Hodentumore (Dr. Pytel)
Werbung

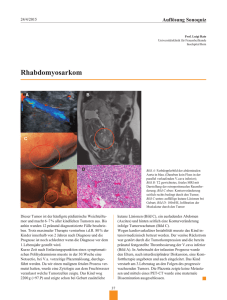
HODENTUMORE Ákos Pytel MD., PhD. Epidemiolog ie I Epidemiologie 0,8 -6,7 neue Faelle jaehrlich/100.000 0,8-6,7 Haufigste bösartige Tumor in den 15 -35 15-35 Jaehrigen Epidemiolog ie II Epidemiologie 3. führende Todesursache wegen Malignomen in diesem Lebensalter Grosse Heilungsrate Positiv M odel für die „„multimodel” multimodel” Therapie Model Alle Stadien Stadien:: Low stage: 80 -90% 80-90% 95 -100% 95-100% Risk F aktoren I Faktoren Un descendierte Hoden (10x) Undescendierte orchidopex ie is icht ppreventiv reventiv orchidopexie istt nnicht US Weissen (4x) in Vergleich mit Afros Östrogen Therapie (3x) Waehrend Schwangerschaft Risk Faktoren (II) High society (2x) gute socio -ökonomicshe Umstaende socio-ökonomicshe Trauma und Atrofie als Ursache ist nicht Nachweisbar Kein Association mit Viren In den 1970’ neue diagnostische und therapeutische Massnahmen AFP und HCG Neue mit der Therapie Zusammenhang zeigende Klassifikation (Mostofi) Klassifikation(Mostofi) Chemotherapie auf Platinum Basis Erkennung der lymphogen System des Hodens Neue chirurgische Techniken Neoplasmen des Hodens I. Keimzellen Tumore (GCT) (~95%) II. Stroma zellen Tumor e (<5%) Stromazellen Tumore Leydig cell, S ertoli cell Sertoli III. Sekundaere Tumore Lymphoma M anifestation Manifestation Metast hasen ((Prostata, Prostata, Lungen Metasthasen Lungen,, Magen Magen)) IV. Andere Tumore Sarcoma, Mesothelioma GCT Seminoma Embr ionale carcinoma Embrionale Teratoma Yolk sac tumor (35%) (20%) (5%) ((selten) selten) Endodermal sinus tumor EDS Choriocarcinoma Gemischte Tumore ((selten) selten) (40%) Streuung Lymphogen P araaortale und paracavale Lymphknoten Paraaortale Choriocarcinoma Choriocarcinoma:: hematogene Streuung Metasthasen (1) Lungen (2) Leber schlechte Prognose Leber,, Gehirn ((schlechte Prognose)) Diagnose Geschichte Physikale Untersuchung Labor (AFP, hCG hCG,, LDH) Scrotal Ultraschall (min. 5 MHz) (T ransillumination) (Transillumination) Ursachen „„Intrascrotale Intrascrotale Raumforderung ” Raumforderung” Tumor E pididimytis, O rchitis Epididimytis, Orchitis H ydrocele, H ematocele Hydrocele, Hematocele V aricocele Varicocele T orsion Torsion S crotal H ernia Scrotal Hernia Symptome Schmerzlose Vergrösserung des Hodens Keine Inflammationssymptome Harte „„Knoten” Knoten” in dem Hoden Oft bei sexulaler Partnerin entdeckt Ziehgefühl oder Schwergefühl IIm m Unterbauchbereich oder scrotal Oligo -asthenozoospermie Oligo-asthenozoospermie Symptome Metasthasen „„Unbekannte” Unbekannte” retroperitoneale Raumforderung Raumforderung,, supraclaviculaere Lymphkonoten Bei Ultraschal oder Palpation inzidental Entdeckt Rückenschmerzen Symptome Metasthasen Beingeschwülste V. cava inf inf.. Kompression Hemoptoe Hemoptoe,, dyspnoe dyspnoe,, Husten Pulmonale Filialien Gynecomastia E ndokrin M anifestation (HCG) Endokrin Manifestation Tumor Markers Specific Human Chorionic Gonadotropin ((hCG) hCG) Alfa -fetoprotein (AFP) Alfa-fetoprotein Non specific La ktat Laktat dehydrogenase (LDH) Carcinoembryon ale Carcinoembryonale antigen (CEA) Tumor Markers Wofür ? Wofür? Diagnose Staging Follow -up Follow-up AFP Glycoprotein 70.000 D „Half Life Time”: 5 Tage ELISA Normalwert /ml Normalwert:: unter 5 ng ng/ml HCG Glycoprotein 38.000 D „Half Life Time”: 1 day ELISA Normal wert: unter 5 mU / ml Normalwert: HCG und AFP AFP hCG AFP or hCG Seminoma – 9% 9% Teratoma 37% 25% 44% Yolk sac.tu. 75% 25% 75% Embryonal cc. 70% 60% 87% – 100% 100% Choriocc. Untersuchungen Labor T umor markers (AFP, HCG, LDH) Tumor Thorax CT //Rtg Rtg ((Seminoma) Seminoma) Bauch CT Fa kultative Untersuchungen Fakultative Iv. Urograph ie Urographie Cavograph ie Cavographie Isotop Untersuchungen dynami sche R enographie, dynamische Renographie, Gehirn Gehirn,, Leber Leber,, Knochen Sperm iogramm Spermiogramm Staging STAGE I STAGE IIA STAGE IIB Nur Hode ist involviert Regionale lymphknotenmetasthase < 2 cm 2-5 cm solitaere oder multiplex RLKM STAGE IIC Über 5 cm RLKM STAGE III Extraregionale oder haematogaene Metasthase Behandlung 1. Etape kale orchiectom ie Etape:: Radi Radikale orchiectomie Hoche Semicastration 2. Etape Etape:: Stage un Hystologie bestimmen Surveillance: Wait and See Bestrahlung Chemotherap ie Chemotherapie RPLND Bestrahlung Nur Seminoma ist radiosensitiv „Ultra High Voltage” Bestrahlung Stage I and II A 7 x Risiko für sekundaere Malignomen 7x nach 10 Jahren Chemotherapie Platin um Basis ((Carbo Carbo (SGCT), Cis(NSGCT Platinum Cis(NSGCT)) Heilungsrate dramatisch besser PVB: Cisplatin Cisplatin,, Vinblastin Vinblastin,, Bleomycin by Einhorn 1977 PEB: Cisplatin Cisplatin,, Etoposid Etoposid,, Bleomycin by Williams 1987 Chirurgie Hoche Semicastration Staging RPLND RPLND Prima ere RPLND Primaere Bilateral, unilateral, modifizierte erve modifizierte,, nnerve sparing Salvage RPLND Nach Chemot -, Radiotherapie Chemot-, Second look RPLND Bei primaere LND nicht operierbare LK, nach Chemo Surveillance für Stage I NSGCT Konzept „„overtreatment” overtreatment” in 75% den Stage I Patienten (RPLND, Chemo Chemo)) Konditionen sorgfaeltige S taging, gute P atientencompliance, Staging, Patientencompliance, pT1 tumor ohne vascula ere IInvasion nvasion vasculaere Nachteil 20 -25% Relasrate die viel agressive Behandlung 20-25% benötigen spaeter Therap ie Therapie Low Stage Seminomas Hoche Semicastration Surveillance ((Stage Stage I) Carboplatin Monotherapie singledose singledose,, mehrere Bestrahlung RPLN Profilaktisch Profilaktisch,, therapeutisch Therap ie Therapie Seminoma Stage IIB, IIC, III Hoche Semicastration Platin um B asis Chemo Platinum Basis 4 ooder der 6 Zycklen Salvage RPLND wenn nötig R esiduale LK Residuale Therapie Stage I NSGCT Hoche Semicastration Surveillance 20 -40% relapse 20-40% Chemo (2 Zyklen PEB) Prima ere RPLND Primaere Unilateral ((modifizierte) modifizierte) ooder der nerve sparing Therapie Stage II ((„non-bulky”) „non-bulky”) NSGCT Prima ere ((radikal) radikal) RPLND und Primaere adjuvant eC hemo (2 Zyklen adjuvante Chemo Zyklen)) C hemotherapie und Chemotherapie salvage RPLND ((residual residual mass es) masses) 33-4 -4 Zyklen P EB (VPB) PEB Therapie NSGCT (Stage II C, III) IIC, Indu ktive C hemo (4 Zyklen Induktive Chemo Zyklen)) und salvage RPLND ((Metastectomie) Metastectomie) Non Germ Cell Tumor e Tumore Stroma zellen T umore (2 -4%) Stromazellen Tumore (2-4%) Sertoli cell tumor: benignoma Leydig cell tumor: bis 30 % bösartig LLymphoma ymphoma über 60 Jahre Jahre)) oft bilateral DANKE FÜR DIE AUFMERSAMMKEIT!