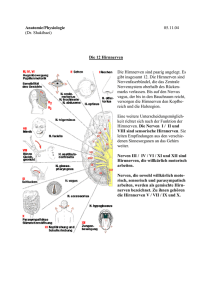
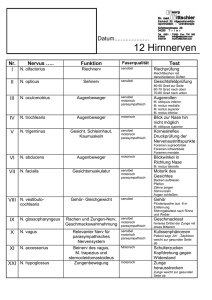
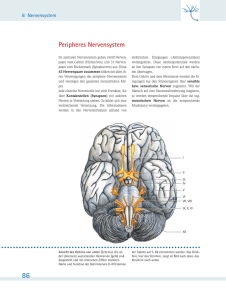
Manipulation kranialer Nerven
Werbung

Barral / Croibier Manipulation kranialer Nerven Leseprobe Manipulation kranialer Nerven von Barral / Croibier Herausgeber: Elsevier Urban&Fischer Verlag http://www.narayana-verlag.de/b6808 Im Narayana Webshop finden Sie alle deutschen und englischen Bücher zu Homöopathie, Alternativmedizin und gesunder Lebensweise. Das Kopieren der Leseproben ist nicht gestattet. Narayana Verlag GmbH, Blumenplatz 2, D-79400 Kandern Tel. +49 7626 9749 700 Email [email protected] http://www.narayana-verlag.de Inhaltsverzeichnis Part I .................................... 1 1 1.1 1.1.1 1.1.2 1.1.3 1.2 1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3 1.2.4 1.3 1.4 1.4.1 1.4.2 1.5 Grundlagen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionelle Anatomie des Nervs . . . . . . . . . . Bindegewebe des Nervs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Vaskularisation des Nervs (Vasa nervorum) . . . Innervation des Nervs (Nervi nervorum) . . . . . . Mechanische Eigenschaften des Nervs . . . . . Mobilität . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Viskoelastizität . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Neurale Belastungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Distale Dauerspannung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionelle Einheit des Nervensystems . . . . Funktionelle Pathologie des Nervs . . . . . . . . . Neurale Fibrose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kompression . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Konzept von Einheit und Globalität . . . . . . . . 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 6 6 6 6 7 7 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.3.1 2.3.2 2.3.3 2.4 2.4.1 2.4.2 Besonderheiten der Hirnnerven . . . . . . . . Wiederholung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Nomenklatur . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Embryologische Besonderheiten . . . . . . . . . . Neuralrohr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Sinnesorgane . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Muskeln und andere Gewebe . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionelle Merkmale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Die sechs verschiedenen Nervenimpulse . . . . . Ähnlichkeiten und Unterschiede zu den Spinalnerven . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Die unterschiedlichen Funktionen der Hirnnerven . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 10 10 10 11 11 11 12 13 2.4.3 3 3.1 3.2 3.2.1 3.2.2 3.2.3 3.3 3.4 . Anatomische Organisation der Hirnnerven . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Intrakranieller Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kranialer Verlauf – die Durchtrittsöffnungen . . . Extrakranialer Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Nervenäste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ganglien . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 15 17 18 18 19 19 19 20 20 4 4.1 4.1.1 4.1.2 4.1.3 4.2 4.3 Durchtrittsstellen im Kranium . . . . . . . . . . Vorderer Abschnitt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lamina cribrosa . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Harter Gaumen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Öffnungen des Gesichtsschädels . . . . . . . . . . . Mittlerer Abschnitt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hinterer Abschnitt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 22 22 22 22 22 23 5 5.1 5.1.1 5.1.2 5.2 5.2.1 5.2.2 5.3 Innervation der Dura mater cranialis . . . . Dura mater – periostales Blatt . . . . . . . . . . . . Supratentorielle Dura mater . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Infraatentorielle Dura mater . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Dura mater – meningeales Blatt . . . . . . . . . . Falx cerebri . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Tentorium cerebelli . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Sensibilität der Dura mater . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27 28 28 28 29 29 29 29 6 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.3.1 6.3.2 6.4 Funktionelle Anatomie der Hirnnerven . . Nervenwurzeln . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Nerven . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Schädelöffnungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Die Rolle der Öffnungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionsweise . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Austrittsstellen der Hirnnerven . . . . . . . . . . . 31 32 32 32 32 33 33 7 Funktionelle Pathologie der Hirnnerven . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Mechanische Funktion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Spannungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Drücke . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Vaskuläre Funktion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Neurovegetative Funktion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Informations- und propriozeptive Funktion . . Zentrale Desinformation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hilton‘sches Gesetz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Elektromagnetische Funktion . . . . . . . . . . . . . Die perineurale Strömung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hirnwellen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Intention . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Chemische und hormonale Funktion . . . . . . . Ätiologie der neuralen Fixierungen . . . . . . . . Beeinträchtigungen der Schädelöffnungen . . . . 35 36 36 36 36 37 37 37 37 37 37 38 38 38 38 38 7.1 7.1.1 7.1.2 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.4.1 7.4.2 7.5 7.5.1 7.5.2 7.5.3 7.6 7.7 7.7.1 Leseprobe von Alain Croibier und Jean-Pierre Barral „Manipulation kranialer Nerven“ Herausgeber: Elsevier Urban & Fischer Leseprobe erstellt vom Narayana Verlag, 79400 Kandern, Tel: 0049 (0) 7626 974 970-0 VI Inhaltsverzeichnis 7.7.2 7.7.3 7.7.4 7.7.5 7.7.6 Schädel- und Gesichtstraumata . . . . . . . . . . . . Infektionsfolgen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Folgen von Schädel- und Gesichtschirurgie . . . Kieferorthopädische Korrekturen . . . . . . . . . . . Entzündungsreaktionen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8 Diagnose und Behandlung der Hirnnerven . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Terminologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Gewebediagnose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlung von Nerven . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Diagnose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Globaler kranialer Ecoute-Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . Exokranielle Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Prinzipien für die Manipulation von Hirnnerven . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Wirkung der Hirnnervenmanipulation . . . . . . . Indikationen und Kontraindikationen . . . . . . . . 8.1 8.1.1 8.1.2 8.2 8.2.1 8.2.2 8.3 8.3.1 8.3.2 8.3.3 Part II 9 . .................................... 9.2 9.2.1 9.2.2 9.3 9.3.1 9.3.2 9.4 9.4.1 9.4.2 9.4.3 Techniken für die Durchtrittsstellen mehrerer Hirnnerven . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ziel der Techniken an den HirnnervenDurchtrittsstellen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Fissura orbitalis superior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Technik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Foramen jugulare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Technik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Foramen magnum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Technik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Technik für die A. vertebralis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10 10.1 10.1.1 10.1.2 10.1.3 10.2 10.2.1 10.3 10.3.1 Nervus olfactorius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . N. olfactorius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Riechepithel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Strukturen des Riechzentrums . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Riechfunktionen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Techniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9.1 39 39 39 39 40 41 42 42 43 43 43 48 49 49 51 52 10.3.2 10.3.3 10.3.4 11 11.1 11.1.1 11.1.2 11.2 11.2.1 11.2.2 11.2.3 11.2.4 11.3 11.3.1 11.3.2 11.3.3 Vorsichtsmaßnahmen und Kontraindikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75 75 75 Nervus opticus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Nervus opticus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Auge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionen der Sehbahn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Klinik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . N.-opticus-Defizite . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . N.-opticus-Läsionen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Chiasma opticum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . N. opticus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79 80 80 83 85 85 86 89 90 90 90 91 95 96 96 96 97 97 97 97 97 97 101 103 103 103 12.3.4 Nervus oculomotorius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lagebeziehungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anastomosen und Verbindungen . . . . . . . . . . . Verteilung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ganglion ciliare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lähmung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Technik für die Fissura orbitalis superior . . . . . . Techniken für den Bulbus oculi . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13 13.1 13.1.1 13.1.2 13.1.3 13.1.4 13.1.5 Nervus trochlearis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lagebeziehungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anastomosen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Versorgungsgebiet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105 106 106 106 106 107 107 94 55 57 58 58 58 59 59 59 60 61 61 62 62 65 66 66 67 68 69 69 70 70 12 12.1 12.1.1 12.1.2 12.1.3 12.1.4 12.1.5 12.1.6 12.2 12.2.1 12.2.2 12.3 12.3.1 12.3.2 12.3.3 Leseprobe von Alain Croibier und Jean-Pierre Barral „Manipulation kranialer Nerven“ Herausgeber: Elsevier Urban & Fischer Leseprobe erstellt vom Narayana Verlag, 79400 Kandern, Tel: 0049 (0) 7626 974 970-0 103 103 Inhaltsverzeichnis 13.2 13.2.1 13.3 13.3.1 13.3.2 13.3.3 13.3.4 14 14.1 14.1.1 14.1.2 14.1.3 14.2 14.2.1 14.2.2 14.3 14.3.1 14.3.2 14.4 14.4.1 14.4.2 14.4.3 14.4.4 15 15.1 15.1.1 15.1.2 15.1.3 15.1.4 15.1.5 15.1.6 15.2 15.2.1 15.2.2 15.2.3 15.2.4 15.2.5 15.2.6 15.2.7 15.2.8 Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Fissura orbitalis superior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bulbus oculi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108 108 108 108 108 Nervus trigeminus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ganglion trigeminale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Klinik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ganglion trigeminale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Nervus trigeminus und Migräne . . . . . . . . . . Bezug zum Nervensystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Streudepolarisierung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verbindung zwischen N. trigeminus und Halswirbelsäule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Physiologie des Migräneanfalls . . . . . . . . . . . . 111 112 112 112 112 113 113 113 115 115 Nervus ophthalmicus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lagebeziehungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anastomosen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kollateralen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Endäste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . N. frontalis und N. occipitalis major . . . . . . . . . N. supraorbitalis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . N. supratrochlearis und N. infratrochlearis . . . . N. lacrimalis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Oberlid und Septum orbitale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anmerkungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119 120 120 120 120 120 120 120 124 124 127 128 128 128 128 128 108 108 15.2.9 Kombinierte Techniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130 16 16.1 16.1.1 16.1.2 16.1.3 16.1.4 16.1.5 16.1.6 16.2 16.2.1 16.2.2 16.2.3 16.2.4 16.2.5 16.2.6 16.2.7 Nervus maxillaris . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kollateralen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Endäste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ganglion pterygopalatinum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktion des N. maxillaris . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Infraorbitales Bündel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Foramen zygomaticofaciale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Augenlid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . N. nasopalatinus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Nn. palatini . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kombinierte Technik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131 132 132 132 132 133 133 136 137 137 138 138 139 139 139 141 142 142 142 142 143 143 145 145 147 17.2.4 17.2.5 Nervus mandibularis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kollateralen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Endäste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Sympathische Ganglien . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Externe Techniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Interne Technik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kombinierte Techniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18 18.1 18.1.1 18.1.2 18.1.3 18.1.4 18.1.5 18.2 18.2.1 18.2.2 Nervus abducens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lagebeziehungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anastomosen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Versorgungsgebiet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Klinik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149 150 150 150 150 150 150 151 151 151 16.2.8 116 116 117 117 117 117 130 VII 17 17.1 17.1.1 17.1.2 17.1.3 17.1.4 17.1.5 17.2 17.2.1 17.2.2 17.2.3 Leseprobe von Alain Croibier und Jean-Pierre Barral „Manipulation kranialer Nerven“ Herausgeber: Elsevier Urban & Fischer Leseprobe erstellt vom Narayana Verlag, 79400 Kandern, Tel: 0049 (0) 7626 974 970-0 140 140 147 147 148 VIII 18.3 18.3.1 18.3.2 18.3.3 Inhaltsverzeichnis Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Fissura orbitalis superior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bulbus oculi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151 151 151 Nervus facialis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . N. intermedius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ganglion geniculi . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lagebeziehungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anastomosen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kollateralen innerhalb der Pars petrosa . . . . . . Kollateralen außerhalb der Pars petrosa . . . . . . Endäste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Klinik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . N. facialis – Felsenbeinanteil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Foramen stylomastoideum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Endäste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155 156 156 156 157 157 157 157 158 159 160 161 161 162 163 163 164 165 169 170 170 170 171 172 172 175 180 180 181 20.3.4 Nervus vestibulocochlearis . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lagebeziehungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Endäste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionelle Anatomie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Klinik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Technik mit Traktion und Ecoute . . . . . . . . . . . Globalisierung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21 21.1 Nervus glossopharyngeus . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183 184 18.3.4 19 19.1 19.1.1 19.1.2 19.1.3 19.1.4 19.1.5 19.1.6 19.1.7 19.1.8 19.1.9 19.2 19.2.1 19.2.2 19.3 19.3.1 19.3.2 19.3.3 19.3.4 19.3.5 20 20.1 20.1.1 20.1.2 20.1.3 20.2 20.2.1 20.2.2 20.3 20.3.1 20.3.2 20.3.3 151 152 166 167 181 181 21.1.1 21.1.2 21.1.3 21.1.4 21.1.5 21.1.6 21.1.7 21.2 21.2.1 21.2.2 21.3 21.3.1 21.3.2 21.3.3 21.3.4 21.3.5 22 22.1 22.1.1 22.1.2 22.1.3 22.1.4 22.2 22.2.1 22.2.2 22.3 22.3.1 22.3.2 22.3.3 22.3.4 23 23.1 23.1.1 23.1.2 23.1.3 23.1.4 23.1.5 23.1.6 23.1.7 23.2 23.2.1 23.2.2 Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lagebeziehungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ganglien . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anastomosen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kollateralen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Endäste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Klinik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Foramen jugulare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Zungenmanipulation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Im Bereich des Halses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184 184 184 185 185 186 187 187 187 188 190 190 190 190 Nervus vagus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf und Lagebeziehungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kollateralen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Beziehungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Klinik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Im Bereich der Ohren . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Im Bereich des Halses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Im Bereich des Hiatus oesophageus . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193 194 194 194 196 199 200 200 202 203 203 203 205 Nervus accessorius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lagebeziehungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anastomosen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Endäste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Versorgungsgebiet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Topographische Schlüsselpunkte . . . . . . . . . . . Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Klinik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209 210 210 210 210 210 211 212 212 214 214 214 Leseprobe von Alain Croibier und Jean-Pierre Barral „Manipulation kranialer Nerven“ Herausgeber: Elsevier Urban & Fischer Leseprobe erstellt vom Narayana Verlag, 79400 Kandern, Tel: 0049 (0) 7626 974 970-0 190 191 208 Inhaltsverzeichnis 23.3 23.3.1 23.3.2 23.3.3 23.3.4 Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Perforierender Nerv des M. trapezius . . . . . . . . Perforierende Nerven des M. sternocleidomastoideus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Bedeutung der Manipulationen des N. accessorius . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215 215 216 216 26.1.2 26.1.3 26.2 26.2.1 26.2.2 26.2.3 26.2.4 Mechanische Sensibilität des Gehirns . . . . . . . . Veränderungen des intrakraniellen Drucks . . . . Behandlung der zerebralen Viskoelastizität . . Atmung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Atmung und kraniale Bewegung . . . . . . . . . . . Untere Extremitäten . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kompression der Augen und des Meatus acusticus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen und Kontraindikationen . . . . . . . . 238 238 238 238 239 239 Part III . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241 27 27.1 27.2 243 244 216 26.2.5 24 24.1 24.1.1 24.1.2 24.1.3 24.1.4 24.1.5 24.2 24.2.1 24.2.2 24.3 24.3.1 24.3.2 219 220 220 220 220 221 221 222 222 222 223 223 24.3.3 Nervus hypoglossus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anatomischer Überblick . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ursprung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verlauf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lagebeziehungen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Anastomosen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kollateralen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pathophysiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Klinik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Inframandibuläre Techniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Entscheidende Punkte der kraniosakralen Mechanik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25 25.1 25.1.1 25.1.2 25.2 25.2.1 25.2.2 25.3 25.3.1 25.3.2 25.3.3 25.3.4 25.4 25.4.1 25.4.2 25.4.3 25.4.4 Das Ohr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Außenohr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ohrmuschel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Meatus acusticus externus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Mittelohr . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Trommelfell . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Paukenhöhle . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Untersuchung der Ohren . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ohrmuschel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Periaurikuläre Region . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Meatus acusticus externus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Trommelfell . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Behandlungstechniken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ohrmuschel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Meatus acusticus externus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indikationen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Vorsicht . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225 226 226 229 231 231 231 232 232 232 233 233 233 233 234 235 236 26 26.1 26.1.1 Behandlungstechniken für das Gehirn . . . Mechanische Merkmale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Zerebrale Viskoelastizität . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237 238 238 223 224 IX . 28 28.1 28.2 29 29.1 29.1.1 29.1.2 Pathologien der Hirnnerven . . . . . . . . . . . Pathologien der einzelnen Hirnnerven . . . . . . Mehrere Hirnnerven betreffende Pathologien . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lymphadenopathien im Hals- und Gesichtsbereich . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Schwellungen im Gesicht . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Seitlich am Hals auftretende Schwellungen . . 239 240 244 247 248 248 249 250 250 29.1.3 29.2 29.2.1 29.2.2 Zervikalgien kranialen Ursprungs . . . . . . . Erhöhter intrakranieller Druck . . . . . . . . . . . . Symptomatologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Hauptursachen für erhöhten intrakraniellen Druck . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Topographische Klinik . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Meningeales Reizsyndrom . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Symptome . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Krankheitszeichen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30 30.1 30.2 30.3 30.4 30.4.1 30.4.2 30.4.3 30.4.4 30.4.5 30.5 Sinusitis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Pneumatische Rolle der Nebenhöhlen . . . . . . Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Symptome . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Lokalisation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Os frontale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Maxilla . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Os ethmoidale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Os sphenoidale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kombinierte Sinusitis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Ätiologie . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 253 254 254 254 254 254 254 254 254 255 255 31 31.1 Autonomes Nervensystem . . . . . . . . . . . . . Sympathikus und Parasympathikus . . . . . . . . 257 258 Leseprobe von Alain Croibier und Jean-Pierre Barral „Manipulation kranialer Nerven“ Herausgeber: Elsevier Urban & Fischer Leseprobe erstellt vom Narayana Verlag, 79400 Kandern, Tel: 0049 (0) 7626 974 970-0 250 250 251 251 251 X Inhaltsverzeichnis 31.2 31.2.1 31.2.2 31.3 31.3.1 31.3.2 31.4 N. glossopharyngeus und N. vagus . . . . . . . . Viszerosensibilität des N. glossopharyngeus . . . Parasympathische Fasern des N. vagus . . . . . . . Halsteil des sympathischen Systems . . . . . . . Die zervikalen Grenzstrangganglien . . . . . . . . . Verteilung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Erhöhter Sympathikotonus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 258 258 259 260 260 262 264 32 32.1 32.2 32.2.1 Neuroglia . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Allgemeines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Verschiedene Gliazellen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Oligodendrozyten . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267 268 268 268 s01 s02 s03 32.2.2 32.2.3 32.3 32.4 32.4.1 32.5 Mikroglia . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Astrozyten . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Motilität der Neuroglia . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Funktionen der Gliazellen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Kommunikation der Astrozyten . . . . . . . . . . . . Pathogene Rolle der Gliazellen . . . . . . . . . . . 268 268 268 269 269 270 33 Schlussbemerkung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271 Anhang . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Glossar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273 275 277 s04 s05 s06 s07 s08 s012 Leseprobe von Alain Croibier und Jean-Pierre Barral „Manipulation kranialer Nerven“ Herausgeber: Elsevier Urban & Fischer Leseprobe erstellt vom Narayana Verlag, 79400 Kandern, Tel: 0049 (0) 7626 974 970-0 Barral / Croibier Manipulation kranialer Nerven 304 Seiten, erschienen 2008 Mehr Bücher zu Homöopathie, Alternativmedizin und gesunder Lebensweise www.narayana-verlag.de