecillinam Sulfonamide Ertapenem Nitrofurantoin NSAR? Ciprofloxacin? Prävention der immer wiederkehrenden Harnwegsinfektion • “Gynäkologische Reparatur“, urologische Abklärung • Low dose oder intermittierende AB Trimethoprim, Ciprofloxacin, Nitrofurantoin? • Ansäuern des Harns (wie?) Saure Zitrone → basischer Harn Mastitis puerperalis Erreger: 95 % S. aureus Mittel der Wahl: Fusidinsäure Abstillen? Mastitis non puerperalis Erreger: Hautkeime Mittel der Wahl: Clindamycin + Chinolon, iv? Cave: Mastitis fatitia Endomyometritis Streptokokken A, B Æ Penicillin G Staphylokokkus aureus Æ Flucloxacillin Anaerobier Æ Metronidazol Bombe: Clindamycin 3 x 1800 mg + Ciprofloxacin/Cephalosporin Alternative: Amoxi/Clav / Ampi/Sulb Nein: Peneme (Selektion MRGN) Saprophyten als Mörder • 30 % aller Frauen sind vaginal besiedelt, nur 1 % der exponierten Kinder werden krank • Anamnese: schon mal Kind an diesem Erreger erkrankt • Vorzeitiger Blasensprung, Frühgeburtlichkeit • Erreger? GBS • Kind: “early und late onset“ Microbiology of acute PID Infect. Dis. Obst. Gyn. 2011 Pelvic Inflammatory disease 2014 Ceftriaxon 2 g Cefotaxime 2 g Doxycyclin 200 mg 14 Tage Metronidazol 1000 mg Clindamycin 3 x 900 mg + Gentamicin 1 x 80 mg Ampi/Sulb 4 x 3 g + Doxycyclin 200 mg wo sind die Chinolone? Schwangere aus Somalia mit Tumorverdacht 1 • 25jährige “gesunde“ Frau 35 SSW • Gewichtsabnahme 15 kg und Husten seit 2 Monaten • Thoraxröntgen: Mediastinalverbreiterung • Sectio 36. Woche • MRT basale Raumforderung mit Infiltration der Wirbelsäure Æ Lymphom? Tuberkulose in der Schwangerschaft • Diagnose durch Quantiferon Biopsie Hauttest • Therapie mit RIF‐INH‐ETH‐PYZ kein Aminoglykosid oder Chinolon • abwarten bis zur Geburt • Bestimmung des Azetylatorstatus (INH) Therapie der akuten Toxoplasmose‐Infektion bis zur 15. SSW ab der 16. SSW Spiramycin Sulfadiazim + Pyrimethamin Folinsäure Clindamycin Trimethoprim + Sulfonamid wirkt Spiramycin überhaupt? Steuerung von Pyrimethamin? Listeria monocytogenes Rheuma und Totgeburt • 34 jährige Patient mit rheumatoider Arthritis, Therapie MTX… anti‐TNF mit guter Wirkung, Stopp wegen Kinderwunsch • nach ½ Jahr schwanger, Patienten fühlt sich nicht krank • “Grippe“, fieberhafter Abort • Listeria monozytogenes Virusinfektionen in der Gynäkologie Papillomaviren Impfung, Cidofovir Herpes genitalis Famciclovir Varicellen HIV Hepatitis B/C EBV, CMV Röteln