5 Elementary Plane Geometry and Solid Geometry
Werbung
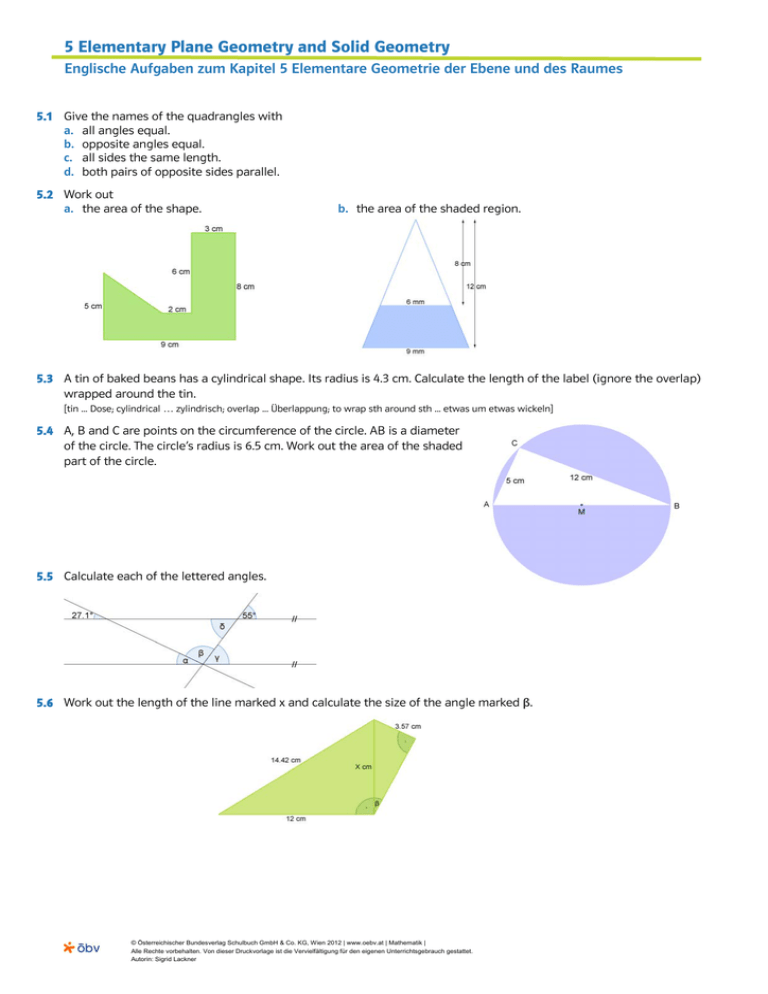
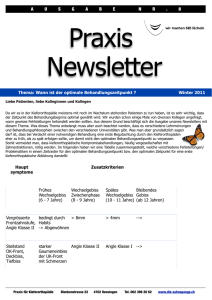
5 Elementary Plane Geometry and Solid Geometry Englische Aufgaben zum Kapitel 5 Elementare Geometrie der Ebene und des Raumes 5.1 Give the names of the quadrangles with a. all angles equal. b. opposite angles equal. c. all sides the same length. d. both pairs of opposite sides parallel. 5.2 Work out a. the area of the shape. b. the area of the shaded region. 5.3 A tin of baked beans has a cylindrical shape. Its radius is 4.3 cm. Calculate the length of the label (ignore the overlap) wrapped around the tin. [tin ... Dose; cylindrical … zylindrisch; overlap ... Überlappung; to wrap sth around sth ... etwas um etwas wickeln] 5.4 A, B and C are points on the circumference of the circle. AB is a diameter of the circle. The circle’s radius is 6.5 cm. Work out the area of the shaded part of the circle. 5.5 Calculate each of the lettered angles. 5.6 Work out the length of the line marked x and calculate the size of the angle marked β. © Österreichischer Bundesverlag Schulbuch GmbH & Co. KG, Wien 2012 | www.oebv.at | Mathematik | Alle Rechte vorbehalten. Von dieser Druckvorlage ist die Vervielfältigung für den eigenen Unterrichtsgebrauch gestattet. Autorin: Sigrid Lackner 5 Elementary Plane Geometry and Solid Geometry Englische Aufgaben zum Kapitel 5 Elementare Geometrie der Ebene und des Raumes 5.7 The three points A, B and C are points on the given circle. Is AB a diameter of the circle? Explain your answer. 5.8 The point A is (3, -2), the point B is (-1, 5) and the point C is (6, 1). AD = (2, -4). a. Write as column vectors: AB and CB b. Calculate the magnitude of the vector AC . c. Work out the coordinates of D. [column vector ... Spaltenvektor; magnitude ... Betrag (eines Vektors)] 5.9 The following regular solids are called the Platonic solids. tetrahedron cube octahedron dodecahedron icosahedron V number of vertices F number of faces E number of edges 8 6 12 a. Complete the following table for each solid. b. Try to find a relationship between V, F and E. Express that relationship in a formula. [solid ... Körper; vertex (plural: vertices) ... Eckpunkt; face ... Fläche; edge ... Kante] 5.10 Victoria wants to model a frustum of a cone out of clay. From a cone with a base of diameter 24 mm and a height of 16 mm she removes a cone with a base of diameter 12 mm and height 8 mm. Calculate the volume of the frustum. [to model ... modellieren; clay ... Ton; to remove ... entfernen] 5.11 A container has the form of a cuboid which is 80 cm (length) by 25 cm (width). 16 litres of water are poured into the container. Calculate the depth of the water. 5.12 Work out the surface area of a square-based (side of 4 cm) pyramid. The vertical height of each of the triangular faces is 12 cm. 5.13 A roly-poly toy is made out of wood. The toy is solid. The toy’s top is a cone of height 13 cm and base radius 2.5 cm. The bottom of the child’s toy is a hemisphere of radius 2.5 cm. Calculate the volume of wood needed to make the toy. [roly-poly toy ... Stehaufmännchen; solid ... massiv] © Österreichischer Bundesverlag Schulbuch GmbH & Co. KG, Wien 2012 | www.oebv.at | Mathematik | Alle Rechte vorbehalten. Von dieser Druckvorlage ist die Vervielfältigung für den eigenen Unterrichtsgebrauch gestattet. Autorin: Sigrid Lackner 5 Elementary Plane Geometry and Solid Geometry Englische Aufgaben zum Kapitel 5 Elementare Geometrie der Ebene und des Raumes Useful Geometry Terms German ¥ English Bogenmaß Cosinus Cotangens Deltoid Drehkegel Drehzylinder Dreieck Durchmesser Flächeninhalt gleichschenklig gleichseitig Gradmaß Höhe Hohlzylinder Hypotenuse Kathete Ankathete Gegenkathete Kegelstumpf Komplementärwinkel Kreis Kreisbogen Kreisring Kreissegment Kreissektor Kugel Kugelkappe Mantelfläche Oberfläche Parallelogramm Prisma Pyramide Pyramidenstumpf Quader Quadrat Radius Raumdiagonale Raute Rechteck rechtwinklig Sinus Steigungsdreieck Steigungswinkel Strecke Streckensymmetrale Supplementärwinkel Tangens Trapez Umfang Viereck Volumen Winkel rechter Winkel stumpfer Winkel spitzer Winkel Winkelsumme Winkelsymmetrale Würfel radian measure cosine cotangent kite cone (of revolution) circular cylinder triangle diameter area isosceles equilateral degree measure height hollow cylinder hypotenuse side adjacent side opposite side frustum of a cone complementary angle circle arc circular ring segment of a circle sector of a circle sphere spherical cap lateral area surface (area) parallelogram prism pyramid frustum of a pyramid rectangular prism, cuboid square radius; plural: radii cubic diagonal rhombus rectangle right-angled, orthogonal, perpendicular sine gradient triangle angle of elevation line segment perpendicular bisector of line segment supplementary angle tangent trapezoid [AE], trapezium [BE] perimeter, circumference quadrangle, quadrilateral volume angle right angle obtuse angle acute angle angle sum angle bisector, bisector of an angle cube © Österreichischer Bundesverlag Schulbuch GmbH & Co. KG, Wien 2012 | www.oebv.at | Mathematik | Alle Rechte vorbehalten. Von dieser Druckvorlage ist die Vervielfältigung für den eigenen Unterrichtsgebrauch gestattet. Autorin: Sigrid Lackner 5 Elementary Plane Geometry and Solid Geometry Englische Aufgaben zum Kapitel 5 Elementare Geometrie der Ebene und des Raumes Useful Geometry Terms English ¥ German angle right angle obtuse angle acute angle angle bisector, bisector of an angle angle of elevation angle sum arc area circle circular cylinder circular ring complementary angle cone (of revolution) cosine cotangent cube cubic diagonal degree measure diameter equilateral frustum of a cone frustum of a pyramid gradient triangle height hollow cylinder hypotenuse isosceles kite lateral area line segment parallelogram perimeter, circumference perpendicular bisector of line segment prism pyramid quadrangle, quadrilateral radian measure radius; plural: radii rectangle rectangular prism, cuboid rhombus right-angled, orthogonal, perpendicular sector of a circle segment of a circle side adjacent side opposite side sine sphere spherical cap square supplementary angle surface (area) tangent trapezoid [AE], trapezium [BE] triangle volume Winkel rechter Winkel stumpfer Winkel spitzer Winkel Winkelsymmetrale Steigungswinkel Winkelsumme Kreisbogen Flächeninhalt Kreis Drehzylinder Kreisring Komplementärwinkel Drehkegel Cosinus Cotangens Würfel Raumdiagonale Gradmaß Durchmesser gleichseitig Kegelstumpf Pyramidenstumpf Steigungsdreieck Höhe Hohlzylinder Hypotenuse gleichschenklig Deltoid Mantelfläche Strecke Parallelogramm Umfang Streckensymmetrale Prisma Pyramide Viereck Bogenmaß Radius Rechteck Quader Raute rechtwinklig Kreissektor Kreissegment Kathete Ankathete Gegenkathete Sinus Kugel Kugelkappe Quadrat Supplementärwinkel Oberfläche Tangens Trapez Dreieck Volumen © Österreichischer Bundesverlag Schulbuch GmbH & Co. KG, Wien 2012 | www.oebv.at | Mathematik | Alle Rechte vorbehalten. Von dieser Druckvorlage ist die Vervielfältigung für den eigenen Unterrichtsgebrauch gestattet. Autorin: Sigrid Lackner