Vortrag ansehen
Werbung

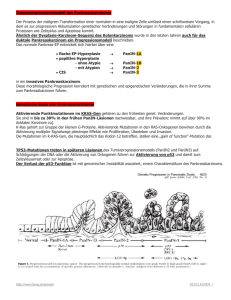
Duktales Pankreaskarzinom ein Update M Schindl Univ. Klinik für Chirurgie Medizinische Universität Wien Bauchspeicheldrüsenkrebs (C.25) Neuerkrankungen und Sterbefälle pro Jahr seit 1983 1.600 Neuerkrankungen: Sterbefälle: 1.500 1.400 1526 1488 1.300 1.200 1.100 1.000 900 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 - Statistik Austria, 2012 M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Bauchspeicheldrüsenkrebs (C.25) Erkrankungsausmaß bei Diagnose 30,0 25,0 ca. 290 (20%) Patienten sind primär resektabel 20,0 15,0 10,0 5,0 - % Carcinoma in Situ Lokalisiert Regionalisiert Disseminiert Unbekannt DCO-Fälle2) Q: STATISTIK AUSTRIA, Österreichisches Krebsregister (Stand 08.09.2010). DCO = Death Certificate Only. M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Herausforderungen beim Pankreaskarzinom 52% (120/329) Hohe Rezidivrate nach R0 Resektion Total recurrence 70% (229/329) Katz et al. Ann Surg Oncol (2009) 16:836–847 M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Herausforderungen beim Pankreaskarzinom • Schwierige Diagnose • Variable Beurteilung der Resektabilität • Komplikationsmanagement • Technisch anspruchsvolle Operation: Morbidität, Mortalität • Histologische Aufarbeitung – R0 Klassifikation • Stellenwert der Chemo- und Strahlentherapie M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Aktuelle Behandlungskonzepte Up to date • Interdisziplinäres Management: Diagnostik und Therapie • Bedingte histologische Diagnosesicherung vor Operation • Interdisziplinäre Beurteilung der Resektabilität: Standardisierung • Histo-pathologische R0 Klassifikation: Standardisierung • Neoadjuvante Therapie: Downstaging (Studien!) • Zentrumsbildung: Steigerung der Behandlungsqualität M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Interdisziplinäres Management Chirurgie Anästhesie und Intensivmedizin Multimodale Diagnostik Onkologie Pathologie Tumorboard GastroenterologieHepatologie RadiologieIntervent.Radiologie Multimodale Therapie Strahlentherapie M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Präoperative Diagnosesicherung Diagnose: MDCT, MRT, Endosono / Biopsie Tumor-Staging: MDCT, MRT, Endosono, PET-CT Resektabilität: MDCT, (MRT), Endosono MDCT= Multidetector computed tomography M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Präoperative Diagnosesicherung Radiologische Diagnose: Direkte und indirekte Tumor-Zeichen M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Präoperative Diagnosesicherung Histologische Diagnosesicherung bei Pankreaskarzinom Methode M Schindl Sensitivität ERCP Bürste 30% ERCP Bürste + Zange US/CT gezielt 62% 60-70% EUS gezielt 80-90% Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Präoperative Diagnosesicherung Histologische Diagnosesicherung vor Chemo- / Strahlentherapie bei unklaren Befunden in bildgebender Diagnostik Endosonographie+Biopsie > ERCP M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Präoperative (ERCP) Drainage ERCP nur bei Cholangitis oder ausgeprägter Cholestase M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Präoperative (ERCP) Drainage • Kein Stent, wenn primär resektabel • Hat keinen Einfluß auf die Mortalität • Verursacht mehr postoperative Infektionskomplikationen* • Kann die Lebensqualität verbessern – nur mit Plastikstents oder beschichteten Metallstents erfolgen – bei Pat. mit einem Bili > 15mg/dl – bei Cholangitis – bei Gerinnungsproblemen – bei langem Intervall bis zur OP oder vor neoadjuvanter Therapie * NA. van der Gaag. NEJM 2010;362:129-37 M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Standardisierte Beurteilung der Resektabilität Resektabel – Borderline – Nicht resektabel Infiltration der Pfortader M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Standardisierte Beurteilung der Resektabilität Tumor Wahrscheinlichkeit Gefäßkontakt Gefäßinvasion Grad 0: kein Kontakt 0% Grad 1: < 90° 0–3% Grad 2: 90–180° ca. 40% Grad 3: 181–270° ca. 90% Grad 4: >270° 100% Tara S Kent et al. HPB 2010, 12, 115-122 Lu, AJR 1997, O´Malley AJR 1999 M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Standardisierte Beurteilung der Resektabilität The Varadhachary/Katz CT staging system for adenocarcinoma of the pancreatic head and uncinate process Varadhachary GR. et al. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13:1035–46. M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Standardisierte Beurteilung der Resektabilität Primär resektabel Operation M Schindl Lokal fortgeschritten Lokal fortgeschritten borderline resektabel nicht resektabel Neoadjuvante (Neoadjuvante) (Palliative) Therapie Therapie Therapie Metastasiert Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Standardisierte Beurteilung der Resektabilität Grad 1: < 90° resektabel M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Standardisierte Beurteilung der Resektabilität Grad 3: > 180 ° Umschriebene Venen-Infiltration Lokal fortgeschritten, borderline M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Downstaging durch neoadjuvante Therapie Primär resektabel Operation Rezidivfreiheit M Schindl Lokal fortgeschritten Lokal fortgeschritten borderline resektabel nicht resektabel Neodjuvante (Neoadjuvante) Palliation Therapie Therapie Resektabilität Metastasiert Resektabilität Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Downstaging durch neoadjuvante Therapie Preoperative/Neoadjuvant Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Sonja Gillen et al. PLoS Medicine. 2010; 7(4), e1000267: 1-15 M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Downstaging durch neoadjuvante Therapie Sonja Gillen et al. PLoS Medicine. 2010; 7(4), e1000267: 1-15 M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Downstaging durch neoadjuvante Therapie Sonja Gillen et al. PLoS Medicine. 2010; 7(4), e1000267: 1-15 M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Downstaging durch neoadjuvante Therapie 2002 2005 Marimastat 5-FU bolus 5-FU/LV Oxaliplatin Capecitabine 2004 Tipifarnib 2006 2007 Exatecan Irinotecan Pemetrexed Cisplatin Oxaliplatin Docetaxel Capecitabine Erlotinib Bevacizumab Cetuximab Gemcitabin e+ Erlotinib FOLFOXIRI Gemcitabine 1997 1999 Gestaltung: G Kornek M Schindl 2001 2003 2005 2007 2010 = No significant benefit observed versus gemcitabine a = Significant benefit versus gemcitabine alone Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Downstaging durch neoadjuvante Therapie möglichst effektivste Therapie mit höchster Ansprechrate: Folfirinox (ORR 31%) Gem plus Platin (Oxaliplatin) (ORR 27%) Nab-Paclitaxel (ORR 23% bzw. 29% gemäß Investigatorassessment) Gem (ORR 10%) +/- Erlotinib ? mit/ohne Radiotherapie ? Wenige randomisierte Studien für RCT: Gem +/- RT Gestaltung: G Kornek M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Downstaging durch neoadjuvante Therapie Randomisierte Phase-III-Studien: Radiochemotherapie (RCT) bei LAPC Studie Regimen RCT RT CT P -Wert vor dem Jahr 2000 GITSG 1988 RT vs. RCT (5-FU + 60 Gy RT) ECOG Cohen 2005 RT vs. RCT (5-FU, Mitomycin C + 59 8.4 Monate 7.1 Monate Gy RT) nach dem Jahr 2000 FFCD GEM vs. RCT Chauffert (GEM, Cisplatin, 60 Gy 2006 RT) ECOG GEM vs. RCT Loehrer 2008 (GEM/50.4 Gy RT) 40 Wochen 20 Wochen <.01 .16 8.6 Monate 13 Monate 11.1 Monate 9.2 Monate .017 GEM+/-Erlotinib vs. RCT 15.3 LAP 07 Gy RT GEM+/Hammel 2013 (54 Monate Erlotinib) 16.5 Monate .03 .83 Gestaltung: G Kornek 5-FU = 5-Fluorouracil; ECOG = Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; FFCD = Fédération Francophone de Cancérologie Digestive; GEM = Gemcitabine; GITSG = Gastrointestinal Tumor Study Group; Gy = Gray; P value = probability value; RT Radiotherapie Downstaging durch neoadjuvante Therapie Standardisierte Strahlentherapie Neoadjuvante Radiochemotherapie bei lokal fortgeschrittenen PDAC M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Neoadjuvante Therapie: Studien PANCREATIC CANCER ABCSG-P02 RANDOMIZED PHASE II TRIAL OF MODIFIED FOLFIRINOX vs. FOLFIRINOX + RCT IN PATIENTS WITH LOCALLY-ADVANCED, non-resectable PANCREATIC CANCER* LAPC (n=68) mod. FOLFOXIRI (6 Mo)* mod. FOLFOXIRI (3 Mo) OP XRT (50.4 Gy)+Cape OP Primärer Endpunkt: R0 Resektionsrate (CT 10% vs. RCT 40%) Weitere Endpunkte: Ansprechraten PFS Gesamtüberleben Toxizität Gestaltung: G Kornek M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Task Force Pankreas Adenokarzinom des Pankreas P01 Resektabel Borderline P02 P04 Lokal fortgeschritten nicht metastasiert „Minimal“ Metastasiert Studie: Studie: Neoadjuvante Studie: Neoadjuvante Studie: neoadjuvante Chemotherapie vs. Chemotherapie vs. Radio- neoadjuvante Kurzzeit Radiatio Radio-chemotherapie chemotherapie Chemotherapie Resektion P03 Adjuvante Chemotherapie Adjuvante Chemotherapie + Radiochemoth. Potential Alternative Treatment Strategies Raising Hope for the Near Future • Targeting of tumor desmoplasia – Stromal SPARC (secreted protein acidic and rich in cystein), an albumine-binding protein overexpressed in APC with nab-Paclitaxel – Hyaluronan with PEGylated human rec. PH20 hyaluronidase – Inhibition of the Hedgehog cellular signaling pathway (IPI 926 + Gem) • Targeting of biomarkers / other signaling pathways – CXC receptor 4 – Insulin-like growth factor receptor – Transforming growth factor ß • Potential biomarkers that predict treatment response – Human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (hENT1) seems to be a valid predictive biomarker for response to gemcitabine – Smad 4 expression status: loss might be predictive for adjuvant chemotherapy benefit Gestaltung: G Kornek Von Hoff DD, et al. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(34):4548-4554. Olive KP, et al. Science. 2009;324(5933):1457-1461. Conroy T, et al. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(19):1817-1825. Voutsadakis IA, et al. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2011;3(11):153-164. Bachet JB et al. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:2327-2335. Standardisierte pathologische Aufarbeitung und Befundung •R1 = RR ≤ 1mm •Lymphovasculäreinfiltration Esposito I. et al. Most pancreatic cancer resections are R1 resections. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008;15:1651–1660. M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Zentrumsbildung Systematic review and meta-analysis of the volume–outcome relationship in pancreatic surgery Hospital volume and postoperative mortality G. A. Gooiker eta al. British Journal of Surgery 2011; 98: 485–494 M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Zentrumsbildung Systematic review and meta-analysis of the volume–outcome relationship in pancreatic surgery Hospital volume and 5-year survival G. A. Gooiker eta al. British Journal of Surgery 2011; 98: 485–494 M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Zentrumsbildung Dustin M. Walters et al. Ann Surg Oncol; 2011 Pancreas-Protocol Imaging at a High-Volume Center Leads to Improved Preoperative Staging of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma >50% Änderung des Behandlungskonzepts Management changes based on repeat cross-sectional imaging. RS resectable; BR borderline resectable; UR unresectable Zentrumsbildung Häufigkeit von Pankreaskarzinom Operationen in Österreichischen Krankenhäusern 7% 7% 22% 64% n= 55 Chirurgische Abteilungen in Österreich >20/Jahr 11-20/Jahr 5-10/Jahr <5/Jahr Persönliche Kommunikation M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Zusammenfassung 1 Up to date Das duktale Pankreaskarzinom stellt eine Herausforderung für Diagnostik und Therapie dar Durch • Zentrumsbildung • Interdisziplinäres Management • Hochauflösende (MDCT, MRT, Endosono) Diagnostik können eine hohe Behandlungsqualität erreicht und unnötige Interventionen verhindert werden M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Zusammenfassung 2 Up to date Eine Standardisierung folgender Bereiche ist wichtig: • Interdisziplinäre Beurteilung der Resektabilität • Pathologische Aufarbeitung und Befundung • Multimodale (neoadjuvante) Behandlungsprotokolle M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Zusammenfassung 3 Up to date Der Stellenwert neo-/adjuvanter Therapieprotokolle sollte im Rahmen multizentrischer Studien beurteilt werden M Schindl Update: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Task Force Pankreas Danke für Ihre Aufmerksamkeit! Onkologie Radiologie Chirurgie Gastroenterologie -Hepatologie Pathologie M Schindl Strahlentherapie Focus: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom Task Force Pankreas Onkologie Radiologie Chirurgie Gastroenterologie -Hepatologie Pathologie M Schindl Strahlentherapie Focus: Duktales Pankreaskarzinom