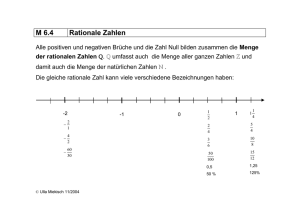
Rationale Funktionen
Werbung

Übung zur Analysis I
WS 2011/12
Rationale Funktionen
Definition: Es seien p, q reelle Polynome mit q nicht die Nullfunktion und M := {x ∈ R : q(x) = 0}.
p(x)
Eine Funktion f : R \ M → R definiert durch f (x) :=
heißt rationale Funktion. Gilt
q(x)
Grad(p) < Grad(q) so heißt f echt gebrochen rationale Funktion.
Wichtig:
p2
p
wie oben, lässt sich schreiben als f = p1 +
mit reellen Polynomen
q
q
p1 , p2 und Grad(p2 ) < Grad(q).
(a) Jede rationale Funktion f =
(b) Jedes Polynom q(x) := a0 + a1 x + · · · + an xn , an 6= 0, besitzt eine Darstellung der Form
(Q) q(x) = an (x − x1 )ρ1 · · · (x − xr )ρr · (x2 + A1 x + B1 )σ1 · · · (x2 + As x + Bs )σs .
Dabei sind ρ1 , . . . , ρr , σ1 , . . . , σs ∈ N, und es ist
ρ1 + · · · + ρr + 2σ1 + · · · + 2σs = n.
Die x1 , . . . , xr sind die reellen Nullstellen von q, die Polynome x2 + Aj x + Bj besitzen keine reellen
Nullstellen.
Partialbruchzerlegung echt gebrochen rationaler Funktionen
p
Es sei f = q eine echt gebrochene rationale Funktion. Das Nennerpolynom q habe die Darstellung
(Q). Dann besitzt f eine Summendarstellung der Form
a1ρ1
a11
a12
+
+ ··· +
2
x − x1 (x − x1 )
(x − x1 )ρ1
+···
arρr
ar1
ar2
+
+
+ ··· +
2
x − xr
(x − xr )
(x − xr )ρr
α11 x + β11
α12 x + β12
α1σ x + β1σ1
+ 2
+ 2
+ ··· + 2 1
2
x + A1 x + B1 (x + A1 x + B1 )
(x + A1 x + B1 )σ1
+···
αs1 x + βs1
αs2 x + βs2
αsσ x + βsσs
+ 2
+ 2
+ ··· + 2 s
,
2
x + As x + Bs (x + As x + Bs )
(x + As x + Bs )σs
f (x) =
wobei die ajk , ανµ und βνµ reelle Zahlen sind.
1