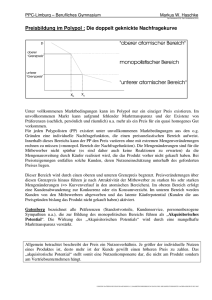
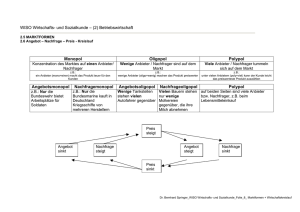
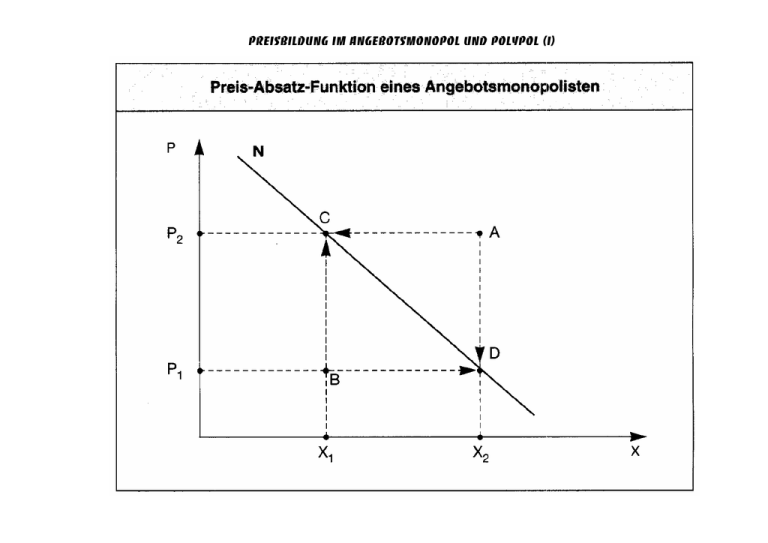
Preisbildung im Angebotsmonopol und Polypol (I)
Werbung
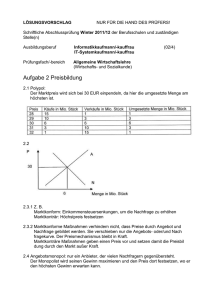
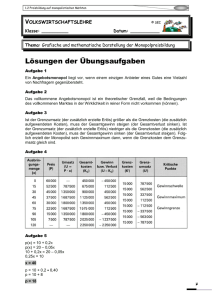
Preisbildung im Angebotsmonopol und Polypol (I) Preisbildung im Angebotsmonopol und Polypol (II) Preisbildung im Angebotsmonopol und Polypol (III) Ein Rechenbeispiel p = 200 − 20 x E = p ⋅ x = 200 x − 20 x 2 E ′ = 200 − 40 x K = 150 + 4,5 x 2 K′ = 9x mit der Gewinnmaximierungsregel folgt daraus : E′ = K ′ 200 − 40 x = 9 x 200 x= = 4,0816326... 49 Über die Nachfragefunktion p kann nun der Preis berechnet werden : pCournot = 200 − 20 x ≈ 118,37 €