Document
Werbung

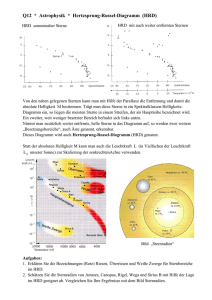
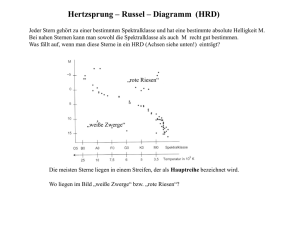
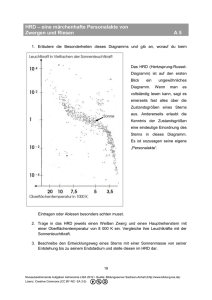
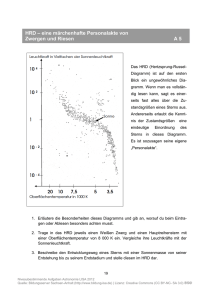
Detektion von DNA Repair Deficiency „Narbe“ vs Mutation (BRCA,BRCAness, HRD) WARUM IST DNA REPAIR SO INTERESSANT? Targeting DNA Repair pathways in Cancer (Helleday et al. 2008) 3 Wirkmechanismus PARP Inhibitoren (Targeting the missing links for cancer therapy Kornelia Polyak & Judy Garber Nature Medicine 17, 283–284 (2011) doi:10.1038/nm0311-283 ) Wirkmechanismus von Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase (PARP) - Inhibitoren DNA Einzelstrangbrüche (SSBs) kommen häufig in Zellen vor. PARP detektiert und repariert SSBs. Während der Replikation führen nicht reparierte SSBs zu Doppelstrangbrüchen Normale Zelle Reparatur durch homologe Rekombination Überleben PARP PARP-Inhibitor Sich replizierende Zellen Tumorzelle mit HRD* Keine Reparatur Tumor-spezifischer Zelltod durch PARPInhibitor Zelltod *Homologe Rekombination-Reparaturdefekt Rationale für Platinsalze bei BRCA-assoziierten Tumoren Platinsalze führen zu intra- und interstrang Crosslinks Replikation Doppelstrangbrüche Reparatur: Homologe Rekombination (HR) • fehler“frei“ Nicht-homologes End-joining (NHEJ) • fehleranfällig HR-Defizienz führt zu genomischer Instabilität und Sensitivität gegenüber Doppelstrangbruch induzierenden Substanzen BRCA ist ein wichtiger Bestandteil der HR-Maschinerie WAS FÜR REPARATUR-MECHANISMEN GIBT ES? Homologous combinational Repair Was ist Homologous recombination/repair (HR) Deficiency? Jedwede Art der HR Deficiency HR funktioniert Überlebt PARP Was ist Homologous recombination/repair (HR) Deficiency? Jedwede Art der HR Deficiency HR funktioniert Überlebt PARP HR Funktioniert nicht Snythetische Letalität: PARPi x HR/FA Gene Swisher E et al., 26th EORTC-NCI-AACR Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics; BARCELONA, Nov. 2014 Was könnte noch HRD Verursachen? Mechanismus Mutation Epigentisches Silencing miRNA Silencing Deletionen Andere Mechanismen BRCA1 BRCA2 PALB2 RAD51 MERIT40 Gen..1 Gen..n Was könnte noch HRD Verursachen? Mechanismus Mutation Epigentisches Silencing miRNA Silencing Deletionen Andere Mechanismen BRCA1 BRCA2 PALB2 RAD51 MERIT40 Gen..1 Gen..n Was könnte noch HRD Verursachen? Mechanismus Mutation Epigentisches Silencing miRNA Silencing Deletionen Andere Mechanismen BRCA1 BRCA2 PALB2 RAD51 MERIT40 Gen..1 Gen..n Was könnte noch HRD Verursachen? Mechanismus Mutation Epigentisches Silencing miRNA Silencing Deletionen Andere Mechanismen BRCA1 BRCA2 PALB2 RAD51 MERIT40 Gen..1 Gen..n ? ? ? Was könnte noch HRD Verursachen? Mechanismus BRCA1 BRCA2 PALB2 RAD51 Mutation MERIT40 Gen..1 Gen..n ? ? ? Epigentisches Silencing ? ? ? ? ? ? ? miRNA Silencing ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Deletionen ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Andere Mechanismen ? ? ? ? ? ? ? WIE KANN NACHGEWIESEN WERDEN, OB IN EINER ZELLE DNA REPAIR VORLIEGT, ODER WAS IST HETEROZYGOSITÄT? Was ist Heterozygosität? A A A G Verlust der Heterozygosität (LOH): Zeichen einer HRD Watkins JA et al., Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Jun 3;16(3):211 Was ist Heterozygosität? Bereiche mit Verlust von HT Bereiche mit Heterozygosität Chr1 Chr2 Chr3 Chr…. Heterozygosität in Tumoren mit und ohne BRCA1 Mutation BRCA1 Normal BRCA1 Mutiert BRCA1 Normal Heterozygosität in Tumoren mit und ohne BRCA1 Mutation BRCA1 Normal BRCA1 Mutiert BRCA1 Normal Vermutung: Diese Tumorzellen sprechen genauso auf eine PARP-I Therapie oder Platin an Verschiedene Auswertungsmechanismen Anzahl der LOH Regionen, die länger sind als z.B. 10 oder 15 Mb Anzahl der LOH Regionen die kürzer sind als z.B. 10 MB Anzahl der LOH Regionen in speziellen Genabschnitten Weitere Kriterien HRD assays erfassen unterschiedliche genomische Veränderungen Bisher unklar, was die beste Methode ist, bzw. welche Kombination Watkins JA et al., Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Jun 3;16(3):211 HRD Scores werden momentan von vielen kommerziellen Anbietern entwickelt Myriad Foundation Medicine Nant Biomarin Quiagen …. …. Limitation LOH- & HRD-Tests HRD Assays erfassen eine „genomische Narbe“ • bleibt erhalten, auch wenn der Tumor eine Platin- bzw. PARPiResistenz entwickelt hat (z.B. durch genetische Reversion) • idealer Weise durch Test auf spez. Resistenzmechanismen ergänzt ERSTE KLINISCHE ERFAHRUNGEN MIT HRD ASSAYS TNT-Studie: ORR nach BRCA1/2-Status Tutt A. et al., SABCS general session abstr. # S3-01 HRD score (Myriad) ARIEL2, Part 1 designed to assess rucaparib sensitivity in three prospectively defined molecular subgroups Key Eligibility (N=206) • High-grade serous or endometrioid OC – Known gBRCA enrollment capped at N=15 • ≥1 prior platinum chemotherapy • Platinum-sensitive, relapsed, measurable disease • Tumor tissue (screening biopsy and archival) BRCAmut NGS of tumor tissue allows patients to be classified Analysis of HRD Subgroups Primary endpoint • PFS BRCA-like 600 mg BID rucaparib until PD Biomarker Negative Secondary endpoints • ORR – RECIST – RECIST + CA125 • Safety • PK gBRCA=germline BRCA. 30 Primary efficacy analysis: PFS in BRCAmut and BRCA-like versus Biomarker Negative patients Progression-free survival by HRD molecular subgroup HRD Subgroup Median PFS, mo (95% CI) 0.9 BRCAmut 12.8 (9.0, NR) 0.8 BRCA-like 5.7 (5.2, 7.6) Biomarker Negative 5.3 (3.5, 7.1) 1.0 PFS 0.7 0.6 0.5 Subgroup Comparison 0.4 0.3 0.2 BRCAmut BRCA-like Biomarker Negative 0.1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 36 (3) 32 (5) 31 (5) Available (endpoint reached) 40 (0) 40 (0) 8 (15) 6 (16) 6 (16) 1 (18) BRCA-like 82 (0) 75 (3) 59 (13) 54 (17) 46 (25) 42 (27) 34 (35) 29 (37) 25 (40) 21 (44) 14 (45) 10 (46) 6 (47) 4 (48) 2 (48) 2 (48) 2 (48) Biomarker Negative 70 (0) 68 (0) 52 (15) 46 (17) 33 (29) 32 (29) 22 (37) 20 (38) 13 (44) 11 (45) 2(51) 1 (51) 0 (51) 38 (1) 36 (3) CI=confidence interval. NR=not reached. p-value BRCAmut vs Biomarker Negative 0.22 (0.12, 0.40) <0.0001 BRCA-like vs Biomarker Negative 0.67 (0.45, 0.99) 0.0445 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Time (months) BRCAmut 38 (1) HR (95% CI) 25 (9) 22 (10) 18 (12) 13 (13) 13 (15) 5 (49) 4 (49) 1 (49) 1 (49) 0 (50) 31 GBG/AGOB STUDIEN ALS INTERNATIONAL FÜHRENDE GRUPPE IM INDIKATIONSBEREICH „KLINISCHE ROLLE VON BRCA ZUR THERAPIEPRÄDIKTION“ San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium - December 08-12, 2015 BRCA mutations, therapy response and prognosis in the neoadjuvant GeparQuinto study Peter A. Fasching, Sibylle Loibl, Holger Eidtmann, Hans Tesch, Michael Untch, Jörn Hilfrich, Christian Schem, Mahdi Rezai, Bernd Gerber, Serban Dan Costa, Jens-Uwe Blohmer, Tanja Fehm, Jens Huober, Cornelia Liedtke, Volkmar Müller, Valentina Nekljudova, Karsten E Weber, Brigitte Rack, Matthias Rübner, Liewei Wang, James N Ingle, Richard M Weinshilboum, Gunter von Minckwitz and Fergus Couch for the GBG/AGO-B study groups This presentation is the intellectual property of the authors/presenters. Contact them at ([email protected] ) for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium - December 08-12, 2015 Core biopsy R E: C: ECBev * DocBev Surgery Doc EC (d28-d35 after last Bev infusion) HER2-negative part of GeparQuinto Recruitment of n=1948 HER2 negative patients, N=678 having triple negative tumors. Epirubicin 90 mg/m² Doc:Docetaxel 100mg/m² Cyclophosphamide 600 mg/m² Bev: Bevacizumab 15 mg/kg (all 3 week cycles) * non responders continued with a prespecified non responder therapy 1von Minckwitz et al. NEJM, 2012; 2Gerber et al. Ann Oncol, 2013 This presentation is the intellectual property of the authors/presenters. Contact them at ([email protected] ) for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium - December 08-12, 2015 BRCA1/2 genotyping and treatment arms N=678 TNBC Patients N=471 patients, TNBC with BRCA1/2 successful genotyping* BRCA1/2 wildtype* N=389 (82.6%) Bevacizumab – N=202 Bevacizumab + N=187 N=147 patients did not take part in scientific germline DNA genotyping, N=60 samples failed QC BRCA1/2 mutation* N=82 (17.4%) N=69 BRCA1, N=13 BRCA2 Bevacizumab – N=47 Bevacizumab + N=35 *Genotyping by custom capture NGS This presentation is the intellectual property of the authors/presenters. Contact them at ([email protected] ) for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium - December 08-12, 2015 pCR according to treatment and BRCA1/2 status Patients with BRCA1/2 mutation p (interaction) = 0.1912 100 pCR (ypT0 ypN0) rate (%) 90 80 70 60 p=0.025 Patients without BRCA1/2 mutation 65.7% p=0.048 50 35.8% 40 30 38.3% 26.2% 20 10 0 BEV-MUT- BEV+MUT- N=202 N=187 Treatment with chemo only BEV-MUT+ N=47 BEV+MUT+ N=35 Treatment with chemo and BEV This presentation is the intellectual property of the authors/presenters. Contact them at ([email protected] ) for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium - December 08-12, 2015 This presentation is the intellectual property of the authors/presenters. Contact them at ([email protected] ) for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium December 8-12, 2015 Early survival analysis of the randomized phase II trial investigating the addition of carboplatin to neoadjuvant therapy for triple-negative and HER2positive early breast cancer (GeparSixto) Gunter von Minckwitz, Sibylle Loibl, Andreas Schneeweiss, Christoph Salat, Eric Hahnen, Mahdi Rezai, Dirk Michael Zahm, Peter Klare, Jens Uwe Blohmer, Hans Tesch, Fariba Khandan, Peter Fasching, Christian Jackisch, Rita Schmutzler, Valentina Nekljudova, Michael Untch for the GBG/AGO-B study groups This presentation is the intellectual property of GBG and AGO-B. Contact [email protected] for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium December 8-12, 2015 Design for Patients with TNBC PM Surgery N=315 patients with centrally confirmed TNBC R cT2, cT3, or cT4a-d or cT1 and cN+ or pNSLN+ PMCb Paclitaxel (P) 80 mg/m² q1w Non-pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (M) 20 mg/m² q1w Carboplatin (Cb) q1w Dose of AUC 2 was reduced to AUC 1.5 after enrolment of 330 patients Bevacizumab 15 mg/kg q3w von Minckwitz et al. Lancet Oncology 2014 This presentation is the intellectual property of GBG and AGO-B. Contact [email protected] for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium December 8-12, 2015 GeparSixto: HRD assay (LOH) Von Minckwitz et This al., presentation ASCO 2015 oral presentation is the intellectual property of GBG and AGO-B. Contact [email protected] for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium December 8-12, 2015 GeparSixto: HRD assay (LOH) This presentation is the intellectual property of GBG and AGO-B. Contact [email protected] for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium December 8-12, 2015 GeparSixto: HRD assay (LOH) This presentation is the intellectual property of GBG and AGO-B. Contact [email protected] for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium December 8-12, 2015 Von Minckwitz et al, SABCS 2015 # S2-04 This presentation is the intellectual property of GBG and AGO-B. Contact [email protected] for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium December 8-12, 2015 Von Minckwitz et al,This SABCS 2015 # S2-04 presentation is the intellectual property of GBG and AGO-B. Contact [email protected] for permission to reprint and/or distribute. San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium December 8-12, 2015 DFS by gBRCA Status and Carboplatin in TNBC This presentation is the intellectual property of GBG and AGO-B. Contact [email protected] for permission to reprint and/or distribute. LAUFENDE UND GEPLANTE STUDIEN Aktive oder geplante Studien im Themenbereich BRCAness und PARP-I Brightness (neoadjuvant, TNBC) GeparOla (neoadjuvant, BRCA mut, HRD high) Olympia (adjuvant, BRCA mut) OlympiaD (metastatic, BRCA mut) Brocade (metastatic, BRCA mut) EMBRACA (metastatic, BRCA mut) ABRAZO (metastatic, BRCA mut) 4 Zusammenfassung BRCA Mutation in der Keimbahn oder im Tumor legen einen Defekt in der DNA Repair nahe. Weiterhin kann ein Defekt in der DNA Repair durch weitere Tests (z.B. HRD Tests) nachgewiesen werden. Das Deutsche Netzwerk klinische Studien / BRCA Testung funktioniert auf internationalem Niveau hoch-kompetitiv Olympia und GeparOLA im Fokus des weiteren Interesses.