Impfungen und Immunsuppression
Werbung
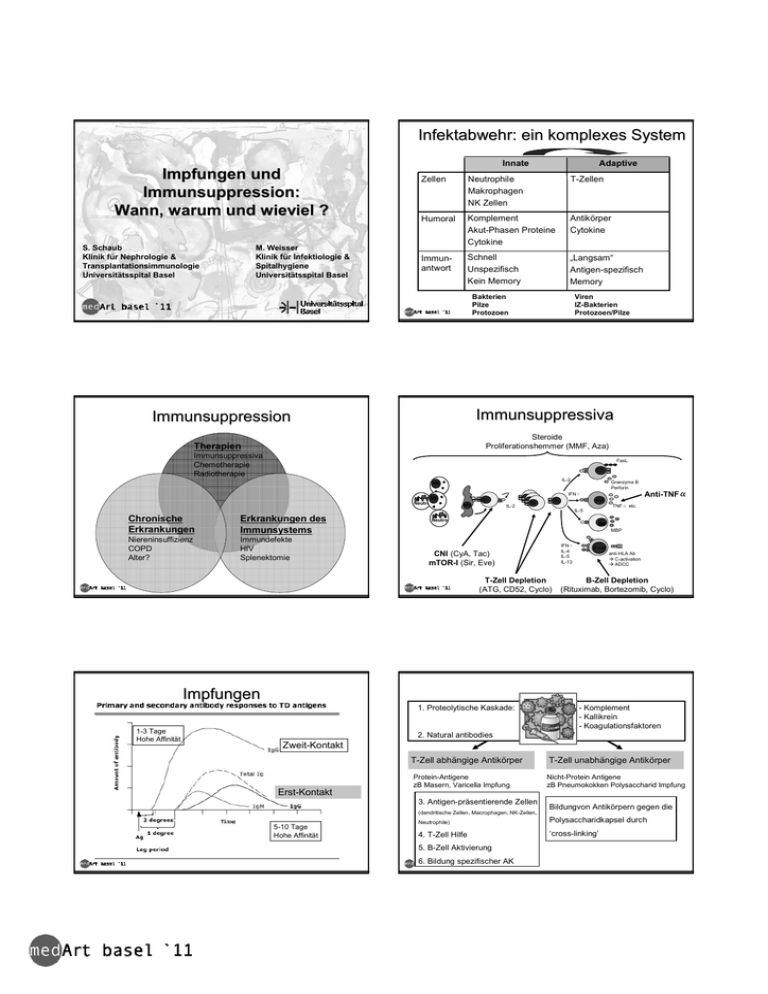
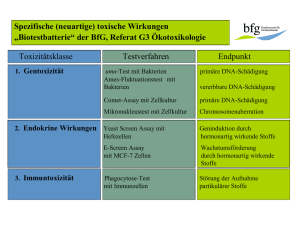
Infektabwehr: ein komplexes System Innate Impfungen und Immunsuppression: Wann, warum und wieviel ? S. Schaub Klinik für Nephrologie & Transplantationsimmunologie Universitätsspital Basel M. Weisser Klinik für Infektiologie & Spitalhygiene Universitätsspital Basel Adaptive Zellen Neutrophile Makrophagen NK Zellen T-Zellen Humoral Komplement Akut-Phasen Proteine Cytokine Antikörper Cytokine Immunantwort Schnell Unspezifisch Kein Memory „Langsam“ Antigen-spezifisch Memory Bakterien Pilze Protozoen Viren IZ-Bakterien Protozoen/Pilze Immunsuppressiva Immunsuppression Steroide Proliferationshemmer (MMF, Aza) Therapien Immunsuppressiva Chemotherapie Radiotherapie FasL CTL IL-2 NK Neutro Granzyme B Perforin IFNγ NK Th APC IL-2 Th Th Th MØ Th Anti-TNFα α TNFα etc. IL-5 Chronische Erkrankungen Erkrankungen des Immunsystems Niereninsuffizienz COPD Alter? Immundefekte HIV Splenektomie Neutro Eo MΦ Φ MBP IFNγ IL-4 IL-5 IL-13 CNI (CyA, Tac) mTOR-I (Sir, Eve) T-Zell Depletion (ATG, CD52, Cyclo) B-cell anti-HLA Ab C-activation ADCC B-Zell Depletion (Rituximab, Bortezomib, Cyclo) Impfungen 1. Proteolytische Kaskade: 1-3 Tage Hohe Affinität - Komplement - Kallikrein - Koagulationsfaktoren 2. Natural antibodies Zweit-Kontakt T-Zell abhängige Antikörper Erst-Kontakt Protein-Antigene zB Masern, Varicella Impfung 3. Antigen-präsentierende Zellen T-Zell unabhängige Antikörper Nicht-Protein Antigene zB Pneumokokken Polysaccharid Impfung Bildungvon Antikörpern gegen die (dendritische Zellen, Macrophagen, NK-Zellen, 5-10 Tage Hohe Affinität Neutrophile) Polysaccharidkapsel durch 4. T-Zell Hilfe ‘cross-linking’ 5. B-Zell Aktivierung 6. Bildung spezifischer AK Pneumokokkenimpfung nach Nierentransplantation Konjugierter Impfstoff ? Kumar L, CID 2008; 47:885-92 PPV23 + PV7 Placebo+ PPV23 Lindemann M, Transplantation 2010; 90: 1463-1467 Kein Unterschied Lindemann M, Transplantation 2010; 90: 1463-1467 Antikörper-Anstieg funktionelle Ak-Antwort Splenektomie Update of Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Infection in Patients with an absent or dysfunctional spleen Wirksamkeit Pneumokokkenimpfung 70-80% Meningokokkenimpfung 100% weniger unter Immunosuppression Zeitpunkt am besten: 2 Wo vor Operation 2. Wahl: nach kataboler Phase Clinical Medicine (Journal of the Royal College of Physicians of London, Vol 2, Nos 5 (Sep/Oct 2002) - p440-443 1 Mo nach Stop Steroide >2mg/kg/d 3 Mo nach Stop Chemotherapie BAG Bulletin, 49/06 AK-Kontrolle Steroide: Equivalenzdosen Anti-inflammatorische Aktivität Mineralokortikoid Aktivität Cortisol 1 1 Hydrocortison 1 1 Prednison 4 0.8 Methylprednisolon 5 0.5 30 0 Dexamethason 4 Wochen nach Impfung Booster / (konjugierter Imfpstoff?) Steroide: wieviel ist InfektInfekt-relevant ? Kein erhöhtes Infektionsrisiko < 10mg Prednison/Tag < 700mg kumulative Dosis Stuck AE. Rev Infect Dis 1989; 11:954