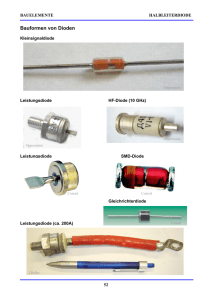
Was ist eine TVS Diode?
Werbung

Overvoltage Protection of Devices and Circuits using TVS Diodes SeCoS GmbH, Germany Inhalt Contents • SeCoS in Kürze SeCoS in brief • Was ist eine TVS Diode? What is a TVS diode? • TVS oder Zener TVS versus Zener • Applikationsbeispiele Application examples • Auswahl des richtigen Bauelements How to select the optimum device 1 Was ist eine TVS Diode? What is a TVS diode? IF VC VBR VWM ID IT VF IPP • Kennlinie wie eine Zenerdiode Curve like Zener diode • Bidirektionale Version erhältlich! Bidirectional Version available! 2 Was ist eine TVS Diode? What is a TVS diode? Transient voltage + clamped voltage + peak current circuit to protect Transient voltage - clamped voltage - Überspannungsschutz! Overvoltage Protection! ⇒ Transient Voltage Suppressor 3 TVS oder Zenerdiode TVS versus Zener diode TVS – Unterdrückung von Spannungsspitzen Suppression of transient voltages Zener – Stabilisierung einer Gleichspannung Stabilization of a DC voltage – Auswahlparameter – Auswahlparameter Parameters for selection: Parameters for selection: • VWM Sperrspannung • VZ Zenerspannung • VC Begrenzerspannung • Ptot Statische Verlustleistung Stand-off voltage Zener voltage Clamping voltage Steady state power dissip. • PPPM Impulsverlustleistung Peak pulse power 4 Gate-Ansteuerung Gate Control • Gate-Schutz: 1 bidirektionale TVS- ersetzt 2 antiserielle Zener-Dioden Gate Protection: 1 bidirectional TVS replaces 2 anti serial Zener diodes on request: 2 in 1! • 2 in 1! Aktive Spannungsbegrenzung: Zener-Dioden standardmäßig bis 200 V, TVS bis 440 V! Active Clamping: Standard Zener diodes up to 200 V, TVS up to 440 V! 5 „Crow Bar“ Schaltung Crow bar circuit Mit/with TVS: Mit/with Diac: 6 TVS Dioden in Schaltnetzteilen TVS diodes in SMPS Beispiel: Sperrwandler Example: flyback converter 5 V= 230 V~ 7 Auswahl des optimalen Bauteils Beispiel: Klemmkreis eines 10 W-Sperrwandlers, Eingangsspannung 230 V~, Spitzenstrom primärseitig 150 mA, Sperrspannung MOSFET 1000 V 1. Sperrspannung der TVS-Diode VWM ≈ √2 x 230 V ≈ 330 V, z. B. 324 V Netztoleranz +10%: √2 x 250 V = 353 V < 360 V = VBRmin √ 2. = 574 V ⇒ Maximale Spannung am MOSFET: 574 V + 330 V = 904 V √ 3. ⇒ P4KE400C mit IPPM = 730 mA √ Dauer-Verlustleistung ca. 500 mW ⇒ P4KE400C mit PM(AV) = 1 W √ 4. Alternativ: 2 x TGL34-200C (SMD MiniMELF!) in Reihe Begrenzerspannung der TVS-Diode mit VWM = 324 V: VC Impulsstrom IPPM ≥ 150 mA 8 Selecting the optimum device Example: Clamping circuit of a 10 W flyback converter, input voltage 230 VAC , primary peak current 150 mA, MOSFET blocking voltage 1000 V 1. Stand-off voltage of TVS diode VWM ≈ √2 x 230 V ≈ 330 V, e. g. 324 V Mains tolerance +10%: √2 x 250 V = 353 V < 360 V = VBRmin √ 2. Clamping voltage of TVS diode (VWM = 324 V): VC = 574 V ⇒ Maximum appearing MOSFET voltage: 574 V + 330 V = 904 V √ 3. Peak pulse current IPPM ≥ 150 mA ⇒ P4KE400C with IPPM = 730 mA √ Steady state power dissipation ~ 500 mW ⇒ P4KE400C with PM(AV) = 1 W√ 4. Alternatively: 2 x SMAJ200A (SMD MiniMELF!) in series 9 Danke Thank you