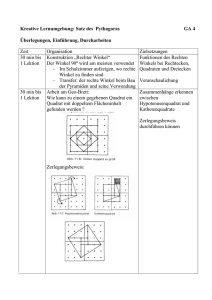
Lektion 11: Webservices
Werbung

Lektion 11: Webservices
Helmar Burkhart
Dep. Informatik
Universität Basel
Helmar.Burkhart@...
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-1
„Klassische“ Webnutzung
• Weltweit verteilte, vernetzte, einfach
zugreifbare Informationen.
• Mensch als Informationsnutzer.
• Beginnende Geschäftsmodelle: B2C
(Business to Consumer).
• Einfaches konzeptionelles Modell: ClientServer.
• Wenige, einfache Standards: http, html.
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-2
Evolution des Web: Von der
Information zum Dienst
• Weltweit vernetzte, lose gekoppelte Dienstleistungen.
• Business to Business (B2B) Middleware.
Anwendung A
Anwendung B
Web Service Middleware
Internet
•
•
•
•
Standardisierte Protokolle und Nachrichtenformate.
Dienstverzeichnisse
Entwicklung verteilter Objektsysteme über das Web.
Evolutionäre Erweiterungen früher Technologien
(RPC, RMI, CORBA).
© Helmar Burkhart
•
11-3
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
Remote Procedure Call: RPC (1)
Client
Server
activate remote method
call
method
return response data
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) allows method
activations on remote objects. It offers higher
abstraction for developing distributed applications by
preserving the object model across networks.
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-4
RPC (2)
Client
Stub
call local stub
return value or
throw exception
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Receiver
marshalled
parameters
Server
local
method call
marshalled
result or
exception
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-5
RMI - Remote Method Invocation
http://java.sun.com/products/jdk/rmi/
Java Remote Method Invocation (Java RMI)
enables the programmer to create distributed
Java technology-based to Java technologybased applications, in which the methods of
remote Java objects can be invoked from
other Java virtual machines, possibly on
different hosts. RMI uses object serialization
to marshal and unmarshal parameters and does
not truncate types, supporting true objectoriented polymorphism.
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-6
Remote Objects and Interfaces
• A remote object is an object whose methods can be
invoked from objects within another Java virtual
machine, possibly on a a different computer. A
method invocation on a remote object has the same
syntax as a method invocation on a local object.
• An object becomes a remote object when it
implements a remote interface (extends
java.rmi.Remote)
• Remote objects are passed by reference, the others
by value.
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-7
Creating RMI-Based Applications
1. Design and implement the components
1.1 Define the remote interfaces
1.2 Implements the remote interfaces
1.3 Implement the server
1.4 Implement the client
2. Compile sources and generate the stubs
2.1 javac to compile the sources
2.2 rmic to generate the stubs (on the remote objects impl.)
3. Make classes network accessible
all classes especially remote interface classes and stubs
4. Start the application
4.1 Start the rmiregistry process
4.2 Start the server
4.3 Start the client
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-8
OMG CORBA
• IDL - Interface Definition Language (language neutral)
• CORBA - Common Object Request Broker Architecture
industry-standard distributed object model
• OMG - Object Management Group
Client
Dynamic
Invocation
IDL
Stubs
Server
ORB
Interface
Static IDL
Skeleton
Dynamic
Skeleton
Object
Adapter
ORB Core
Interface identical for all ORB implementations
Possibly multiple object adapters
Stubs and skeletons for each object type
ORB dependent interfaces
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-9
Java IDL
• Java IDL provides ORB
• ORB - Object Request Broker - class library that
enables low-level communication between Java IDL
applications and other CORBA-compliant
applications.
• Programming: IDL Interfaces, Stubs, Skeletons,
Naming Service
• ORB includes stubs and skeletons
• Communication between ORBs through IIOP
• IIOP-Internet Inter ORB Protocol (based on TCP/IP)
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-10
IDL to Java
// squareServer.IDL
interface squareServer{
double sqrt(in double x)
raises(NegativeNumber);
}
// squareServer.JAVA
public interface squareServer
extends org.omg.CORBA.Object {
public double sqrt(double x)
throws NegativeNumber;
}
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-11
Was ist ein Web Service ? (1)
GI – Lexikon der Informatik:
http://www.gi-ev.de/informatik/lexikon/index.html
Web Services lassen sich wie folgt charakterisieren:
• Programmierbar
• Selbstbeschreibend
• Kapselung
• Lose gekoppelt
• Ortstransparenz
• Protokolltransparenz
• Komposition
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-12
Was ist ein Webservice ? (2)
W3C Web services Architecture group:
http://www.w3.org/TR/2004/NOTE-ws-arch-20040211/
A Web service is a software system designed to
support interoperable machine-to-machine
interaction over a network. It has an interface
described in a machine-processable format (specifically
WSDL). Other systems interact with the Web service in
a manner prescribed by its description using SOAP
messages, typically conveyed using HTTP with an XML
serialization in conjunction with other Web-related
standards.
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-13
Web Service Dreieck
UDDI: Universal Discovery, http://www.ibm.com/services/uddi
Description and Integration http://uddi.microsoft.com
…
Service
Registry
Find
Publish
WDSL ← UDDI
WDSL → UDDI
Service
Requestor
SOAP over HTTP
Service
provider
Bind
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-14
SOAP
(Simple Object Access Protocol)
•
•
•
•
•
•
UDDI
Service
User
Service
Provider
Interaktion zwischen einer
Client- und einer ServerAnwendung
RPC-Stil (request – response)
Benutzt XML
Nutzt HTTP als TransportLayer-Protokoll
• Header Elemente für
Kontextinformationen
• Fehler- und
Ausnahmebehandlung
SOAP
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-15
WSDL
(Web Services Definition Language)
UDDI
WSDL
WSDL
Service
User
© Helmar Burkhart
Service
Provider
•
Definition der Interfaces:
Neben den Operationen des Web
Services wird hier auch
angegeben, auf welchem Rechner
im Internet der Web Service
verfügbar ist.
WSDL bietet XML-Sprachregeln für die Beschreibung
-was ein Webservice leistet
-wo er sich befindet und
-wie er aufzurufen ist
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-16
UDDI
(Universal Description, Discovery, and
Integration )
UDDI
Service
User
© Helmar Burkhart
Service
Provider
•
Dient zur Registrierung von Web
Services.
Neben dem Interface auch
Beschreibung des Web Service
sowie Daten über den Anbieter
etc.
Folgende Anforderungen müssen
abgedeckt werden:
• Datenstruktur für Web Services
• Schnittstellenbeschreibung
• Möglichkeit die Informationen
zu finden und die technischen
Informationen zu nutzen
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-17
Web Services Technology Stack
• Basis Schichten sind bereits
fest etabliert.
• Höhere Schichten befinden
sich noch im Aufbau.
• UDDI, WSFL sind dennoch
feste Bestandteile des
Stacks.
• Weitere Konzepte:
– Security
– Authentifizierung
– Quality of Service
– Transaktions
Management
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-18
Java XML Technology
http://java.sun.com/xml/index.jsp
Spezifiziert 5 APIs
– JAXP:
– JAXB:
– JAXR:
– JAX-RPC:
– SAAJ:
© Helmar Burkhart
•
XML Processing
XML Binding
Registries
RPC über SOAP
SOAP with Attachments API
for Java
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-19
JAX RPC
•
•
•
•
Ziel der Spezifikation: Einfachheit der Schnittstelle
Kapselung der SOAP Nachrichtenbildung
Unterstützung von WSDL: wscompile
Unterstützung von Static Stubs, Dynamic Stubs und
Dynamischen Proxies
http://java.sun.com/j2ee/1.4/docs/tutorial/doc/index.html
© Helmar Burkhart
•
Webtechnologies (CS211) • Lektion 11: Webservices
11-20