Present Perfect - have-ever-before
Werbung
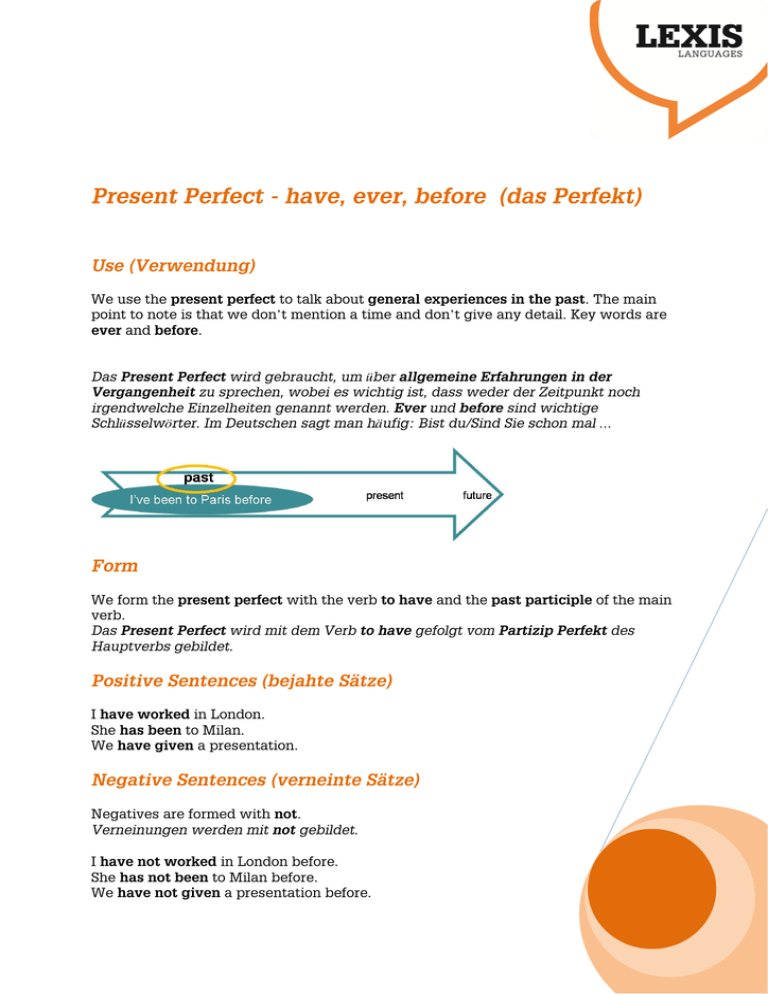
Present Perfect - have, ever, before (das Perfekt) Use (Verwendung) We use the present perfect to talk about general experiences in the past. The main point to note is that we don’t mention a time and don’t give any detail. Key words are ever and before. Das Present Perfect wird gebraucht, um über allgemeine Erfahrungen in der Vergangenheit zu sprechen, wobei es wichtig ist, dass weder der Zeitpunkt noch irgendwelche Einzelheiten genannt werden. Ever und before sind wichtige Schlüsselwörter. Im Deutschen sagt man häufig: Bist du/Sind Sie schon mal … Form We form the present perfect with the verb to have and the past participle of the main verb. Das Present Perfect wird mit dem Verb to have gefolgt vom Partizip Perfekt des Hauptverbs gebildet. Positive Sentences (bejahte Sätze) I have worked in London. She has been to Milan. We have given a presentation. Negative Sentences (verneinte Sätze) Negatives are formed with not. Verneinungen werden mit not gebildet. I have not worked in London before. She has not been to Milan before. We have not given a presentation before. Irregular verbs (Unregelmäßige Verben) Questions (Fragen) Questions are formed by inverting the subject and verb to have. Fragen werden durch Umstellung des Subjekts und des Verbs to have gebildet. Have you worked in London before? Has she been to Milan before? Have they given a presentation before? Short Form (Kurzform) The following short forms are used in speech and informal writing: Die folgenden Kurzformen werden im gesprochenen Englisch und in informellen Schreiben verwendet: I have – I've you have – you've he has – he's she has – she's it has – it's we have – we've you have – you've they have – they've The full form should be used in formal writing. In förmlichen Schreiben sollte man die (vollständigen) Langformen benutzen.