Diagnose Häufige Erreger Substanz 1. Wahl (Tagesdosis
Werbung
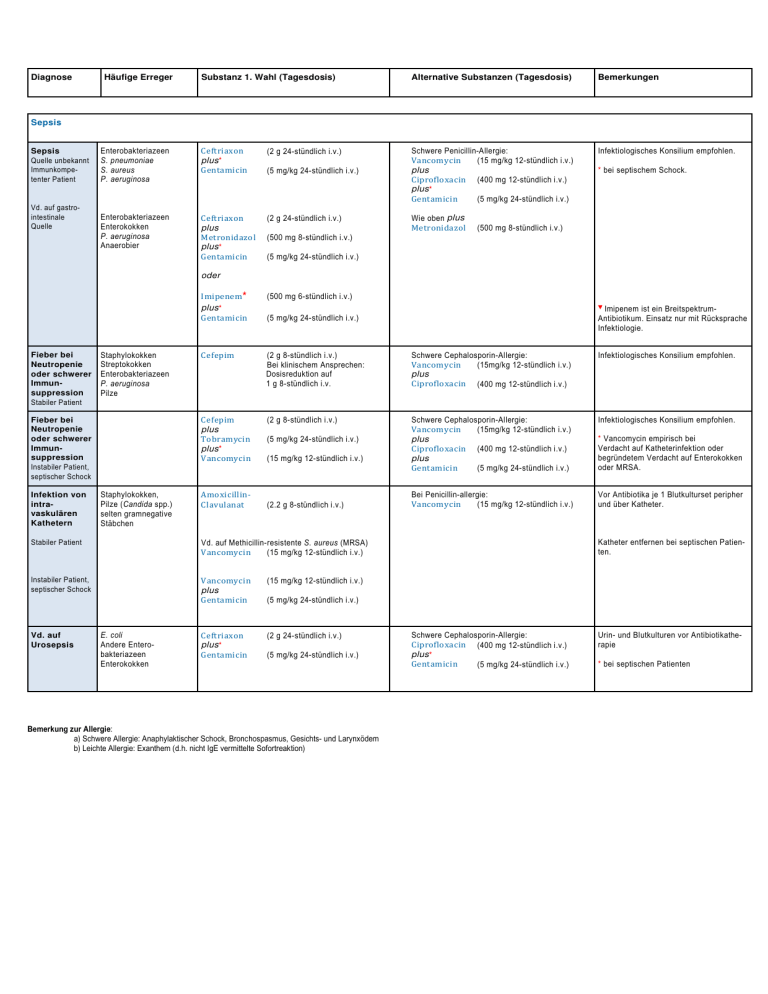
Diagnose Häufige Erreger Substanz 1. Wahl (Tagesdosis) Alternative Substanzen (Tagesdosis) Bemerkungen Schwere Penicillin-Allergie: Vancomycin (15 mg/kg 12-stündlich i.v.) plus Ciprofloxacin (400 mg 12-stündlich i.v.) plus* Gentamicin (5 mg/kg 24-stündlich i.v.) Infektiologisches Konsilium empfohlen. Sepsis Sepsis Quelle unbekannt Immunkompetenter Patient Vd. auf gastrointestinale Quelle Enterobakteriazeen S. pneumoniae S. aureus P. aeruginosa Ceftriaxon plus* Gentamicin (2 g 24-stündlich i.v.) Enterobakteriazeen Enterokokken P. aeruginosa Anaerobier Ceftriaxon plus Metronidazol plus* Gentamicin (2 g 24-stündlich i.v.) (5 mg/kg 24-stündlich i.v.) Wie oben plus Metronidazol * bei septischem Schock. (500 mg 8-stündlich i.v.) (500 mg 8-stündlich i.v.) (5 mg/kg 24-stündlich i.v.) oder Fieber bei Neutropenie oder schwerer Immunsuppression Stabiler Patient Staphylokokken Streptokokken Enterobakteriazeen P. aeruginosa Pilze Fieber bei Neutropenie oder schwerer Immunsuppression Instabiler Patient, septischer Schock Infektion von intravaskulären Kathetern Staphylokokken, Pilze (Candida spp.) selten gramnegative Stäbchen Imipenem * plus* Gentamicin (500 mg 6-stündlich i.v.) Cefepim (2 g 8-stündlich i.v.) Bei klinischem Ansprechen: Dosisreduktion auf 1 g 8-stündlich i.v. Schwere Cephalosporin-Allergie: Vancomycin (15mg/kg 12-stündlich i.v.) plus Ciprofloxacin (400 mg 12-stündlich i.v.) Infektiologisches Konsilium empfohlen. Cefepim plus Tobramycin plus* Vancomycin (2 g 8-stündlich i.v.) Schwere Cephalosporin-Allergie: Vancomycin (15mg/kg 12-stündlich i.v.) plus Ciprofloxacin (400 mg 12-stündlich i.v.) plus Gentamicin (5 mg/kg 24-stündlich i.v.) Infektiologisches Konsilium empfohlen. Bei Penicillin-allergie: Vancomycin (15 mg/kg 12-stündlich i.v.) Vor Antibiotika je 1 Blutkulturset peripher und über Katheter. AmoxicillinClavulanat (5 mg/kg 24-stündlich i.v.) (15 mg/kg 12-stündlich i.v.) (2.2 g 8-stündlich i.v.) Stabiler Patient Vd. auf Methicillin-resistente S. aureus (MRSA) Vancomycin (15 mg/kg 12-stündlich i.v.) Instabiler Patient, septischer Schock Vancomycin plus Gentamicin (15 mg/kg 12-stündlich i.v.) Ceftriaxon plus* Gentamicin (2 g 24-stündlich i.v.) Vd. auf Urosepsis E. coli Andere Enterobakteriazeen Enterokokken ▼Imipenem ist ein BreitspektrumAntibiotikum. Einsatz nur mit Rücksprache Infektiologie. (5 mg/kg 24-stündlich i.v.) * Vancomycin empirisch bei Verdacht auf Katheterinfektion oder begründetem Verdacht auf Enterokokken oder MRSA. Katheter entfernen bei septischen Patienten. (5 mg/kg 24-stündlich i.v.) (5 mg/kg 24-stündlich i.v.) Bemerkung zur Allergie: a) Schwere Allergie: Anaphylaktischer Schock, Bronchospasmus, Gesichts- und Larynxödem b) Leichte Allergie: Exanthem (d.h. nicht IgE vermittelte Sofortreaktion) Schwere Cephalosporin-Allergie: Ciprofloxacin (400 mg 12-stündlich i.v.) plus* Gentamicin (5 mg/kg 24-stündlich i.v.) Urin- und Blutkulturen vor Antibiotikatherapie * bei septischen Patienten