Genetische Disposition für Infektion und Sepsis
Werbung

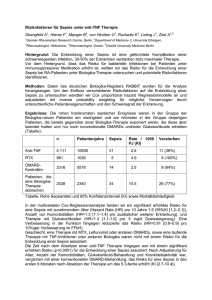
Genetische Disposition für Infektion und Sepsis Martijn van Griensven TRAUMA Forschungszentrum für Traumatologie der AUVA Ludwig Boltzmann Institut für experimentelle und klinische Traumatologie AUVA Lorenz Böhler Unfallkrankenhaus Gene Umgebung Krankheit Polymorphismus Different alleles, none of which is predominant in the population Alberts, Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th Edition Genetische Varianz, ohne das normale Leben zu stören Polymorphismus 1 Umgebung Risiko Polymorphismus 2 Risiko Trauma: Polymorphismus oder Umgebung? Welche Menschen erleiden ein Trauma? d.h.: wer sind diese Patienten im genetischen Sinne? Trauma Posttraumatischen Verlauf genetische Polymorphismen bland Komplikationen Leben tot outcome Welche Gene untersuchen? TRAUMA SIRS/Sepsis n i e t o r MODS P † Überleben Trauma vs. Zytokine Welche Zytokine? Assoziiert mit dem Outcome? Bestehende Polymorphismen? Assoziation Polymorphismen und Outcome? Zytokinverlauf nach Sepsis primär PRO-INFLAMMATORISCHE REAKTION TNF-α IL-1 Problem: Niedrige Halbwertzeit Undulierende Spiegel sekundär PRO ANTI INFLAMMATORISCHE INFLAMMATORISCHE REAKTION REAKTION IL-6 IL-10 IL-8 IL-1RA Gute Halbwertzeit Stabiles Niveau Interleukin-6 12000 [IL-6] (pg/ml) 10000 * +MODS -MODS 8000 MODS * 6000 * 4000 * * * * 2000 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Tage nach Trauma 10 11 12 13 14 IL-6 Sepsis 1200 * [IL-6] (pg/ml) 1000 +Sepsis -Sepsis 800 600 400 200 * * * 6 8 * * 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 7 9 10 11 12 13 14 Zeit nach Trauma (Tage) IL-10 MODS 90 [IL-10] (pg/ml) 80 70 +MODS -MODS 60 50 MODS 40 * 30 20 * * 10 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Zeit nach Trauma (Tage) IL-10 Sepsis 100 90 [IL-10] (pg/ml) 80 70 60 +Sepsis -Sepsis 50 * 40 * 30 * 20 10 * * * 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Zeit nach Trauma (Tage) IL-10 80 IL-10 in pg/ml 70 60 * 50 Verstorben Überlebt * 40 30 20 * * * 10 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Tage 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Zytokine Posttraumatischen Verlauf Trauma Gene Zellaktivität Immunzellen Endothelzellen Zytokine Organe Dysfunktion Villar et al. Crit Care. 2004; 8: 180–189 LBP SIRS vs. Sepsis 140 [LBP] (µg/ml) 120 * 100 Sepsis * * * * * * * 80 * * * * * 60 40 20 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Zeit nach Trauma (Tage) +SIRS-Sepsis +Sepsis Holmes, C. L. et al. Chest 2003;124:1103-1115 Untersuchte Polymorphismen Gen Marker Assoziation BPI Lys-Glu (216) - BPI Noncoding PstI - BPI Synonymous TaqI (545) - LBP Cys-Gly (98) + (male) LBP Leu-Pro (436) - LBP Synonymous HpaII (291) - CD14 -260 (-159) promoter - TLR-4 Asp-Gly (299) + TLR-4 Thr-Ile (399) - TLR-4 Rare coding mutations + TLR-2 Arg-Gln (753) + TLR-2 Rare coding mutations Villar et al. Crit Care. 2004; 8: 180–189 Weitere Faktoren Gen Marker Assoziation Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 Promoter single base indela + Tissue-type plasminogen activator Noncoding indela - IL-1 receptor antagonist Noncoding microsatellite + IL-1β Synonymous TaqI (297) - IL-6 -174 promoter - IL-10 -1082 promoter + TNF-α -308 promoter + TNF-β (LTA) Noncoding NcoI + Villar et al. Crit Care. 2004; 8: 180–189 Sepsis Experiment Gram- Gram+ 6h und 24h Geweben für RNA Identifizierte Gene Gram+ und Gram- Gram- 4 65 22 Gram+ Funktionskategorien Protein processing 9% Nucleic acid Processing 8% Cytoskeleton organization 9% Cell proliferation 6% Cell communication 3% Transport function 7% Energy pathway 6% Signal transduction 9% Detoxification 3% Immune response 7% Metabolism 19% Acute phase protein 2% ROS/Stress response 12% DNA chips RNA SSH-Libraries Clone-Set I + II cDNA Microarrays Identifikation von dysregulierten Genen Validierungskriterien Power der Studie prospektiv vs. retrospektiv Genetik der Familie genetische Assoziationen/Epiphenomene genetische Konstellation der Population Reproduzierbarkeit (2. Kohort) Medline sepsis AND polymorphism 492 AND cytokines 163 TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IFN-γ 104 Polymorphismen TNF -308 TNF1 TNF2 TNF NcoI TNFB1 TNFB2 IL-1β TaqI klein groß IL-6 –174G/C GG IL-10 Rx/Gx IFNγ-receptor 1 D6S471 GC CC TNF -308 TNF2 allel anwesend TNF-α ↑ nach LPS Stimulierung Louis, Clin.Exp.Immunol. 113 (1998) mehr Sepsis Inzidenz der Sepsis und † nach Trauma ↑ TNF2: ↑ Inzidenz derOutcome postoperativen Sepsis O‘Keefe, J.Trauma 52 (2002) Tang, Crit.Care Med. 28 (2000) Inzidenz der Sepsis interne ITS ↑ Mira, JAMA 282 (1999) TNF -308 Keine Assoziation gefunden mit TNF1 oder TNF2: TNF2 Inzidenz der Sepsis TNF-α Produktion nach LPS Stüber, J.Inflamm. 46 (1995) TNF NcoI TNFB2 homozygote Inzidenz der schwere Sepsis nach Trauma ↑ Majetschak, Ann.Surg. 230 (1999) mehr Sepsis TNFB2: Mortalität in postoperative schwere Sepsis ↑ Outcome Ex vivo TNF-α ↑ in posttraumatische Sepsis Flach, Cytokine 11 (1999) Stüber, Crit.Care Med. 24 (1996) Inzidenz von MODS nach post-OP schwere Sepsis ↑ Stüber, Crit.Care Med. 24 (1996) IL-1β TaqI Großes Fragment (13.4 kb) allel + In vitro: mehr IL-1β Produktion - Pociot, Eur.J.Clin.Invest. 22 (1992) keine Assoziation mit Outcome nach post-OP sepsis Fang, Crit.Care Med. 27 (1999) IL-6 –174G/C CC homozygote IL-6 bei Inflammation ↓ IL-6 ↓ LPS Stimulation: IL-6 Sekretion ↓ IL-6 –174C: Outcome Mortalität nach post-OP schwere sepsis ↑ Osiri, Genes Immun. 1 (1999) Fishman, J.Clin.Invest. 102 (1998) Schlüter, Crit.Care Med. 30 (2002) SIRS Inzidenz nach Trauma ↑ Hildebrand, van Griensven, Shock 24 (2005) IL-6 nach Typhus Impfung Bennermo et al. Clin Chem 2004; 50:2136-2140 IL-10 Rx/Gx IL-10 R3/G7 niedrigste IL-10 Sekretion IL-10 R2/G14 höchste IL-10 SeKretion Eskdale, PNAS 95 (1998) Bedeutung bei Trauma/Sepsis? IFNγ-receptor 1 D6S471 AA homozygote starke Korrelation mit Infektion bei stumpfem Trauma Davis, Surgery 128 (2000) n=38 TLR4 Asp299Gly und Thr399Ile Humane endotoxinämie Marsik, C. et al. Clin Chem 2005;51:2178-2180 Grenzen Genetische Abhängigkeiten nicht untersucht Keine Vergleiche mit der Normalbevölkerung Reproduzierbarkeit nicht untersucht Häufig kleine Patientenzahlen Gibt es genetische Prädisposition beim (posttraumatischen) Sepsis? TNF2 „JA“ TNFB2 IL-6 –174 CC Offene Fragen Kombination „schlechte“ Polymorphismen? Andere Gene? Welche Endpunkten sollte man untersuchen? Kosten? Durchführbarkeit in der Routine? Ethische Bedenken? Und dann?! Risiko-Abschätzung Timing der Operation Art der chirurgischen Prozedur (?) Verabreichung von Modulatoren? Polymorphismus Gene Zellaktivität Immunzellen Endothelzellen Trauma Zytokine Organe Dysfunktion