10_FW_Betriebskapital_2
Werbung

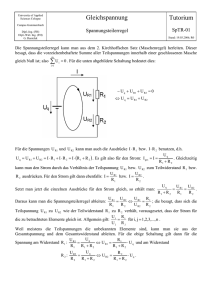
Finanzwirtschaft 10. Vorlesung Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft Betriebskapital 2 Übungsaufgabe „Bodyshop" Lieferbedingungen Kreditwürdigkeit Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft 1 Net Working Capital Analysis • 2.1. What are the days in Inventory, the days in A/R and the days in A/P for The Body Shop? How does it compare with the competitors? • 2.2. What are the operating cycle and the cash cycle? How could The Body Shop improve its cash cycle? Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft Betriebskapital 2 Übungsaufgabe „Bodyshop" Lieferbedingungen Kreditwürdigkeit Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft 2 2 Lieferbedingungen 1 • Ein Unternehmen, das auf Ziel Ware kauft, leiht sich Geld von seinen Lieferanten. Eine Firma, die Waren auf Ziel liefert, stellt ihren Kunden de facto Geld zur Verfügung. • Diese „Kreditpolitik" hat einen Preis: die effektive jährliche Verzinsung Effective Annual Rate (EAR) Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft Aufgabe 1 • Eine Firma verkauft Waren im Wert von $100 zu der Kondition 2% Skonto bei Zahlung in 10 Tagen, Betrag netto fällig in 40 Tagen. (2/10, net 40) • Wie hoch ist die effektive jährliche Verzinung (EAR)? Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft 3 3 Lieferbedingungen 2 365 Skonto EAR = 1 +■ Tage der Kreditdauer -1 Preis - Skonto Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft Lieferbedingungen 3 • Eine Firma sollte die „Kreditpolitik" wechseln, wenn der Nutzen (Ertrag) größer ist als die Kosten. • drei Fragen • Wie viel wird der Umsatz steigen? Dies ist abhängig vom Wettbewerb in der Branche. • Wie lange wird die Umsatzsteigerung anhalten? Dies ist abhängig von der Wettbewerb in der Branche. • Wie hoch ist das Risiko von Zahlungsausfällen bei den Kunden? Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft 4 Aufgabe 2: Frage 1 • Last year, Epsilon sold $40 million on credit, with terms of net 40. Accounts Receivable (a/r) at the beginning and at the end of the year were $4 million and $6 million, respectively. • The disscount rate is 10%. 1. What is the present value of the current credit policy? Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft Aufgabe 2: Frage 2-3 Epsilon is considering offering a new credit policy, with terms of 3/10, net 40. The company anticipates that 75% of the customers will take advantage of the discount. As a result, the average days in A/R will be reduced by 15 days. 2. What is the present value of the new credit policy? Should Epsilon implement it? 3. What is the growth in sales that Epsilon should experience, in order to implement the new credit policy? Is it realistic? Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft 5 5 Betriebskapital 2 Übungsaufgabe „Bodyshop" Lieferbedingungen Kreditwürdigkeit Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft Kreditanalyse 1 • Das Ziel einer Kreditanalyse ist es, die Kreditwürdigkeit des Kunden festzustellen. • Eine Kreditanalyse ist notwendig bei • großen Kunden und • wenn es einen Zweifel über die Rückzahlung durch den Kunden gibt. Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft 6 6 Kreditanalyse 2 • Die Kreditwürdigkeit eines Kunden ist zu beurteilen durch: • Externe Analyse (Dun & Bradstreet) und • Interne Analyse. • Die Multiple Discriminant Analysis (MDA) ist ein Technik, die von Altman (1968) entwickelt wurde um die Kreditwürdigkeit des Kunden zu beurteilen. Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft Kreditanalyse 3 • Z-Score = 1.0 x ( Sales / Total Assets ) + 3.3 x ( EBIT / Total Assets ) + 1.4 x ( Retained Earnings / Total Assets ) + 1.2 x ( Net Working Capital / Total Assets ) + 0.6 x ( MV Equity / BV Debt ) • Je höher der Z-Score, umso geringer das Risiko des Zahlungsverzuges, das heißt desto höher die Kreditwürdigkeit des Kunden. Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft 7 7 Ausblick • Durcharbeiten • Alles Wiederholen • Das tolle Projekt • Vorbereiten auf die 11. Vorlesung Fachhochschule Lausitz Prof. Dr. Wilhelm University of Applied Sciences Produktionswirtschaft 8