"MRSA" von Ron Hendrix
Werbung

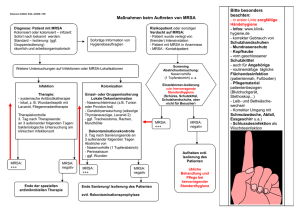
MRSA Ron Hendrix, MD. PhD. Chefarzt microbiology/hygiene/infectiologie Medisch Spectrum Twente, Enschede, University of Twente, Enschede University medical centre Groningen, University Munster Laboratorium Microbiologie Twente-Achterhoek, Enschede Krankenhausinfektionen • In 30-50% der Fälle vermeidbare Komplikation • Häufigster Grund: Bakterien • Antibiotika wirken nicht mehr: Multiresistente Bakterien (z.B. MRSA, MRAB) • Signifikant erhöhte Sterblichkeit • Mehrkosten Allianz-Report 2007 Kosten für nosokomialen Infektionen Europäischer Union: • 4.1 Million Patienten • 16.1 Million extra stationäre Aufnahme tagen jährlich • Extra Kosten: € 7 Billion jährlich • USA: • 44,000-98,000 toten jährlich • Extra Kosten: $ 17-29 Billion jährlich „The big Five“ of healthcare MRSA - ha, ca, la VRE C. difficile MDR-Non-fermenter Acinetobacter spp. Pseudomonas spp. ESBL and KPC (E. coli Klebsiella) Multi-resistenter Erreger: E.Coli (3rd gen. Ceph. R) K.pneumoniae (3rd gen. Ceph. R) MRSA operationelles Beispiel: MRSA Gründe für die Zunahme von MRSA (Europa) Selektionsdruck durch Antibiotika Insuffiziente Hygienemaßnahmen: Klonale Ausbreitung epidemischer MRSA zwischen Krankenhäuser und auch in der Population Keine Durchführung von aktivem Screening potentiell kolonisierter Patienten (RKI Richtlinie) Keine Durchführung von MRSA Sanierung Monnet DL et al. 2004 Emerg Infect Dis. 8 Afif, 2002. Am J Infect Control. 30 Karchmer et al, 2002. J Hosp Infect. 51 Pittet, et al. 2000. Lancet;356 MacKinnon et al. 2000. J Hosp Infect. 46 Karchmer et al. 2002. J Hosp Infect. 51 Diller et al. 2008. Int J Hyg Environ Health :8 MRSA mortality comes On top of the “standard” S.aureus epidemiology MRSA Mortalität S.Aureus Mortalität Effect on patient outcome (death) Cosgrove CID 2003;36:53-9 Effect of MRSA bacteremia versus S.aureus bacteremia Rein Ökonomische Effekte (1) MRSA Besiedlung bei stationäre Aufnahme: (MRSA Besiedlung versus S.aureus Besiedlung) Risiko auf eine post operative Wundinfektion: S.aureus Besiedlung: 2% MRSA Besiedlung: 25% (Relative Risk: 13) (Davis CID 2004;39:776-82) Rein Ökonomische Effekte (2) Risiko auf eine post-operatieve wund Infektion (MRSA Infektion versus S.aureus Infektion) Stationäre Aufnahme dauer: 5 tage extra Extra kosten: 2 mahl mehr (+ € 20.000) (Engeman CID 2003;36:592-8) overall impact (very conservative) For example a division of surgery 25% patients admitted are S.aureus carriers 10% of MRSA carriers become “problem patients” Extra costs per “problem patient”: € 5.000, Secondary transmission rates: 0,5-2 MRSA prevalence: 0-20% 5.000 admissions per year (community hospital with 300 beds and 10.000 admission annually) Extra costs at different levels of MRSA colonization on admission %% MRSA 0% 5% 10% 15% number number extra costs sec number extra MRSA problem transmission MRSA carriers patients rate carriers 0% 62 124 188 0 6 12 18 €0 € 30.000 € 60.000 € 90.000 extra problem patients extra costs total costs preventable 1 0 0 €0 €0 2 0 0 €0 €0 0,5 31 3 € 15.000 € 45.000 2 124 12 € 60.000 € 90.000 0,5 62 6 € 30.000 € 90.000 2 248 24 € 120.000 € 180.000 0,5 94 9 € 45.000 € 135.000 2 376 37 € 185.000 € 275.000 (more likely these costs will be up to 5 times higher) Wahrscheinlich gleiche kosten ebene MRSA - ha, ca, la VRE C. difficile MDR-Non-fermenter Acinetobacter spp. Pseudomonas spp. ESBL and KPC (E. coli Klebsiella) Und Ist das der Europäischer Zukunft ? NO !! We can do better !! Gibt es noch Hoffnung für Europa? (mit oder ohne Griechenland MRSA: 40%) Ja!! • The Dutch-Scandinavian paradox • Das Französische Beispiel • Euregio Twente-Münsterland Hintergrund: Multi resistenter Keime im Alltag „the infection control system“ The infection control system exposure Susceptible population selection expansion resistant clones spread MDR-bug-carrier Antibiotic use Hygiene measures Community (CA-MRSA) ????? Lifestock (vet-MRSA) Healthcare system Care facility (hospital 1) Care facility (nursing home) Care facility (hospital) Niedergelassene Hausarzt Care facility (hospital 2) Care facility (rehab clinic) The infection control system exposure Susceptible population selection expansion resistant clones spread MDR-bug-carrier Antibiotic misuse Bad Hygienic practice The infection control system interventions: screening Controlled antibiotic prescription Hygienic protocols diagnostics Susceptible population resistant clones Antibiotic misuse Antibiotic stewardship spread Bad Hygienic practice Infection control Infection control triangle: search Diagnostics, screening restrict Controlled antibiotic prescription control Hygienic protocols Gibt es noch Hoffnung für Europa? Ja!! • The Dutch-Scandinavian paradox (wie schaffen es die Holländer und die Skandinavier ?) • Das Französische Beispiel • Euregio Twente-Münsterland „The dutch-scandinivian Paradox“ „Search and destroy“ Oder besser: search, control and follow Search: MRSA Risiko Kategorien Kategorien: 1. Bewiesen MRSA Besiedelung/ Infektion 2. Hohes Risiko auf MRSA Besiedelung (Ausland) 3. Niedriches Risiko auf MRSA Besiedelung 4. Kein Risiko auf MRSA Besiedelung Diese Kategorien sind für Patienten und Personal gleich Control: Patienten und personal Patienten Kategorie 1 und 2: • Strickte Isolation: – Einzel zimmer mit unterdrück und schleuse – Schutz Kleidung – abstriche Personal Kategorie 1 und 2: • Keine Verpflegung von Patienten bis MRSA negativ Follow: follow-up von MRSA besiedelte Patienten (80% wird innerhalb von 12 Monate wieder aufgenommen) • Ear-mark MRSA besiedelte Patienten • erzähle bei übergaben das ein Patient MRSA besiedelt ist • Versuche den MRSA besiedelte Patient zu sanieren und ebenso fuhr Personal WWW.MRSA-net.eu Gibt es noch Hoffnung für Europa? Ja!! • The Dutch-Scandinavian paradox • Das Französische Beispiel • Euregio Twente-Münsterland Antibiotika und Probleme country Antibiotic consumption Netherlands 8,9 Denmark 11,3 Sweden 13,5 Germany 13,6 Belgium 26,7 Portugal 28,8 Spain 32,4 France 36,5 ESAC data 2004 DDD/1000 inhabitant days (European Surveillance Antimicrobial Consumption) Only very few new antibiotics are in the pipeline The next 10-20 years Practically no new antibiotics will be available! Frankreich: Massiver Aufklärung Compagnien Bevölkerung (AB-verbrauch) Gibt es noch Hoffnung für Europa? Ja!! • The Dutch-Scandinavian paradox • Das Französische Beispiel • Euregio Twente-Münsterland • Cross border regio slide Cross border infection control EUREGIO MRSA-net, Project coordinators Hauptzielen MRSA-net: • Key-leaders: Aufklärung und zusammenbringen (netze aufbauen) • Qualität Siegel • MRSA case-management • Epidemiologisch Plattform • Unterstützung Patienten und professional Decolonization of MRSA carriers: Decontamination procedure: • 5 days treatment with: – Skin and hair desinfection: • Daily use of: povidon-iodine shampoo or chlorohexidine scrub – Nose disinfection: • Mupirocine • 2-4 days no treatment and than again MRSA cultures are taken • If this procedure doesn’t work systemic antibiotics are added 12 Monats-MRSA Case-Management Andreas Kintrup, Dr. Nierhoff (Kassenärztliche Vereinigung Westfalen-Lippe) Recall ! MRSA decolonization was not reimbursed !! EUREGIO Sonderziffern: Problem: wer bezahlt? 90830: MRSA-Patient Besiedlung+Infektion Beratung, Diagnostik, Therapie Praxisbesonderheit 32006: Abstriche Wirtschaftlichkeitsbonusneutral ! 80033: Kontaktpersonen Keine Praxisgebühr für Screening Muprirocin receipts at pharmacy for outpatients in the EUREGIO Jan to Jun 2005 (n = 32) Muprirocin receipts at pharmacy for outpatients in the EUREGIO Jan to Jun 2008 (n = 265) Ambulant MRSA case management Kreis Praxen Patienten Sanierungs versuch Sanierung erfolgreich 208 Arztpraxen: 54%Hausärzte 46% Fachärzte Borken 21% 81 46 46 Steinfurt 25% 175 111 94 Sanierungsversuch:64% Sanierungserfolg: 90% Warendorf 14% 79 51 45 Coesfeld 15% 99 76 65 Münster 25% 91 57 55 100% 525 (100%) 338 (64%) 303 (90%) EUREGIO MRSA Im Euregio MRSA-Blutkulturen in der Euregio (De) (Daten: vorläufige Trendanalyse) ww.mrsa-net.eu 47 veröffentl. am 18.11.2008 EurSafety Health-net Euregional network for patient safety and infection control www.eursafety.eu Projektgebiet 5 Euregios (4+1) 38 Kreise/Regios 19,2 Mio. Einwohner 32 ÖGD/GGD 12 Expertenzentren ca. 300 Krankenhäuser the Dutch Scandinavian paradox Haupt Faktoren für erfolg: • Screening von Risiko Patienten (search) • Strenge Isolation Maßnahmen (Control) • Sanierung Patienten mit MRSA (destroy, follow) • Strenge Antibiotika-Politik (Restrict) (wie schaffen es die Holländer) EUREGIO Qualitätssiegel (EQS) Versorgungsnetz 5 Weiterbehandlung Hygienepersonal MRE/Rationaler Antibiotikaeinsatz MRSA‐Prävention, Screening 4 3 2 1 On behalf of all contributors: Hartelijk bedankt! Vielen Dank für Ihre Aufmerksamkeit thank you for your attention! Intervention: Hand hygiene: Harrington (infect control hosp epidemiol 2007;28::837-44) • 80% reduction of MRSA-STR Gagne (j hosp infect 2010;75:269-72) • 50% reduction of MRSA-STR Cummings (infect control hosp epidemiol 2010;31:357-64) • 200 bed hospital situation: • 1,0% increase in hand hygiene compliance: cost reduction of $ 39.000