Exercises
Werbung

Prof. Dr. Stefan Böttcher
Exercises for the course
Databases and Information Systems I
WS 2006/2007
Special exercise – JDBC
1. Preliminary configurations
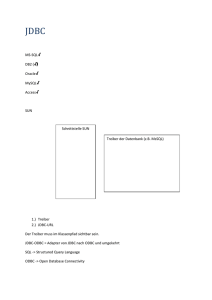
1.1. Register ODBC database
Chose „Arbeitsplatz“ | “Systemsteuerung” | “Verwaltung” | “Datenquellen(ODBC)” and then the tab
“Benutzer-DSN”.
If the name "odbc2access" is not yet registered:
• Select the button "Hinzufügen“, and then chose from the list of drivers the driver
"Microsoft Access-Driver (*.mdb)".
• Click "Fertigstellen". Chose "odbc2access" as name of the data source.
• Click "Auswählen" in the panel “Datenbanken” and select the database db2000.mdb which is
contained in the zip-file,
• Click OK repeatedly to leave the ODBC data source administrator.
1.2 Configure variables
The batch file j5pool.bat configures the variables PATH and CLASSPATH. This batch file has to be
executed in each DOS-shell.
Open a DOS-shell, execute the batchfile and compile and execute the program dbinit.java:
working directory > j5pool
working directory > javac dbinit.java
working directory > java dbinit
1.3 Overview of examples
The program dbinit.java generates a small example database. It demonstrates how to create and to delete
tables and how to insert entries in to the database.
The program dbselect.java demonstrates how to execute queries on the database with JDBC and how to
process the results in the java program.
The programs dbinf.java and dbtab.java demonstrate how to access meta information of the database and of
the database tables.
The programs exinit.java, exselect.java, exselect.java, exinf.java and extab.java demonstrate the same issues
on an excel spreadsheet instead of an access database.
The program excel2db.java shows the conversion of an excel spreadsheet into an access table and vice versa.
2. Exercises
2.1. Creating a database and executing queries
E1.1. Compile and execute dbinit.java and dbselect.java to initialize and query the database
Page 1 of 7
E1.2. Add two stmt.executeUpdate commands in dbinit.java to insert the following information:
"Dell supplies a pc400, price: 1800, duration: 2 days" and
"Reich orders a pc500 " .
Compile and execute dbinit.java once again and then execute dbselect.java to verify the modifications.
E1.3. Add the query:
„Who supplies (at least) one item that has been ordered by Reich“
to the program dbselect.java and output the results via JDBC.
Modify – if necessary – the database to verify the correctness of your modifications.
2.2. Querying meta data
E2: Implement a program that outputs the complete content of all tables of the database.
(Hint: Combine dbinf.java and dbtab.java)
2.3. Searching for Strings in the whole database
E3: Implement a program that searches for a given String (e.g. “pc400”) in the whole database, i.e.,
that outputs each tuple of the database that contains the given String, no matter in which table or in
which table-column this string is contained.
Page 2 of 7
3. Examples
3.1. Initializing a database: source code dbinit.java
import java.sql.*;
public class dbinit
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
String ergebnis = "" ;
try {
Class c = Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
// Treiber für ODBC
Connection con =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:odbc:odbc2access");
//
:
:DB-Name unter ODBC
ergebnis = makeDB( con ) ;
System.out.println( ergebnis ) ;
con.close() ;
// darf nicht von einer Exception aus makeDB übersprungen werden!
}
catch (Exception e) { System.out.println( e ) ; }
}
public static String makeDB( Connection con )
{
String ausgabe="" ; // String zum Sammeln der Ausgabe
try
{
Statement stmt = con.createStatement() ;
try
{
stmt.executeUpdate( "drop table Liefert" );
} catch (Exception e) { }
stmt.executeUpdate(
"create table Liefert( Lieferant char(10), Teil char(10), " +
" Preis int, Lieferzeit int ) " );
stmt.executeUpdate(
"Insert into Liefert
stmt.executeUpdate(
"Insert into Liefert
stmt.executeUpdate(
"Insert into Liefert
stmt.executeUpdate(
"Insert into Liefert
stmt.executeUpdate(
"Insert into Liefert
stmt.executeUpdate(
"Insert into Liefert
Page 3 of 7
values('Vobis ','pc400',1700,3)" );
values('Dell
','pc500',2000,6)" );
values('IBM
','pc500',2500,6)" );
values('Vobis ','pc500',2000,3)" );
values('IBM
','pc600',3500,4)" );
values('Vobis ','pc600',2500,3)" );
try
{
stmt.executeUpdate( "drop table Auftrag" );
} catch (Exception e) { }
stmt.executeUpdate(
"create table Auftrag( Kunde char(10), PC char(10) ) " );
stmt.executeUpdate(
"Insert into Auftrag values('Arm ','pc400') " );
stmt.executeUpdate(
"Insert into Auftrag values('Meier','pc500') " );
stmt.executeUpdate(
"Insert into Auftrag values('Reich','pc600') " );
stmt.close();
// Statement schließen
ausgabe += "\nDatenbank initialisiert.\n" ;
} catch (Exception e) { ausgabe += "\n" + "Fehler: " + e ; }
return ausgabe ;
} // makeDB zuende
}
// class
zuende
3.2. Selecting data: source code dbselect.java
import java.sql.*;
public class dbselect
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
String ergebnis = "" ;
try {
Class c = Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
// Treiber für ODBC
Connection con =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:odbc:odbc2access");
//
:
:DB-Name unter ODBC
ergebnis = selectTab( con , "2200" ) ;
System.out.println( ergebnis ) ;
con.close() ;
}
catch (Exception e) { System.out.println( e ) ; }
}
public static String selectTab( Connection con, String limit )
{
String ausgabe="" ; // String zum Sammeln der Ausgabe
try {
Statement stmt = con.createStatement() ;
ResultSet rsLiefert = stmt.executeQuery(
"SELECT * FROM Liefert WHERE Preis < " + limit ) ;
//
Page 4 of 7
Strings in SQL müßten zusätzlich in einfache Hochkommas:
//
"SELECT * FROM Liefert WHERE Teil = '" + limit + "'" ) ;
ausgabe += "\n\nLiefert:\n( Lieferant Teil" +
"
Preis Lieferzeit )" ;
while (rsLiefert.next())
// hole nächstes Tupel aus Result-Set
{
ausgabe += "\n" + rsLiefert.getString("Lieferant") +
"
" + rsLiefert.getString("Teil") +
"
" + rsLiefert.getInt("Preis") +
"
" + rsLiefert.getInt("Lieferzeit") ;
}
rsLiefert.close() ;
stmt.close() ;
// Result-Set schließen
// Statement schließen
}
catch (Exception e)
{
ausgabe += "\nFehler bei Anfrage an die Datenbank:\n" + e ;
}
return ausgabe ;
} // selectTab zuende
}
// class
zuende
Page 5 of 7
3.3. Querying database meta data: source code dbinf.java
import java.sql.*;
public class dbinf
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
String ergebnis = "" ;
try {
Class c = Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
// Treiber für ODBC
Connection con =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:odbc:odbc2access");
//
:
:DB-Name unter ODBC
ergebnis = accessDB( con ) ;
System.out.println( ergebnis ) ;
con.close() ;
}
catch (Exception e) { System.out.println( e ) ; }
}
public static String accessDB( Connection con )
{
String ausgabe="" ; // String zum Sammeln der Ausgabe
try {
DatabaseMetaData md = con.getMetaData(); // Metadaten holen
// Hilfsvariable
final String[] tabellen = {"TABLE"};
// Hole Tabellennamen
ResultSet tablesNames =md.getTables(null,null,null,tabellen);
while (tablesNames.next())
{
// Hole Tabellenname
String tablename = new String(tablesNames.getString(3));
ausgabe += tablename + "\n" ;
}
}
catch (Exception e) { ausgabe += e ; }
return ausgabe;
} // accessDB
} // dbinf
Page 6 of 7
3.4. Querying table meta data: source code dbtab.java
import java.sql.*;
public class dbtab
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
String ergebnis = "" ;
try {
Class c = Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
// Treiber für ODBC
Connection con =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:odbc:odbc2access");
//
:
:DB-Name unter ODBC
ergebnis = accessTab( con , "Auftrag" ) ;
System.out.println( ergebnis ) ;
con.close() ;
}
catch (Exception e) { System.out.println( e ) ; }
}
public static String accessTab( Connection con , String tabelle )
{ int spalte;
String ausgabe="" ; // String zum Sammeln der Ausgabe
try {
Statement stmt = con.createStatement(); // Statement anlegen
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from " + tabelle);
// Hole Meta-Daten für dieses Result Set
ResultSetMetaData rsmd= rs.getMetaData();
int spaltenAnzahl = rsmd.getColumnCount();
for( spalte=1 ; spalte <= spaltenAnzahl ; spalte++ )
{ ausgabe += rsmd.getColumnLabel( spalte ) + "\t\t" ; }
ausgabe += "\n-------------------------------------\n" ;
while (rs.next())
{
for( spalte=1 ; spalte <= spaltenAnzahl ; spalte++ )
{ ausgabe += rs.getString(spalte) + "\t" ; }
ausgabe += "\n" ;
}
}
catch (Exception e) { ausgabe += e ; }
return ausgabe;
} // accessTab
} // dbtab
Page 7 of 7