Informationsgehalt von DNA
Werbung

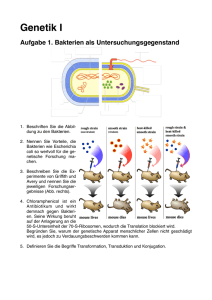
Informationsgehalt von DNA Topics • Genes – code, gene organisation, signals, gene detection • Genomes – genome organisation, nucleotide patterns, junk DNA DNA als Informationsträger DNA Building Blocks Desoxyribose Phosphate Base DNA Konformationen Neben der Normalform (B) gibt es noch weitere Konformationen A B A und Z Formen könnten möglicherweise regulatorische Funktionen besitzen Z DNA ist das genetische Material 1920th tote infektiöse Bakterien harmlose Bakterien lebende infektiöse Bakterien + 1944 (Avery): harmlose Bakterien tote infektiöse Bakterien DNAse behandelt harmlose Bakterien + harmlose Bakterien tote infektiöse Bakterien Proteinase behandelt + lebende infektiöse Bakterien DNA als Informationsquelle sie trägt lineare Information die Information ist veschlüsselt die Information muss übersetzt werden sie kann kopiert werden sie kann verändert werden sie lebt nicht Mögliche Kodierungsarten Überlappende Kodes dies bedeutet Einschränkungen in der Aminosäurenutzung Tripletts, die von Kommata unterbrochen sind 1 Base für das Komma, 27 Möglichkeiten für Aminosäuren Komma-freier Triplettkode 20 Aminosäuren 64 Möglichkeiten > wobble code Wobble Code 1 Startkodon 3 Stopkodonen Bis zu 6 Kodonen/Aminosäure What is a Protein Coding Gene? the transcribed unit consists of: coding frame from Start to Stop Codon 5' untranslated region (5' UTR) from transcription start site to ATG 3' untranslated region (3' UTR) from Stop to termination/polyA signal introns from donor to acceptor Gen-Organisation Prokaryotes Promotor ATG TAA TAG TGA Terminator ATG TAA TAG TGA polyA-Signal Gene locus mRNA Protein Eukaryotes Promotor Gene locus hnRNA mRNA Protein =intron Signale in DNA Signal-Detektion Probleme: schwache Signale konservierte Motive sind sehr kurz (z.B. Splice Donoren und Acceptoren) Konservierung ist nicht zu 100 % Species specifische Signale Structurkomponenten der Signale sind schwer zu berechnen Gene Signals in DNA CpG islands methylation patterns promotors polymerase binding site cofactors binding sites enhancer silencer transcription start sites introns donors acceptors branch point splice enhancers/silencers polyadenylation signals termination signals Unterschied Sequenz- Motiv - Signal Sequenz Eine eindeutige Anzahl von Basen. Position und Reihenfolge stehen fest Motiv Basenabfolge unbestimmter Länge, aber erkennbarem Muster Signal Positionsabhängige Häufigkeitsverteilungen von Basen bezogen auf mehrere zugrundeliegende Sequenzen Motive Das Motiv: ATN1-3G2CGTNxTGA4,5 kann in viele mögliche Sequenzen übersetzt werden: ATGGGCGTAGAGGAGACTTTATGAAAAA ATCGGCGTTGAAAA ATAAGGCGTGAGTGAAAAA etc. =stabile Motivanteile IUPAC Beschreibung von Signalen a a; adenine c c; cytosine g g; guanine t t; thymine in DNA; uracil in RNA m a or c Beispielmotiv r a or g w a or t s c or g y c or t k g or t v a or c or g; not t h a or c or t; not g d a or g or t; not c b c or g or t; not a n a or c or g or t mit IUPAC wobble NNGTAWBTSRWM IUPAC=International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry ‚Positional Weight Matrix‘ Berechnung Erstellung einer ‚position frequency matrix‘ PFM Normalisierung ergibt Wahrscheinlichkeiten für eine Base an einer Position normalisierte PFM Berechnung der Wahrscheinlichkeit einer Sequenz, ein Profil widerzuspiegeln Das Produkt der Wahrscheinlichkeit jeder Base an der entsprechenden Position Für die Computeranalyse: Umrechnung in Log Werte mit Korrekturfaktor (Korrekturfaktor sehr unterschiedlich, z.B. Quadratwurzel der Anzahl an Positionen) +Korrektur für die Nukleotidfrequenzen =PWM ‚Score values‘: Summierung aller PWM Werte über die Länge des Profils Positional Weight Matrix (PWM) # scale = ln (frequency) # frequency counts are based on N(seq) = 21 # A C G T 1.50 1.25 2.25 1.50 1.70 0.92 2.01 1.87 2.01 0.92 1.50 2.01 The smaller the differences in base values -0.69 -0.69 -0.69 2.80 the lower is the information content 2.35 -0.69 1.87 -0.69 0.41 0.41 2.67 -0.69 -0.69 2.44 -0.69 1.70 The larger the differences in base values 0.41 0.41 1.50 2.35 the higher is the information content 0.41 2.25 0.41 1.70 2.80 -0.69 -0.69 -0.69 0.41 -0.69 2.67 0.41 0.92 0.41 -0.69 2.60 0.41 2.01 -0.69 2.14 -0.69 -0.69 2.80 -0.69 -0.69 -0.69 2.80 -0.69 Produced from an alignment of 0.92 0.92 -0.69 2.53 21 sequences of A-Box motifs 2.53 0.92 0.41 1.70 in D. discoideum 1.87 0.92 2.25 1.25 2.35 0.92 1.25 1.70 PWM Graphics A-Box Motif from tRNAs in D. discoideum PWM Formulas from: Nature Reviews Genetics 2004, 5 276-287 Sliding Windows Sequence Window window size step 55 58 59 54 56 Result (GC%) Scanning for Sequence Motifs ...CACGGTAAATTATTTA... Score value according to occurence of bases