1 2 3 4 5 _ + Batterie 0
Werbung
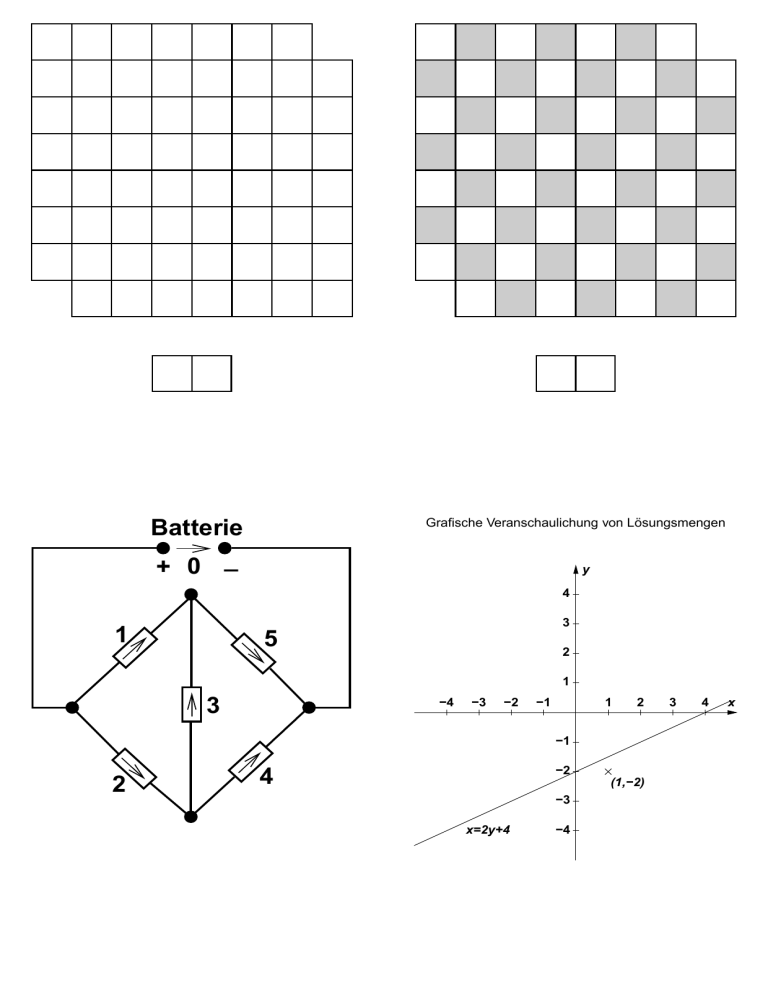
Grafische Veranschaulichung von Lösungsmengen
Batterie
+ 0 _
y
4
3
1
5
2
1
3
−4
−3
−2
−1
1
2
−1
2
−2
4
(1,−2)
−3
x=2y+4
−4
3
4
x
2-dimensionales Koordinatensystem
3-dimensionales Koordinatensystem
y
y
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
z
4
3
−4
−3
−2
−1
1
2
3
4
−4
x
−3
−2
−1
1
2
2
3
4
x
3
4
x
−1−1
−1
−2
−2
−2
−3
−4
−3
−3
−5
−4
−4
Addition von Vektoren
Vielfache von Vektoren
y
y
4
4
3
3
2
1
−4
−3
−2
−1
2
a+b
b
2u
1
2
a
3
4
x
−4
−3
−2
u
−1
1
1
2
Gerade in Parameterform
Satz des Pythagoras
y
4
3
2
1
−4
−3
−2
−1
1
2
3
4
x
−1
b
a
c
−2
−3
−4
Beweis für Satz des Pythagoras
Beweis für die Umkehrung des Satzes des Pythagoras
c
a
b
b
c
a
c
b−a
b
a
b
a
c
Länge von Vektoren
Abstand von Punkten in der Ebene
y
y
4
4
3
a=
2
a1
a2
1
1
|
2
{z
a1
3
}
3
a2
4 x
2
b
b−a
1
−4
−3
−2
Länge von Vektoren im Raum
−1
1
2
a
3
Sinus und Cosinus
y
1
y
P
4
1
Q
α
−1
3
a
O|
z
−1
2
4
3
1
1
2
2
3
4
x
{z
cos α
}
sin α
x
1
4
x
Länge der Differenz zweier Vektoren
Cosinussatz
B
y
4
a
h
B
3
c
A
2
γ
q
p
C
1
A
b
ϕ
B−A
1
2
3
4
c2 = a 2 + b2 − 2 · a · b · cos γ
Geometrische Interpretation des Skalarprodukts
Normalenform einer Geraden in der Ebene
q
y
3
b
2
a
b
1
−4
−3
−2
−1
1
−1
−2
ϕ
p
O
a
b
ϕ
p
q
a
2
3
4
x
x
Normalenform einer Ebene im Raum
Kürzeste Entfernung von Punkt zu Gerade
p
n
v
q’−p
x
q−p
q’
w
q
Kreuzprodukt
Winkel zwischen Geraden/Ebenen
α
α
b
a
ϕ
Zentrische Streckung
Zentrische Streckung
y
−6
−5
−4
−3
−2
y
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
−1
1
2
3
4
x
−6
−5
−4
−3
−2
−1
1
−1
−1
−2
−2
−3
−3
−4
−4
Drehung
Drehung
y
y
1
−1
3
4
x
1
x
1
1
−1
2
x
−1
−1
Projektion
Scherung
y
−4
−3
−2
y
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
−1
1
2
3
4
x
−4
−3
−2
−1
1
−1
−1
−2
−2
−3
−3
−4
−4
Achsenspiegelung
t=1/2
2
3
4
x
Alle Dreiecke sind gleichseitig!
C
y
4
3
2
G
F
1
−1
−4
−3
1
2
3
4
x
E
−2
−1
−2
−3
−4
A
D
B

