D1A5 Starke Verben [Strong Verbs]
Werbung
![D1A5 Starke Verben [Strong Verbs]](http://s1.studylibde.com/store/data/005537802_1-7c1b99dd5766654382e175dbf31adcce-768x994.png)
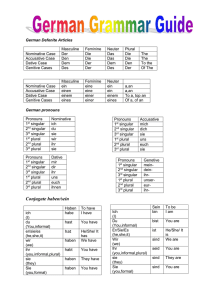
D1A5 Starke Verben [Strong Verbs ] In Aufgabe 2 we learned about regular verbs – the first major verb pattern - and how to create verb forms using a stem and an ending. The second major verb pattern is the strong verb pattern. We create strong verb forms again using a stem and the same endings we used earlier. The stem for the strong verbs often exihibits more than one form. The verb ‘haben’ from Aufgabe 2 is an example of a strong verb and shows where the stem changes occur. Below is the information from Aufgabe 2 concerning the endings that we will use for the strong verbs. The endings in red are the personal endings on the verb stem for the different personal pronouns shown at the left side in blue and green. The verb stem for each of the verb forms that has a green pronoun will be different for the strong verbs in this section. Personal pronoun (sing.) Deutsch English ich I Associated article Ending (‘der’,’die’,’das’) Personal pronoun (plural) Deutsch du (fam.sing.) you English -e wir we -en -st ihr (fam. pl.) you -t they -en er he/it der (maskulin) -t sie she/it die (feminin) -t sie es it das (neutral) -t (Plural article = die) wer who -t Sie (polite) Sie Note: “Sie” (polite) can be singular or plural, but the form is always capitalized and the same spelling as the form for ‘they’ Look carefully at the forms of the verb ‘haben’ and note where the verb stem changes: haben [to have ] ich habe du HAst er HAt sie HAt Copyright © 2002 Robert A. Morrey Ending wir haben ihr habt sie haben Sie haben -en In order to create all the forms for the verb ‘haben’, one needs to know that the verb follows the strong verb pattern and one needs to know the infinitive form (‘haben’) of the verb and the form for ‘er’ (‘er hat’). In Vocabulary Lessons 4, 7 and 9, you have learned a number of strong verbs. These verbs are listed below with the form for ‘er’ which you should learn well and then practice with the computer programs ‘Strong V form’ and ‘Strong Vb Sent’. Infinitiv Englisch to speak to see to give to take to bake Deutsch sprechen sehen geben nehmen backen ‘er’ Form er spricht er sieht er gibt er nimmt er bäckt to read to eat to forget lesen essen vergessen er liest (du liest)* er isst (du isst)* er vergisst (du vergisst)* Beispiel [example] ich gebe wir geben du gibst ihr gebt er gibt sie gibt sie geben es gibt wer gibt? * These three verbs have a pattern similar to the verb ‘heissen’ in Aufgabe 2. In this pattern the verb ending used with the pronoun ‘du’ is not ‘-st’, but rather just ‘-t’ because the verb stem ends in an /s/ sound. (See ‘Verb Stems Ending with an /s/ Sound’ sheet) Beispiel: ich lese du liest er liest sie liest es liest wer liest? Copyright © 2002 Robert A. Morrey wir lesen ihr lest sie lesen



![D1A70204 Befehlformen [Command Forms] Commands (Befehle](http://s1.studylibde.com/store/data/006295093_1-ded304d13987e352eae01a2a5fa30f24-300x300.png)