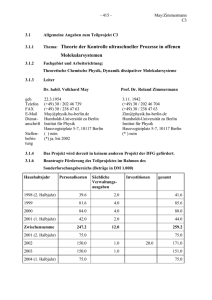
Word-Dokument - Archiv Physik
Werbung

Inhalt I 1 2 II 1 2 3 4 5 III 1 2 3 4 Darstellung des Faches am Standort .............................................................................. 3 Strukturelle Rahmenbedingungen .................................................................................. 3 1.1 Organisatorische Gliederung .................................................................................. 3 1.2 Studiengänge und Abschlussmöglichkeiten ........................................................... 4 1.3 Förderung des wissenschaftlichen Nachwuchses ................................................... 4 Forschungsprofil............................................................................................................. 9 2.1 Geschichte und Entwicklung des Fachs ................................................................. 9 2.2 Profil und Selbstverständnis des Faches .............................................................. 10 2.3 Forschungsverbünde und –programme ................................................................ 11 2.4 Perspektiven und zukünftige Entwicklung ........................................................... 12 2.5 Herausragende Ergebnisse aus den Forschungsprogrammen .............................. 13 2.6 Rufe, Preise und Auszeichnungen ........................................................................ 14 Darstellung der Forschungseinheiten ........................................................................... 15 Angewandte Physik ...................................................................................................... 15 1.1 Elektrooptik .......................................................................................................... 15 1.2 Magnetooptik ....................................................................................................... 17 Didaktik der Physik ...................................................................................................... 18 2.1 Theoretische Physik und Didaktik der Physik ..................................................... 18 Experimentalphysik ...................................................................................................... 20 3.1 Elektronenspektroskopie ...................................................................................... 20 3.2 Laserspektroskopie ............................................................................................... 22 3.3 Nichtlineare Optik ................................................................................................ 24 3.4 Magnetische Resonanzspektroskopie ................................................................... 26 3.5 Oberflächenphysik und Nanostrukturen ............................................................... 28 3.6 Umweltphysik- Prozessstudien ............................................................................ 30 3.7 Umweltphysik-Feldmessungen ............................................................................ 32 Kristallzucht ................................................................................................................. 34 4.1 Kristallzucht ......................................................................................................... 34 Theoretische Physik ..................................................................................................... 36 5.1 Festkörperphysik .................................................................................................. 36 5.2 Magnetismus ........................................................................................................ 38 5.3 Makroskopische Systeme und Quantentheorie .................................................... 39 5.4 Numerische Physik ............................................................................................... 41 5.5 Theoretische Optik ............................................................................................... 42 Anhang zur Darstellung der Forschungseinheiten ................................................. 45 Angewandte Physik ...................................................................................................... 45 1.1 Elektrooptik (Krätzig) .......................................................................................... 45 1.2 Magnetooptik (Dötsch) ........................................................................................ 65 Didaktik der Physik ...................................................................................................... 70 2.1 Theoretische Physik und Didaktik der Physik (Schürmann) ............................... 70 Experimentalphysik ...................................................................................................... 71 3.1 Elektronenspektroskopie (Neumann) ................................................................... 71 3.2 Laserspektroskopie (Kapphan) ............................................................................ 82 3.3 Nichtlineare Optik (Betzler) ................................................................................. 88 3.4 Magnetische Resonanzspektroskopie (Schirmer) ................................................ 90 3.5 Oberflächenphysik und Nanostrukturen (Heiland, Schleberger) ....................... 100 3.6 Umweltphysik-Prozessstudien (Rühl) ................................................................ 111 3.7 Umweltphysik-Feldmessungen (Kallenrode) ..................................................... 121 Kristallzucht ............................................................................................................... 124 2 5 IV 1 2 3 4 V 4.1 Kristallzucht (Hesse) .......................................................................................... 124 Theoretische Physik ................................................................................................... 130 5.1 Festkörperphysik (Borstel) ................................................................................. 130 5.2 Magnetismus (Blügel) ........................................................................................ 136 5.3 Makroskopische Systeme und Quantentheorie (Bärwinkel, Schmidt).............. 138 5.4 Numerische Physik (Hertel) ............................................................................... 141 5.5 Theoretische Optik (Ringhofer) ...................................................................... 145 Anhang Grunddaten ................................................................................................ 150 Stellen und Personal der Lehreinheit ......................................................................... 150 Mittel für Lehre und Forschung ................................................................................. 154 Studierende ................................................................................................................. 156 Post-Graduierte........................................................................................................... 159 Anhang Entwicklungsplan .......................................................................................... 161 3 I Darstellung des Faches am Standort 1 Strukturelle Rahmenbedingungen 1.1 Organisatorische Gliederung Der Fachbereich gliedert sich in 17 Arbeitsgruppen: Angewandte Physik Elektrooptik Magnetooptik Didaktik der Physik Experimentalphysik Elektronenspektroskopie Laserspektroskopie Magnetische Resonanzspektroskopie Nanostrukturen Nichtlineare Optik Oberflächenphysik Umweltphysik-Prozessstudien Umweltphysik-Feldmessungen Kristallzucht Krätzig Dötsch Schürmann Neumann Kapphan Schirmer Schleberger Betzler Heiland Rühl Kallenrode Hesse Theoretische Physik Festkörperphysik Magnetismus Makroskopische Systeme und Quantentheorie Numerische Physik Theoretische Optik Theoretische Physik und Didaktik der Physik Borstel Blügel Bärwinkel Schmidt Hertel Ringhofer Schürmann 4 1.2 Studiengänge und Abschlussmöglichkeiten o Diplomstudiengang Physik o Fach Physik im Studiengang Lehramt an o Grund-, Haupt- und Realschulen o Gymnasien o Berufsbildenden Schulen o Magister mit Physik als 2. Hauptfach o Diverse Diplomstudiengänge mit Nebenfach Physik o Promotionsstudiengang Physik o Internationaler Promotionsstudiengang „Advanced Materials“ o Bachelor of Science „Physik mit Informatik“ o Master of Science „Physik mit Informatik“ 1.3 Förderung des wissenschaftlichen Nachwuchses Der Förderung des wissenschaftlichen Nachwuchses dienen unter anderem die umfangreichen Drittmittelaktivitäten des Fachbereichs. So konnten im Durchschnitt des Berichtszeitraum fast 40 % der Diplomabgänger später promovieren, zum größten Teil auf Drittmittelstellen im Rahmen von Sonderforschungsbereich, Graduiertenkolleg oder anderen Drittmittelprojekten. Im Sinne eines Promotionsstudiengangs „Physik“ werden regelmäßig Lehrveranstaltungen angeboten, die speziell auf die Bedürfnisse der Doktoranden1 zugeschnitten sind. In Inhalt, Umfang und Qualität sind sie mit dem in Promotionsstudiengängen üblichen Standard vergleichbar. Ein stärker formalisierter Promotionsstudiengang „Advanced Materials“ befindet sich zurzeit im Genehmigungsverfahren. Doktoranden und Postdoktoranden wird sehr frühzeitig die Möglichkeit eröffnet, in der Lehre mitzuarbeiten und sich damit auch in diesem Bereich zu qualifizieren. Der Fachbereich wird durch die geplante Einrichtung von Juniorprofessuren die Weiterqualifikation des wissenschaftlichen Nachwuchses für die Hochschullehrerlaufbahn fördern. Die Hochschule bietet seit kürzerem Kurse zur hochschuldidkatischen Weiterbildung der Mitarbeiter an (Kursleiter Dr. Wolff-Dietrich Webler, Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Hochschuldidaktik Bielefeld). Vier Mitarbeiter des Fachbereichs Physik haben davon mehrfach Gebrauch gemacht. 1.3.1 1.3.1.1 Graduiertenkollegs/Graduate School Graduiertenkolleg 15 Das Graduiertenkolleg 15 "Mikrostruktur oxidischer Kristalle" wurde zum 01.07.1991 eingerichtet und lief am 30.06.2000 nach einer maximalen Förderungsdauer von 9 Jahren aus. Es diente der forschungsorientierten Förderung des wissenschaftlichen Nachwuchses auf einem aktuellen und expandierenden Wissenschaftsgebiet. Nach einem zügig abgeschlossenen Diplomstudium in Physik wurden die Kollegiaten in einem Forschungszusammenhang in möglichst kurzer Zeit zur Promotion geführt, der den bestehenden materialwissenschaftlichen Forschungsschwerpunkt "Oxidische Kristalle für elektro- und magnetooptische Anwendungen" (SFB 225) sinnvoll umfasste und erweiterte. Insgesamt wurden 23 Doktoranden und 6 Postdoktoranden gefördert. 1 Aus Gründen der besseren Lesbarkeit wird in diesem Report bei geschlechtsspezifischen Personenbezeichnungen häufig nur die männliche Form verwendet, ohne dass dadurch Frauen in irgendeiner Art zurückgesetzt werden sollen. So sind selbstverständlich mit „Doktoranden“, „Kollegiaten“, „Hochschullehrern“ o. ä. immer Frauen und Männer in gleicher Weise gemeint. 5 Unter anderem wurden folgende Projekte bearbeitet: 1.3.1.2 Ab-initio Spindynamik in magnetischen Oxiden (Theorie) Nichtreziproke Lichtausbreitung in magnetooptischen Wellenleitern (Experiment) Lichtausbreitung in integriert-optischen Strukturen (Theorie) Photoelektronenspektroskopie an modifizierten Oxidoberflächen (Experiment) Photoelektronenspektroskopie an 3d-Metall-Oxiden (Experiment) Elektronische Strukturberechnungen in reinem und dotierten LiNbO3 (Theorie) Ladungsträgerbeweglichkeit in oxidischen Kristallen (Experiment) Charakterisierung der Luminizenz-Zentren in oxidischen Kristallen durch ODMR (Experiment) ODMR über den magnetischen Zirkulardichroismus von paramagnetischen Störstellen in oxidischen Kristallen (Experiment) Graduiertenkolleg „Molekulare Physiologie: Wechselwirkungen zwischen zellulären Nanostrukturen“ Der Fachbereich Physik ist in diesem Graduiertenkolleg, das im Fachbereich Biologie angesiedelt ist und seit 2000 läuft, mit einem Projekt vertreten, bei dem die Rastertunnel- und Rasterkraft-Mikroskopie für die Analyse biologischer Nanostrukturen adaptiert werden und damit längerfristig zahlreichen Projekten zugute kommen soll. Auch nach der Pensionierung des Projektleiters Prof. Heiland (2002) ist eine Kontinuität in der Zusammenarbeit mit den Physikern durch die Arbeitsgruppe "Nanostrukturen" gesichert. Der Fachbereich Physik sieht überdies in seiner Entwicklungsplanung vor, dass bei den demnächst anstehenden Neubesetzungen eine C4- und eine C3-Arbeitsgruppe eingerichtet werden, die sich mit der Aufklärung biologischer Strukturen beschäftigen. 1.3.1.3 Graduiertenkolleg 695 Die DFG hat zum 01.01.2001 am Fachbereich Physik das Graduiertenkolleg 695 „Nichtlinearitäten optischer Materialien“ eingerichtet und dafür neben Sachmitteln 12 Doktoranden- und ein Postdoktorandenstipendium bewilligt. 16 Hochschullehrer des Fachbereichs sind am Kolleg als wissenschaftliche Lehrer und Betreuer der Promotionsarbeiten beteiligt. Der Schwerpunkt des Kollegs liegt auf dem Gebiet der Photonik, die als Ergänzung und Erweiterung der Elektronik in der modernen Informationstechnologie eine immer wichtigere Rolle spielt. Im Forschungsprogramm geht es um das grundlegende Verständnis nichtlinearer Effekte, die entscheidenden Einfluss auf die Eigenschaften optischer Materialien haben. Dabei soll die wissenschaftliche Expertise und die gute Ausstattung des ausgelaufenen Sonderforschungsbereiches 225 genutzt werden. Das Graduiertenkolleg ist, wie üblich, zunächst für drei Jahre bewilligt und kann zweimal verlängert werden. Zunächst wird das Kolleg drei Themenkreise bearbeiten: „Photorefraktive Nichtlinearitäten“, „Frequenzkonversion“ und „Nichtlinearitäten bei der Wellenleitung“. Laufende Projekte: Photorefractive nonlinearities: o Pattern formation in photorefractive crystals o Nonlinear optical properties of photorefractive strontium-barium niobate crystals o Critical phenomena in optics o Dielectric and optical properties of doped SBN 6 1.3.1.4 Frequency conversion: o Optical nonlinearities near the phase transition of SBN o Growth and characterization of nonlinear SBN crystals o Light-induced absorption changes in ferroelectric crystals o Development of optical parametric oscillators o Nonlinear optical processes in atomic and molecular clusters o Nonlinear optical properties of levitated microparticles Nonlinearities with wave guiding: o Optical frequency conversion in oxide waveguides o Criteria for the existence and stability of solitons o Nonlinear wave equations and solitons o Magnetic solitons in magnetic molecules International Graduate School „Advanced Materials“ Der geplante Forschungsschwerpunkt „Molekulare Architektur niedrigdimensionaler Systeme“ wird durch ein kürzlich genehmigtes Promotionsprogramm „Synthesis and Characterisation of Surfaces and Interfaces assembled from Clusters and Molecules“ des Landes Niedersachsen unterstützt. Im Rahmen einer interdisziplinären und internationalen Graduiertenschule „Advanced Materials“ werden voraussichtlich ab Ende 2001 zehn Stipendiaten an den genannten Themen arbeiten. Der entsprechende Promotionsstudiengang durchläuft zur Zeit das Genehmigungsverfahren. Als wissenschaftliche Lehrer und Betreuer sind 16 Hochschullehrer aus den Gebieten Physik, Chemie und Biologie beteiligt. Die Koordination liegt beim Fachbereich Physik. Das Promotionsprogramm hat zum Ziel, wissenschaftliche Fragestellungen bei der Herstellung, Modifikation, Charakterisierung und Vorbereitung technologisch attraktiver Anwendungen von molekular- bzw. clusterformierten Festkörperoberflächen interdisziplinär in Lehre und Forschung zu bearbeiten. Dabei stehen die Modifikationen und Phänomene, die sich aus der erniedrigten Dimension des Systems ergeben sowie die dynamischen Eigenschaften der erzeugten Schichten im Zentrum des Interesses. Die Themenpalette der Forschungsprojekte umfasst dabei die Herstellung neuartiger Oberflächen aus magnetischen Molekülen und Clustern, die Deponierung von Übergangsmetallclustern auf geeigneten Substraten, die Analyse der Synthese von Chitosan mit dem Ziel der gezielten Modifikation der Schichteigenschaften, die Beschichtung von Elektroden mit elektroaktiven Dendrimeren sowie die Herstellung von Keramik-Fasern mit bestimmten Größen ihrer mikrokristallinen Regionen. Das Promotionsprogramm soll den internationalen Promotionsstudiengang „Advanced Materials“ stärken, der den Grundstein eines geplanten interdisziplinären Graduiertenzentrums unter Einbeziehung der Physik, Chemie sowie der Biologie bildet. Das Zentrum lehnt sich an bereits vorhandene erfolgreiche Forschungsschwerpunkte der Materialwissenschaften in den Bereichen Physik, Chemie und Biologie an der Universität Osnabrück an und will den in diesen Fächern vorhandenen materialwissenschaftlichen Kompetenzen eine kohärentere Ausrichtung geben. Die Forschung soll durch konsequente Aktivierung schon bestehender internationaler Forschungskooperationen mit leistungsstarken Institutionen vernetzt werden. Zentrale Elemente der Ausbildung sind ein leistungsfähiges Curriculum, das sich an internationalen Standards orientiert, strenge Zulassungsanforderungen an die künftigen Doktoranden sowie eine kontinuierliche Evaluation des Promotionsfortschritts sowie des Zentrums als Ganzen. Das Zentrum ist institutionell in eine auf der gesamtuniversitären Ebene bereits bestehende Entwicklungsplanung eingebettet und dient damit auch dem Ziel eines kontinuierlichen Strukturwandels an der Universität Osnabrück. 7 1.3.2 Strukturbildende Maßnahmen Durch die im Aufbau befindliche Graduate School und das Graduiertenkolleg 695 wird die Ausbildung von Promotionsstudenten stärker strukturiert, siehe 1.3.1. Wesentliche Elemente sind: Breitere fachliche Ausbildung Betreuung durch mehrere Wissenschaftler Einbeziehung von Promotionsstudenten in die Lehre Interdisziplinarität 1.3.3 Dauer von Promotionen und Habilitationen 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 2,5 - 3 3 - 3,5 3,5 - 4 4 - 4,5 4,5 - 5 5 - 5,5 5,5 - 6 6 - 6,5 6,5 - 7 Jahre >7 Abbildung 1: Verteilung der Zeitdauern zwischen Diplomabschluss und Promotion für diejenigen Promotionen, die im Berichtszeitraum abgeschlossen wurden. Im Berichtszeitraum wurden 68 Promotionen durchgeführt. Die Zeitdauer zwischen Diplomabschluss und Promotion betrug im Median 53 Monate. Die reinen Promotionszeiten sind in der Regel kürzer, konnten aber mit vertretbarem Aufwand nicht ermittelt werden. Im Berichtszeitraum wurden acht Habilitationen durchgeführt. Die Zeitdauern zwischen Promotion und Habilitation schwankten zwischen 3 ½ und 11 ½ Jahren mit einem Median von 7 ½ Jahren. Auch hier sind die reinen Habilitationszeiten kürzer anzusetzen. 8 1.3.4 Berufungen von Mitarbeiter/innen Prof. Dr. Hilmar Franke Prof. Dr. Hans-Joachim Schlichting Prof. Dr. Hermann Rauh Prof. Dr. Kenneth Snowdon Prof. Dr. Udo Backhaus Prof. Dr. Gerald Timmer Im Berichtszeitraum: Prof. Dr. Reinhard Werner Prof. Dr. Romano Rupp Prof. Dr. Karsten Buse Prof. Dr. Sylvia Speller 1.3.5 1989 1991 1994 1994 1995 1995 Univ. GH Duisburg Univ. GH Essen, Univ. Münster (1999) TU Darmstadt Univ. Leipzig, Univ. of Newcastle Univ. Koblenz-Landau, Univ. GH Essen (2001) FH Osnabrück 1996 1997 2000 2001 Univ. Braunschweig Univ. Wien Univ. Bonn Univ. Nijmegen Querverbindungen von Forschung und Lehre Die verschiedenen Forschungsrichtungen im Fachbereich beeinflussen naturgemäß auch die Ausbildungsinhalte in Lehre und Studium. Insbesondere betrifft dies Wahlpflichtveranstaltungen, Seminare und Kolloquien. Neben Inhalten aus dem Gesamtbereich der Physik werden dort auch aktuelle Spezialthemen aus den Forschungsgebieten des Fachbereichs behandelt. Diplomarbeiten und Promotionen bearbeiten in allen Forschungsgruppen Teilinhalte der jeweils aktuellen Forschungsthematik. Dies zeigt sich unter anderem darin, dass im Regelfall auch schon Diplomarbeiten zumeist mehreren - Veröffentlichungen führen. Darüber hinaus besteht für Studierende höherer Semester die Möglichkeit, an Forschungsvorhaben in den Gruppen mitzuarbeiten und dadurch schon frühzeitig das Forschungsgebiet kennen zu lernen. Das Prüfungsfach Angewandte Physik im Diplomstudiengang umfasst die Angewandte Festkörperphysik sowie die Angewandte Optik, zugleich Forschungsschwerpunkte der verschiedenen Promotionsprogramme, sowie die Umweltphysik. 1.3.6 Allgemeine und standortspezifische Probleme Der Fachbereich leidet, wie alle Physik-Fachbereiche, unter dem Rückgang und der Stagnation der Anfängerzahlen im Diplomstudiengang während der letzten Jahre. Dies wird sich in den nächsten Jahren verstärkt in Form fehlender Diplomanden und Doktoranden auswirken. Ein wesentliches Problem stellt die chronische Unterfinanzierung der Universitäten in WestNiedersachsen dar, die die Berufungsfähigkeit des Fachbereichs in einer sensiblen Phase des Generationswechsels beeinträchtigt. Die relativ geringe Personalausstattung und die dadurch bedingte begrenzte Angebotsbreite wirken sich negativ auf die Attraktivität des Studienstandortes aus. Als weiteres standortspezifisches Problem wäre das Fehlen einschlägiger 'physikalischer' Industrie in der Region zu nennen, ebenso das Fehlen technischer Fächer im Spektrum der Universität. Das wird sich zukünftig allerdings durch eine sehr verstärkte Zusammenarbeit mit der Universität Twente ändern, die von der Universität in der Breite angestrebt wird. Ein anderes lokales Problem im Bereich Frauen- und Familienförderung ergibt sich durch das Fehlen einer Kinderkrippe am Westerberg. Der Fachbereich hat die genannten Probleme allerdings nie als Entschuldigung für fehlende Aktivitäten akzeptiert, sondern im Gegenteil in ihnen eine Herausforderung für besondere Anstrengungen gesehen. 9 1.3.7 Ansprechpartner Dekan des Fachbereichs Physik Apl. Prof. Dr. H.-J. Schmidt, Tel. 0541-969 2660, [email protected] 2 2.1 Forschungsprofil Geschichte und Entwicklung des Fachs 1973 wurde die Osnabrücker Pädagogische Hochschule zu einer Universität ausgebaut. Der Gründungsausschuss wollte eine Reihe damals populärer Reformideen realisieren: Projektstudium, einphasige Lehrerausbildung, Interdisziplinarität statt traditioneller Gliederungen, Praxisbezug, Integration mit der Fachhochschule usw. So gründete man einen Fachbereich „Naturwissenschaften: Festkörper und Festkörpertechnologie“, in dem die Gebiete Werkunterricht, Physikdidaktik, Oberflächenphysik und Optische Spektroskopie zusammenarbeiten sollten. Im Fachbereich „Dynamische Systeme“ waren die Theoretische und Mathematische Physik, die Angewandte Mathematik und Informatik sowie die Biologiedidaktik zusammengefasst. Der Studienbetrieb begann im Sommersemester 1974. 1980 musste die Universität gemäß dem neuen Hochschulgesetz gegliedert werden. Die Naturwissenschaftler wirkten maßgeblich daran mit, dass die gesamte Physik im Fachbereich Physik zusammengefasst wurde. 1981 nahm der neue Fachbereich Physik an der Universität Osnabrück seine Arbeit auf. 1983 wurde der Neubau für die Physik bezogen, bei dessen Planung die künftigen Nutzer erfreulicherweise mitwirken konnten. Die durch die Ersteinrichtung der Labors mit neuen Geräten deutlich verbesserte Grundausstattung ermöglichte einen kräftigen Schub bei der Drittmittelfinanzierung von Forschungsvorhaben. Außerdem nutzte der Fachbereich den Standortvorteil, der sich dadurch ergibt, dass er als Teil einer neugegründeten Universität nicht in Institute und Lehrstühle zergliedert ist. 1984 beantragten der Fachbereich Physik und das Fach Anorganische Chemie die Einrichtung eines Sonderforschungsbereiches „Oxidische Kristalle für elektro- und magnetooptische Anwendungen“ - mit Erfolg. Seit Juli 1985 war dieser Sonderforschungsbereich (SFB 225), an dem mehrere theoretische und fast alle experimentellen Gruppen beteiligt waren, der Schwerpunkt in der Forschung und ein Bezugspunkt für die Lehre. Er erreichte die maximale Laufzeit von 15 Jahren. Manche seiner Aktivitäten mündeten in darauf aufbauende Projekte des Transferbereichs 13 „Optische Anwendungen oxidischer Kristalle“. In thematischer Nähe zum Sonderforschungsbereich wurde im Fachbereich zum im Juli 1991 das Graduiertenkolleg „Mikrostruktur oxidischer Kristalle“ eingerichtet und bis 2001 gefördert . Noch im Jahr 2001 sind dann die neuen koordinierten Drittmittelinitiativen angelaufen: Graduiertenkolleg 695 (siehe 1.3.1.2) und die International Graduate School „Advanced Materials“ (siehe 1.3.1.3). Im Bereich der Lehre wird seit dem Wintersemester 2000 ein neuer Studiengang „Physik mit Informatik“ nach dem Bachelor/Master-Schema angeboten. Der Antrag auf Akkreditierung liegt der ZEvA vor. Die Kompatibilität mit dem Diplomstudiengang wurde – nach einer größeren Studienreform - durch eine konsequente Modularisierung des Lehrangebots und die Ausrichtung auf das ECTS-Prüfungssystem erreicht. 10 2.2 Profil und Selbstverständnis des Faches Ein großer Teil der am Fachbereich arbeitenden Wissenschaftler waren am Sonderforschungsbereich 225 „Oxidische Kristalle für elektro- und magnetooptische Anwendungen“ oder am Graduiertenkolleg 15 „Mikrostruktur oxidischer Kristalle“ beteiligt. Im Jahr 2000 wurden beide erfolgreich abgeschlossen, jeweils nach ihrer maximal möglichen Laufzeit (15 bzw. 9 Jahre). Beide Strukturen – zusammen mit einer Vielzahl von Einzelprojekten, meist auch dem Bereich der Festkörperphysik zugehörig – prägten das Profil des Fachbereichs in Forschung und Lehre im vergangenen Jahrzehnt. Die experimentelle und die angewandte Physik haben ihre Schwerpunkte im Bereich der Festkörperphysik: Oberflächenphysik, optische Spektroskopie sowie Elektro- und Magnetooptik. Hinzugekommen ist seit 1996 die Umweltphysik. Die Theoretische Physik orientiert sich zum Teil an diesen Schwerpunkten, verfolgt aber auch eigene Fragestellungen und trägt so zur Verbreiterung des wissenschaftlichen Spektrums bei. Die Fachdidaktik ist im Zuge der Verringerung der Ausbildungskapazität im Lehramtsbereich mehrfach verkleinert worden. Mit ihren Beiträgen zur Verbesserung von Physikunterricht an den Schulen und mit ihrer praxisgerechten Ausbildung ist die Physikdidaktik fest in den Fachbereich eingebunden. Derzeit befindet sich der Fachbereich in einer Phase des Generationenwechsels, die als Möglichkeit zur Gestaltung der zukünftigen Struktur genutzt werden soll. Durch eine Mischung von behutsamen und tatkräftigen Maßnahmen soll die Basis für erfolgreiche zukünftige Forschungsleistungen gelegt werden. Der Fachbereich wird sich dabei sowohl auf die vorhandene wissenschaftliche Expertise und den erreichten guten Ausbaustand stützen, als auch die Chancen zum Aufbau neuer zukunftsträchtiger Arbeitsfelder wahrnehmen. Ein Teil dieser Maßnahmen ist bereits eingeleitet worden: Seit 1994 verfolgt der Fachbereich den Aufbau einer experimentellen Arbeitsgruppe „Umweltphysik“. Dazu wurden zwei Professuren für Mathematische bzw. Theoretische Physik nach Freiwerden entsprechend umgewidmet. Nachdem eine erste Professur C4: „Experimentalphysik-Umweltphysik“ zum 01.10.1996 besetzt werden konnte, wird hier Laborforschung zu Prozessen in der Erdatmosphäre betrieben. Ein komplementärer Arbeitsbereich wird durch die zum 01.04.2000 besetzte Professur C3: „Experimentalphysik, Schwerpunkt umweltphysikalische Feldmessungen“ erschlossen. Er befindet sich derzeit im Aufbau. Die Wiederbesetzung freiwerdender Professorenstellen ist gemäß dem im März 1999 beschlossenen Entwicklungsplan (siehe Anlage) vorgesehen. Danach ist neben der Umweltphysik ein neuer materialwissenschaftlicher Schwerpunkt „Molekulare Architektur niedrigdimensionaler Systeme“ geplant. Im Rahmen dieser Planungen wurde eine Professur C3:“Theoretische Physik-Magnetismus“ zum 01.04.2001 besetzt und eine weitere Stelle C4:“Experimentalphysik-Makromoleküle“ befindet sich im Besetzungsverfahren. Die letztgenannte Stelle soll die Zusammenarbeit mit dem Sonderforschungsbereich 431 "Membranproteine - Funktionelle Dynamik und Kopplung an Reaktionsketten" im Fachbereich Biologie/Chemie verstärken. Der genannte Schwerpunkt „Molekulare Architektur niedrigdimensionaler Systeme“ wird durch ein kürzlich genehmigtes Promotionsprogramm „Synthesis and Characterisation of Surfaces and Interfaces assembled from Clusters and Molecules“ des Landes Niedersachsen unterstützt (siehe 1.3.1.3). Die im SFB 225 und im Graduiertenkolleg 15 erarbeitete materialwissenschaftliche Expertise wird im Rahmen des DFG-Transferbereichs „Optische Anwendungen oxidi- 11 2.3 2.3.1 scher Kristalle“ seit 1998 weiter genutzt und fortgeführt. In Zusammenarbeit mit industriellen Partnern werden darin anwendungsrelevante Fragestellungen behandelt. Das neue Graduiertenkolleg 695 „Nichtlinearitäten optischer Materialien“ bearbeitet einen weiteren Aspekt der Materialforschung, den Bereich neuer Materialien, die für optische Anwendungen interessant sind. Forschungsverbünde und –programme Sonderforschungsbereich 225 Der SFB 225 „Oxidische Kristalle für elektro- und magnetooptische Anwendungen“, im wesentlichen getragen von Wissenschaftlern aus dem FB Physik und der Abteilung Anorganische Chemie des FB Biologie/Chemie der Universität Osnabrück, wurde im Zeitraum 19852000 von der DFG und dem Land Niedersachsen gefördert. Licht kann die Eigenschaften von Kristallen modifizieren, und so modifizierte Kristalle können ihrerseits Licht beeinflussen. Mit ihnen lässt sich also Licht durch Licht steuern. Insbesondere unter oxidischen Kristallen, meist ferroelektrischen Perovskiten und davon abgeleiteten Materialien, finden sich solche, deren Brechungsindizes bereits durch geringe Lichtintensitäten stark beeinflusst werden; sie sind photorefraktiv und bieten damit das Potential, die Wechselwirkung von Licht mit Licht in zahlreichen Konfigurationen zu studieren. Vielfältig sind auch die Möglichkeiten, mit denen der Magnetismus mancher transparenter Oxide die Ausbreitung von Licht steuern kann. Ziel des SFB war es, geeignete Kristalle aufzufinden, herzustellen und zu optimieren. Photorefraktive und magnetooptische Phänomene wurden mit ihnen studiert und in anwendungsnahen Schemata eingesetzt. Diesem Ziel entsprechend, verknüpfte der SFB verschiedene Arbeitsgebiete in enger Kooperation: Kristallzüchtung, Kristallcharakterisierung und Anwendungen. In dreijährigem Rhythmus hatte sich der SFB einer Begutachtung durch von der DFG ausgewählte Experten zu stellen. Regelmäßig wurden die gewonnenen Resultate so hoch bewertet, dass eine Verlängerung empfohlen wurde. Der SFB erreichte daher Ende des Jahres 2000 mit 15,5 Jahren die längste mögliche Laufzeit eines SFB. Insgesamt sind ca. 850 Publikationen und 350 Dissertationen und Diplomarbeiten sowie 5 Habilitationen aus dem SFB hervorgegangen. Durch diese Veröffentlichungen, durch Präsentationen auf Konferenzen sowie durch Kooperationen mit ca. 50 in- und ausländischen Universitäten, Forschungsinstituten und Firmen hat der SFB weltweit stark zur Förderung seines Arbeitsgebietes beigetragen. Weitere Informationen sind über das internet http://www.sfb225.uni-osnabrueck.de/ abrufbar. 2.3.2 Transferbereich „Optische Anwendungen oxidischer Kristalle“ Die anwendungsmotivierte Forschung im SFB hatte in einigen Gebieten die Schwelle zum Transfer in die industrielle Nutzung erreicht. Aus dem SFB ist daher ein Antrag an die DFG auf Einrichtung eines Transferbereiches „Optische Anwendungen oxidischer Kristalle“ hervorgegangen. Nach einem intensiven Begutachtungsverfahren wurde der Antrag zum November 98 genehmigt. Er umfasst bis jetzt drei Teilprojekte (A1, A2, A3), die aus den SFBTeilprojekten ‚Störstellen - Struktur und photorefraktive Wirksamkeit’, ‚Herstellung und Charakterisierung magnetischer Granatschichten’ bzw. ‚Der lichtinduzierte Ladungstransport in elektro-optischen Materialien’ entstanden sind. Kooperationspartner sind Unternehmen in Rheinland-Pfalz, Niedersachsen und Schleswig-Holstein. 12 Bei allen Projekten werden die wissenschaftlichen Arbeiten im Fachbereich Physik durch die DFG gefördert, die jeweiligen Industriepartner wenden entsprechende Mittel für die begleitende Entwicklung vor Ort auf. Ziel der Projekte ist die Weiterentwicklung der SFBErgebnisse auf einen für die Produktion geeigneten Status. Das Projekt A1 wurde zum 31. 10. 2000 erfolgreich abgeschlossen; Projekt A2 begann am 1.4.99 und wird am 31. 3. 02 beendet. Das Projekt A3 läuft vom 1.4.00 bis zum 31.3.03. 2.3.3 Graduiertenkollegs Siehe Ausführungen unter 1.3.1 2.3.4 Einzelprojekte In einer Vielzahl von Einzelprojekten wird Forschung betrieben, die in europäische Netzwerke oder andere Formen der Verbundforschung eingebettet ist. Hier seien beispielhaft nur folgende genannt: RTN-Netzwerk: "Computational Magnetoelectronic“ TMR-Netzwerk: "Electronic structure calculations for materials properties and processes for industry and basic sciences". ESF-Netzwerk: "Electronic Structure Calculations for elucidating the complex atomistic behaviour of solids and surfaces." ESF-Netzwerk: “Elementary steps of layer growth in the fabrication of novel materials by atomic layer epitaxy” BMBF Ozonforschungsprogramm BMBF Aerosolforschungsprogramm BMBF Verbundforschung mit Synchrotonstrahlung BMBF Verbundprojekt: Grundlegende Untersuchungen zu hybrid-integrierten Hochleistungs-Diodenlasern für den sichtbaren und ultravioletten Spektralbereich NFFG: Niedersächsischer Forschungsverbund für Frauen- und Geschlechterforschung Schwerpunktprogramm Erdmagnetische Variationen Weitere Einzelheiten kann man den Einzelberichten der Forschungsgruppen entnehmen. 2.4 Perspektiven und zukünftige Entwicklung Ein kleiner Fachbereich mit begrenzten Ressourcen kann nur dann in der bundesweiten und internationalen Konkurrenz bestehen , wenn er wesentliche Kapazitäten auf ein Gebiet konzentriert, in dem er hochrangige eigene Forschungsleistungen erbringen kann. In der Vergangenheit ist dies im Sonderforschungsbereich 225 gelungen. Eine Wiederholung dieses Erfolges ist nicht planbar, jedoch will der Fachbereich versuchen, günstige Bedingungen für die Entstehung neuer Ideen und Kristallisation von Forschungsverbünden, wie etwa einer Forschergruppe oder einem neuen SFB, herzustellen. Das wesentliche Instrument dafür ist die Berufungspolitik. Durch den Entwicklungsplan von 1999 wurden die Leitlinien zukünftiger Berufungspolitik festgelegt, die sich durch die Stichworte 13 Konsolidierung der Umweltphysik Zusammenarbeit mit Chemie und Biologie Materialwissenschaftlicher Schwerpunkt „Molekulare Architektur niedrigdimensionaler Systeme“ charakterisieren lassen. Die oben erwähnten Berufungsverfahren ( C3: „Experimentalphysik, Schwerpunkt umweltphysikalische Feldmessungen“, C3: „Theoretische PhysikMagnetismus“ und C4: „Experimentalphysik-Makromoleküle“) wurden bereits im Einklang mit den Festlegungen des Entwicklungsplans durchgeführt. Die nächste voraussichtlich im Herbst 2001 auszuschreibende Stelle C4: “Experimentalphysik-Lokale Sonden“ wird eine zentrale Rolle für den Aufbau des materialwissenschaftlichen Schwerpunkts spielen. Die weitere Planung wird im Wesentlichen dem Strukturplan folgen, jedoch sind einige zusätzliche Entwicklungen zu berücksichtigen, die ab 1999 eingetreten sind und im Entwicklungsplan nicht vorausgesehen werden konnten. Die Einrichtung des Graduiertenkollegs 695 und der International Graduate School stärken den Schwerpunkt Materialwissenschaften im Fachbereich nachhaltig. Eine Konsolidierung der Bereiche – etwa durch Juniorprofessuren – ist zu diskutieren. Die Universität Osnabrück hat Pläne zum Ausbau der Informatik entwickelt, die nur realisierbar sind, wenn auch andere Fachbereiche dafür freiwerdende Stellen zur Verfügung stellen. Der Fachbereich Physik ist an diesem Ausbau der Informatik nachdrücklich interessiert, u. a. wegen seines Studienganges „Physik mit Informatik“. Er hat daher seine Bereitschaft signalisiert, eine im Jahre 2004 freiwerdende C3-Stelle im Bereich Theoretische Physik für „Technische Informatik“ umzuwidmen. Sie war laut Entwicklungsplan für „Umweltphysik-Modellierung“ vorgesehen. Damit wird zunächst der Ausbau der Umweltphysik retardiert. Andererseits bietet eine verstärkte Informatik auch Chancen für das Gebiet Computational Physics. Durch die Rufe, die vor kurzem an die Kollegen Blügel und Rühl ergingen, ist eine neue Situation entstanden, die in dem vorliegenden Selbstbericht noch nicht berücksichtigt werden konnte. Der Fachbereich Physik begreift diese Situation als Chance, seine Planung zu überdenken, insbesondere das Ergebnis der Forschungsevaluation einzubeziehen. 2.5 Herausragende Ergebnisse aus den Forschungsprogrammen Stellvertretend für andere exzellente Forschungsergebnisse seien hier die im Berichtszeitraum mit Auszeichnung bewerteten Dissertationen genannt. Name Sugg, Bertram Zeitpunkt Thema der Dissertation 26.07.1996 Untersuchungen zu photorefraktiven Effekten bei tiefen Temperaturen Shamonina, Eka- 22.10.1998 Zur Theorie der dynamischen Holographie in photorefraktiterina ven Kristallen Kasemir, Kay04.12.1998 Spontane nichtkollineare optische Frequenzverdopplung und Uwe ihre Einsatzmöglichkeiten zur Kristallcharakterisierung Lohmeyer, 22.07.1999 Guided waves in rectangular integrated magnetooptic devicManfred es. Hukriede, Jörg 18.01.01 Photorefraktive Streifenwellenleiter in Lithiumniobat als integriert optische Wellenlängenfilter für infrarotes Licht 14 2.6 Rufe, Preise und Auszeichnungen o o o o o o o o o o Ruf an Prof. Dr. E. Rühl auf eine C4-Professur Univ. Würzburg Ruf an Prof. Dr. S. Blügel auf eine C4-Professur Univ. Kaiserslautern Vier Rufe an Mitarbeiter siehe 1.3.4 Young Scientist Award der European Materials Research Society an Dr. B. Sugg Young Scientist Award der European Materials Research Society an Dr. U. Schellhorn Max-Auwärter-Preis an Dr. Th. Schlathölter NASA technical briefs award an Dr. K. Buse Emmy-Noether-Stipendium für Frau Dr. E. Chamonina Heisenberg-Stipendium für Frau PD Dr. M. Schleberger Osnabrücker Preise für hervorragende Diplomarbeiten und Dissertationen (mehrmals) und Habilitationen (einmal). 15 II Darstellung der Forschungseinheiten 1 Angewandte Physik 1.1 Elektrooptik 1.1.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 1.1.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt (Voraussichtliches) Ausscheiden Prof. Dr. Eckhard Krätzig Prof. Dr. Karsten Buse Priv.-Doz. Dr. Detlef Kip Dr. Udo von Stevendaal Dipl.-Phys. Monika Wesner Dipl.-Phys. Jörg Imbrock Dipl.-Phys. Henning Vogt C4 Akad. Rat Wiss. Oberassistent C2 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa Wiss. Mitarbeiterin BAT IIa Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa/2 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa/2 01/1980 09/1991 02/1991 04/1995 12/1998 07/1998 12/1998 09/2004 03/2000 09/2005 11/1998 11/2001 12/2002 12/2002 1.1.1.2 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden Zur Zeit werden 6 Diplomarbeiten und 9 Dissertationen betreut. 1.1.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Die Gruppe bearbeitet die Forschungsschwerpunkte ‘Photorefraktive Effekte und Materialien‘, ‘Lichtinduzierter Ladungstransport‘, ‘Volumenphasenhologramme‘ und ‘Integrierte Optik‘. Weitere Themen sind den unten aufgeführten Schlüsselpublikationen zu entnehmen. Die Gruppe war am Sonderforschungsbereich 225 und am Graduiertenkolleg 15 beteiligt und arbeitet am Graduiertenkolleg 695 und am Transferbereich 13 mit. Insgesamt sind im Berichtszeitraum 21 geförderte Projekte durchgeführt worden (Drittmittel ca. 6 Millionen DM). Seit 1996 haben wir etwa 200 Arbeiten veröffentlicht, darunter mehrere Buch- und Übersichtsartikel. Wir erhielten im Berichtszeitraum mehr als 20 Einladungen zu Hauptvorträgen bei Internationalen Konferenzen und haben insgesamt über 100 Vorträge bei solchen Veranstaltungen gehalten. Wir waren dabei zwölfmal an der Organisation beteiligt, ebenso an der Herausgabe von Sonderbänden verschiedener Zeitschriften (Applied Physics, Journal of the Optical Society of America). Mitarbeiter der Forschungsgruppe erhielten dreimal den Promotionspreis der Universität Osnabrück (H. C. Külich, K. Buse, B. Sugg), zweimal den ‘Young Scientist Award‘ der ‘European Materials Research Society‘ (B. Sugg, U. Schellhorn) und einmal den ‘Rudolf Kaiser-Preis‘ der DPG für eine besonders herausragende Arbeit eines Nachwuchswissenschaftlers (K. Buse). 1.1.2 Publikationstätigkeit 1.1.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen 1. 2. 3. 4. J. Hukriede, I. Nee, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Thermally Fixed Reflection Gratings for Infrared Light in LiNbO3:Ti:Fe Channel Waveguides, Opt. Lett. 23, 1405 (1998) K. Buse, A. Adibi, D. Psaltis, Non-Volatile Holographic Storage in Doubly-Doped Lithium Niobate, Nature 393, 665-668 (1998) D. Kip, M. Wesner, E. Krätzig, V. Shandarov, P. Moretti, All-Optical Beam Deflection and Switching in Strontium-Barium Niobate Waveguides, Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 1960 (1998) M. P. Petrov, V. V. Bryksin, V. M. Petrov, S. Wevering, E. Krätzig, Study of the Dispersion Law of Photorefractive Waves in Sillenites, Phys. Rev. A 60, 2413 (1999) 16 5. K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Light-Induced Charge Transport in Photorefractive Crystals, in 'Photorefractive Optics: Materials, Properties and Applications', Editors F. Yu and S. Yin, Academic Press, Chapter 2, S. 25 - 41, 2000 K. Peithmann, J. Hukriede, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Photorefractive Properties of Lithium Niobate Volume Crystals Doped by Copper Indiffusion, Phys. Rev. B 61, 4615 (2000) S. Odoulov, B. Sturman, E. Krätzig, Seeded and Spontaneous Light Hexagons in LiNbO3:Fe, Appl. Phys. B 70,645 (2000) M. P. Petrov, A. P. Paugurt, V. V. Bryksin, S. Wevering, E. Krätzig, Spatial Rectification of the Electric Field of Space Charge Waves, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 5114 (2000) D. Kip, M. Soljacic, M. Segev, E. Eugenieva und D. Christodoulides, Modulation Instability and Pattern Formation in Spatially Incoherent Light Beams, Science 290, 495 (2000) E. Krätzig and K. Buse, Two-step processes and IR recording in photorefractive crystals, in 'IR Holography for Optical Communications – Techniques, Materials and Devices', Editors P. Boffi, D. Piccinin, M. C. Ubaldi, Topics in Applied Physics, Springer-Verlag, erscheint 2002 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 1.1.3 Forschungskooperationen Innerhalb der Universität Osnabrück haben wir mit fast allen am SFB 225 beteiligten Gruppen zusammengearbeitet (apl. Prof. K. Betzler, Prof. R. Blachnik, Prof. H. Dötsch, Dr. B. Gather, Prof. P. Hertel, Dr. H. Hesse, Prof. S. Kapphan, apl. Prof. M. Neumann, Dr. H.-J. Reyher, Prof. K. Ringhofer, Prof. O. Schirmer). Außerhalb gab es Kooperationen mit gemeinsamen Publikationen mit dem GKSS Forschungszentrum, Geesthacht (Dr. J. Vollbrandt), der Universität Münster (Prof. G. von Bally), der Universität Wien, Österreich (Prof. R. Rupp), dem Institut INAOE, Puebla, Mexiko (Dr. S. Stepanov), der Universität Campinas, Brasilien (Prof. J. Frejlich), dem Caltech, USA (Prof. D. Psaltis), dem Institute of Physics, Kiev, Ukraine (Prof. S. Odoulov), dem Ioffe-Institut, St. Petersburg, Russland (Prof. M. Petrov), dem Institut für Automatisierung, Novosibirsk, Russland (Dr. B. Sturman), dem Technion, Haifa, Israel (Prof. M. Segev), der Universität Dijon, Frankreich (Prof. P. Jullien), dem RisØ National Lab., Roskilde, Dänemark (Prof. P. M. Johansen), der Universität Lyon, Frankreich (Dr. P. Moretti), der Universität Tomsk, Russland (Dr. V. Shandorov), der Universität Athen (Prof. I. Zouboulis), der Universität Kemorovo, Russland (Dr. S. M. Kostritskii), der Universität Princeton, USA (Dr. M. Soljacic), der Universität Lehigh, USA (Prof. Dr. D. Christodoulidis) und der Nankai Universität, Tianjin, China (Prof. Jingjun Xu). 1.1.4 Drittmittelakquisition SFB 225: Teilprojekte A6, C5, D9 (96 - 00); Förderung DFG Gradiertenkolleg 15 (96 – 00, 2 Teilprojekte) und Gradiertenkolleg 695 (ab 01, 3 Teilprojekte); Förderung DFG Transferbereich 13: Teilprojekt A3 (gemeinsam mit K. Betzler, ab 00); Förderung DFG DFG-Projekte: KR 846/8-1(98 - 99), BU 913/8-1 (98 - 00), 446 CHV 112/18/01 (01); Förderung DFG VW-Projekte: I/70 343 (96 - 97), I/70980 (96 – 97, gemeinsam mit S. Odoulov, Kiev), I/72 347 (gemeinsam mit S. Stepanov, Mexiko, 97 98), I/72 919 (gemeinsam mit M. Petrov, Russland, 97 - 98), I/73 920 (99 - 00), VW I/75 292 (gemeinsam mit N. Korneev, 99 - 00), ZN 1154 (gemeinsam mit M. Segev, 01 - 02); Förderung Volkswagenstiftung BMBF-Projekte: 03-Ru4OSN-0 (96-98), 13N6926/8 (96-99), 13N8076 (ab 01, gemeinsam mit H. Hesse); Förderung BMBF Summe 1.813.800.- DM 485.000.- DM 462.500.- DM 220.800.- DM 1.179.800.- DM 1.994.200.- DM 6.156.100.- DM 17 1.1.5 Technologie- oder Wissenstransfer Die Gruppe unterhält seit Jahren intensive Industriekontakte; ein Grund dafür ist sicherlich, dass der Gruppenleiter selbst langjährige Industrieerfahrungen besitzt. Im Berichtszeitraum hat es u. a. Kooperationen mit den Firmen Siemens, LITEF(LITTON), FEE Idar-Oberstein, Felix Schöller und Coherent Radiation gegeben. Von der Zusammenarbeit hat die Gruppe stets profitiert. So hat uns die Firma Siemens bereits vor 5 Jahren ein Pulslasersystem als Leihgabe kostenlos überlassen (Neuwert 180 kDM); im Gegenzug führen wir Messungen für die Firma durch. Dann hat ein früherer Mitarbeiter (K. Buse) selbst eine Firma (Ondax) gegründet, in die bereits drei weitere Mitarbeiter gefolgt sind. Zur Zeit wird ein Transferprojekt gemeinsam mit der Firma Coherent Radiation durchgeführt. Es geht um den 'Einfluss von Störstellen in verschiedenen nichtlinearen Kristallen auf die Effizienz bei Frequenzverdopplung und –verdreifachung innerhalb des Resonators (Intracavity)'. Weiter sind wir am Verbundprojekt des BMBF 'Miniaturisierte Laserstrahlquellen mit hohen Intensitäten im sichtbaren und im nahen ultravioletten Spektralbereich' beteiligt, in dem wir mit den Firmen OSRAM, Opto Speed, FEE, LINOS und LIMO zusammenarbeiten. 1.2 Magnetooptik 1.2.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 1.2.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt Prof. Dr. Horst Dötsch Dr. Wolfgang Bodenberger Dipl.-Phys. Reinald Gerhardt Dipl.-Phys. Ludger Wilkens C3 Akad. Oberrat A14 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa 05/1983 11/1975 10/1993 04/1999 1.2.1.2 (Voraussichtliches) Ausscheiden 03/2002 03/2004 09/1998 03/2002 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 3 Diplomanden, 4 Doktoranden 1.2.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Herstellung und Charakterisierung magnetischer Granatschichten für Anwendungen in der integrierten Optik und der Sensorik. Laser und Modulatoren in magnetooptischen Wellenleitern. Hochfrequenzanregungen magnetischer Domänenwände und periodischer Domänengitter. Räumliche Strukturbildung bei starker Anregung der Ferrimagnetischen Resonanz. Visualisierung der räumlichen Verteilung magnetischer Streufelder. Publikationstätigkeit 1.2.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen 1.2.2 M. Fehndrich, A. Josef, L. Wilkens, J. Kleine--Börger, N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel and H. Dötsch: Experimental investigation of the nonreciprocal phase shift of a transverse electric mode in a magneto--optic rib waveguide. Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 74, p. 2918 (1999) R. Gerhardt, J. Kleine-Börger, L. Beilschmidt, M. Frommeier, B. Gather and H. Dötsch: Efficient channel-Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 75, p. 1210 (1999) 18 1.2.3 1.2.4 1.2.5 O. Zhuromskyy, H.Dötsch, M.Lohmeyer, L.Wilkens, P. Hertel: Magneto-optical waveguides with polarization independent nonreciprocal phase shift. J. Lightw. Techn., vol. 19, p. 214 (2001) M. Shamonin, M. Klank, O. Hagedorn, H. Dötsch: Magneto-optical visualization of metalloss defects in a ferromagnetic plate: Experimental verification of theoretical modeling. Appl. Optics, vol. 40, p. 3182 (2001) F. Popkov, T. Wöbbeking, H. Dötsch and V. I. Korneev: Spatial instability of the nonlinear ferromagnetic resonance in uniaxial films. Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 76, p. 2415 (2000) Forschungskooperationen Universität Konstanz Universität Kaiserslautern Research Institute of Physical Problems, Zelenograd, Russland Forschungszentrum Jülich Charles University und Academy of Science, Prague Columbia University, New York Drittmittelakquisition Projekte A2 und D11 im SFB 225 (1996 – 2000): DM 199 204.- und DM 200 700.Projekt A2 im TFB 13 (1999 – 2001): DM 485 948.DLR Projekt TSR 002 – 97: Defects in ferrites. Wissenschaftlich – Technologische Zusammenarbeit mit der Tschechischen Republik (1997 – 1999) Reisemittel etwa DM 24 000.DLR Projekt RUS 99/184: Nichtreziproke Lichtausbreitung in magnetooptischen Wellenleiter-Strukturen. Wissenschaftlich – Technologische Zusammenarbeit mit Russland (1999 – 2001) Reisemittel etwa DM 9 000.INTAS Projekt 97 – 0366: Metastable photoexcited states in magnetic garnets. (1998 – 2001) Reisemittel etwa DM 5000.- Technologie- oder Wissenstransfer Transferprojekt: Magnetooptische Sensoren und bildgebende Verfahren für Pipelineinspektionen. H. Rosen Engineering GmbH, Lingen. 2 Didaktik der Physik 2.1 Theoretische Physik und Didaktik der Physik 2.1.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 2.1.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt Prof. Dr. Werner Schürmann Dipl.-Phys. Karen Riek Dipl.-Phys. Andreas Geisler C4 Wiss. Mitarbeiterin BAT IIa Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa 04/1996 11/1995 11/1998 (Voraussichtliches) Ausscheiden 03/2004 03/1997 10/2003 19 2.1.1.2 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 6 Examensarbeiten, 2 Doktoranden 2.1.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Theoretische Physik: Nichtlineare Optik, Solitonenlösungen der nichtlinearen Schrödinger-Gleichung Didaktik der Physik: Didaktik der Nichtlinearen Optik, Einführung physikalischer Grundbegriffe auf der Basis des Ludwig-Konzepts 2.1.2 Publikationstätigkeit 2.1.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen H. W. Schürmann: Travelling-wave solutions of the cubic-quintic nonlinear Schrödinger equation, Physical Review E 54, 4312 (1996) H. W. Schürmann: TE-polarized waves guided by a lossless nonlinear three-layer structure, Physical Review E 58, 1 (1998) 2.1.3 Forschungskooperationen Betreuer im Graduiertenkolleg „Nichtlinearitäten optischer Materialien“ des Fachbereichs Physik der Universität Osnabrück (Arbeitsrichtung: Nichtlineare Optik) Dept. of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics, Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia (Prof. Dr. V. Serov) Dept. of Engineering Sciences, Physics, and Mathematics, Karlstad University , Karlstad, Sweden (Prof. Dr. Y. V. Shestopalov) Penza State University, Penza, Russia (Prof. Dr. Y. Smirnov) Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach (Februar 1999, November 2000) 2.1.4 Drittmittelakquisition Beihilfe der DFG für Forschungskooperation mit der Moscow State University, Az. 436 Rus 17/150/96 (s. 3.) ca. 4.000.-- DM Anteil am Graduiertenkolleg „Nichtlinearitäten optischer Materialien“ der DFG, Z. III GK-GRK 695/1-01, 18.10.2000, für 3 Jahre (s. 3) ca. 115.500,-- DM Nds. Ministerium für Wissenschaft und Kultur: Mittel für Hilfskräfte, Literatur und Lehrmaterial (1997, 1998) 90.000,-- DM 20 3 Experimentalphysik 3.1 Elektronenspektroskopie 3.1.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 3.1.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle apl. Prof. Dr. Manfred Neumann Hochschuldozent C2 3.1.1.2 Eintritt 03/1976 Voraussichtliches Ausscheiden 09/2010 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 7 Doktoranden 3.1.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Die Arbeitsgruppe beschäftigt sich vorwiegend mit der Untersuchung der elektronischen Eigenschaften von interessanten neuen Materialien, darunter Oxide (auch supraleitende, mit Riesenmagnetowiderstand, mit elektrooptischen Anwendungen, Grundlagenuntersuchungen), intermetallische Verbindungen (Studium des Magnetismus und der elektronischen Korrelationswechselwirkung) und Polymere (dünne Schichten und modifizierte Oberflächen, auch plasmabehandelte). In der Vergangenheit wurden diverse Adsorptionssysteme mit kleineren und größeren Molekülen mit Erfolg studiert. Bevorzugte Untersuchungsmethode ist die Photoelektronenspektroskopie unter Anregung von monochromatisierter Röntgenstrahlung oder polarisierter UV-Strahlung im Labor, sowie mit Synchrotron-Strahlung. Darüberhinaus stehen viele weitere oberflächenanalytische Methoden (wie LEED, XPD, Auger, TDS, usw.) der Arbeitsgruppe zur Verfügung. 3.1.2 Publikationstätigkeit 3.1.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen Electronic Structure of Titanium Monoxide, S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, E. Z. Kurmaev, V. V. Fedorenko, S. N. Shamin, V. M. Cherkashenko, S. N. Nemnonov, A. Winiarski, D. Rubie, Phys. Rev. B56, 10656-10667 (1997) X-Ray Photoelectron Diffraction of ABO3-Type Perovskites: Site Determination for Dopants, B. Schneider, R. Niemann, Ch. Kuper, H. Hesse and M. Neumann, J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 96, 37 - 42 (1998) Analysis of XPS Valence Band Spectra of Polymers using DFT Band Calculations of Model Oligomers, S. Mähl, M. Neumann, B. Schneider, V. Schlett, A. Baalmann, J. Polymer Science A37, 95 - 103 (1999) Electronic Structure of FeCr2S4 and Cu0.5Fe0.5Cr2S4, E.Z. Kurmaev, A. V. Postnikov, H. M. Palmer, C. Greaves, St. Bartkowski, V. Tsurkan, M. Demeter, D. Hartmann, M. Neumann, D. A. Zatsepin, V.R. Galakhov, S. N. Shamin, V. Trovimova, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 5411 – 5421 (2000) Weak ferromagnetism induced by atomic disorder in Fe2TiSn, A. Slebarski, M. B. Maple, E. J. Freeman, C. Sirvent, D. Tworuszka, M. Orzechowska, A. Wrona, A. Jezierski, S. Chiuzbaian, M. Neumann, Phys. Rev. B62, 3296 - 3299 (2000) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of a hexanuclear cluster S. G. Chiuzbaian, M. Neumann, O. Waldmann, B. Schneider, I. Bernt, R. W. Saalfrank, Surf. Sci. 482-485, 1272 – 1276 (2001) Origin of magnetic circular dichroism in soft x-ray fluorescence of Heusler alloys at threshold excitation, M. V. Yablonskikh, V. I. Grebennikov, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, E. Z. 21 Kurmaev, S. M. Butorin, L.-C. Duda, J. Nordgren, S. Plogmann, M. Neumann, Phys. Rev. B63, 235117(10) (2001) 3.1.3 Forschungskooperationen Innerhalb der Hochschule gibt es Kooperationen mit den Kollegen der Theoretischen Physik und der Chemie. Regional gibt es Kooperationen mit der Fachhochschule und mehreren Industriebetrieben (siehe Technologietransfer). National und international gibt es Kooperationen mit vielen wissenschaftlern anderer Universitäten (siehe Publikationsliste). Mit folgenden Institutionen bestehen formelle, zeitlich nicht befristete Kooperationsverträge: Institut für Physik, Schlesische Universität, Kattowitz (Polen); Institut für Metallphysik, Akad. d. Wissenschaften, Jekaterinburg (Rußland); Fakultät für Physik, Babes-BolyaiUniversität Klausenburg (Rumänien). In den letzten fünf Jahren wurden, bzw. werden mit folgenden Institutionen gemeinsame Forschungsprojekte durchgeführt: Lab. L. Néel, CNRS, Grenoble (Frankreich); Institut für Chemie, Universität Birmingham (England); Anorganische Chemie, Universität Uppsala (Schweden); Department für Techn. Elektronik, Politechnische Universität, Madrid (Spanien), Faraday Research Laboratory London (England), Physik, Universität Saskatchewan (Kanada). Außerdem bestehen Kooperationen mit mehreren Synchrotronstrahlungslaboren in USA (ALS Berkeley), Italien (Elettra Triest), Frankreich (ESRF Grenoble) und Deutschland (Hasylab Hamburg, Delta Dortmund und BESSY Berlin). Es erfolgt ein äußerst reger und regelmäßiger Wissenschaftleraustausch mit Gastaufenthalten bis zu 20 Monaten pro Jahr. 3.1.4 Drittmittelakquisition Drittmittelakquisition in den letzten fünf Jahren: ca. 3,5 Mio DM Einzelheiten siehe Anhang 3.1.5 Technologie- oder Wissenstransfer Es erfolgt ein ständiger wissenschaftlich-technologischer Transfer von Know-How durch zwei Institute. Der Leiter der AG ist seit über 10 Jahren wissenschaftlicher Leiter am Institut für TechnischWissenschaftliche Innovation (ITI) an der Fachhochschule und an der Universität Osnabrück GmbH und hat zusammen mit der Universität Twente das Euregio-Institut zur Oberflächenanalyse „Euregio Centre for Surface Engineering“ ECSE gegründet (seit 1.1.2000). Eine Beschreibung der Institutionen befindet sich unter: http://www.iti.fh-osnabrueck.de/iti/oa/welcome.html http://zeus.physik.uni-osnabrueck.de/ecse/ Das Tätigkeitsgebiet erstreckt sich über alle Bereiche der Analyse und Charakterisierung von Oberflächen und dünnen Schichten (Polymere, Metalle, Keramiken, Halbleiter, etc.), vorwiegend unter Verwendung elektronenspektroskopischer Verfahren. Es werden mit namhaften Firmen bei der Entwicklung neuer Produkte Untersuchungen und Beratungen durchgeführt. Bei der Herstellung neuer Produkte werden projektbegleitend Analysen zur Produkt- und Verfahrensoptimierung durchgeführt. Zur Qualitätssicherung werden Fehlerursachen umfassend erforscht. Das „ECSE“ war mit einem Stand an der Euregio-weiten Messe TECHNO 2000 in Enschede vertreten und hat sich mit mehreren Vorträgen präsentiert. 22 3.2 Laserspektroskopie 3.2.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 3.2.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt Prof. Dr. Siegmar Kapphan Dr. Georg Greten Dipl.-Phys. Stefan Porcher Dipl.-Phys. Christian auf der Horst Dipl.-Phys. Jörg Licher Dipl.-Phys. Maria Wierschem C3 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa/2 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa/2 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa/2 02/1974 10/1992 12/1997 01/1993 (Voraussichtliches) Ausscheiden 03/2005 02/1996 01/1998 12/1997 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa/2 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa/2 07/1998 08/1998 06/2001 07/2001 3.2.1.2 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 1 Doktorand 3.2.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Wasserstoffstörstellen in oxidischen Kristallen (1996 – 2001, 6 Publikationen) Lumineszenz und Ramanstreuung von Störstellen in oxidischen Kristallen (1998 – 2001, 13 Publikationen) Optische Ausrichtung und Untersuchung von Fe-Zentren in KTaO3 (1996 – 2001, 6 Publikationen) Lichtinduzierte Umladungsprozesse in Chrom- und Cer-dotierten Sr1-xBaxNb2O6 (SBN)-Kristallen (1996 – 2001, 11 Publikationen) SrTiO3-KTaO3 Mischkristallsysteme (1998 – 2001, 3 Publikationen) Polaronische Komplexe in oxidischen Kristallen (1998 – 2001, 8 Publikationen) Optische Frequenzverdopplung (SHG) an oxidischen Kristallen (1996 – 2001, 14 Publikationen) Fourier-IR-Untersuchungen an LaMnO3 (1999 – 2001, 1 Publikation) 3.2.2 Publikationstätigkeit 3.2.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen A. Gröne and S. Kapphan, ‘Direct OH and OD Librational Absorption Bands in LiNbO3’, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, Vol. 57, 325 (1996) K. Buse, S. Breer, K. Peithmann, S. Kapphan, M. Gao, and E. Krätzig, Origin of thermal fixing in photorefractive lithium niobate crystals, Physical Review B, Vol. 56, 1225 (1997) V. S. Vikhnin and S. Kapphan, Vibronic charge-transfer excitons: possible nature of the unusual properties of virtual perovskitelike ferroelectrics, Physics of the Solid State, Vol. 40, 834 (1998) S. Eden, S. Kapphan, and H. Hesse, V. Trepakov and V. Vikhnin, I. Gregora and L. Jastrabik, J. Seglins, Observations of the absorption, infra-red emission, and excitation spectra of Cr in BaTiO3, Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 10, 10775 – 10786 (1998) 23 P.G. Johannsen and V. Schäferjohann, S. Kapphan, Effect of pressure on OH and OD impurities in LiNbO3, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 11, 583 – 591 (1999) M. Gao, R. Pankrath, S. Kapphan, V. Vikhnin, Light-induced charge transfer and kinetics of the NIR absorption of Nb4+ polarons in SBN crystals at low temperatures, Appl. Phys., B 68, 849-858 (1999) S.E. Kapphan, Spatially resolved second-harmonic generation in ABO3-type ferroelectric crystals, Journal of Luminescence, 83-84, 411-415 (1999) V. A. Trepakov, M. E. Savinov, E. Giulotto, P. Galinetto, P. Camagni, G. Samoggia, L. A. Boatner, S. E. Kapphan, ‘Dipole ordering effects and reentrant dipolar glass state in KTaO3:Li,Nb’, Phys. Rev. B, Vol. 63, 172203 (2001) S. A. Basun, A. A. Kaplyanskii, A. B. Kutsenko, V. Dierolf, T. Tröster, S. E. Kapphan, and K. Polgar, ‚Dominat Cr3+ Centers in LiNbO3 under Hydrostatic Pressure’ Phys. of Sol. State, Vol. 43, No. 6, 1043-1051 (2001) 3.2.3 Forschungskooperationen Innerhalb der Hochschule Durch Projekte im bis 2000 bestehenden SFB 225 Zusammenarbeit mit verschiedenen Teilprojekten und mehrere gemeinsame Publikationen Durch Projekte im Graduiertenkolleg (I und II) Wechselwirkung und Zusammenarbeit, derzeit auf dem Gebiet der Nichtlinearitäten optischer Materialien Außerhalb der Hochschule Prof. Feng, Xiqi, SICAS, Shanghai, China Prof. A. Kaplyanskii, Ioffe Inst., AS, St. Petersburg, Russland Prof. V. Vikhnin, Ioffe Inst., AS, St. Petersburg, Russland Prof. V. Trepakov, Ioffe Inst., AS, St. Petersburg, Russland, and Inst. of Optics, Prague, Cz. Rep. Prof. J. Zhao, Dept. Appl. Phys., N-W Polytechn. Univ. Xian, China Prof. C. Jastrabik, Inst. of Optics, CzAS, Prague, Cz. Rep. Prof. S. Prosandeyev, Rostov St. Univ., Rostov-Don, Russland Prof. B. Pedko, Tver Univ., Tver, Russland Prof. M. S. Li, Sao Carlos-Camp., Univ. Sao Paulo, Dept. Fisica, Brasilien Prof. Dr. J. Schneider, DESY, Hamburg 3.2.4 Drittmittelakquisition Drittmittelakquisition in den letzten fünf Jahren: ca. 1,2 Mio DM Einzelheiten siehe Anhang 3.2.5 Technologie- oder Wissenstransfer Pro Jahr zwei bis drei Beratungsgespräche oder Probenmessungen zu optischen Eigenschaften, Vorbereitung von Patentanmeldungen, Ausarbeitung von Gutachten. 24 3.3 Nichtlineare Optik 3.3.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 3.3.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt apl. Prof. Dr. Klaus Betzler Akad. Dir. A15 04/1975 3.3.1.2 Voraussichtliches Ausscheiden 03/2011 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 1 Doktorand 3.3.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Optische Eigenschaften neuer Materialien: Untersuchung optischer (Brechungsindex, etc.) und elektrooptischer Eigenschaften (elektrooptischer Materialtensor) von neuen Materialien für elektrooptische Anwendungen. Modellbildung, theoretische Beschreibung von Materialeigenschaften: Modellierung insbesondere optischer Eigenschaften, Beschreibung von Brechungsindizes verschiedener Materialien in Abhängigkeit von Temperatur, Zusammensetzung, Dotierung mit verallgemeinerten Ansätzen. Neue Kristalle für die nichtlineare Optik: Charakterisierung neuer Materialien für die nichtlineare Optik in Zusammenarbeit mit der anorganischen Chemie und der Kristallzüchtung, Bestimmung der grundlegenden Materialtensoren. Entwicklung neuer Meßmethoden: Neue interferometrische Methode zur Brechungsindexbestimmung, verschiedene neue Verfahren zur Kristalltopographie, die auf kollinearer und nichtkollinearer optischer Frequenzverdopplung beruhen. Untersuchung von keramischen Materialien: Es werden insbesondere Glaskeramiken für optische Anwendungen untersucht. Multimedia-Anwendungen: Multimedia-Einsatz in Lehrveranstaltungen, insbesondere in physikalischen Praktika. 3.3.2 Publikationstätigkeit 3.3.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen D. Xue, K. Betzler: Influence of optical-damage resistant dopants on the nonlinear optical properties of lithium niobate. Applied Physics B 72, 641 (2001). D. Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse: Dielectric properties of I-III-VI2 type chalcopyrite semiconductors. Physical Review B15, 62, 13546 (2000). K. Betzler, H. Hesse, R. Jaquet, D. Lammers: Optical second-harmonic generation in lead formate. J. Appl. Physics 87, 22 (2000). K.-U. Kasemir, K. Betzler: Characterization of photorefractive materials by spontaneous noncolinear frequency doubling. Applied Physics B 68, 763 (1999). Reichert, K. Betzler: Induced noncolinear frequency doubling: A new characterization technique for electrooptic crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 2209 (1996). 25 3.3.3 Arbeitsgruppe Kristallzüchtung des Fachbereichs (neue Kristalle für nichtlinear optische Anwendungen, keramische Materialien – Sonderforschungsbereich 225, Graduiertenkolleg 695, International Graduate School “Advanced Materials”). Institut für Chemie der Universität Osnabrück (Untersuchung von neuen Materialien – Sonderforschungsbereichs 225. Forschungsgruppe Elektrooptik des Fachbereichs (Projekt A3 des Transferbereichs 13 der DFG). Institut für Mineralogie der Universität Köln (Projekt A3 des Transferbereichs 13 der DFG). Firma Coherent, Lübeck (Projekt A3 des Transferbereichs 13 der DFG). Dr. Dongfeng Xue, Universität Dalian, China (Berechnung optischer Eigenschaften von Kristallen). Prof. Dr. Eberhard Schwarzer, Universität Hildesheim (Multimedia-Einsatz in Lehrveranstaltungen). Prof. Dr. Tatjana Volk, Russische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Moskau (Eigenschaften von Lithiumniobat und Strontium-Barium-Niobat). Prof. Dr. M. D. Fontana, Dr. M. Aillerie, ESE Metz (Optische Untersuchungen an Lithiumniobat). 3.3.4 Drittmittelakquisition Projekt A10 „Nichtkollineare Frequenzverdopplung“ des Sonderforschungsbereichs 225 (1996–2000) WAP-Antrag (1999) Alexander-von-Humboldt-Stipendium Dr. Dongfeng Xue (1999/2000) Beteiligung am Projekt A3 des Transferbereichs 13 (2000–2002) Projekt “Optical nonlinearities near the phase transition of SBN” des Graduiertenkollegs 695 (2001–2003) Projekt “Growth and characterization of nonlinear SBN crystals” des Graduiertenkollegs 695 (gemeinsam mit Dr. R. Pankrath, 2001–2003) Projekt “Linear and nonlinear optical properties of borate glass ceramics” der International Graduate School (gemeinsam mit Dr. H. Hesse, 2001– 2004) Projekt „Online-Experimente per Internet“ (gemeinsam mit Prof. Dr. E. Schwarzer, Uni Hildesheim, 1999–2001) 3.3.5 Forschungskooperationen 345.000,– 130.500,– 80.000,– 462.500,– 115.000,– 115.000,– 160.000,– 77.000,– Technologie- oder Wissenstransfer Patent Nr. 19836716: Vorrichtung und Verfahren zur Kristallcharakterisierung mittels spontaner nichtkollinearer optischer Frequenzverdopplung. Projekt A3 des Transferbereichs 13: „Der Einfluss von Störstellen in verschiedenen nichtlinearen Kristallen auf die Effizienz bei Frequenzverdopplung und –verdreifachung innerhalb des Resonators (intracavity)“, Zusammenarbeit mit Firma Coherent, Lübeck. 26 3.4 Magnetische Resonanzspektroskopie 3.4.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 3.4.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt Prof. Dr. Ortwin F. Schirmer Dr. Hans-Jürgen Reyher apl. Prof. Dr. Manfred Wöhlecke Dr. Susanne Lenjer Dr. Andreas Rüdiger Dipl.-Phys. Martin Meyer C4 03/1983 (Voraussichtliches) Ausscheiden 03/2002 Akad. Rat A13 Akad. Oberrat A14 04/1989 04/1986 08/2016 04/2008 Wiss. Mitarbeiterin BAT IIa 04/1996 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa/2 04/1999 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa/2 11/1999 03/1999 08/2001 03/2002 3.4.1.2 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden Zur Zeit werden 5 Doktor-Arbeiten betreut. 3.4.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Die Arbeitsgruppe befasst sich - mit der Analyse der Struktur von Störstellen insbesondere in oxidischen Kristallen - den Eigenschaften von freien und gebundenen Polaronen und Bipolaronen in Oxiden - den Ausprägungen der Phasenseparation in Hochtemperatur-Supraleitern. - mit der spektroskopischen Untersuchung von OH-Streckschwingungen - mit der Vermeidung photorefraktiver Prozesse (‚optical damage’) - mit dem Einfluss der Ferroelektrizität auf photorefraktive Eigenschaften Wesentliche Untersuchungsmethoden sind Elektronen-paramagnetische Resonanz (EPR), Elektron-Kern-Doppel-Resonanz (ENDOR), optisch detektierte magnetische Resonanz (ODMR) in Absorption und Emission, optische Absorptionsspektroskopie im UV, Vis und NIR, kombinierte EPR/optische Absorption sowie theoretische Defektsimulation auf der Basis von Embedded-Cluster-Verfahren. Ein großer Teil der Arbeiten wurde bisher im Rahmen des SFB 225 und des TFB 13 durchgeführt. Primäres Ziel ist die Entschlüsselung der geometrischen, chemischen, elektronischen und energetischen Struktur von Defekten in ihren Grund- und angeregten Zuständen in Hinsicht auf ihre Auswirkung auf das photorefraktive Verhalten der Materialien (insb. BaTiO3, Ba1- xCaxTiO3, LiNbO3, Sr1-xBaxNb2O6). Auf dieser Basis können u.a. die Wege des lichtinduzierten Ladungstransfers zwischen den Störstellen aufgeklärt und die photorefraktiven Eigenschaften der Materialien optimiert werden. Allgemeinere Bedeutung auch haben die Analyse der Eigenschaften von Ladungsträgern, die sich unter der starken Träger-Gitter-Kopplung in den oxidischen Materialien als freie und gebundene Polaronen und Bipolaronen ausbilden. Zu erwähnen sind ferner Studien über Störstellen mit Relevanz für Lasermaterialien und über ‚Weißmacher’ in weißen LEDs. 27 3.4.2 Publikationstätigkeit 3.4.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen H. J. Reyher, M. Pape, N. Hausfeld, Photoactive Pb3+ host lattice ions in photorefractive Pb5Ge3O11 investigated by magnetic resonance techniques J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13, 3767 (2001) M. Wöhlecke, L. Kovacs, OH- ions in Oxide Crystals, Critical Reviews in Solid State and Materials Sciences 26, 1 (2001) T. Volk, L. Ivleva, P. Lykov, D. Isakov, V. Osiko, and M. Wöhlecke, Modification of the optical and photorefractive properties of Ce-doped strontium–barium niobate by co-doping with a nonphotorefractive La impurity, Appl. Phys. Letters 79, 854 (2001) O. F. Schirmer, EPR investigations of small electron and hole polarons in oxide perovskites in ‘Defects and surface-induced effects in advanced perovskites’, G. Borstel et al. (eds.), Kluwer 2000, p. 75 – 88 V. Grachev, G. I. Malovichko, EPR, ENDOR and optical absorption study of Cr3+ centers substituting for niobium in Li-rich lithium niobate crystals, Phys. Rev. B 62, 7779 (2000) H. Donnerberg, A. Birkholz, An initio study of oxygen vacancies in barium titanate J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 8239 (2000) O. F. Schirmer, Light-induced charge transfer between defects in photorefractive materials, Radiation effects and defects in solids 149, 281 (1999) G. Malovichko, V. Grachev, O. Schirmer, Interrelation of intrinsic and extrinsic defects. Congruent, stoichiometric and regularly ordered lithium niobate, Appl. Phys. B 68, 785 (1999) S. Köhne, O. F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, T. W. Kool, V. Vikhnin, Ti3+ Jahn-Teller polarons and bipolarons in BaTiO3 , J. Superconductivity 12, 193 (1999) E. Ruza, H. J. Reyher, J. Trokss, M. Wöhlecke, Optically detected magnetic resonance via the blue luminescence of Ti-doped Al2O3 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 10, 4297 (1998) 3.4.3 Forschungskooperationen im Fachbereich Physik: Abteilung Kristallzüchtung1 (Dr. Hesse, Dr. Pankrath), Arbeitsgruppe „Elektrooptik“ (Prof. Krätzig) national: Forschungsinstitut für Mineralische und Metallische Werkstoffe, Edelsteine/Edelmetalle GmbH, Idar-Oberstein2; Universität zu Köln, Kristallographisches Institut1 international: Department of Physical Chemistry, University of Amsterdam1,3; Ukrainian Academy of Sciences, Institute of Physics, Kiev1,3; Armenian Academy of Sciences, Ashtarak1,3; Ungarische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Crystal Physics Laboratory, Budapest1,3; Russische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Shubnikov Crystallographic Institute, Moskau1,3 1 gemeinsame Publikationen gemeinsames Projekt 3 Wissenschaftleraustausch 2 28 3.4.4 Drittmittelakquisition (Quellen: SFB 225, TFB 13, Sachbeihilfen DFG) Drittmittel (in TDM) 1996 271,6 SFB, Sachb. 3.4.5 1997 1998 496,6 197,5 SFB, Sachb. SFB, Sachb. 1999 2000 204,6 146,6 SFB, TFB, Sachb. SFB, TFB 2001 115,0 Sachb., DFG Technologie- oder Wissenstransfer Antragstellung zur Einrichtung eines Transferbereiches. Durch die DFG genehmigt als TFB 13. Durchführung eines Projektes zusammen mit einer Industriefirma in Rheinland-Pfalz. 3.5 Oberflächenphysik und Nanostrukturen 3.5.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 3.5.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt Prof. Dr. Werner Heiland Dr. Herbert Koschmieder Prof. Dr. Sylvia Speller C4 Akad. Oberrat Wiss. Assistentin C1 07/1980 07/1975 04/1996 (Voraussichtliches) Ausscheiden 03/2002 03/2002 08/2001 Frau PD Dr. M. Schleberger war bis 04/2001 Mitglied der Arbeitsgruppe „Oberflächenphysik“ und leitet seitdem eine eigene Arbeitsgruppe „Nanostrukturen“. Sie nimmt ein Heisenberg-Stipendium wahr. 3.5.1.2 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 2 Diplomanden, 6 Doktoranden, 1 Habilitandin 3.5.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen II Wechselwirkung schneller Ionen mit Festkörperoberflächen: Energieverlust, Ladungsaustausch und Dissoziation. II Oberflächenmagnetismus und Magnetismus dünner Schichten: Untersuchungen mit Ionenstreuung III Die Struktur von Festkörperoberflächen: Untersuchungen mit Rastertunnelmikroskopie und Ionenstreuung IV Die Struktur biologischer Materie: Untersuchungen mit Rasterkraftmikroskopie und Rastertunnelmikroskopie 29 3.5.2 Publikationstätigkeit 3.5.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen 3.5.3 W. Heiland and E. Taglauer, Eds., Inelastic Ion-Surface Collisions Proc. 11th Int. Workshop on Inelastic Ion-Surface Collisions, Wangerooge, Germany 1996 (North Holland, Amsterdam 1997), Nucl. Instr. Meth. B 125 (1997) Chr. Schröder, W. Heiland, R. Held, W. Loose Analysis of reverse current-voltage characteristics of Ti/6H-SiC Schottky diodes Appl. Phys. Lett. 68 (1996) 1957 – 1959 N. Hatke, M. Dirska, M. Grether, E. Luderer, A. Robin, A. Närmann, W. Heiland Surface channeling experiments at 20 MeV and resonant coherent excitation of N6+ ions Phys. Rev. Lett. 79 (1997) 3395-3398 M. Schleberger, M. Dirska, J. Manske, A. Närmann Measuring hysteresis of magnetic surfaces by ion scattering Appl. Phys. Lett. 71 (1997) 3156-3158 P. Walser, M. Schleberger, P. Fuchs, M. Landolt Heat Induced Antiferromagnetic coupling in Multilayers with Ge Spacers Phys. Rev. Letters 80 (1998) 2217-2220 E. Ortega, S. Speller, A. R. Bachmann, A. Mascaraque, E. G. Michel, A. Närmann, A. Mugarza, A. Rubio, F. J. Himpsel The electron wave function at a vicinal surface: Switch from terrace to step modulatin Phys. Rev. Letters, 84 (2000) 6110 V.Arnau, F. Aumayr, P. M. Echenique, M. Grether, W. Heiland, J. Limburg, R. Morgenstern, P. Roncin, S. Schippers, R. Schuch, N. Stolterfoht, P. Varga, T. J. M. Zouros, H. P. Winter Interaction of slow multicharges ions with solid surfaces Surf. Sci. Reports 27 (1997) 113-239 M. Schleberger, S. Speller, W. Heiland Surface Characteristion Methods in Experimental Physics, vol. 30 (1998) 291-327 S. Speller, W. Heiland and M. Schleberger Surface Characterisation: Composition, Structure and Topography Handbook of Surface Science, Ed.: S. Nalwa (Academic Press, New York 2001) Forschungskooperationen 28 Forschungskooperationen, Einzelheiten siehe Anhang 3.5.4 Drittmittelakquisition Im Berichtszeitraum ca. 4,4 Mio DM, Einzelheiten siehe Anhang 3.5.5 Technologie- oder Wissenstransfer Jahr 1996 Firma Oriental Scientific Instruments Shanghai, China Stockholm University Stockholm, Schweden Harting GmbH 1996 1997 Titel „90° spherical electrostatic energy analyzer“ Ion source with accessories Inbetriebnahme des MehrkomponentenIndustriegasschrankes hier: Untersuchungen an Prüfblechen zur Ermittlung 30 1997 Deutsche Post Osnabrück VW, Wolfsburg Harting GmbH Espelkamp Harting GmbH Espelkamp 1998 1998 1998 1998 2000 2001 Harting GmbH, Espelkamp Karsten Schröder, Hasbergen Hewing GmbH Ochtrup der Korrosionsprodukte auf der Oberfläche nach der Schadgasbelastung soiwe Untersuchung der Oberflächenbeschaffenheit Untersuchung von elektrostatischen Aufladungen im Briefzentrum Osnabrück Untersuchungen mit MOKE an metallischen Proben Untersuchungen zur elektrischen Leitfähigkeit und Wärmeleitfähigkeit Computersimulation zur Bestimmung von Industriegaszusammensetzungen und den dazugehörigen Konzentrationen Analyse an metallischen Proben AFM-Messungen an Kunststofffolien Rastertunnelmikroskopuntersuchungen an gestellten Proben 3.6 Umweltphysik- Prozessstudien 3.6.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 3.6.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt Prof. Dr. Eckart Rühl Dr. Roman Flesch Dr. Werner Tappe Dr. Björn Steiner Dr. Wolfgang Mikosch Dr. Max-Christian Schürmann C4 Akad. Rat A13 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa Wiss. Angestellter 10/1996 10/1996 03/1999 02/1997 07/1999 07/2001 3.6.1.2 (Voraussichtliches) Ausscheiden 09/2023 01/2026 08/2001 03/1999 06/2004 06/2006 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 2 Diplomanden, 5 Doktoranden, 3 Habilitanden 3.6.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Größenabhängige Eigenschaften der Materie: Untersuchung und Optimierung der geometrischen und elektronischen Struktur von freien und deponierten Clustern im Hinblick auf materialwissenschaftlich relevante Systeme. Als Methoden werden genutzt: Synchrotronstrahlung; Freier-ElektronenLaser; Tunnel- und Kraft-Mikroskopie sowie optische Spektroskopie. Dynamik elektronisch angeregter Zustände von Atomen, Molekülen, Clustern und Adsorbaten: Untersuchung von kurzlebigen Zuständen in der Frequenz- und Zeitdomäne. Im Vordergrund stehen: Nutzung von gepulsten Lasern (künftig: Freier-Elektronen-Laser); XUV- und Röntgen-Plasmaquellen; Stoßexperimente mit hochgeladenen Ionen und Synchrotronstrahlung. Als Meßmethoden dienen: Massenspektrometrie, Photoelektronenspektroskopie, Konzidenz-Experimente, Fluoreszenz-Experimente. 31 Physikalische und chemische Eigenschaften von Aerosolen: Charakterisierung von nanoskopischen und mikroskopischen Partikeln und deren chemische wie physikalischen Veränderungen mit Hilfe von Levitationsexperimenten (einschließlich technologischer Anwendungen). Als Methoden werden genutzt: Elastische und inelastische Lichtstreuung; Massenspektrometrie; Neutronenkleinwinkelstreuung und Synchrotronstrahlung. Prozeßstudien zur Umweltphysik und Umweltchemie: Charakterisierung atmosphärischer Modellaerosole; Untersuchung heterogener Reaktionen der Atmosphäre; kinetische Experimente zum Abbau von nicht-flüchtigen wie partikelgebundenen Umweltchemikalien; Charakterisierung atmosphärischer Photoprozesse. Entwicklung und Aufbau von Meßgeräten und Verfahren in der Grundlagenforschung und angewandten Forschung: Entwicklung von Meßgeräten für Feldmessungen in der Atmosphärenforschung (u.a. zur Diagnostik des atmosphärischen Aerosols); Entwicklung von Methoden zur schnellen, berührungsfreien Diagnostik von Mikropartikeln; Entwicklung von Spektrometern und Lichtquellen; Entwicklung von Meßverfahren zum Abbau von Umweltchemikalien; Entwicklung und Aufbau von Messplätzen und Strahlrohren an Speicherringen. 3.6.2 Publikationstätigkeit 3.6.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen A. Knop, B. Wassermann und E. Rühl "Site-Specific Excitation in Free Krypton Clusters" Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2302 (1998). B. Steiner, B. Berge, R. Gausmann, J. Rohmann und E. Rühl "A Fast in-situ Sizing Technique for Single Levitated Liquid Aerosols" Appl. Opt. 38, 1523 (1999). R. Flesch, M.C. Schürmann, M. Hunnekuhl, H. Meiss, J. Plenge und E. Rühl "A Pump-Probe Photoionization Mass Spectrometer Utilizing Tunable XUV-LaserProduced-Plasma-Radiation" Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71, 1319 (2000). M. Schwell, H. Baumgärtel, I. Weidinger, B. Krämer, H. Vortisch, L. Wöste und T. Leisner und E. Rühl "Uptake Dynamics and Diffusion of HCl in Sulfuric Acid Solution Measured in Single Levitated Microdroplets" J. Phys. Chem. 104, 6726 (2000). R. Flesch, A.A. Pavlychev, J.J. Neville, J. Blumberg, M. Kuhlmann, W. Tappe, F. Senf, O. Schwarzkopf, A.P. Hitchcock und E. Rühl "Dynamic Stabilization in 1 u1 g-Excited Nitrogen Clusters" Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 3767 (2001). 3.6.3 Forschungskooperationen 35 Forschungskooperationen, Einzelheiten siehe Anhang 32 3.6.4 Drittmittelakquisition Im Berichtszeitraum ca. 5 Mio DM, Einzelheiten siehe Anhang 3.6.5 Technologie- oder Wissenstransfer Diverse Beratungen, Gutachten, Diplom- und Doktorarbeiten für Wirtschaft, Verwaltung, Politik, Einzelheiten siehe Anhang 3.7 Umweltphysik-Feldmessungen 3.7.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 3.7.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt Voraussichtliches Ausscheiden Prof. Dr. May-Britt Kallenrode Dr. Bernd Heber C3 BAT IIa 04/2000 11/2000 09/2027 09/2003 3.7.1.2 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 1 Diplomand und 1 Doktorandin in Osnabrück sowie 2 Doktoranden in Lüneburg 3.7.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Die Arbeitsgruppe ‚Umweltphysik – Feldmessungen’ beschäftigt sich mit natürlichen Veränderungen der mittleren Atmosphäre. Untersuchte Ursache dieser Veränderungen ist die solare Variabilität, insbesondere der Einfall energiereicher Teilchen. Forschungsthemen umfassen: Numerische Untersuchungen zu den Auswirkungen prezipierender solarer und magnetosphärischer Teilchen und die sich daraus ergebenden Konsequenzen für die atmosphärische Chemie, insbesondere das Ozon. Momentaner Schwerpunkt ist in Zusammenarbeit mit der Uni Bremen die Validierung des kombinierten Ionisations- und Chemiemodells durch Vergleich mit beobachteten Veränderungen der NOx und OzonKonzentrationen in den vergangenen Jahren. Die Erzeugung kosmogener Nuklide wird ebenfalls betrachtet, da mit deren Hilfe durch die Auswertung terrestrischer Archive (z.B. Eisbohrkerne) Untersuchungen über längere Zeiträume möglich werden. Bestimmung der solaren/interplanetaren Bedingungen, die zu Teilchenereignissen mit starker Auswirkung auf die terrestrische Atmosphäre führen. Entwicklung eines Teilchenteleskops zur Messung energiereicher Teilchen in der mittleren Atmosphäre sowie Teilchenmessungen im Rahmen langdauernder Ballonflüge (angestrebter Mitflug bei SUNRISE). Untersuchungen zur Variabilität der galaktischen kosmischen Strahlung und deren Auswirkungen auf die Atmosphäre durch vergleichende Beobachtungen und numerische Modelle. Bedingt durch die frühere Tätigkeit der Leiterin befasst sich ein weiterhin in Lüneburg ansässiger Teil der Arbeitsgruppe mit der Lehrerbildung. Dazu gehören: Bestandsaufnahme (Fragebogen) über die Quellen der physikalischen Bildung, auf die die LehrerInnen im Sachunterricht zurückgreifen können, und darauf aufbauend die Entwicklung eines Curriculums zur Lehrerfortbildung in diesem Bereich Detailierte Untersuchungen zur physikalischen Vorbildung bei SachunterrichtslehrerInnen und –studierenden zur Entwicklung eines verbesserten Curriculums zur Ausbildung angehender SachunterrichtslehrerInnen. 33 3.7.2 Publikationstätigkeit 3.7.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen 3.7.3 Kallenrode, M.-B., 2001: Magnetic clouds and interplanetary transport, submitted to J. Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics Landwehr, B., M.-B. Kallenrode, R. Pacena, und W. Engelhardt, 2001: Konzeption einer verbesserten physikalischen Ausbildung von SachunterrichtslehrerInnen auf der Grundlage einer empirischen Untersuchung mit dem Ziel einer besseren naturwissenschaftlichen Frühförderung von Jungen und Mädchen, in Niedersächsischer Forschungsverbund für Frauen- und Geschlechterforschung in Naturwissenschaft, Technik und Medizin (NFFG): Tagungsbeiträge und Forschungsergebnisse 1997-2000 (Hrsg. U. Paravicini und C. Riedel), Wiss. Reihe, Hannover Quack, M., M.-B. Kallenrode, M. Von König, K. Künzi, J. Burrows, B. Heber and E. Wolff, 2001: Ground level events and its consequences for stratospheric chemistry, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 10, 4023-4026 Forschungskooperationen apl. Prof K. Betzler (Instrumentdesign) Air Force Geophysical Laboratories, Bedford MA (energiereiche Teilchen) Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam (energiereiche Teilchen) Boston College (energiereiche Teilchen) Kiepenheuer Institut für Sonnenphysik, Freiburg (Mission Sunrise) Max-Planck Institut für Aeronomie, Lindau (Mission Sunrise, energiereiche NASA GSFC, Maryland (Ozonmodellierung) University of Arizona (energiereiche Teilchen) Universität Bonn (Modulation, galaktische kosmische Strahlung) Universität Braunschweig (Paläomagnetosphären, DFG-Schwerpunkt) Universität Bremen (Ozonmodellierung, DFG-Schwerpunkt) University of Chicago (energiereiche Teilchen) Universität Kiel (Paläonuklide, Instrumentdesign, energiereiche Teilchen) Universität Lüneburg (Lehrerbildung) University of New Hampshire (energiereiche Teilchen) University of Potchefstroom (Modulation, energiereiche Teilchen) 3.7.4 Teilchen) Drittmittelakquisition DFG-Ka1297/2-1: Numerical simulation of the atmospheric ionization and the generation of cosmogenic nuclides for different topologies of the geomagnetic field (Schwerpunktprogramm Erdmagnetische Variationen) (ca. DM 250 000,-?) Niedersächsischer Forschungsverbung für Frauen- und Geschlechterforschung (NFFG): Konzeption einer verbesserten physikalischen Ausbildung von Sachunterrichtslehrer/innen auf der Grundlage einer empirischen Untersuchung mit dem Ziel einer besseren naturwissenschaftlichen Frühförderung von Mädchen (und Jungen) – Projekt läuft in Lüneburg (ca. DM 290 000,-) Bezirksregierung Lüneburg: Untersuchungen zur Lehrerfortbildung im Bereich physikalische Themen des Sachunterrichts – Projekt läuft ebenfalls in Lüneburg (ca. DM 10 000,-) DFG-Ka1297/3-1: Einfluß magnetischer Wolken auf die Ausbreitung und Beschleunigung energiereicher Teilchen im interplanetaren Raum, in Begutachtung 34 3.7.5 Technologie- oder Wissenstransfer Abschätzung der Strahlenbelastung für die Raumsonde Solar Probe (Tsurutani, B.T., M.-B. Kallenrode, R.P. Kemsky, J.W. Klein, R.P. Lin, J.C. Ling, J.A. Miller, J.M. Ratcliff, B.Sanahuja, S.T. Suess, A. Vourlidas, Y.C. Whang, S.T. Wu, and L.D. Zhang, 2000: Radiation environment near the Sun: Solar Probe, WT Paper) 4 Kristallzucht 4.1 Kristallzucht 4.1.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 4.1.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Dr. Hartmut Hesse Dr. Rainer Pankrath Akad. Direktor A15 07/1975 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT Ib 11/1989 4.1.1.2 Eintritt Voraussichtliches Ausscheiden 05/2006 03/2021 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 3 Doktoranden 4.1.1.3 se Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Züchtung und holographische Charakterisierung von Sillenit-Kristallen Bearbeiter Dipl.-Phys. H. Vogt, Betreuer E. Krätzig, H. Hesse Züchtung und Optimierung von LiTaO3 –Kristallen für die Frequenzverdopplung (BMBF-Verbundprojekt), Bearbeiter Dipl.-Phys C. Bäumer, Betreuer E. Krätzig, H. HesHerstellung und Charakterisierung nichtlinearer SrxBa1-xNb2O6-Kristalle (Graduiertenkolleg 695) Bearbeiter Dipl.-Phys. M. Ulex, Betreuer K. Betzler, R. Pankrath Züchtung dotierter SrxBa1-xNb2O6-Kristalle, Bearbeiter R. Pankrath Züchtung dotierter CaxBa1-xTiO3-Kristalle, Bearbeiter R. Pankrath Herstellung von Glaskeramiken auf der Basis von Boraten (Promotionsprogamm des Landes Niedersachsen), Bearbeiter H. Hesse 4.1.2 Publikationstätigkeit 4.1.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen Ch. Kuper, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse, „Growth and dielectric properties of congruently melting Ba1-x CaxTiO3 crystals“, Appl. Phys. A 65, 301 (1997) S. Mendricks, X. Yue, T. Nikolajsen, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse und D. Kip, „Growth and photorefractive properties of doped Pb5Ge3O11 and (Pb1-xBax)5Ge3O11 solid solutions“, Proc. SPIE 3554, 205 (1998) A. Mazur, C. Veber, O. F. Schirmer, C. Kuper, H. Hesse, „Light-induced charge transport processes in photorefractive Ba0.77Ca0.23TiO3 doped with iron“, J. Appl. Phys. 85, 6751 (1999) H. Veenhuis, T. Börger, K. Peithmann, M. Flaspöhler, K. Buse, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse und E. Krätzig, „Light-Induced Charge Transport Properties of Photorefractive BariumCalcium-Titanate Crystals Doped with Rhodium“, Appl. Phys. B 70, 797, (2000) 35 4.1.3 Forschungskooperationen Innerhalb der Hochschule In der Arbeitsgruppe werden Kristalle für folgende Forschungsgruppen gezüchtet: Angewandte Physik. Prof. E. Krätzig Magnetische Resonanzspektroskopie, Prof. O. F. Schirmer Laserspektroskopie, Prof. S. Kapphan Nichtlineare Optik, Prof. K. Betzler Elektronenspektroskopie, Prof. M. Neumann Außerhalb der Hochschule Verschiedenen Forschungsgruppen werden Kristalle für ihre Arbeiten zur Verfügung gestellt. Beispiele sind Dr. Th. Woike, Institut für Kristallographie der Universität zu Köln Dr. K. Szot, Institut für Festkörperforschung, Forschungszentrum Jülich Dr. F. Wilhelm, European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Grenoble Dr. M. Flörsheimer, Physikalisches Institut der Universität Münster Im Rahmen des BMBF-Verbundprojektes `Gundlegende Untersuchungen zu hybridintegrierten Hochleistungs-Diodenlasern für den sichtbaren und ultravioletten Spektalbereich´ bearbeiten wir zusammmen mit der Forschungsgruppe von Prof. Krätzig das Teilvorhaben `Herstellung von LiTaO3-Kristallen und Optimierung für die Frequenzverdopplung´. Beteiligt sind u.a. die Firmen OSRAM, Opto Speed, LINOS, Forschungsinstitut für mineralische und metallische Werkstoffe (FEE) GmbH sowie die Universitäten Kaiserslautern und Ulm. 4.1.4 Drittmittelakquisition SFB 225, Teilprojekt A1, Laufzeit 1996-2000: Graduiertenkolleg 695, Laufzeit 01.01.2001 – 31.12.2003: BMBF-Verbundprojekt, Laufzeit 01.04.2001 – 31.03.2004: 4.1.5 659.600.- DM 115.000.- DM 428.500.- DM Technologie- oder Wissenstransfer Die Firma FEE GmbH (Idar-Oberstein) stellt oxidische Kristalle für Laser und elektrooptische Anwendungen her. Seit sechs Jahren findet mindestens einmal pro Jahr ein Treffen statt, bei dem Probleme bei der Züchtung dieser Kristalle diskutiert werden. Im Rahmen des BMBF-Verbundprojektes ist eine noch intensivere Zusammenarbeit vorgesehen. 36 5 Theoretische Physik 5.1 Festkörperphysik 5.1.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 5.1.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt Prof. Dr. Gunnar Borstel apl. Prof. Dr. Jürgen Braun Dr. Roberts Eglitis C3 Oberassistent C1 Wiss. Assistent C1 05/1978 01/1984 04/2000 5.1.1.2 (Voraussichtliches) Ausscheiden 03/2011 07/1999 03/2003 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 1 Doktorand, 1 Habilitand 5.1.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Theorie der elektronischen Struktur von oxidischen Kristallen: Rund 24 unserer Publikationen befassen sich im Berichtszeitraum mit der Berechnung der elektronischen und atomaren Struktur von technologisch wichtigen Oxiden (z.B. KNbO3, KTaO3, LiNbO3, SrTiO3) auf der Grundlage von quantentheoretischen ab-initio Verfahren. Elektronische Struktur von Störstellen in oxidischen Kristallen: Rund 31 Zitate haben die ab-initio Berechnung von Störstelleneigenschaften (z.B. Li, Fe, Cr) in technologisch wichtigen Oxiden (z.B. KNbO3, LiNbO3) zum Inhalt. Diese Störstellen sind für spezifische Materialeigenschaften von besonderer Bedeutung. Theorie der Photoemission von Festkörperoberflächen: Diese Untersuchungen (25 Zitate) befassen sich mit der Weiterentwicklung der allgemeinen Photoemissionstheorie sowie ihrer Anwendung auf bestimmte Modellsysteme (hauptsächlich Metalle). In diesem Bereich gibt es eine starke Kooperation mit der Experimentalphysik. Elektronische Struktur von intermetallischen 3d und Seltenen-Erd-Verbindungen: Die theoretischen Untersuchungen (9 Zitate) zielen auf Verbindungen wie GdAl2 oder Co2MnSn, deren magnetische Eigenschaften interessant sind. Auch in diesem Bereich gibt es eine starke Kooperation mit der Experimentalphysik Elektronische Struktur von Mikroclustern: Hierhin gehören 2 neuere Arbeiten über Metallcluster in Elektrolyten als Modell für moderne Li-Batterien. 5.1.2 Publikationstätigkeit 5.1.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen Die vier laut „Citation Index“ seit 1996 bisher von anderen Autoren am häufigsten zitierten Arbeiten der Arbeitsgruppe sind derzeit: R.I.Eglitis, A.V.Postnikov, and G.Borstel, Semiempirical Hartree - Fock calculations for pure and Li – doped KTaO3, - Phys. Rev. B, 55, p. 12976 - 12981, 1997 (26 Zitate) 37 R.I.Eglitis, A.V.Postnikov, and G.Borstel, Semiempirical Hartree - Fock calculations for KNbO3, - Phys. Rev. B, 54, p. 2421 - 2427, 1996 (22 Zitate) R.I.Eglitis, N.E.Christensen, E.A.Kotomin, A.V.Postnikov, and G.Borstel, First-principles and semi- empirical calculations for F centers in KNbO3 crystal, - Phys. Rev. B, 56, p. 8599 - 8604, 1997 (15 Zitate) Slebarski, A. Jezierski, A. Zygmunt, S. Mähl, M. Neumann and G. Borstel, Phys. Rev. B 54, 13551, 1996 (10 Zitate) 5.1.3 Forschungskooperationen Es bestanden im Berichtszeitraum zu Physikalischen Instituten an den folgenden in- und ausländischen Institutionen Forschungskooperationen: Humboldt-Universität Berlin Universität Bielefeld Universität Bonn Universität Duisburg Universität Hamburg Universität Kassel Universität Mainz Universität Münster Universität Rostock MPI Festkörperphysik, Stuttgart Universität Würzburg 5.1.4 Univ. of Wales Cardiff, England Technion Haifa, Israel Ben-Gurion Univ., Beer Sheva, Israel Universität Riga, Lettland Technische Universität Wien, Österreich Universität Kattowitz, Polen Inst. Molecular Physics, Akad. d. Wiss., Posen, Polen Inst. Metal Physics, Akad. d. Wiss., Jekatarinburg, Russland Ioffe Inst., St. Petersburg, Russland Inst. Low. Temp. Physics, Troisk (Moskau), Russland Inst. Mater. Research & Engineering, Singapore Universität Valladolid, Spanien Drittmittelakquisition Im Berichtszeitraum gab es in der Arbeitsgruppe insgesamt 16 Drittmittelvorhaben, bei denen die Einwerbungssumme größer als 10.000.- DM war. Die Förderungsgeber waren: DFG (10), NATO (2), VW-Stiftung (1), Land Niedersachsen (1), DAAD (1), BMBF (1) Die gesamte Drittmittelakquisition der Arbeitsgruppe aus diesen größeren Projekten beträgt für den Zeitraum Anfang 1996 bis Mitte 2001 (5,5 Jahre) rund DM 2.772.000.-. Damit wurden von unserer Arbeitsgruppe im Durchschnitt etwa DM 504.000.- pro Jahr eingeworben. Da diese Mittel weit überwiegend Personalmittel sind, kann man feststellen, dass die aus 2 wissenschaftlichen Landesstellen bestehende Arbeitsgruppe in den letzten Jahren ständig rund 4 wissenschaftliche Stellen (Doktoranden, Postdoktoranden, Gastprofessoren) als Drittmittel akquiriert hat. Anders ausgedrückt: Die Arbeitsgruppe hat rund das Doppelte ihrer eigenen Personalkosten für das Land Niedersachsen eingeworben. 5.1.5 Technologie- oder Wissenstransfer Der Beitrag einer Theoretischen Arbeitsgruppe in der Physik zum Technologie-Transfer ist traditionell eher niedrig anzusetzen. Zudem war der Leiter der Arbeitsgruppe „Theoretische Festkörperphysik“ durch seine vierjährige Tätigkeit als Vizepräsident der Universität im Zeitraum 1996-2000 stark in der Hochschulleitung engagiert. Dort war er jedoch u.a. für den Bereich Technologie- und Wissenstransfer zuständig. 38 5.2 Magnetismus 5.2.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 5.2.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Prof. Dr. Stefan Blügel 5.2.1.2 Stelle C3 Eintritt Voraussichtliches Ausscheiden 04/2001 03/2022 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 2 Doktoranden 5.2.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Die Theorie des itineranten Magnetismus von Elektronen ist eines der zentralen Probleme der Physik der kondensierten Materie. Wir entwickeln einzigartige Methoden der computergestützen Festkörperphysik (computational physics) um die komplexen Eigenschaften und Prozesse in diesen Magneten mittels der Dichtefunktionaltheorie (Nobelpreis 1998) aus der Quantenmechanik des Vielelektronenproblems zu verstehen. Die Vorhersagekraft der Dichtefunktionaltheorie wird benutzt und Rechnungen werden ausgeführt um neue Materialien, Prozesse und Effekte (mit wenig oder keinem experimentellen Input) vorherzusagen um bei der Analyse experimenteller Ergebnisse zu assistieren um Informationen zu gewinnen, komplementär zu experimentellen Resultaten Im Brennpunkt unser Forschungsinteresses liegt derzeit auf: Magnetismus nanoskaliger Systeme Theorie der Rastersondenmethoden; Kraftmikroskopie und Tunnelmikroskopie Transporteigenschaften aus der elektronischen Struktur Mikroskopische Prozesse des Wachstums Entwicklung neuer Methoden für die Elektronentheorie 5.2.2 Publikationstätigkeit 5.2.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen D. Wortmann, S. Heinze, Ph. Kurz, G. Bihlmayer, S. Blügel, Resolving Complex Atomic-Scale Spin-Structures by SP-STM, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 4132 (2001). Stefan Heinze und Stefan Blügel, Magnetische Ordnung wird sichtbar, Physik in unserer Zeit 32 (4), 154 (2001). 5.2.3 Forschungskooperationen RTN-Netzwerk: "Computational Magnetoelectronic": Europäisches Netzwerk zur theoretischen Untersuchung neuer magnetischer Materialien für die Magneto- und Spinelektronik, so wie dem Verständnis der Transporteigenschaften von magnetischen Bauelementen aus der elektronischen Struktur heraus. TMR-Netzwerk: "Electronic structure calculations for materials properties and processes for industry and basic sciences". Europäisches Netzwerk von Theoriegruppen, die sich mit der Methodenentwicklung und Anwendung von First-Principles Methoden auf der Basis der Dichtefunktionaltheorie beschäftigen. 39 ESF-Netzwerk: "Electronic Structure Calculations for elucidating the complex atomistic behaviour of solids and surfaces." Netzwerk für den Transfer von Studenten und Mitarbeiter zum Wissenstransfer, und Organisation gemeinsamer Projekte, Organisation gemeinsamer Workshops und Konferenzen. Dr. G. Bihlmayer, IFF, Forschungszentrum Jülich, Strategiefonds der HelmholtzGesellschaft für Forschung (Magnetoelectronik). Prof. Dr. A.-M. Llois, Centro Atomico Constituyentes, CNEA, Buenos Aires, Argentina (Nichtkollineare Magnetismus und inverser Riesenmagnetowiderstandseffekt). Prof. Dr. H. Ishida, Nihon University, Tokyo, Japan, DAAD und Alexander-vonHumboldt (Transporteigenschaften in Nanostrukturen). Dr. I. Turek, D. J. Kudrnovsky, and Dr. V. Drchal, Akademie der Wissenschaften der Tschechischen Republik (Bilaterales Deutsch-Tschechische WissenschaftlichTechnische Zusammenarbeit: "Computational Magnetoelectronics". Prof. Dr. Wilfried Wurth, Universität Hamburg, Projekt Synchrotron Strahlung zur Erforschung der Materie (Magnetische Eigenschaften kleiner, größenselektierter, deponierter Übergangsmetallcluster). Prof. Dr. W. Gudat, Dr. O. Rader, Universität Potsdam, Projekt Synchrotron Strahlung zur Erforschung der Materie (Elektronische Struktur von Spin-Gap Materialien an Grenzflächen). Prof. Dr. R. Wiesendanger, Zentrum für Mikrostrukturforschung, Universität Hamburg (Atomarauflösende Rasterkraftmikroskopie). 5.2.4 Drittmittelakquisition BMBF-Projekt: Theorie magnetischer ÜbergangsmetallNanocluster deponiert auf Oberflächen. BMBF-Projekt: Elektronische Struktur von Spin-Gap Materialien01.08.01–31.03.04 (DM 156.550,00) an Grenzflächen DFG-Projekt: Theorie der atomar auflösenden Rasterkraftmikro- 01.07.01–30.06.03 (DM 207.400,00) skopie 01.08.0–31.03.04 (DM 306.100,00) 5.3 Makroskopische Systeme und Quantentheorie 5.3.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 5.3.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt Prof. Dr. Klaus Bärwinkel Prof. Dr. Alois Hartkämper apl. Prof. Dr. Heinz-Jürgen Schmidt Prof. Dr. Reinhard Werner Dr. Jürgen Schnack C4 C3 Hochschuldozent C2 12/1975 03/1974 08/1975 (Voraussichtliches) Ausscheiden 03/2009 09/1998 03/2013 C2 Wiss. Assistent C1 02/1980 10/1997 08/1996 09/2003 5.3.1.2 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden 1 Diplomand, 2 Doktoranden, 1 Habilitand 40 5.3.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Magnetische Moleküle: Magnetische Moleküle stellen eine neue hochinteressante Stoffklasse dar. Die Beschreibung der Moleküle erfolgt im Heisenbergmodell. Wichtige Forschungsergebnisse sind die Entdeckung von Grundzustandseigenschaften nicht bipartiter Spinringe sowie die Untersuchung und Beschreibung von Rotationsmoden. Diese Arbeiten werden durch DAAD-, DFG- und Landesprojekte unterstützt. Wir sind an der erfolgreichen Antragstellung des DFG-SPP „Molekularer Magnetismus“ beteiligt. Thermodynamik/Statistik kleiner Quantensysteme: Entwicklung einer isothermen Quantendynamik (Nose-Hoover) sowie Beschreibung von idealen Quantengasen im Zusammenhang mit Bose-Einstein-Kondensation in magnetischen Fallen, Entdeckung und Beschreibung einer Fermion-Boson-Symmetrie Transporttheorie: kinetische Theorie und Molekulardynamik Nichtlineare Wellengleichungen: optische und magnetische Solitonen (Mitarbeit im Graduiertenkolleg 695) Grundlagenfragen in allgemeiner Relativitätstheorie und Quantentheorie 5.3.2 Publikationstätigkeit 5.3.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen K. Bärwinkel, H.-J. Schmidt, J. Schnack, Ground state properties of antiferromagnetic Heisenberg spin rings, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 220 (2000) 227 J. Schnack, M. Luban, Rotational modes in molecular magnets with antiferromagnetic Heisenberg exchange, Phys. Rev. B 63 (2001) 014418 H. Feldmeier, J. Schnack, Molecular Dynamics for Fermions, Rev. Mod. Phys. 72 (2000) 655-688 H.-J. Schmidt, J. Schnack, Thermodynamic fermion-boson symmetry in harmonic oscillator potentials, Physica A 265 (1999) 584-589 K. Bärwinkel, J. Schnack, U. Thelker, Quasi-Particle Picture for Monatomic Gases, Physica A 262 (1999) 496-504 5.3.3 Ames-Lab, Ames, Iowa, USA ; Prof. Dr. M. Luban, Prof. Dr. R. Modler, Dr. P. Koegerler GSI, Darmstadt, Deutschland; Prof. Dr. H. Feldmeier, Dr. R. Roth, Dipl.-Phys. T. Neff TU Magdeburg, Deutschland; Prof. Dr. J. Richter, Dipl.-Phys. J. Schulenburg TU Braunschweig, Deutschland; Dr. A. Honecker Telelogic GmbH, Bielefeld, Deutschland; Dr. Chr. Schröder Universität Göttingen, Institut für Wissenschaftsgeschichte, Deutschland; Prof. Dr. U. Majer 5.3.4 Forschungskooperationen Drittmittelakquisition DFG-Sachbeihilfe, J. Schnack, 1998, 3.500,- DM DFG-Sachbeihilfe, J. Schnack, 2000-2002, 49.000,- DM/Jahr DFG-Graduiertenkolleg, Bärwinkel, Schmidt, Schnack, 2001-2003, 230.000,- DM/Jahr DAAD-NSF, Bärwinkel, Schmidt, Schnack, 2000-2001, 10.000,- DM/Jahr Summe: 351.500,- DM 41 5.4 Numerische Physik 5.4.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 5.4.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt Prof. Dr. Peter Hertel Dr. Manfred Lohmeyer C4 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa 02/1975 04/1995 5.4.1.2 (Voraussichtliches) Ausscheiden 09/2003 03/2000 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden Der Leiter fungiert zur Zeit als Vizepräsident der Universität und betreut daher gegenwärtig weder Diplomanden noch Doktoranden noch Habilitanden. 5.4.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Bis 2000 hat sich die Arbeitsgruppe mit der theoretischen Behandlung dielektrischer Wellenleiterstrukturen beschäftigt, und zwar im Rahmen des Sonderforschungsbereiches 225. Insbesondere wurden neue Algorithmen zur Ausbreitung von Licht in komplizierten Strukturen entwickelt, erprobt und eingesetzt. Im Vordergrund stand dabei der lineare magnetooptische Effekt, der einen optischen Isolator für die integrierte Optik ermöglicht. Die Untersuchungen waren sehr eng mit den experimentellen Arbeiten der Gruppe Magnetooptik abgestimmt. Insbesondere sind die Anforderungen der prospektiven Industriepartner mehr und mehr in den Vordergrund gerückt: optische Isolation unabhängig von der Polarisierung, Hauptaugenmerk auf Herstellungstoleranzen, einfaches Design. Es erscheint zur Zeit wenig sinnvoll, die theoretischen Untersuchungen weiterzutreiben, ehe nicht Prototypen gebaut und von Seiten der Entwicklung neue Anforderungen definiert werden. Der Leiter wird sich demnächst mit allgemeinen theoretischen Überlegungen zu nichtlinearen Effekten der Optik befassen. 5.4.2 Publikationstätigkeit 5.4.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen O. Zhuromskyy, H. Dötsch, M. Lohmeyer, L. Wilkens, P. Hertel Magnetooptical waveguides with polarization-independent nonreciprocal phase shift IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology 19 (2), 214-221 O. Zhuromskyy, M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, P. Hertel, H. Dötsch, A. F. Popkov Analysis of nonreciprocal light propagation in multimode imaging devicesOptical and Quantum Electronics 32 (6/8), 885-897 (2000) M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, O. Zhuromskyy, H. Dötsch, P. Hertel Unidirectional magnetooptic polarization converters IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology 17 (12), 2605-2611 (1999) M. Lohmeyer Vectorial wave-matching-method mode analysis of integrated optical waveguides Optical and Quantum Electronics 30 (5/6), 385-396 (1998) H. Dötsch, A. Erdmann, M. Fehndrich, R. Gerhardt, P. Hertel, B. Lührmann, M. Shamonin, M. Wallenhorst Application of magnetic garnet films in optical communication, in R. Marcelli (ed.), Microwave Nonlinear Effects and Signal Processing Applications in 42 Magnetic Films, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1996) 5.4.3 Forschungskooperationen im Fachbereich: Angewandte Physik (Elektrooptik, Magnetooptik) international: Universität Twente (Mesa+) 5.4.4 Drittmittelakquisition ca. 250 TDM (SFB 225, Projekt D10) 5.5 Theoretische Optik 5.5.1 Struktur der Arbeitseinheit 5.5.1.1 Professoren und Wissenschaftliche Mitarbeiter Name Stelle Eintritt Prof. Dr. Klaus H. Ringhofer Dr. Jekaterina Chamonina Dr. Anna Gorkunova Dr. Maxim Gorkunov C3 Wiss. Mitarbeiterin BAT IIa Wiss. Mitarbeiterin BAT IIa/2 Wiss. Mitarbeiter BAT IIa/2 02/1974 01/1995 11/2000 11/2000 (Voraussichtliches) Ausscheiden 09/2004 06/2000 11/2003 11/2003 Frau Dr. J. Chamonina hält sich im Rahmen ihres Emmy-Noether-Stipendiums an der Universität Oxford auf und wird zum April 2002 wieder in die Arbeitsgruppe zurückkehren. 5.5.1.2 Anzahl der derzeit betreuten Abschlussarbeiten, Doktoranden und Habilitanden Keine 5.5.1.3 Darstellung der Forschungsthemen Untersuchung des sekundären elektro-optischen Effektes Die durch Zweiwellenmischung in Silleniten erzeugten Raumladungsfelder sind nicht sehr stark. Es existieren zwar Verstärkungmechanismen, die man aber, besonders bei genauen Messungen, gerne vermeiden möchte. Eine Möglichkeit, größere Raumladungsfelder zu erhalten, ist es, die Geometrie des Experimentes zu optimieren, und zwar durch geeigneten Kristallschnitt, Wahl der Gitterrichtung und der Polarisationsvektoren. Dieses Problem ist analytisch kaum zu lösen, da man den sekundären elektro-optischen Effekt (und auch die optische Aktivität) berücksichtigen muss. Es ist inzwischen gelungen, die optimale Geometrie für die gebräuchlichsten Sillenite zu ermitteln. Rückkopplung bei photorefraktiver Zweiwellenmischung Der Regelkreis besteht darin, dass der phasenmodulierte transmittierte Signalstrahl der von einer Elektronik in ein Spannungssignal umgewandelt wird, das einen Piezospiegel antreibt. Der eintreffende Signalstrahl wird über diesen Piezospiegel geleitet. Es ergeben sich ganz neue Orbits und damit die Möglichkeit zu stabilisieren und vollständig diffraktive oder auch vollständig durchsichtige Beugungsgitter zu erhalten. In diesem Zusammenhang erhält man für große Zeiten auch "periodische Zustände" anstelle von stationären Zuständen, wie man sie von der gewöhnlichen Zweiwellenmischung her kennt. In einem geeignet gewählten Phasendiagramm zeigt es sich, dass diese periodischen Zustände keineswegs einheitlich sind, sondern in Klassen zerfallen, die durch sehr verschiedenartige Attraktoren zu beschreiben sind. 43 Kritische Phänomene in der Optik In den letzten Jahren hat eine Reihe von optischen Phänomenen Aufmerksamkeit hervorgerufen, welche sich dadurch auszeichnen, dass oberhalb einer Schwelle spontan ein Objekt auftaucht, das hohe Symmetrie in Bezug auf die bestehende Anordnung zeigt. Beispiele dafür sind räumliche Subharmonische bei der Zweiwellenwechselwirkung in kubischen photorefraktiven Kristallen, die sich durch Auftauchen eines dritten Strahls in der Mitte der beiden Schreibstrahlen bemerkbar machen, oder auch das Erscheinen von Sechsecken, Quadraten und ähnlichen Figuren um gegenläufige Laserstrahlen in photorefraktiven Ferroelektrika. Sowohl die Subharmonischen als auch die geometrischen Muster haben ihre Ursache in der parametrischen Instabilität der (nichtlinearen) Ratengleichungen, welche die Ladungsumverteilung beschreiben. Es ist jedoch in letzter Zeit klar geworden, dass es nicht genügt, die Ratengleichungen allein zu studieren; auch die optische Nichtlinearität muss berücksichtigt werden. Damit kann z. B. nahe der Schwelle der Erzeugung von Subharmonischen die dort auftretende kritische Verstärkung behandelt werden. 5.5.2 Publikationstätigkeit 5.5.2.1 Schlüsselpublikationen E. Shamonina, G. Cedilnik, M. Mann, A. Kießling, D. J. Webb, R. Kowarschik, and K. H. Ringhofer, "Investigation of two-wave mixing in arbitrary oriented sillenite crystals," Appl. Phys. B, vol. 64, pp. 49-56, 1997. J. Frejlich, P. M. Garcia, K. H. Ringhofer, and E. Shamonina, "Phase modulation in two-wave mixing for dynamically recorded gratings in photorefractive materials," J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, vol. 14, pp. 1741-1749, 1997. E. Shamonina, V. Kamenov, K. H. Ringhofer, G. Cedilnik, A. Kießling, and R. Kowarschik, "The optimum orientation of phase volume gratings in photorefractive sillenites: is it always [111]?," J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, vol. 15, pp. 25, 552-2559, 1998. E. Shamonina, K. H. Ringhofer, B. I. Sturman, V. Kamenov, G. Cedilnik, M. Esselbach, A. Kießling, R. Kowarschik, A. A. Kamshilin, V. V. Prokofiev, and T. Jaaskelainen, "Giant momentary readout by switching electric fields during two-wave mixing in sillenites," Opt. Lett., vol. 23, 1998, 1435-1437. B. I. Sturman, A. I. Chernykh, E. Shamonina, V. P. Kamenov, and K. H. Ringhofer, "Rigorous 3d-theory of the subharmonic instability in sillenites, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, 1999. B. I. Sturman, F. V. Podivilov, K. H. Ringbofer, E. Shamonina, V. P. Kamenov, E. Nippolainen, V. V. Prokofiev, and A. A. Kamshilin, "Theory of photorefractive vectorial wave coupling in cubic crystals," Phys. Rev., vol. E 60, pp. 3332-3352, 1999. E. V. Podivilov, B. I. Sturman, S. G. Odoulov, S. L. Pavlyuk, K. V. Shcherbin, V. Ya. Gayvoronsky, K. H. Ringhofer, and V. P. Kamenov, "Attractors and autooscillations for feedback controlled photorefractive beam coupling", Opt. Commun. 192, pp. 399-405, 2001. 5.5.3 Forschungskooperationen Innerhalb der Universität: Graduiertenkolleg 605: Nichtlinearitäten optischer Materialien. Außerhalb der Universität: Dr. Boris I. Sturman, Russische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Akademgorodok, Russland, Zusammenarbeit auf dem Gebiet der photorefraktiven Kristalle. Dr. Sergei G. Odulov, Ukrainische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Kiev, Ukraine, Zusammenarbeit auf dem Gebiet der photorefraktiven Kristalle. 44 Prof. Dr. L. Solymar, Engineering Department der Universität, Oxford, U. K., Zusammenarbeit auf dem Gebiet der Antennen und der Mikroskopie. 5.5.4 Drittmittelakquisition Sonderforschungsbereich 225: Oxidische Kristalle für elektro- und magneto-optische Anwendungen Graduiertenkolleg: Mikrostruktur oxidischer Kristalle Graduiertenkolleg 695: Nichtlinearitäten optischer Materialien INTAS-Projekt 96-954: Feedback controlled nonlinear phenomena in photorefractive crystals INTAS-Projekt: Optical critical phenomena (beantragt) 45 III 1 Anhang zur Darstellung der Forschungseinheiten Angewandte Physik 1.1 Elektrooptik (Krätzig) 1.1.1 Publikationstätigkeit 1.1.1.1 1.1.1.1.1 Veröffentlichungen Prof. Dr. Eckhard Krätzig Zeitschriftenartikel (referiert) S. Loheide, E. Krätzig, Light-Induced Charge Transport in Tetragonal KTa1-xNbxO3:Fe Crystals, Ferroelectrics 185, 293 (1996) G. Jäkel, J. Neumann, S. Odoulov, E. Krätzig, Two Examples of Mirrorless Parametric Oscillation in Photorefractive Barium Titanate, Ferroelectrics 183, 185 (1996) K. Buse, U. van Stevendaal, R. Pankrath, E. Krätzig, Light-Induced Charge Transport Properties of Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce Crystals, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 13, 1461 (1996) M. Simon, K. Buse, R. Pankrath, E. Krätzig, A. A. Freschi, Photo Conductivity of Photorefractive Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce Crystals at High Light Intensities, J. Appl. Phys. 80, 251 (1996) M. Yu Goulkov, S. G. Odoulov, B. I. Sturman, A. I. Chernykh, E. Krätzig, G. Jäkel, Bright Light Dots Caused by Interference of Parametric Scattering Processes in LiNbO 3 Crystals, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 13, 2602 (1996) J. Neumann, G. Jäkel, E. Krätzig, Holographic Scattering Lines Observed with Photorefractive BaTiO3, Appl. Phys. B 13, 599 (1996) Kip, S. Aulkemeyer, K. Buse, F. Mersch, R. Pankrath, E. Krätzig, Refractive Indices of Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 Single Crystals, phys. stat. sol. (a) 154, K5 (1996) P. M. Garcia, A. A. Freschi, J. Frejlich, E. Krätzig, Scattering Reduction For Highly Diffractive Holograms in LiNbO3 Crystals, Appl. Phys. B 63, 207 (1996) K. Buse, F. Havermeyer, L. Glabasnia, K. Schlömp, E. Krätzig, Quadratic Electrooptic Coefficients of Cubic KTa1-xNBxO3 Crystals, Optics Commun. 13, 339 (1996) U. van Stevendaal, K. Buse, S. Kämper, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, Light-Induced Charge Transport Processes in Photorefractive Barium Titanate Doped with Rhodium and Iron, Appl. Phys. B 63, 315 (1996) K. Buse, S. Loheide, D. Sabbert, E. Krätzig, Photorefractive Properties of Tetragonal KTa0.52Nb0.48:Fe Crystals and Explanation with the Three-Valence Charge-Transport Model, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 13, 2644 (1996) M. Simon, S. Wevering, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Bulk Photovoltaic Effect of Photorefractive LiNbO3:Fe Crystals at High Light Intensities, J. Physics D 30, 144 (1997) A. Gerwens, M. Simon, E. Krätzig, Activation of Cerium-Doped Strontium-Barium Niobate for Infrared Holographic Recording, Optics Commun. 135, 347 (1997) M. Simon, F. Mersch, Ch. Kuper, S. Mendricks, S. Wevering, J. Imbrock, E. Krätzig, Refractive Indices of Photorefractive Bismuth Titanate, Barium-Calcium Titanate, Bismuth Germanium Oxide and Lead Germanate, phys. stat. sol. (a) 159, 559 (1997) I. Sturmann, E. Krätzig, S. G. Odoulov, Coupling of Orthogonally Polarized Eigenwaves in BaTiO3 via Light-Induced Parametric Scattering, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 14, 2295 (1997) X. Yue, J. Xu, F. Mersch, R. A. Rupp, E. Krätzig, Photorefractive Properties of Bi4Ti3O12, Phys. Rev. B 55, 9495 (1997) K. Buse, S. Breer, K. Peithmann, S. Kapphan, M. Gao, E. Krätzig, Origin of Thermal Fixing in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Crystals, Phys. Rev. B 56, 1225 (1997) A. Mazur, U. van Stevendaal, K. Buse, M. Weber, O. F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, Light-Induced Charge Transport Processes in Photorefractive Barium Titanate Crystals Doped with Iron, Appl. Phys. B 65, 481 (1997) 46 X. Yue, F. Mersch, R. A. Rupp, E. Krätzig, Absorption Gratings in Ferroelectric Bi 4Ti3O12, Appl. Phys. B 65, 505 (1997) M. P. Petrov, V. M. Petrov, V. V. Bryksin, I. Zouboulis, A. Gerwens, E. Krätzig, Grating Oscillations in Photorefractive Crystals, Optics Lett. 22, 1083 (1997) S. M. Kostritskii, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Improvement of Photorefractive Properties of ProtonExchanged LiTaO3 Waveguides, Appl. Phys. B 65, 517 (1997) G. Jäkel, E. Krätzig, J. Neumann, S. Dankers, S. Odoulov, Mirrorless Oscillation in Photorefractive Crystals, Ferroelectrics 202, 87 (1997) A. Gerwens, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Alternating Photocurrents and Modulated Photoconductivities in Photorefractive Sillenite Crystals, Ferroelectrics 202, 203 (1997) X. Yue, K. Buse, F. Mersch, R. A. Rupp, E. Krätzig, Diffraction-Efficiency Enhancement of Photorefractive Gratings in Bi4Ti3O12 at Low Temperatures, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 142 (1998) N. Korneev, D. Mayorga, S. Stepanov, A. Gerwens, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Enhancement of the Photorefractive Effect by Homogeneous Pyroelectric Fields, Appl. Phys. B 25, 393 (1998) N. Korneev, D. Mayorga, S. Stepanov, A. Gerwens, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Characterization of Photorefractive Strontium-Barium Niobate with Non-Steady-State Photocurrents, Optics Commun. 146, 215 (1998) S. Breer, K. Buse, K. Peithmann, H. Vogt, E. Krätzig, Stabilized Recording and Thermal Fixing of Holograms in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Crystals, Review of Scientific Instruments 69, 1591 (1998) J. Hukriede, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Thermal Fixing of Holographic Gratings in Planar LiNbO3:Ti Waveguides, Appl. Phys. B 25, 333 (1998) J. Neumann, S. Mendricks, E. Krätzig, M. Goulkov, S. Odoulov, Photorefractive Light Amplification by Forward Four-Wave Mixing in BaTiO3, Optics Commun. 146, 220 (1998) S. Wevering, K. Buse, M. Simon, R. Pankrath, E. Krätzig, Time-resolved Measurements of Photoconductivity in Cerium-Doped Photorefractive Strontium-Barium Niobate using Nanosecond Light Pulses, Optics Commun. 148, 85 (1998) D. Kip, E. Krätzig, V. Shandarov, P. Moretti, Thermally-Induced Self-Focusing and Optical Beam Interaction in Planar SBN Waveguides, Optics Lett. 23, 343 (1998) D. Kip, M. Wesner, E. Krätzig, V. Shandarov, P. Moretti, All-Optical Beam Deflection and Switching in Strontium-Barium Niobate Waveguides, Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 1960 (1998) J. Neumann, M. Röwe, E. Krätzig, Photorefractive Amplification and Generation of Light Beams in BaTiO3 Controlled by the Intensity of the Pump Light , Appl. Phys. B 67, 73 (1998) D. Kip, J. Hukriede, E. Krätzig, Holographic Measurement of Dark Conductivity in LiNbO3:Ti:Fe Planar Optical Waveguides, phys. stat. sol. (a) 168, R3 (1998) Ch. Kuper, K. Buse, U. van Stevendaal, M. Weber, T. Leidlo, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, Electrooptic and Photorefractive Properties of Ferroelectric Barium-Calcium Titanate Crystals, Ferroelectrics 208, 213 (1998) K. Buse, A. Gerwens, S. Wevering, E. Krätzig, Charge Transport Parameters of Photorefractive Strontium-Barium Niobate Crystals Doped with Cerium, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 1674 (1998) M. P. Petrov, V. M. Petrov, V. V. Bryksin, A. Gerwens, S. Wevering, E. Krätzig, Grating Oscillations and Nonlinear Effects in Photorefractive Crystals, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 1880 (1998) A. Gerwens, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, N. Korneev, S. Stepanov, Hall Measurement with Strontium-Barium-Niobate Using Non-Steady-State Holographic Currents, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 2143 (1998) E. Krätzig, Nondestructive Read-Out of Holograms in Photorefractive Crystals, Journal of Optoelectronics · Laser 9, 307 (1998) J. Hukriede, I. Nee, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Thermally Fixed Reflection Gratings for Infrared Light in LiNbO3:Ti:Fe Channel Waveguides, Optics Lett. 23, 1405 (1998) 47 X. Yue, E. Krätzig, R. A. Rupp, Photorefractive Charge Compensation during Holographic Recording in Bi4Ti3O12, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 2383 (1998) U. van Stevendaal, K. Buse, H. Malz, H. Veenhuis, E. Krätzig, Reduction of Light-Induced Refractive-Index Changes by Decreased Modulation of Light Patterns in Photorefractive Crystals, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 2868 (1998) V. M. Petrov, S. Wevering, M. P. Petrov, E. Krätzig, Estimation of Trap Concentration in Photorefractive Crystals by a Technique of Adaptive Holographic Interferometry, Appl. Phys. B 68, 73 (1999) N. Korneev, D. Mayorga, S. Stepanov, H. Veenhuis, K. Buse, C. Kuper, E. Krätzig, Holographic and Non-Steady-State Characterization of Photorefractive Barium-CalciumTitanate, Optics Commun. 160, 98 (1999) X. Yue, S. Mendricks, T. Nikolajsen, H. Hesse, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Transient Enhancement of Photorefractive Gratings in Lead Germanate by Homogeneous Pyroelectric Fields, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 16, 389 (1999) J. Hukriede, B. Gather, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Copper Diffusion into Lithium Niobate, phys. stat sol. (a) 172, R3 (1999) T. Nikolajsen, P. M. Johansen, X. Yue, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Two-Step Two-Color Recording in a Photorefractive Praseodymium Doped La3Ga5SiO14 Crystal, Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, 4037 (1999) Xuefeng Yue, S. Mendricks, T. Nikolajsen, H. Hesse, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Multiple Phase Gratings in Pure, Yb- and P-Doped Pb5Ge3O11 After Different Thermal Treatments, J. Appl. Phys. 86, 1186 (1999) U. van Stevendaal, K. Buse, H. Malz, E. Krätzig, Persistent Light-Induced Absorption in Oxidized Iron-Doped Barium Titanate Crystals, Optics Lett. 24, 908 (1999) J. Neumann, M. Röwe, H. Veenhuis, R. Pankrath, E. Krätzig, Linear Electrooptic Coefficient r42 of Tetragonal Potassium-Tantalate-Niobate and Barium-Calcium-Niobate, phys. stat. sol. (b) 215, R9 (1999) J. Imbrock, S. Wevering, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Nonvolatile Holographic Storage in Photorefractive Lithium Tantalate Crystals with Laser Pulses, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 16, 1302 (1999) J. Imbrock, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Nonvolatile Holographic Storage in Ion-Doped Lithium Tantalate with Continuous-Wave Laser Light, Optics Lett. 24, 1302 (1999) M. P. Petrov, A. P. Paugurt, V. V. Bryksin, S. Wevering B. Andreas, E. Krätzig, Dynamic Light Beam Deflection Caused by Space Charge Waves in Photorefractive Crystals, Appl. Phys. B 69, 341 (1999) M. P. Petrov, V. V. Bryksin, V. M. Petrov, S. Wevering, E. Krätzig, Study of the Dispersion Law of Photorefractive Waves in Sillenites, Phys. Rev. A 60, 2413 (1999) H. Veenhuis, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, N. Koorneev, D. Mayorga, Non-Steady-State Photoelectromotive Force in Reduced Lithium Niobate Crystals, J. Appl. Phys. 86, 2389 (1999) N. Korneev, D. Mayorga, H. Veenhuis, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Dynamic Bulk Photovoltaic Effect in Photorefractive Barium-Calcium Titanate, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 16, 1725 (1999) M. Röwe, J. Neumann, E. Krätzig, S. Odoulov, Holographic Scattering in Photorefractive Potassium Tantalate-Niobate Crystals, Optics Commun. 170, 121 (1999) J. Hukriede, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Thermal Tuning of a Fixed Bragg Grating for IR Light Fabricated in a LiNbO3:Ti Channel Waveguide, Appl. Phys. B 70, 73 (2000) K. Peithmann, J. Hukriede, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Photorefractive Properties of Lithium Niobate Volume Crystals Doped by Copper Indiffusion, Phys. Rev. B 61, 4615 (2000) S, Odoulov, B. Sturman, E. Krätzig, Seeded and Spontaneous Light Hexagons in LiNbO3:Fe, Appl. Phys. B 70,645 (2000) K. Peithmann, N. Korneev, M. Flaspöhler, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Investigation of Small Polarons in Reduced Iron-Doped Lithium-Niobate Crystals by Non-Steady-State Photocurrent Techniques, phys, stat. sol. (a) 178, R1 (2000) F. Havermeyer, R. A. Rupp, D. W. Schubert, E. Krätzig, Neutron Diffraction from Holographic Gratings in PMMA, Physica B 276 – 278, 330 (2000) 48 M. P. Petrov, A. P. Paugurt, V. V. Bryksin, S. Wevering, E. Krätzig, Spatial Rectification of the Electric Field of Space Charge Waves, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84, 5114 (2000) H. Veenhuis, T. Börger, K. Peithmann, M. Flaspöhler, K. Buse, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, Light-Induced Charge-Transport Properties of Photorefractive Barium-CalciumTitanate Crystals Doped with Rhodium, Appl. Phys. B 70, 797 (2000) K. Peithmann, A. Wiebrock, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Low-Spatial-Frequency Refractive-index Changes in Iron-Doped Lithium-Niobate Crystals upon Illumination with a Focused Continuous-Wave Laser Beam, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 17, 586 (2000) H. Veenhuis, T. Börger, K. Buse, C. Kuper, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, Light-induced ChargeTransport Properties of Photorefractive Barium-Calcium-Titanate Crystals doped with Iron, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 1042 (2000) J. Hukriede, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Investigation of Titanium- and Copper-Indiffused Channel Waveguides in Lithium Niobate and Their Application as Holographic Filters for Infrared Light, J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 2, 481 (2000) I. Nee, M. Müller, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Role of Iron in Lithium-Niobate Crystals for the Dark-Storage Time of Holgrams, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 4282 (2000) M. Goul'kov, S. Odoulov, O. Shinkarenko, E. Krätzig, R. Pankrath, Threshold of Oscillation in a Ring-Loop Phase Conjugator as a Second Order Optical Phase Transition, Appl. Phys. B 72, 187 (2001) F. Havermeyer, C. Pruner, R. A. Rupp, D. W. Schubert, E. Krätzig, Absorption Changes under UV Illumination in doped PMMA, Appl. Phys. B 72, 201 (2001) P. Jullien, P. Lompré, P. Mathey, S. Odoulov, E. Krätzig, Photorefractive AmplifierConverter and Coherent Oscilator with Nonexponential Gain, J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 3, 114 (2001) M. Wesner, C. Herden, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, P. Moretti, Photorefractive Steady State Solitons up to Telecommunication Wavelengths in Planar SBN Waveguides, Optics Commun. 188, 69 (2001) A. Shumeliuk, S. Odoulov, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Electric-Field Enhancement of Beam Coupling in Sn2P2S6, Appl. Phys. B 72, 707 (2001) J. Hukriede, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Permanent Narrow-Band Reflection Holograms for Infrared Light Recorded in LiNbO3:Ti:Cu Channel Waveguides, Appl. Phys. B 72, 749 (2001) Th. Woike, D. Berben, M. Imlau, K. Buse, R. Pankrath, E. Krätzig, Lifetime of Small Polarons in Strontium-Barium-Niobate Single Crystals Doped with Cerium or Chromium, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 5663 (2001) S. Wevering, J. Imbrock, E. Krätzig, Relaxation of Light-Induced Absorption Changes in Photorefractive Lithium-Tantalate Crystals, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 18, 472 (2001) M. P. Petrov, A. P. Paugurt, V. V. Bryksin, S. Wevering, E. Krätzig, Dynamic Electrooptic Effect Induced by Space Charge Waves in Sillenites, Optical Matrials, accepted N. Korneev, H. Veenhuis, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Thermal Fixing of Holograms and Their Electrical Development in Barium-Calcium-Titanate Crystals, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, accepted Yi Hu, D. Kip, S. Mendricks, Xuefeng Yue, E. Krätzig, Influence of Oxidizing Treatments on the Photorefractive Properties of Ferroelectric Lead Germanate Crystals, Ferroelectrics, accepted H. Vogt, K. Buse, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, R. R. García, Growth and Holographic Characterization of Nonstoichiometric Sillenite-Type crystals, J. Appl. Phys., accepted M. P. Petrov, V. V. Bryksin, S. Wevering, E. Krätzig, Nonlinear interactions and scattering of space charge waves in sillenites, Appl. Phys. B, accepted 1.1.1.1.2 Konferenzbeiträge (referiert) D. Kip, B. Kemper, I. Nee, P. Moretti, R. Pankrath, E. Krätzig, Investigation of the Photorefractive Properties of Ion-Implanted Planar Waveguides in SBN Crystals, Conference Proceedings Lasers '96, S. 501 - 506 (1996) 49 E. Krätzig, K. Buse, Recent Advances in Inorganic Ferroelectric Holographic Media: Light-Induced Charge Transport, Optics and Imaging in the Information Age, IST/OSA, S. 115 - 120, 1997 S. M. Kostritskii, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Improvement of Photorefractive Properties of ProtonExchanged LiTaO3 Waveguides, Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Integrated Optics, Stockholm, Sweden, S. 424 - 427, 1997 K. Buse, U. van Stevendaal, M. Weber, A. Mazur, O. F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, Photorefractive Properties of Barium Titanate Crystals Doped with Iron, Proceedings 1997 Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 149 - 152, Chiba, Japan, 1997 K. Buse, S. Breer, K. Peithmann, E. Krätzig, Improved Development of Thermally Fixed Holograms in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Crystals with High Intensity Laser Pulses, Proceedings 1997 Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 234 -237, Chiba, Japan, 1997 D. Kip, B. Kemper, K. Buse, P. Moretti, E. Krätzig, Holographic Investigation of IonImplanted Optical Waveguides in Cer-Doped SBN Crystals, Proceedings 1997 Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 442 - 445, Chiba, Japan, 1997 S. M. Kostritskii, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Increase of Holographic Efficiency in Photorefractive LiTaO3 Waveguides by a Combined Proton and Copper Exchange, S. 216 - 219, Proceedings 1997 Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, Chiba, Japan, 1997 B. Sturman, S. Odoulov, E. Krätzig, Indirect Coupling of Orthogonally Polarized Light Beams in BaTiO3, Proceedings 1997 Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, 262 - 265, Chiba, Japan, 1997 V. M. Petrov, M. P. Petrov, I. Zouboulis, A. Gerwens, E. Krätzig, Non-Bragg Diffraction and Grating Oscillations in Photorefractive Holograms, Proceedings 1997 Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 101 - 102, Chiba, Japan 1997 X. Yue, K. Buse, R. A. Rupp, E. Krätzig, Temperature-Dependent Photorefractive Effects in Bi4Ti3O12, Proceedings of SPIE 3554, Photorefractive Materials: Phenomena and Related Applications II, 26 (1998) A. Shumeliuk, S. Odoulov, G. Brost, U. Hellwig, Hu Yi, E. Krätzig, Ti – Sapphire Laser Beamcoupling in Sn2P2S6, Proceedings CLEO'98, 171 (1998) R. A. Rupp, F.Havermeyer, J. Vollbrandt, R. Kampmann, E. Krätzig, HOLONS – a New Facility for the Development of Optically Recorded Diffraction Elements for Neutron Scattering, Proceedings of SPIE 3491, Applications of Photonic Technology, p. 310 - 315 (1998) D. Kip, M. Wesner, E. Krätzig, V. Shandarov, P. Moretti, Bright Photorefractive Spatial Solitons in Optical Waveguides on SBN, Proceedings of SPIE 3733, Nonlinear Optical Phenomena and Coherent Optics in Information Technologies, 155 - 162 (1998) E. Krätzig, K. Buse, Light-Induced Charge Transport in Photorefractive Crystals, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 10 - 17,1999 J. Imbrock, S. Wevering, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Sensitizing Lithium Tantalate Crystals for Holographic Recording with Infrared Laser Pulses, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 38 - 41,1999 K. Peithmann, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Photorefractive Properties of Highly Iron- or CopperDoped Lithium Niobate Crystals, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 50 - 53, 1999 M. P. Petrov, V. V. Bryksin, V. M. Petrov, S. Wevering, E. Krätzig, Dispersion Law of Photorefractive Waves, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 214 - 218,1999 H. Veenhuis, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, N. Korneev, D. Mayorga, Dynamic Bulk Photovoltaic Effect, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 219 - 223,1999 50 P. Jullien, P. Lompré, P. Mathey, S. Odoulov, E. Krätzig, Parametric Coherent Oscillation with Feedback via an Orthogonally Polarized Wave, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 250 253,1999 J. Neumann, M. Röwe, E. Krätzig, Photorefractive Parametric Amplification and Generation of Light Beams in BaTiO3 by Forward Four-Wave Mixing, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 347 - 352,1999 M. Wesner, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, V. Shandarov, P. Moretti, Thermally Induced All-Optical Beam Steering and Switching Properties of SBN Waveguides, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 441 - 446,1999 S. Odoulov, B. Sturman, E. Krätzig, Light Hexagons in LiNbO3:Fe, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 447 - 450,1999 J. Hukriede, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Integrated Wavelength Filters for IR-Light Utilizing LiNbO3:Ti Channel Wavesguides, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 602 - 606,1999 T. Nikolajsen, P. M. Johansen, X. Yue, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Optical Fixing in a La 3Ga5SiO14 Crystal Doped with Praseodymium, Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, PR' 99, Post-Deadline Papers, S. 43 - 46,1999 T. Nikolajsen, P. M. Johansen, X. Yue, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Self-Fixation of Holograms in a Piezoelectric La3Ga5SiO14:Pr3+ Crystal, CLEO'99, Technical Digest, 1999 K. Buse, K. Peithmann, A. Wiebrock, I. Nee, E. Krätzig, Optimization of Iron-Doped Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Crystals for Hologram Multiplexing, CLEO'99, Technical Digest, 280 (1999) K. Buse, S. Breer, H. Vogt, I. Nee, E. Krätzig, Thermally Fixed Volume-Phase Holograms in Lithium-Niobate Crystals for Optical Interconnects, CLEO'99, Technical Digest, 331 (1999) D. Kip, J. Hukriede, M. Wesner, E. Krätzig, Photorefractive Waveguides, Proceedings of SPIE 3801, S. 9 – 23 (1999) D. Berben, K. Buse, S. Wevering, P. Herth, Th. Woike, E. Krätzig, Lifetime of Polarons in Lithium-Niobate Crystals, Proceedings of SPIE 3802, S. 84 – 92 (1999) A. Shumeliuk, S. Odoulov, E. Krätzig, D. Kip, Electric Field Enhancement of Beam Coupling in Sn2P2S6, Technical Digest CLEO 2000, 69 (2000) J. Hukriede, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Photorefraction and Thermal Fixing in Channel Waveguides Fabricated in Lithium Niobate by Titatium and Copper Indiffusion, Technical Digest CLEO Europe, 119 (2000) M. P. Petrov, V. V. Bryksin, V. M. Petrov, S. Wevering, E. Krätzig, Spectra of Space Charge Waves in Photorefractive Crystals, Technical Digest CLEO Europe, 121 (2000) N. Korneev, H. Veenhuis, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Thermal Fixing of Holograms and Their Electrical Development in Barium-Calcium-Titanate Crystals, Technical Digest CLEO Europe, 122 (2000) K. Buse, I. Nee, M. Müller, E. Krätzig, Developement of Thermally Fixed Holograms in Photorefractive Crystals without Light, Technical Digest CLEO Europe, 376 (2000) M. P. Petrov, A. P. Paugurt, V. V. Bryksin, S. Wevering, E. Krätzig, Spatial Rectification of the Electric Field of Space Charge Waves in Sillenites, Technical Digest CLEO Europe, 377 (2000) E. Krätzig, IR Recording in Photorefractive Crystals via Two-Step Processes, Technical Digest CLEO Europe, 379 (2000) J. Imbrock, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Nonvolatile Holographic Storage in Lithium Tantalate with a Two-Step Process using Continuous-Wave Laser Light, Technical Digest CLEO Europe, 380 (2000) J. Hukriede, D. Kip, E. Krätzig, Permanent Narrow-Band Reflection Holograms in Copper-Doped Lithium Niobate Channel Waveguides for Optical Communications, OSA 51 Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 62, Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 57 – 62, 2001 H. Vogt, K. Buse, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, R. R. García, Photorefractive Properties of Nonstoichiometric Bi12GeO20 Crystals, OSA Trends in Optics and Photonics, Volume 62, Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices, S. 496 – 503, 2001 E. Krätzig, IR Recording in Photorefractive Crystals via Two-Step Processes, Proceedings of SPIE, accepted 1.1.1.1.3 Buchbeiträge K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Light-Induced Charge Transport in Photorefractive Crystals, in 'Photorefractive Optics: Materials, Properties and Applications', Editors F. Yu and S. Yin, Academic Press, Chapter 2, S. 25 - 41, 2000 K. Buse, E. Krätzig, Inorganic Photorefractive Materials, Holographic Storage, Editors H. Coufal, D. Psaltis, G. Sincercbox, Springer-Verlag Berlin, Heidelberg, S. 113 – 125, 2000 E. Krätzig and K. Buse, Two-step processes and IR recording in photorefractive crystals, in IR Holography for Optical Communications – Techniques, Materials and Devices, Editors P. Boffi, D. Piccinin, M. C. Ubaldi, Topics in Applied Physics, Springer-Verlag, to appear in 2002 1.1.1.2 1.1.1.2.1 Veröffentlichungen Prof. Dr. K. Buse Zeitschriftenartikel 67. D. Berben, B. Andreas und K. Buse „Photorefractive X-Ray Imaging“ Phys. Rev. Lett., eingereicht 66. H. Vogt, K. Buse, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig und R. R. García „Growth and Holographic Characterization of Nonstoichiometric SilleniteType Crystals” J. Appl. Phys, eingereicht 65. M. Mützel, D. Haubrich, D. Meschede, K. Peithmann, M. Flaspöhler und K. Buse „Atom Lithography with a Holographic Light Mask: Fabrication of Tailored Structures at Nanometre Scales“ Appl. Phys. Lett., eingereicht 64. Y. Yang, I. Nee, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „Ionic and Electronic Dark Decay of Holograms in LiNbO3:Fe Crystals” Appl. Phys. Letters, eingereicht 63. Y. Yang, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „Photorefractive Properties of LiNb03:Mn“ Opt. Lett., eingereicht 62. A. Adibi, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „Comparison of Gated Holographic Recording Schemes“ Phys. Rev. B, eingereicht 52 61. N. Korneev, H. Veenhuis, K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Thermal Fixing of Holograms and their Electrical Development in BariumCalcium-Titanate Crystals“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, im Druck 60. A. Adibi, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „Two-Center Holographic Recording“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, im Druck 59. A. Adibi, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „The Role of Carrier Mobility in Holographic Recording in LiNbO3“ Appl. Phys. B 72, 653-659 (2001) 58. D. Berben, B. Andreas und K. Buse „X-Ray-Induced Photochromic Effects in Copper-Doped Lithium-Niobate Crystals“ Appl. Phys. B 72, 729-732 (2001) 57. A. Adibi, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „Theoretical Analysis of Two-Step Holographic Recording with HighIntensity Pulses“ Phys. Rev. A 63, 3813-3829 (2001) 56. I. Nee, M. Müller und K. Buse „Development of Thermally Fixed Photorefractive Holograms Without Light“ Appl. Phys. B 72, 195-200 (2001) 55. K. Buse und M. Luennemann „3D Imaging: Wave Front Sensing Utilizing a Birefringent Crystal“ Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 3385-3387 (2000) 54. K. Peithmann, N. Korneev, M. Flaspöhler, K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Investigation of Small Polarons in Reduced Iron-Doped Lithium-Niobate Crystals by Non-Steady-State Photocurrent Techniques“ phys. stat. sol. (a) 178, R1-R3 (2000) 53. H. Veenhuis, T. Börger, K. Buse, C. Kuper, H. Hesse und E. Krätzig „Light-Induced Charge-Transport Properties of Photorefractive BariumCalcium-Titanate Crystals Doped with Iron“ J. Appl. Phys. 88, 1042-1049 (2000) 52. A. Adibi, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „Sensitivity Improvement in Two-Center Holographic Recording“ Opt. Lett. 25, 539-541 (2000) 51. H. Veenhuis, T. Börger, K. Peithmann, M. Flaspöhler, K. Buse, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse und E. Krätzig „Light-Induced Charge Transport Properties of Photorefractive BariumCalcium-Titanate Crystals Doped with Rhodium“ Appl. Phys. B 70, 797-801 (2000) 50. I. Nee, M. Müller und K. Buse „Role of Iron in Lithium-Niobate Crystals for the Dark-Storage-Time of Holograms“ J. Appl. Phys. 88, 4282-4286 (2000) 53 49 K. Peithmann, A. Wiebrock, K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Low-Spatial-Frequency Refractive-Index Changes in Iron-Doped LithiumNiobate Crystals upon Illumination with a Focused cw Laser Beam“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 17, 586-592 (2000) 48. X. Yue, A. Adibi, T. Hudson, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „Role of Cerium in Lithium Niobate for Holographic Recording“ J. Appl. Phys. 87, 4051-4055 (2000) 47. D. Berben, K. Buse, S. Wevering, P. Herth, M. Imlau und Th. Woike „Lifetime of Small Polarons in Iron-Doped Lithium-Niobate Crystals“ J. Appl. Phys. 87, 1034-1041 (2000) 46. K. Peithmann, J. Hukriede, K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Photorefractive Properties of Lithium Niobate Volume Crystals Doped by Copper Diffusion“ Phys. Rev. B 61, 4615-4620 (2000) 45. I. Nee, K. Buse, F. Havermeyer, R. A. Rupp, M. Fally und R. P. May „Neutron Diffraction from Thermally Fixed Gratings in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Crystals“ Phys. Rev. B 60, 9896-9899 (1999) 44. A. Adibi, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „Effect of Annealing in Two-Center Holographic Recording“ Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, 3767-3769 (1999) 43. J. Imbrock, S. Wevering, K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Nonvolatile Holographic Storage in Photorefractive Lithium Tantalate Crystals with Laser Pulses“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 16, 1392-1397 (1999) 42. N. Korneev, D. Mayorga, H. Veenhuis, K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Dynamic Bulk Photovoltaic Effect in Photorefractive Barium-Calcium Titanate Crystals“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 16, 1725-1729 (1999) 41. U. van Stevendaal, K. Buse, H. Malz und E. Krätzig „Persistent Light-Induced Absorption in Oxidized Iron-Doped Barium Titanate Crystals“ Opt. Lett. 24, 908-910 (1999) 40. H. Veenhuis, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, N. Korneev und D. Mayorga „Non-Steady-State Photoelectromotive Force in Reduced Lithium Niobate Crystals“ J. Appl. Phys. 86, 2389-2392 (1999) 39. A. Adibi, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „Multiplexing Holograms in LiNbO3:Fe:Mn Crystals“ Opt. Lett. 24, 652-654 (1999) 38. K. Buse, A. Adibi und D. Psaltis „Efficient Non-Volatile Holographic Recording in Doubly-Doped Lithium Niobate“ Journal of Optics A – Pure and Applied Optics 1, 237-238 (1999) 54 37. K. Peithmann, A. Wiebrock und K. Buse „Photorefractive Properties of Highly Doped Lithium Niobate Crystals in the Visible and Near-Infrared“ Appl. Phys. B 68, 777-784 (1999) 36. N. Korneev, D. Mayorga, H. Veenhuis, K. Buse, C. Kuper, H. Hesse und E. Krätzig „Holographic and Non-Steady-State Photocurrent Characterization of Photorefractive Barium-Calcium Titanate“ Opt. Commun. 160, 98-102 (1999) 35. S. Breer, H. Vogt, I. Nee und K. Buse „High-Performance Wavelength Division Multiplexing with Volume Holograms“ Electronics Letters 34, 2419-2421 (1998) 34. K. Peithmann, A. Wiebrock und K. Buse „Incremental Holographic Recording in Lithium Niobate with Active Phase Locking“ Opt. Lett. 23, 1927-1929 (1998) 33. U. van Stevendaal, K. Buse, H. Malz, H. Veenhuis und E. Krätzig „Reduction of Light-Induced Refractive-Index Changes by a Decreased Modulation of Light Patterns in Photorefractive Crystals“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 2868-2876 (1998) 32. K. Buse, A. Adibi und D. Psaltis „Non-Volatile Holographic Storage in Doubly-Doped Lithium Niobate“ Nature 393, 665-668 (1998) 31. A. Gerwens, K. Buse, E. Krätzig, N. Korneev und S. Stepanov „Hall Measurements with Photorefractive Strontium-Barium Niobate by Application of a Non-Steady-State Photocurrent Method“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 2143-2146 (1998) 30. K. Buse, A. Gerwens, S. Wevering und E. Krätzig „Charge Transport Parameters of Photorefractive Strontium-Barium Niobate Crystals Doped with Cerium“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 1674-1677 (1998) 29. Ch. Kuper, K. Buse, U. van Stevendaal, M. Weber, T. Leidlo, H. Hesse und E. Krätzig „Electrooptic and Photorefractive Properties of Ferroelectric Barium-Calcium Titanate Crystals“ Ferroelectrics 208, 213-223 (1998) 28. K. Buse „Strontium-Barium Niobate as a Storage Material“ SPIE’s Optical Processing and Computing Newsletter, S. 10, April (1998) 27. S. Wevering, K. Buse, M. Simon, R. Pankrath und E. Krätzig „Time-Resolved Measurements of Photoconductivity in Cerium-Doped Photorefractive Strontium-Barium Niobate using Nanosecond Light Pulses“ Opt. Commun. 148, 85-89 (1998) 55 26. N. Korneev, D. Mayorga, S. Stepanov, A. Gerwens, K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Characterization of Photorefractive Strontium-Barium Niobate with NonSteady-State Holographic Photocurrents“ Opt. Commun. 146, 215-219 (1998) 25. S. Breer, K. Buse, K. Peithmann, H. Vogt und E. Krätzig „Stabilized Recording and Thermal Fixing of Holograms in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Crystals“ Rev. Sci. Instr. 69, 1591–1594 (1998) 24. S. Stepanov, N. Korneev, A. Gerwens und K. Buse „Self-Diffraction from Free Surface Relief Gratings in a Photorefractive Bi12TiO20 Crystal“ Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 879-881 (1998) 23. N. Korneev, D. Mayorga, S. Stepanov, A. Gerwens, K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Enhancement of the Photorefractive Effect by Homogeneous Pyroelectric Fields“ Appl. Phys. B 66, 393-396 (1998) 22. S. Breer und K. Buse „Wavelength Demultiplexing with Volume Phase Holograms in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate“ Appl. Phys. B 66, 339-345 (1998) 21. S. Breer, K. Buse und F. Rickermann „Improved Development of Thermally Fixed Holograms in Photorefractive LiNbO3 Crystals with High-Intensity Laser Pulses“ Opt. Lett. 23, 73-75 (1998) 20. Xuefeng Yue, K. Buse, F. Mersch, E. Krätzig und R. A. Rupp „Diffraction-Efficiency Enhancement of Photorefractive Gratings in Bi4Ti3O12 at Low Temperatures“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 142-147 (1998) 19. F. Rickermann, S. Riehemann, G. von Bally, S. Breer und K. Buse „A High Resolution Real-Time Temporal Heterodyne Interferometer for Refractive Index Topography“ Opt. Commun. 144, 173-179 (1997) 18. A. Mazur, U. van Stevendaal, K. Buse, M. Weber, O. F. Schirmer, H. Hesse und E. Krätzig „Light-Induced Charge Transport Processes in Photorefractive Barium Titanate Crystals Doped with Iron“ Appl. Phys. B 65, 481-487 (1997) 17. A. Gerwens, K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Alternating Photocurrents and Modulated Photoconductivities in Photorefractive Sillenite Crystals“ Ferroelectrics 202, 203-210 (1997) 16. K. Buse, S. Breer, K. Peithmann, S. Kapphan, M. Gao und E. Krätzig „Origin of Thermal Fixing in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Crystals“ Phys. Rev. B 56, 1225-1235 (1997) 56 15. K. Buse „Light-Induced Charge Transport Processes in Photorefractive Crystals II: Materials“ Appl. Phys. B 64, 391-407 (1997) 14. K. Buse „Light-Induced Charge Transport Processes in Photorefractive Crystals I: Models and Experimental Methods“ Appl. Phys. B 64, 273-291 (1997) 13. A. Gerwens, M. Simon, K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Activation of Cerium-Doped Strontium-Barium Niobate for Infrared Holographic Recording“ Opt. Commun. 135, 347-351 (1997) 12. M. Simon, St. Wevering, K. Buse und E. Krätzig „The Bulk Photovoltaic Effect of Photorefractive LiNbO3:Fe Crystals at High Light Intensities“ J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 30, 144-149 (1997) 11. K. Buse, S. Loheide, D. Sabbert und E. Krätzig „Photorefractive Properties of Tetragonal KTa0.52Nb0.48O3:Fe Crystals and Explanation with the Three-Valence Charge-Transport Model“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 13, 2644-2651 (1996) 10. K. Buse, F. Havermeyer, L. Glabasnia, K. Schlömp und E. Krätzig „Quadratic Polarization-Optic Coefficients of Cubic KTa1-xNbxO3 Crystals“ Opt. Commun. 131, 339-342 (1996) 9. U. van Stevendaal, K. Buse, S. Kämper, H. Hesse und E. Krätzig „Light-Induced Charge Transport Processes in Photorefractive Barium Titanate doped with Rhodium and Iron“ Appl. Phys. B 63, 315-321 (1996) 8. F. Rickermann, S. Riehemann, K. Buse, D. Dirksen und G. von Bally „Diffraction Efficiency Enhancement of Holographic Gratings in Bi12Ti0.76V0.24O20 Crystals After Recording“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 13, 2299-2305 (1996) 7. K. Buse „Pyroelektrische Felder und der photorefraktive Effekt“ Phys. Bl. 52, 881-883 (1996) 6. M. Weber, U. van Stevendaal, K. Buse, Z. G. Zhang, A. M. Yin, P. M. Fu, Y. Ding und H. J. Eichler „Light-Induced Charge Transport Properties of Potassium Niobate Crystals Doped with Nickel“ phys. stat. sol. (a) 156, 433-439 (1996) 5. M. Simon, K. Buse, R. Pankrath, E. Krätzig und A. A. Freschi „Photoconductivity of Photorefractive Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce Crystals at High Light Intensities“ J. Appl. Phys. 80, 251-255 (1996) 57 4. R. Niemann, K. Buse, R. Pankrath und M. Neumann „XPS Study of Photorefractive Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce Crystals“ Solid State Commun. 98, 209-213 (1996) 3. D. Kip, S. Aulkemeyer, K. Buse, F. Mersch, R. Pankrath und E. Krätzig „Refractive Indices of Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 Single Crystals“ phys. stat. sol. (a) 154, K5-K7 (1996) 2. K. Buse, U. van Stevendaal, R. Pankrath und E. Krätzig „Light-Induced Charge Transport Properties of Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce Crystals“ J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 13, 1461-1467 (1996) 1. A. A. Freschi, P. M. Garcia, I. Rasnik, J. Frejlich und K. Buse „Avoiding Hologram Bending in Photorefractive Crystals“ Opt. Lett. 21, 152-154 (1996) 1.1.1.2.2 Referierte schriftliche Beiträge zu internationalen Konferenzen 28. D. Berben, B. Andreas und K. Buse “A New Photorefractive Imaging X-Ray Sensor” Photorefractive Fiber and Crystal Devices: Materials, Optical Properties and Applications VII SPIE’s 46th Annual Meeting, San Diego, California, USA (2001) Technical Digest, to be published by SPIE, im Druck 27. A. Adibi, K. Buse, H. Hesse und D. Psaltis “Performance Trade-Offs in Holographic Recording in LiNbO3 Crystals” Photorefractive Effects, Materials, and Devices PR ‘01 Optical Society of America, TOPS Vol. 62, Seiten 113-121, Lake Lawn Lodge, Wisconsin, USA (2001) 26. H. Vogt, K. Buse, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig und R. Ramos García “Photorefractive Properties of Nonstoichiometric Bi12GeO20 Crystals” Photorefractive Effects, Materials, and Devices PR ‘01 Optical Society of America, TOPS Vol. 62, Seiten 496-503, Lake Lawn Lodge, Wisconsin, USA (2001) 25. Y. Yang, A. Adibi, D. Berben, K. Buse und D. Psaltis “The Role of Mn in Photorefractive LiNbO3” Photorefractive Effects, Materials, and Devices PR ‘01 Optical Society of America, TOPS Vol. 62, Seiten 101-106, Lake Lawn Lodge, Wisconsin, USA (2001) 24. D. Berben, B. Andreas und K. Buse “Photorefractive X-Ray Imaging” Photorefractive Effects, Materials, and Devices PR ‘01 Optical Society of America, TOPS Vol. 62, Seiten 26-32, Lake Lawn Lodge, Wisconsin, USA (2001) 23. M. Müller, I. Nee und K. Buse “Development of Thermally Fixed Refractive-Index Patterns in Iron-Doped Lithium-Niobate Crystals without Light” 10th European Conference on Integrated Optics ECIO ’01 Proceedings, Seiten 301-304, Paderborn, Germany (2001) 58 22. Y. Yang, I. Nee, K. Buse und D. Psaltis “Mechanisms of the Dark Decay of Holograms in LiNbO3:Fe Crystals” Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics CLEO ’00 Optical Society of America, TOPS Vol. 56, Seite 510, Baltimore, Maryland, USA (2001) 21. M. Lünnemann und K. Buse “A New Wave-Front Sensor” Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics CLEO ’00 Optical Society of America, TOPS Vol. 56, Seiten 189-190, Baltimore, Maryland, USA (2001) 20. K. Buse, I. Nee, M. Müller und E. Krätzig “Development of Thermally Fixed Holograms in Photorefractive LithiumNiobate Crystals without Light” Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics CLEO/Europe-IQEC ’00 Technical Digest, Seite 376, Nizza, Frankreich (2000) 19. I. Nee, M.Müller und K. Buse “Development of Thermally Fixed Photorefractive Hologramms without Light” Photorefractive Fiber and Crystal Devices: Materials Optical Properties, and Applications VI (AM332) Technical Digest to be published, San Diego, California, USA (2000) 18. K. Buse, I. Nee, M. Müller und E. Krätzig “Development of Thermally Fixed Holograms in Photorefractive LithiumNiobate Crystals without Light” E-MRS Spring Meeting 2000, Strasbourg, Frankreich Optical Material, to be published 17. K. Buse “Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Crystals: State of the Art and Perspectives” Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) ’00 Technical Digest, Seiten 7-8, San Francisco, USA (2000) 16. K. Buse, D. Berben, S. Wevering, P.Herth, Th. Woike und E. Krätzig “Lifetime of Polarons in Lithium Niobate Crystals” SPIE Annual Meeting (Denver, Colorado, USA) Technical Digest, SPIE 3802, Seiten 84-92, Denver, Colorado (1999) 15. K. Buse, A. Adibi und D. Psaltis „A Novel Method for Persistent Holographic Recording in Doubly-Doped Lithium Niobate“ Photonics West ’99 (San Jose, California, USA) Technical Digest, SPIE 3638, Seiten 15-21, San José, California, USA (1999) 14. I. Nee, S. Breer, H. Vogt und K. Buse “Wavelength Division Multiplexing with Thermally Fixed Volume-Phase Holograms in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Crystals” Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices PR ’99 Optical Society of America, TOPS Vol. 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, Elsinore, Dänemark (1999) 59 13. E. Krätzig und K. Buse “Light-Induced Charge Transport in Photorefractive Crystals” Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices PR ’99 Optical Society of America, TOPS Vol. 27, Advances in Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, Elsinore, Dänemark (1999) 12. K. Buse, S. Breer, H. Vogt, I. Nee und E. Krätzig „Thermally Fixed Volume-Phase Holograms in Lithium-Niobate Crystals for Optical Interconnects“ Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) ’99 Technical Digest, Seiten 331-332, Baltimore, USA (1999) 11. K. Buse, K. Peithmann, A. Wiebrock, I. Nee und E. Krätzig „Optimization of Iron-Doped Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Crystals for Hologram Multiplexing“ Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) ’99 Technical Digest, Seiten 280-281, Baltimore, USA (1999) 10. A. Adibi, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „Hologram Multiplexing Using Two-Step Recording“ Technical Digest, SPIE 3468, Seiten 20-29 (1998) 9. K. Buse „Light-Induced Charge Transport Processes in Photorefractive Crystals“ Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics CLEO/Europe-IQEC ’98 Technical Digest, Seite 371, Glasgow, UK (1998) 8. X. Yue, K. Buse, R. A. Rupp und E. Krätzig „Temperature-Dependent Photorefractive Effects in Bi4Ti3O12“ Technical Digest, SPIE 3554, Seiten 26-32 (1998) 7. A. Adibi, K. Buse und D. Psaltis „A Novel Method for Non-Volatile Recording in Lithium Niobate“ Nonlinear Optics ’98 Technical Digest, Seiten 262-264, Princeville, Hawaii, USA (1998) 6. K. Buse „Photorefractive Crystals for Holographic Storage: What are the Performance Limits?“ Nonlinear Optics ’98 Technical Digest, Seiten 254-256, Princeville, Hawaii, USA (1998) 5. K. Buse, A. Adibi und D. Psaltis „Efficient Non-Volatile Holographic Recording in Doubly-Doped Lithium Niobate“ Optics in Computing ’98 Technical Digest, SPIE 3490, Seiten 582-584, Bruegge, Belgien (1998) 4. S. Stepanov, N. Korneev, A. Gerwens und K. Buse „Light Diffraction from Piezoelectric Surface-Relief Gratings in a Photorefractive Bi12TiO20 Crystal“ Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO) ’98 Technical Digest, Seiten 458-459, San Francisco, USA (1998) 60 3. K. Buse, U. van Stevendaal, M. Wever, A. Mazur, O. F. Schirmer, H. Hesse und E. Krätzig „Photorefractive Properties of Barium Titanate Doped with Iron“ Topical Meeting Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices ’97 Technical Digest, Seiten 149-152, Chiba, Japan (1997) 2. K. Buse, S. Breer, K. Peithmann und E. Krätzig „Improved Development of Thermally Fixed Holograms in Photorefractive Lithium Niobate Crystals with High Intensity Laser Pulses“ Topical Meeting Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices ’97 Technical Digest, Seiten 234-237, Chiba, Japan (1997) 1. E. Krätzig und K. Buse „Recent Advances in Inorganic Ferroelectric Holographic Media: LightInduced Charge Transport“ Optics & Imaging in the Information Age – Optical Society of America, Annual Meeting’96 Proceedings, Seiten 115-120, Rochester, USA (1996) 1.1.1.2.3 Bücher / Buchbeiträge 2. K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Holographic Memories“ Kapitel „Inorganic Recording Materials“ Herausgeber H. Coufal, D. Psaltis und G. Sincerbox Springer-Verlag, 2000 1. K. Buse und E. Krätzig „Photorefractive Optics: Materials, Properties and Applications“ Kapitel „Light-Induced Charge-Transport in Photorefractive Crystals“ Herausgeber Francis T. S. Yu und Shizhou Yin Academic Press, 1999 1.1.1.3 1.1.1.3.1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Veröffentlichungen PD Dr. D. Kip Referierte Beiträge in internationalen Zeitschriften D. Kip, S. Aulkemeyer, R. Pankrath, F. Mersch, K. Buse und E. Krätzig, Refractive indices of Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 single crystals. phys. stat. sol. (a) 154, K5 (1996) D. Kip, B. Kemper, I. Nee, R. Pankrath und P. Moretti, Photorefractive properties of ion-implanted waveguides in strontium barium niobate crystals. Appl. Phys. B 65, 511 (1997) S. M. Kostritskii, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Improvement of photorefractive properties of proton-exchanged LiTaO3 waveguides. Appl. Phys. B 65, 517 (1997) D. Kip, S. Mendricks und P. Moretti, Optical waveguides in lead germanate formed by MeV proton and helium implantation. phys. stat. sol. (a), 166, R3 (1998). J. Hukriede, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Thermal fixing of holographic gratings in planar LiNbO3:Ti:Fe waveguides. Appl. Phys. B 66, 333 (1998) D. Kip, E. Krätzig, V. Shandarov und P. Moretti, Thermally induced self-focusing and optical beam interactions in planar strontium barium niobate waveguides. Opt. Lett. 23, 343 (1998) X. Yue, S. Mendriks, Y. Hu, H. Hesse und D. Kip, Photorefractive effect in doped Pb5Ge3O11 and in (Pb1-xBax)5Ge3O11. J. Appl. Phys. 83, 3473 (1998) 61 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. D. Kip, M. Wesner, E. Krätzig, V. Shandarov und P. Moretti, All-optical beamdeflection and switching in planar strontium barium niobate waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, 1960 (1998) D. Kip, M. Wesner, V. Shandarov, P. Moretti, Observation of bright spatial photorefractive solitons in a planar strontium-barium niobate waveguide. Opt. Lett. 23, 921 (1998) D. Kip, J. Hukriede und E. Krätzig, Holographic measurement of dark conductivity in LiNbO3:Ti:Fe planar optical waveguides. phys. stat. sol. (a) 168, R3 (1998) D. Kip, Photorefractive waveguides in oxide crystals: fabrication, properties, and applications. Appl. Phys. B 67, 131 (1998) J. Hukriede, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Thermally fixed reflection gratings in LiNbO 3:Ti:Fe channel waveguides. Opt. Lett. 23, 1405 (1998) S. M. Kostritskii und D. Kip, Holographic recording in planar Cu:H:LiTaO3 waveguides. phys. stat. sol. (a) 169, 171 (1998) X. Yue, S. Mendricks, T. Nikolajsen, H. Hesse, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Transient enhancement of photorefractive gratings in lead germanate by homogeneous pyroelectric fields. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 16, 389 (1999) J. Hukriede, B. Gather, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Copper diffusion into lithium niobate, phys. stat. sol. (a) 172, R3 (1999) S. Mendricks, X. Yue, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse und D. Kip, Dynamic properties of multiple grating formation in doped and thermally treated lead germanate. Appl. Phys. B 68, 887 (1999) D. Kip, M. Wesner, C. Herden und V. Shandarov, Interaction of spatial photorefractive solitons in a planar waveguide. Appl. Phys. B 68, 971 (1999) X. Yue, S. Mendricks, T. Nikolajsen, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Multiple gratings in pure, Yb- and P-doped Pb5Ge3O11 after different thermal treatments. J. Appl. Phys. 86, 1186 (1999) T. Nikolajsen, P.M. Johansen, X. Yue, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Two-step two-color recording in a photorefractive praseodymium doped La3Ga5SiO14 crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, 4037 (1999) J. Neumann, K. Schulte-Wieking und D. Kip, Direct laser writing of surface reliefs in dry self-developing photopolymer films. Appl. Opt. 38, 5418 (1999) J. Imbrock, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Nonvolatile holographic storage in iron-doped lithium tantalate with continuous-wave laser light. Opt. Lett. 24, 1302 (1999) J. Hukriede, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Thermal tuning of a fixed Bragg grating for IR light fabricated in a LiNbO3:Ti channel waveguide. Appl. Phys. B. 70, 73 (2000) T. Carmon, C. Anastassiou, S. Lan, D. Kip, Z. Musslimani und M. Segev, Observation of two-dimensional multimode solitons. Opt. Lett. 25, 1113 (2000) V. Shandarov, M. Wesner, J. Hukriede und D. Kip, Observation of dark spatial photovoltaic solitons in planar waveguides in lithium niobate. J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 2, 500 (2000) D. Kip, M. Soljacic, M. Segev, E. Eugenieva und C. Christodoulides, Modulation instability and pattern formation in spatially incoherent light beams. Science 290, 495 (2000) C. Anastassiou, M. Soljacic, M. Segev, D. Kip, E. Eugenieva, D. Christodoulides und Z. Musslimani, Eliminating the transverse instability of Kerr solitons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 4888 (2000) J. Hukriede, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Investigation of titanium- and copper-indiffused channel waveguides in lithium niobate and their application as holographic filters for infrared light. J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 2, 481 (2000) D. Kip, M. Soljacic, M. Segev, E. Eugenieva und D. N. Christodoulides, Modulation instability of spatially-incoherent light beams and pattern formation in incoherent wave systems. Opt. & Photon. News 12, 326 (2000) D. Kip, C. Anastassiou und M. Segev, Transmission of images through highly nonlinear media using light-induced GRIN lenses. Opt. Lett. 26, 524 (2001) 62 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. M. Wesner, C. Herden, D. Kip und P. Moretti, Photorefractive steady-state solitons up to telecommunication wavelengths in planar SBN waveguides. Opt. Commun. 188, 69 (2001) J. Hukriede, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Permanent narrow-band reflection holograms for infrared light recorded in LiNbO3:Ti:Cu channel waveguides. Appl. Phys. B 72, 749 (2001) Y. Hu, D. Kip, S. Mendricks, X. Yue und E. Krätzig, Influence of oxidizing treatments on the photorefractive properties of ferroelectric lead germanate crystals. Ferroelectrics, im Druck (2001) C. Anastassiou, C. Pigier, M. Segev, D. Kip, E. Eugenieva und D. N. Christodoulides, Self-trapping of bright rings. Opt. Lett. 26, 524 (2001) M. Wesner, C. Herden und D. Kip, Electrical fixing of waveguide channels in strontium-barium niobate crystals. Appl. Phys. B 72, 733 (2001) A. Shumelyuk, S. Odoulov, E. Krätzig und D. Kip, Electric field enhancement of beam coupling in Sn2P2S6. Appl. Phys. B 72, 707 (2001) D. Kip, M. Wesner und C. Herden, All-optical signal routing using interaction of mutually incoherent spatial solitons. Eingereicht bei Europhys. Lett. (2001) D. Kip, M. Soljacic, M. Segev, E. Eugenieva und D. N. Christodoulides, (1+1) Dimensional modulation instability of spatially incoherent light. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, im Druck (2001) M. Wesner, C. Herden, R. Pankrath und D. Kip, Temporal development of photorefractive solitons up to telecommunication wavelengths in SBN. Phys. Rev. E, im Druck (2001) 1.1.1.3.2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Referierte Beiträge zu internationalen Konferenzen D. Kip, B. Kemper, I. Nee, R. Pankrath und P. Moretti, Investigation of the photorefractive properties of ion-implanted waveguides in SBN waveguides. Technical Digest Intern. Conf. on Lasers '96, 2. bis 6. Dezember 1996, Portland, USA, 501-506 (1996) P. Moretti, D. Kip, B. Kemper und J. Hukriede, Buried double waveguide by H+ implantation in LiNbO3. ECIO '97, 8th European Conference on Integrated Optics, 2. bis 4. April 1997, Stockholm, Schweden, Technical Digest, 408-411 (1997) S. M. Kostritskii, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Improvement of photorefractive properties of proton-exchanged LiTaO3 waveguides. ECIO '97, 8th European Conf. on Integrated Optics, 2. bis 4. April 1997, Stockholm, Schweden, Technical Digest, 424-427 (1997) D. Kip, B. Kemper, K. Buse, P. Moretti und E. Krätzig, Photorefractive properties of ion-implanted waveguides in strontium barium niobate crystals. Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices 1997, 11. bis 13. Juni 1997, Chiba, Japan, 442-445 (1997) S.M. Kostritskii, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Photorefractive waveguides in LiTaO3 fabricated by combined proton and copper exchange. Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices 1997, 11. bis 13. Juni 1997, Chiba, Japan, 216-219 (1997) D. Kip, L. Glabasnia, R.M. Beaulieu, R.A. Lessard und M. Bolte, Self-developing photopolymer system with ultraviolet sensitivity. SPIE Annual Meeting 1997, 27. Juli bis 1. August 1997, San Diego, USA, Proc. SPIE 3135, 141-146 (1997) R. Beaulieu, R.A. Lessard, M. Bolte und D. Kip, Surface relief gratings in selfdeveloping photopolymer films. Photonics West '98, 24. bis 30. Januar 1998, San Jose, USA, Proc. SPIE 3294, 17-23 (1998) D. Kip, M. Wesner, E. Krätzig, V. Shandarov und P. Moretti, Bright photorefractive spatial solitons in optical waveguides on SBN. ICONO, XVI Intern. Conf. on Coherent and Nonlinear Optics 1998, 29. Juni bis 3. Juli 1998, Moskau, Russland, Proc. SPIE 3733, 155 (1998) 63 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. S. Mendricks, X. Yue, T. Nikolajsen, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse und D. Kip, Growth and photorefractive properties of doped Pb5Ge3O11 and of (Pb1-xBax)5Ge3O11 solid solutions. Proc. SPIE 3554, 205 (1998) T. Nikolajsen, P.M. Johansen, X. Yue, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Self-fixation of holograms in a piezoelectric La3Ga5SiO14:Pr3+ crystal. CLEO/QELS '99, Technical Digest CFB7, 23. bis 28. Mai 1999, Baltimore, USA D. Kip, M. Wesner, C. Herden, V. Shandarov und P. Moretti, Spatial photorefractive solitons in planar strontium barium niobate waveguides. Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices 1999,27. bis 30. Juni 1999, Elsinore, Dänemark, TOPS 27, 479 (1999) M. Wesner, D. Kip, V. Shandarov und P. Moretti, Thermally-induced all-optical beam steering and switching properties of SBN waveguides. Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices 1999, 27. bis 30. Juni 1999, Elsinore, Dänemark, TOPS 27, 441 (1999) J. Hukriede, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Integrated wavelength filters for IR-light utilizing LiNbO3:Ti channel waveguides. Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices 1999, 27. bis 30. Juni 1999, Elsinore, Dänemark, TOPS 27, 602 (1999) T. Nikolajsen, P.M. Johansen, X. Yue, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Optical fixing in a La3Ga5SiO14 crystal doped with praseodymium . Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices 1999, 27. bis 30. Juni 1999, Elsinore, Dänemark, postdeadline paper, conference proceedings, 43-46 (1999) D. Kip, J. Hukriede, M. Wesner und E. Krätzig, Photorefractive waveguides. Invited Talk, SPIE Annual Meeting 1999, 18. bis 23. Juli 1999, Denver, USA, Proc. SPIE 3801, 9-23 (1999) D. Kip und J. Neumann, Formation of diffractive optics in photopolymer films by direct laser beam writing. SPIE Annual Meeting 1999, 18. bis 23. Juli 1999, Denver, USA, Proc. SPIE 3778, 163-170 (1999) D. Kip, C. Anastassiou, E. Eugenieva, D. N. Christodoulides und M. Segev, Image transmission in self-focusing media by means of incoherent solitons. Technical Digest CLEO 2000, San Francisco, USA, CTuJ3, 221 (2000) E. Eugenieva, D N. Christodoulides, D. Kip, C. Anastassiou und M. Segev, Dynamics of two-dimensional partially incoherent beams and solitons in saturable nonlinear media. Technical Digest CLEO 2000, San Francisco, USA, 65 (2000) A. Shumelyuk, S. Odoulov, E. Krätzig und D. Kip, Electric field enhancement of beam coupling in Sn2P2S6. Technical Digest CLEO 2000, San Francisco, USA, CMN6, 221 (2000) V. Shandarov, D. Kip, M. Wesner und J. Hukriede, Features of dark spatial optical solitons in planar waveguides on lithium niobate. Technical Digest CLEO Europe 2000, Nizza, Frankreich, CMG5, 25 (2000) D. Kip, C. Herden und M. Wesner, Electrical fixing of waveguide channels using dynamic self-focusing in strontium-barium niobate crystals. Technical Digest CLEO Europe 2000, Nizza, Frankreich, CFF1, 376 (2000) M. Wesner, D. Kip und P. Moretti, Infrared photorefractive effects in ion-implanted SBN waveguides. Technical Digest CLEO Europe 2000, Nizza, Frankreich, CFF6, 378 (2000) J. Hukriede, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Lithium niobate by titanium and copper indiffusion. Technical Digest CLEO Europe 2000, Nizza, Frankreich, 119 (2000) J. Imbrock, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Nonvolatile holographic storage in lithium tantalate with a two-step process using continuous-wave laser light. Technical Digest CLEO Europe 2000, Nizza, Frankreich, CFF9, 380 (2000) D. Kip, M. Soljacic, M. Segev, S. Sears und D. N. Christodoulides, Modulation instability of spatially incoherent beams. NLGW 2001, Florida, USA (2001) D. Kip, M. Soljacic, M. Segev, E. Eugenieva und D. N. Christodoulides, Modulation instability of spatially-incoherent light beams and pattern formation in incoherent wave systems. CLEO 2001, Baltimore, USA (2001) 64 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. C. Anastassiou, C. Pigier, M. Segev, D. Kip, E. Eugenieva und D. N. Christodoulides, Self-trapping of bright rings. CLEO 2001, Baltimore, USA (2001) J. Hukriede, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, Permanent narrow-band reflection holograms in copper-doped lithium niobate channel waveguides for optical communications. Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices 2001, 8. bis 12. Juli 2001, Delavan, Wisconsin, USA, TOPS 62, 57 (2001) M. Wesner, C. Herden und D. Kip, A new method of electrical fixing in strontiumbarium niobate crystals. Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices 2001, 8. bis 12. Juli 2001, Delavan, Wisconsin, USA, TOPS 62, 152 (2001) D. Kip, C. Herden und M. Wesner, All-optical signal router based on the interaction of mutually incoherent solitons. Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices 2001, 8. bis 12. Juli 2001, Delavan, Wisconsin, USA, TOPS 62, 685 (2001) V. Shandarov, D. Kip und M. Wesner, Distinctions of the characteristics of bright spatial solitons in SBN crystals form existence curve predictions. Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects, and Devices 2001, 8. bis 12. Juli 2001, Delavan, Wisconsin, USA, TOPS 62, 690 (2001) 65 1.2 1.2.1 1.2.1.1 Magnetooptik (Dötsch) Publikationstätigkeit Publikationen in referierten Zeitschriften: K. Wagner, H. Lütgemeier, W. Zinn, R. Gerhardt, H. Dötsch, M.Kucera, J. Englich, K. Nitsch and P. Novak: Influence of impurities and defects on the nuclear relaxation in YIG films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater., vol. 161, p. 57 (1996). N. Bahlmann, R. Gerhardt and H. Dötsch: Optical investigation of domain resonances in magnetic garnet films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater., vol. 161, p. 22 (1996) H. Dötsch, N. Bahlmann, M. Fehndrich, R. Gerhardt, B. Lührmann and H.P. Winkler: High Frequency Light Modulation by Excitations of Domain Lattices in Magnetic Garnet Films. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 32, p. 4162 (1996) V. T. Synogach and H. Dötsch: High--frequency domain wall excitations in magnetic garnet films with in--plane magnetization. Phys. Rev. B,, vol. 54, p. 15266 (1996) M. Shamonin, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel and H. Dötsch: Optimization of a nonreciprocal phase shifter comprising a magneto--optic slab waveguide. Optics Comm., vol. 131, p. 37 (1996) N. Bahlmann, R. Gerhardt, M. Wallenhorst and H. Dötsch: Determination of the ferrimagnetic precession cone of in--plane magnetized garnet films using optical modulation technique. J. Appl. Phys., vol. 80, p. 3977 (1996) M. Fehndrich and H. Dötsch: Excitations of stripe domain lattices in perpendicularly magnetized garnet films. phys. stat. sol. (a), vol. 157, p. 127 (1996) J. Eisenmenger, S. Kambach, S. Saleh, A. Tihi, P. Leiderer, M. Wallenhorst and H. Dötsch: Structures in superconducting YBa2Cu3O(7-delta) thin films investigated by magneto--optic technique. J. Low Temp. Phys., vol. 105, p. 1123 (1996) 66 N. E. Kulagin, A. F. Popkov, V. T. Synogach and H. Dötsch: Spin wave excitations of single domain walls in orthorhombic ferromagnets. J. Appl. Phys., vol. 81, p. 2336 (1997) M. Bauer, C. Mathieu, S. O. Demokritov, B. Hillebrands, P. A. Kolodin, S. Sure, H. Dötsch, V. Grimalsky, Yu. Rapoport and A. N. Slavin: Direct observation of two-dimensional self--focusing of spin waves in magnetic films. Phys. Rev. B, vol. 56, p. R8483 (1997) N. Bahlmann, V. Chandrasekhara, A. Erdmann, R. Gerhardt, P. Hertel, R. Lehmann, D. Salz, F. Schröteler, M. Wallenhorst and H. Dötsch: Improved design of magneto-optic rib waveguides for optical isolators. J. Lightwave Techn., vol. 16, p. 818 (1998) A. F. Popkov, M. Fehndrich, M. Lohmeyer and H. Dötsch: Nonreciprocal TE--mode phase shift by domain walls in magneto--optic rib waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 72, p. 2508 (1998) A. F. Popkov, M. Fehndrich, H. Dötsch and O. Zhuromskyy: Nonreciprocal light channeling in a film by a magnetic non--uniformity akin to a Néel--like domain wall. J. Appl. Phys., vol. 84, p. 3020 (1998) T. Wöbbeking, H. Dötsch and A. F. Popkov: Spatial pattern formation in strongly driven ferromagnets. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., vol. 31, p. 2751 (1998) N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, H. Dötsch and P. Hertel: Integrated magneto--optic Mach--Zehnder interferometer isolator for TE--modes. Electr. Lett., vol. 34, p. 2122 (1998) O. Büttner, M. Bauer, C. Mathieu, S.O. Demokritov, B. Hillebrands, P.A. Kolodin, M.P. Kostylev, S. Sure, H. Dötsch, V. Grimalsky, Yu. Rapoport and A.N. Slavin: Mode beating of spin wave beams in ferrimagnetic Lu2.04 Bi0.96 Fe5 O12 films. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 34, p. 1381 (1998) N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, M. Wallenhorst, H. Dötsch and P. Hertel: An improved design of an integrated optical isolator based on nonreciprocal Mach--Zehnder inter- 67 ferometry. Opt. Quantum Electron., vol.30, p. 323 (1998) M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, O. Zhuromskyy, H. Dötsch and P. Hertel: Phase-matched rectangular magneto--optic waveguides for applications in integrated optics isolators: Numerical assessment. Opt. Comm., vol. 158, p. 189 (1998) N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, H. Dötsch and P. Hertel: Finte-element analysis of nonreciprocal phase shift for TE modes in magnetooptic rib waveguides with a compensation wall. J. Quantum Electron., vol.35, p. 250 (1999) N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, O. Zhuromskyy, H. Dötsch, and P. Hertel: Nonreciprocal coupled waveguides for integrated optical isolators and circulators for TM-modes. Opt. Comm., vol. 161, p. 330 (1999) O. Zhuromskyy, M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, H. Dötsch, P. Hertel and A.F. Popkov: Analysis of polarization independent Mach--Zehnder--type integrated optical isolator. J. Lightw. Techn., vol. 17, p. 1200 (1999) M. Fehndrich, A. Josef, L. Wilkens, J. Kleine--Börger, N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel and H. Dötsch: Experimental investigation of the nonreciprocal phase shift of a transverse electric mode in a magneto--optic rib waveguide. Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 74, p. 2918 (1999) R. Gerhardt, J. Kleine-Börger, L. Beilschmidt, M. Frommeier, B. Gather and H. Dötsch: Efficient channel--waveguide laser in Nd:GGG at 1.062 m wavelength. Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 75, p. 1210 (1999) N. Bahlmann, M. Wallenhorst, L. Wilkens, V. Backherms, A. Josef, P. Hertel and H. Dötsch: Reduction of the temperature dependence of the nonreciprocal effect of magneto--optic channel--waveguides. Appl. Opt., vol. 38, p. 5747 (1999) J. Fujita, M. Levy, R.M. Osgood, Jr., L. Wilkens and H. Dötsch: Waveguide optical isolator based on Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 76, p. 2158 (2000) 68 A. F. Popkov, T. Wöbbeking, H. Dötsch and V. I. Korneev: Spatial instability of the nonlinear ferromagnetic resonance in uniaxial films. Appl. Phys. Lett., vol. 76, p. 2415 (2000) O. Zhuromskyy, M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, P. Hertel, H. Dötsch and A. F. Popkov: Analysis of nonreciprocal light propagation in multimode imaging devices. Optical and Quantum Electronics, vol. 32, p. 885 (2000) M. Shamonin, T. Beuker, P. Rosen, M. Klank, O. Hagedorn and H. Dötsch: Feasibility of magneto-optic flaw visualization using thin garnet films. NDT & E, vol. 33, p. 547 (2000) J. Fujita, M. Levy, R.M. Osgood, Jr., L. Wilkens and H. Dötsch: Polarization-independent waveguide optical isolator based on nonreciprocal phase shift. IEEE Photonics Techn. Lett., vol. 12, p. 1510 (2000) O. Zhuromskyy, H.Dötsch, M.Lohmeyer, L.Wilkens, P. Hertel: Magneto-optical waveguides with polarization independent nonreciprocal phase shift. J. Lightw. Techn., vol. 19, p. 214 (2001) M. Lohmeyer, L. Wilkens, O. Zhuromskyy, H. Dötsch, P. Hertel: Integrated magnetooptic cross strip isolator. Opt. Comm., vol. 189, p. 251 (2001) M. Shamonin, M. Klank, O. Hagedorn, H. Dötsch: Magneto-optical visualization of metal-loss defects in a ferromagnetic plate: Experimental verification of theoretical modeling. Appl. Optics, vol. 40, p. 3182 (2001) L. Wilkens, D. Träger, A.F. Popkov, A. Alexeev, H. Dötsch: Nonreciprocal phase shift of TE modes induced by a compensation wall in a magneto--optic rib waveguide. Submitted 69 1.2.1.2 Tagungsbeiträge: M. Shamonin, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel and H. Dötsch: Magneto--optic waveguides: modeling and applications. SPIE, vol. 2695, p. 344 (1996) M. Shamonin, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel and H. Dötsch: Radiatively coupled magneto-optic waveguides. SPIE, vol. 2695, p. 355 (1996) H. Dötsch, A. Erdmann, R. Gerhardt, P.Hertel, B. Lührmann, M. Shamonin, M. Wallenhorst and H.P. Winkler: Applications of magnetic garnet films in optical communication. Article in the book on ''Nonlinear Microwave Signal Processing: Towards a New Range of Devices'' , pp 411--465, Kluwer Academic Publishers, November 1996, ISBN: 0-7923-4358-1 70 2 Didaktik der Physik 2.1 Theoretische Physik und Didaktik der Physik (Schürmann) 2.1.1 Publikationstätigkeit 2.1.1.1 Zeitschriften Solutions to the Helmholtz Equation on the Line Describing Guided Waves in a Nonlinear ThreeLayer Structure, Journal of Mathematical Physics, submitted (mit V. Serov und Y. Shestopalov) Reflection and transmission of a plane TE-wave at a lossless nonlinear dielectric film Physica D, accepted (mit V. Serov und Y. Shestopalov) Criteria for existence and stability of soliton solutions of the cubic-quintic nonlinear Schrödinger equation, Physical Review E 62,2, (2000) (mit V. Serov ) Propagation of TE Waves through a Layer Having Pemittivity Depending on the Transverse Coordinate and Lying between Two Half-Infinite Nonlinear Media, Doklady Akademii Nauk, Math., 60, 2, (1999) (mit V. Serov und Y. Shestopalov) TE-polarized waves guided by a lossless nonlinear three-layer structure, Physical Review E 58, 1 (1998) (mit V. Serov und Y. Shestopalov) Traveling-wave solutions of the cubic-quintic nonlinear Schrödinger equation, Physical Review E 54, 4 (1996) Optical response of a nonlinear absorbing dielectric film, Optics Letters, 21, 387 (1996) (mit R. Schmoldt) On the theory of the TE-polarized waves in a linear three-layer structure, Electromagnetic Waves L 1, 49 (1996) (mit V. Serov und Y. Shestopalov) Existence of eigenwaves and of solitary waves in the lossy linear and lossless nonlinear layered waveguides, Doklady Akademii Nauk, Math., 53, 1 (1996) (mit V. Serov und Y. Shestopalov) 2.1.1.2 Tagungsbeiträge Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium, PIERS, Innsbruck: Waves in Lossy Linear and Lossless Nonlinear Layered Media, July 1996, p. 35 (mit V. S. Serov und Y. Shestoplaov) Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium, PIERS, Boston, Massachusetts: Waves in Lossless Nonlinear Layered Media July 7-12, 1997, p. 325 (mit V. S. Serov und Y. Shestoplaov) Proc. Int. Conf. on Coherent and Nonlinear Optics, Moscow: Waves in a Nonlinear Three-layer Structure, June 29-July 3, 1998, p. 63 (mit V. S. Serov und Y. Shestoplaov) Report of the Research-in-Pairs Project: Solution to the linear and nonlinear Helmholtz equations with complex-valued coefficients in domains with noncompact boundaries I Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, Februar 1999 (mit Youri K. Podlipenko, Valeri S. Serov and Youri V. Shestopalov) Report of the Research-in-Pairs Project: Solution to the linear and nonlinear Helmholtz equations with complex-valued coefficients in domains with noncompact boundaries II Mathematisches Forschungsinstitut Oberwolfach, November 2000 (mit Y. Smirnov, Valeri S. Serov and Youri V. Shestopalov) Progress in Electromagnetics Research Symposium, PIERS, Osaka: On the Theory of TE-Polarized Waves Guided by a Lossless Nonlinear Three-Layer Structure, July 2001, p. 46 (mit V. S. Serov und Y. Shestoplaov) 71 3 Experimentalphysik 3.1 Elektronenspektroskopie (Neumann) 3.1.1 Drittmittelakquisition Drittmittelaquisition in den letzten fünf Jahren: ca. 3,5 Mio DM Liste der bedeutenderen eingeworbenen Projekte: 1. Elektronische und geometrische Struktur von reinen und adsorbatbedeckten Festkörperoberflächen BMBF 1996 bis 2001 734 827,75 DM 2. Untersuchung von oxidischen Materialien mit Hilfe der Röntgenphotoelektronenspektroskopie und der Röntgenemissionsspektroskopie DFG SFB225/A8 1996 bis 2000 ca. 352 000,- DM 3. Grundlegende Untersuchungen zur Strukturaufklärung von plasmamodifizierten Polyolefinoberflächen mittels der Röntgenphotoelektronenspektroskopie DFG 1996 bis 1999 188 876,- DM 4. Untersuchungen zur elektronischen Struktur modifizierter Oxidoberflächen DFG Graduiertenkolleg 1996 bis 1998 ca. 81 600,- DM 5. Richtungsaufgelöste Photoelektronenspektroskopie an intermetallischen Seltene Erdverbindungen und oxidischen Materialien BMBF 1996 bis 2001 331 300,- DM 6. Analysis of Oxyanion Substitutions in High-Tc Superconductors by Means of X ray Emission and Photoelectron Spectroscopy 1994 bis 1996 93 464,31 DM 7. Electronic and Structural Properties of Superconductors Containing Sulphur und Networking Infrastructure und Computer Networking NATO 1997 bis 2000 64 201,- DM 8. Röntgenphotoelektronenbeugung zur Untersuchung von Grenzflächenstrukturen DFG 1996 bis 2001 268 250,- DM 9. Röntgenphotoelektronenspektroskopie an intermetallischen Verbindungen, Hochtemperatursupraleitern und anderen neuen Materialien DAAD-Ostpartnerschaften 1996 bis 2001 72 741,73 DM weitere Mittel aus EU-Sokrates-Programm ,- DM 10. Electronic Structure of Transition Metal Silicides and Buried Solid-Solid Interfaces EU INTAS 78 233,- DM 11. Elektronische Struktur von stark korrelierten Oxidsystemen DFG-RFFI 1998 bis 2000 75 602,26 DM 12. Halbleiter-Metall-Phasenübergänge an Heuslerartigen Phasen DFG 1996 bis 1998 261 610,- DM 13. Elementarprozesse bei Plasmabehandlungen an hochmolekularen Olefinen und deren Nachbildung mittels Elektronen- und Photoneneinwirkung DFG 2000 bis 2001 226 500,- DM plus 106 500,- DM für 2002 14. Untersuchungen zur elektronischen Struktur Seltener Erdoxide mittels Röntgenphotoelektronenspektroskopie. DFG Graduiertenkolleg 1996 bis 1997 ca. 76 800,- DM 15. Untersuchungen zur elektronischen Struktur der intermetallischen Seltene Erdverbindungen und Molekularmagnete mittels Röntgenphotoelektronenspektroskopie. DFG Graduiertenkolleg 1999 bis 2001 ca. 74 400,- DM 16. Spectroscopic Study of Transition Metal Compounds DFG Graduiertenkolleg 1998 bis 2001 ca. 84 000,- DM 17. Electronic Structure of New Superconductors NATO 2001 bis 2003 17 500,- DM 18. Euregio Centre for Surface Engineering EU-Interreg II 2000 bis 2001 191 411,21 DM 19. Synthesis and Characterisation of Surfaces and Interfaces assembled from Clusters and Molecules Land Nds. Promotionskolleg ab 2001 ,- DM 72 3.1.2 Publikationstätigkeit Eine komplette Auflistung der Publikationen befindet sich unter: http://zeus.physik.uni-osnabrueck.de/neumann/veroeff_1.html 3.1.2.1 Referierte Zeitschriftenaufsätze 1. Analysis of Oxyanions (BO33-, CO32-, SO42-, PO43-, SeO44-) Substitution in Y123 Compounds Studied by Photoelectron Spectroscopy E. Z. Kurmaev, V. V. Fedorenko, V. R. Galakhov, S. Bartkowski, St. Uhlenbrock, M. Neumann, P. R. Slater, C. Greaves, Y. Miyazaki, J. Superconductivity 9, 97-100 (1996) 2. Investigation of CuxGayCrzSe4 single crystals, A. Winiarski, I. Okonska-Kozlowska, J. Heimann, M. Neumann, J. Alloys and Compounds 232, 63-66 (1996) 3. Coherent forward emission (CPE) from adsorbed molecules: ( 3x 3 )R30° CO/Pd (111) and (2x1)CO+O/Pd (111), H. Geisler, J. Wambach, H. Kuhlenbeck, H.-J. Freund, M. Neuber and M. Neumann, J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 77, 33-44 (1996) 4. XPS Study of Photorefractive Sr0,61Ba0,39Nb2O6:Ce Crystals, R. Niemann, K. Buse, R. Pankrath and M. Neumann, Solid State Commun. 98, 209-213 (1996) 5. Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Magnetism of some Gadolinium Intermetallic Compounds, J. Szade and M. Neumann, J. Alloys and Compounds 236, 132-136 (1996) 6. X-ray photoelectron diffraction of pure and Nb-doped KTaO3: Site determination of the Nb atoms, R. Niemann, H. Hartmann, H. Hesse, M. Neumann, J. Physics: Condens. Matter 8, 1-6 (1996) 7. XPS-Satellites in Transition-Metal Oxides, B. Mayer, St. Uhlenbrock, M. Neumann, J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom.81, 63-67 (1996) 8. Innovative Methods for a Deconvolution of XPS-Spectra from Plasma Oxidized Polyethylene S. Mähl, J. Lachnitt, R. Niemann, M. Neumann, A. Baalmann and V. Schlett, Surf. Interface Anal. 24, 405-410 (1996) 9. Electronic Structure Investigations of the Gd(Al1-xMx)2 Laves Phase System with M = V, Ti, G. Chelkowska, H. Ufer, G. Borstel and M. Neumann, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 157/158, 719 (1996) 10. The Crystallographic, Magnetic and Electronic Properties of RM2X2 (R = La, Ce, Pr; M = Cu, Ni; X = Sn, Sb) A. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, A. Zygmunt, M. Neumann, S. Mähl, G. Borstel, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 159, 179-191 (1996) 11. Degree of the covalency of LiCoO2: X-ray emission and photoelectron study V. R. Galakhov, E. Z. Kurmaev, St. Uhlenbrock, M. Neumann, D. G. Kellerman, V. S. 73 Gorshkov, M. V. Kuznetsov, Solid State Commun. 99, 221-224 (1996) 12. Information about the electronic structure of SrTiO3, BaBiO3 and LiNbO3 deduced from the XPS-satellites and their relevance to optical functions, B. Mayer, S. Mähl, M. Neumann, Z. Physik B101, 85-90 (1996) 13. Electronic Structure of CuV2S4 Z. W. Lu, B. M. Klein, E. Z. Kurmaev, V. M. Cherkashenko, V. R. Galakhov, S. N. Shamin, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, V. A. Trofimova, St. Uhlenbrock, M. Neumann, T. Furubayashi, T. Hagino, S. Nagata Phys. Rev. B53, 9626-9633 (1996) 14. X-ray emission and photoelectron spectra of fluorine atoms in strontium and calcium copper oxyfluorides, St. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, E. Z. Kurmaev, L. V. Elokhina, V. V. Fedorenko, C. Greaves, P. P. Edwards and M. Al-Mamouri, J. Physics.: Condens. Matter 8, 48474854 (1996) 15. Full-potential photoemission calculations for KTaO3 M. Grass, J. Braun, A. Postnikov, G. Borstel, H. Ünlü, M. Neumann, Surf. Sci. 352-354, 760-764 (1996) 16. Effect of alloying on the electronic structure in CeNiSn A. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, A. Zygmunt, S. Mähl, M. Neumann, G. Borstel, Phys. Rev. B54, 13551-13557 (1996) 17. Magnetic Properties of the Binary Oxide LiMnO2 D. G. Kellerman, V. S. Gorshkov, V. G. Zubkov, V. A. Pereljev, V. R. Galakhov, E. Z. Kurmaev, S. Uhlenbrock, M. Neumann, Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 42, 914-918 (1997), translated from Zhurnal Neorganicheskoi Khimii 42, 1012-1017 (1997) 18. X-Ray Photoemission Spectra of Dy(Co1-xAlx)2 Systems A. Szajek, A. Jezierski, A. Kowalczyk, J. Baszynski, St. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, G. Borstel Acta Physica Polonica A91, 439-442 (1997) 19. High resolution Gd4d photoemission from different intermetallic compounds J. Szade, J. Lachnitt, M. Neumann, Phys. Rev. B55, 1430-1434 (1997) 20. Photoemission investigation for GdCu J. Lachnitt, H. Ufer, I. Karla, M. Neumann, J. Braun, G. Borstel, Surface Sci. 377-379, 238-241 (1997) 21. Single-ion approach to the interpretation of XPS valence band spectra of 3d transition metal monoxides L. D. Finkelstein, E. I. Zabolotzky, V. R. Galakhov, E. Z. Kurmaev, St. Uhlenbrock, St. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, Sov. Phys.: Solid State 39, 1056-1063 (1997) (in russisch); Phys. Solid State 39, 948-954 (1997) (in englisch) 22. Synthesis, Structure and XPS Characterisation of the New Stoichiometric Phase Sr2CuO2F2, J. L. Kissick, C. Greaves, P. P. Edwards, V. M. Cherkashenko, E. Z. Kurmaev, S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, Phys. Rev. B56, 2831-2835 (1997) 74 23. Valence Band Spectra and Electronic Structure of CuFeO2, V. R. Galakhov, A. I. Poteryaev, E. Z. Kurmaev, V. I. Anisimov, St. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, Z. W. Lu, B. M. Klein, T.-R. Zhao, Phys. Rev. B56, 4584-4591 (1997) 24. Spectral noise distortion in photoelectron spectroscopy by acquiring data with multidetector systems, S. Mähl, M. Neumann, V. Schlett, A. Baalmann, Surface Interface Anal. 25, 823-826 (1997) 25. Characterisation of the VG ESCALAB instrumental broadening function by XPS measurements at the Fermi edge of silver S. Mähl, M. Neumann, S. Dieckhoff, V. Schlett and A. Baalmann, J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 85, 197-203 (1997) 26. X-ray and Low Energy Electron Induced Damage in Alkanethiolate Monolayers on Ausubstrates, B. Jäger, H. Schürmann, H. U. Müller, H.-J. Himmel, M. Neumann, M. Grunze, Ch. Wöll, Z. Phys. Chemie 202, 263-272 (1997) 27. Electronic Structure of Titanium Monoxide S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, E. Z. Kurmaev, V. V. Fedorenko, S. N. Shamin, V. M. Cherkashenko, S. N. Nemnonov, A. Winiarski, D. Rubie, Phys. Rev. B56, 10656-10667 (1997) 28. Valence band spectra of 3d and 5d silicides, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, S. N. Shamin, L. V. Elokhina, V. E. Dolgih, E. Z. Kurmaev, S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, D. L. Ederer, K. Göransson, B. Noläng, I. Engström, J. Physics.:Condens. Matter 9, 9403-9414 (1997) 29. Electronic Structure of CeNi1-xPdxSn and LaMSn (M = Ni, Cu , Pd) A. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, S. Mähl, M. Neumann and G. Borstel, Phys. Rev. B56, 72457254 (1997) 30. Electronic Structure of Crystalline ZnS:Co and ZnSe:Co V. R. Galakhov, V. Giriat, S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, T. P. Surkova. Phys.Solid State 39, 1762-1764 (1997) translated from Fizika Tverdogo Tela 39, 19711974 (1997) 31. Kondo Insulators, A. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, A. Zygmunt, M. Neumann, Proc. Int. Symposium „Condensed Matter Physics“ p. 131-135, ed. E. Talik and J. Zio³o, Katowice-Ustroƒ Jaszowiec 1997 32. Properties of Dy3Rh Single Crystal, E. Talik, M. Neumann, T. Mydlarz, Proc. Int. Symposium „Condensed Matter Physics“ p. 137-143, ed. E. Talik and J. Zio³o, Katowice-Ustroƒ Jaszowiec 1997 33. Magnetic Properties and Electronic Structure of Zr1-xHfxV2 M. Coldea, A. Jezierski, M. Neumann, P. Lucaci and L. Lazar Balkan Physics Letters, Suppl. 5, 531-534 (1997) 34. Magnetic Susceptibility and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy of GdNi5 and GdNi4Al M. Coldea, M. Neumann, M. Bitu, St. Lütkehoff and B. Schneider Balkan Physics Letters, Suppl. 5, 1051-1054 (1997) 35. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Magnetism of CeNi5-xAlx Intermetallic Compounds 75 M. Coldea, M. Neumann, M. Bitu, S. Mähl and St. Plogmann Balkan Physics Letters, Suppl. 5, 1083-1086 (1997) 36. Excitation energy dependence of S L2,3 X-ray fluorescent emission of BaNiS2 near the S 2p threshold E. Z. Kurmaev, S. Stadler, D. L. Ederer, I. Hase, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, M. Neumann, D. A. Zatsepin, A. Fujimori, M. Sato, R. C. C. Perera, M. Grush, T. A. Callcott, Phys. Lett. A 235, 191194 (1997) 37. Electronic Structure of YNi1-xCuxBC Studied by Means of X-ray Emission and Photoelectron Spectroscopy E. Z. Kurmaev, A. V. Ezhov, V. M. Cherkashenko, S. N. Shamin, S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, Anup K. Gangopadhyay, Solid State Commun. 105, 65-70 (1998) 38. Spectroscopic evidence of sulphur precipitation in annealed sulphur-doped nickel studied by fluorescent x-ray emission E. Z. Kurmaev, S. Stadler, D. L. Ederer, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, D. A. Zatsepin, M. Neumann, T. A. Callcott, M. M. Grush, R. C. C. Perera, S. E. Danilov, V. L. Arbuzov, Materials Transactions, JIM, 39, 570-573 (1998) 39. Magnetism of manganese in RMn2 and RMn4Al8 (R = Y, Gd, Er) intermetallics E. Talik, M. Neumann, T. Mydlarz, J. Kusz, H. Böhm, A. Winiarski, A. Gilewski, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10, 581-592 (1998) 40. Valence states of copper ions and electronic structure of LiCu2O2, D. A. Zatsepin, V. R. Galakhov, M. A. Korotin, V. V. Fedorenko, E. Z. Kurmaev, S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, R. Berger, Phys. Rev. B57, 4377-4381 (1998) 41. Observation of Magnetic Splitting in XPS Mn L-Spectra of Co2MnSn and Pd2MnSn Heusler Alloys, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, M. I. Katsnelson, E. I. Shreder, E. Z. Kurmaev, A. Slebarski, S. Plogmann, T. Schlathölter, J. Braun, M. Neumann, Eur. Phys. J. B 2, 1-3 (1998) 42. Experimental and Theoretical Investigation of the Electronic Structure of Transition Metal Sulfides: CuS, FeS2 and FeCuS2 E. Z. Kurmaev, J. van Ek, D. L. Ederer, L. Zhou, T. A. Calcott, R. C. C. Perera, V. M. Cherkashenko, S. N. Shamin, V. A. Trofimova, S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, A. Fujimori and V. P. Moloshag, J. Physics: Condens. Matter. 10, 1687-1697 (1998) 43. Origin of near-infrared optical damage on proustite surfaces, B. Sugg, D. Hartmann, M. Neumann, R. A. Rupp, K. V. Shcherbin and S. G. Odoulov Phil. Mag. B77, 859-870 (1998) 44. Electronic structure and Magnetization of Gd3Pd Intermetallic Compound, E. Talik, M. Neumann, T. Mydlarz, Universitas Jagiellonicae Folia Physica XXXIX, 149-153 (1998) 45. Electronic Structure of X2ZrSn and XZrSn type Heusler alloys with X = Co or Ni, A. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, S. Lütkehoff, M. Neumann, G. Borstel, Phys. Rev. B57, 64086412 (1998) 46. Suppression of the Gap Energy in Zr-Ni-Sn and Ti-Ni-Sn by Partial Substitution of Zr and Ti by Ce 76 A. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, A. Zygmunt, S. Mähl, M. Neumann Phys. Rev. B57, 9544-9549 (1998) 47. Some Aspects to the Fitting of XPS Core Spectra of Polymers S. Mähl, M. Neumann, V. Schlett, A. Baalmann, Surf. Interface Anal. 26, 204-212 (1998) 48. Electronic Structure of Co2-xPdxTiSn alloys, A. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, M. Neumann, S. Plogmann, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 185, 43-48 (1998) 49. Electronic structure of VO2 studied by x-ray photoelectron and x-ray emission spectroscopies E. Z. Kurmaev, V. M. Cherkashenko, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, St. Bartkowski, A. V. Postnikov, M. Neumann, L.-C. Duda, J. H. Guo, J. Nordgren, V. A. Perelyaev, W. Reichelt, J. Physics: Condens. Matter. 10, 4081-4091 (1998) 50. Electronic structure of ternary transition metal oxides and sulphides: X-ray photoelectron and X-ray emission spectroscopy study E. Z. Kurmaev, St. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, S. Stadler, D. L. Ederer, V. R. Galakhov, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, Solovyev, S. N. Shamin, V. A. Trofimova, D. A. Zatsepin, J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 88-91, 441-447 (1998) 51. Properties of Er3Rh single crystals, E. Talik, M. Neumann, J. Kusz, H. Böhm, T. Mydlarz, J. Heimann, A. Winiarski, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 186, 33–40 (1998) 52. Spin and Valence Fluctuations in CeMn4Al8 and CeMn6Al6 M. Coldea, M. Neumann, St. Lütkehoff, S. Mähl, R. Coldea J. Alloys and Compounds 278, 72-79 (1998) 53. Electronic Structure of Nd3Co11B4, A. Jezierski, A. Kowalczyk, S. Mähl, M. Neumann, G. Borstel, J. Physics: Condens. Matter. 10, 6277-6283 (1998) 54. Influence of the „Kondo-hole“ impurities of CeNiSn and CeRhSb A. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, S. Mähl, M. Neumann, G. Borstel, Phys. Rev. B58, 4367-4371 (1998) 55. Band gap stability in CeRhSb A. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, A. Zygmunt, S. Mähl, M. Neumann, Phys. Rev. B58, 13498 – 13505 (1998) 56. Valence band spectra of BaCo1-xNixS2 E. Z. Kurmaev, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, M. Neumann, S. Stadler, D. L. Ederer, I. Hase, A. Fujimori, M. Sato, Y. Yasui, R. C. C. Perera, M. M. Grush, T. A. Callcott, D. A. Zatsepin, V. A. Trofimova, V. Sokolov, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 59, 1459 – 1467 (1998) 57. X-Ray Photoelectron Diffraction of ABO3-Type Perovskites: Site Determination for Dopants, B. Schneider, R. Niemann, Ch. Kuper, H. Hesse and M. Neumann, J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 96, 37 - 42 (1998) 58. Photoemission study and magnetization of Gd3Pd intermetallic compound E. Talik, M. Neumann and T. Mydlarz, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 189, 183 – 188 (1998) 77 59. Excitation energy dependence of X-ray emission spectra and electronic structure of Eu1xCaxMnO3, E. Z. Kurmaev, V. M. Cherkashenko, M. Neumann, S. Stadler, D. L. Ederer, Ya M. Mukovskii, I. V. Solovyev, N. Ovechkina, V. R. Galakhov, A. Fujimori, M. M. Grush, T. A. Callcott, R. C. C. Perera, J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 96, 187 - 194 (1998) 60. Valence and Spin Fluctuations in RMn4Al8 and RMn6Al6(R=Y, La, Ce) M. Coldea, M. Neumann, St. Lütkehoff, S. Mähl, R. Coldea Balkan Physics Letters 6, 189 – 197 (1998) 61. Investigation of the mixed-valent system V2-xMoxO5 by XPS M. Demeter, St. Bartkowski, E. Z. Kurmaev, M. Neumann, V. M. Cherkashenko, V. L. Volkov, G. S. Zakharova, SPIE 3724, 296 - 300 (1999) 62. X-Ray Emission and Photoelectron Spectra of Pr0.5Sr0.5MnO3, E. Z. Kurmaev, M. A. Korotin, V. R. Galakhov, L. D. Finkelstein, E. I. Zabolotzky, N. N. Efremova, N. I. Lobashevskaya, S. Stadler, D. L. Ederer, A. Moewes, S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, J. Matsuno, A. Fujimori, J. Mitchell, Phys. Rev. B59, 12799 – 12806 (1999) 63. Analysis of XPS Valence Band Spectra of Polymers using DFT Band Calculations of Model Oligomers S. Mähl, M. Neumann, B. Schneider, V. Schlett, A. Baalmann, J. Polymer Science A37, 95 - 103 (1999) 64. Photoemission Investigation of Gd-Cu Compounds J. Szade, I. Karla, D. Gravel and M. Neumann, J. Alloys and Compounds 286, 153-157 (1999) 65. Electronic structure investigation of Gd Intermetallics J. Szade, M. Neumann, J. Physics: Condens. Matter 11, 3887 - 3896 (1999) 66. X-Ray Emission and Photoelectron Spectra of Pr0.5Sr0.5MnO3, E. Z. Kurmaev, M. A. Korotin, V. R. Galakhov, L. D. Finkelstein, E. I. Zabolotzky, N. N. Efremova, N. I. Lobashevskaya, S. Stadler, D. L. Ederer, A. Moewes, S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, J. Matsuno, A. Fujimori, J. Mitchell, J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. 101 – 103, 793 - 798 (1999) 67. Band Approach to the excitation-energy dependence of x-ray fluorescence of TiO2, L. D. Finkelstein, E. Z. Kurmaev, M. A. Korotin, A. Moewes, B. Schneider, S. M. Butorin, J.-H. Guo, J. Nordgren, D. Hartmann, M. Neumann, D. L. Ederer, Phys. Rev. B60, 2212 - 2217 (1999) 68. Electronic Structure of KNbO3: Nb M4,5 X-ray Fluorescence Measurements, A. Moewes, A. V. Postnikov, B. Schneider, E. Z. Kurmaev, M. Matteucci, V. M. Cherkashenko, D. Hartmann, H. Hesse, M. Neumann, Phys. Rev.B60, 4422 - 4425 (1999) 69. Local moments in Mn-based Heusler alloys and their electronic structures, St. Plogmann, T. Schlathölter, J. Braun, M. Neumann, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, M. V. Yablonskikh, E. I. Shreder, E. Z. Kurmaev, A. Wrona, A. Slebarski, Phys. Rev. B60, 6428 - 6438 (1999) 78 70. Local and Electronic Structure of Vitamine B-12:X-ray Fluorescence Measurements, M. Matteucci, E. Z. Kurmaev, A. Moewes, B. Schneider, V. R. Galakhov, M. Neumann, L. Randaccio, Bull. Am. Phys. Soc. 44, 749 (1999) 71. Influence of vacancies on the electronic structureof Co2-xZrSn Heusler alloys, A. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, M. Neumann, S. Plogmann, Eur. Phys. J. B12, 519 - 523 (1999) 72. Valence Band Spectra and Electronic Structure of Perovskites, B. Mayer, M. Neumann, A. V. Postnikov, E. Z. Kurmaev, V. V. Fedorenko, L. V. Elokhina, L. D. Finkelstein, Russian J. Inorg. Chem. 44, 1931-1940 (1999) 73. Electronic Structure of Superconducting Inorganic Polymer (SN)x: Band Structure Calculations, X-ray Fluorescence and Ultraviolet Photoemission Measurements, E.Z. Kurmaev, A.I. Poteryaev, V.I. Anisimov, I. Karla, A. Moewes, B. Schneider, M. Neumann, D.L. Ederer, R.N. Lyubovskaya, Physica C 321, 191 - 198 (1999) 74. X-ray fluorescence study of organic-inorganic polymer conversion into ceramics induced by ion irradiation, E. Z. Kurmaev, A. Moewes, M. Krietemeyer, K. Endo, T. Ida, S. Shimada, R.P. Winiarski, M. Neumann, S. N. Shamin, D. L. Ederer, Phys. Rev.B60, 15100 - 15106 (1999) 75. X - Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and Magnetism of GdNi5-xAlx, M. Coldea, M. Neumann, D. Todoran, M. Demeter, R. Tetean, V. Pop, Studia Univ. Babes-Bolyai, Ser. Physica XLIV, Nr. 2 (1999) 35 76. Crystalline electric field in RNiSb compounds investigated by inelastic neutron diffraction, I. Karla, J. Pierre, A. Murani, M. Neumann, Physica B 271, 294 – 303 (1999) 77. Combined study of KNbO3 and KTaO3 by different techniques of photoelectron and x-ray emission spectroscopy, A. V. Postnikov, B. Schneider, M. Neumann, D. Hartmann, H. Hesse, A. Moewes, E. Z. Kurmaev, M. Matteucci, J.Phys.Chem.Solids 61, 265 - 269 (2000) 78. Electronic structure, magnetic and electrical properties of Fe3-xVxAl compounds, W. Zarek, E. Talik, J. Heimann, M. Kulpa, A. Winiarska, M. Neumann, J. Alloys and Compounds 297, 53 – 58 (2000) 79. Electronic Structure of Cu1-xNixRh2S4 and CuRh2Se4: Band Structure Calculations, X-ray Photoemission and Fluorescence Measurements G. L. W. Hart, W. E. Pickett, E. Z. Kurmaev, D. Hartmann, M. Neumann, A. Moewes, D. L. Ederer, R. Endoh, K. Taniguchi, S. Nagata, Phys. Rev. B61, 4230 – 4237 (2000) 80. Electronic structure of LiMnO2: X-ray emission and photoelectron spectra and band structure calculations V. R. Galakhov, M. A. Korotin, N. A. Ovechkina, E. Z. Kurmaev, V. S. Gorshkov, D. G. Kellerman, S. Bartkowski, and M. Neumann, Eur. Phys. J. B 14, 281-286 (2000). 81. Exchange splitting of the Cr, Fe and Mn 3s XPS spectra in some ternary magnetic semiconductor sulphides, V.Tsurkan, M. Demeter, B. Schneider, D. Hartmann, M.Neumann, Solid State Commun. 114, 149 - 154 (2000) 79 82. Mixed-valence vanadium oxides studied by XPS M. Demeter, M.Neumann, W. Reichelt, Surf. Sci. 454 – 456, 41 - 44 (2000) 83. Electronic structure of Ni2-xPdxTiSn alloys A. Wrona, A. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, A. Zygmunt, S. Plogmann, M. Neumann, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 213, 157 - 163 (2000) 84. Splitting of 2p Cr ion XPS Spectra in Some Ternary Magnetic Semiconductor Sulphides and Selenides, V.Tsurkan, St. Plogmann, M. Demeter, D. Hartmann, M.Neumann, Eur. Phys. J. B 15, 401 - 403 (2000) 85. Electronic Structure of FeCr2S4 and Cu0.5Fe0.5Cr2S4 E.Z. Kurmaev, A. V. Postnikov, H. M. Palmer, C. Greaves, St. Bartkowski, V. Tsurkan, M. Demeter, D. Hartmann, M. Neumann, D. A. Zatsepin, V.R. Galakhov, S. N. Shamin, V. Trovimova, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 5411 – 5421 (2000) 86. Photon energy dependence of Gd 4d photoemission J. Szade, M. Neumann, I. Karla, B. Schneider, F. Fangmeyer, M. Matteucci, Solid State Comm. 113, 709 - 712 (2000) 87. Magnetic properties of 3d-doped TiSe2 and TiTe2 intercalate compounds A. V. Postnikov, M. Neumann, St. Plogmann, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, M. V. Yablonskikh, A. N. Titov and A. V. Kuranov, Comput. Mat. Science 17, 450 – 454 (2000) 88. Magnetic and electronic properties of the LaNi5-xCux system E. Burzo, S. G. Chiuzbaian, L. Chioncel, M. Neumann, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 5897 – 5904 (2000) 89. Interaction of Cu 3d and O 2p states in Mg1-xCuxO-solid solutions with the NaClstructure: x-ray photoelectron and x-ray emission study V. R. Galakhov, L. D. Finkelstein, D. A. Zatsepin, E. Z. Kurmaev, A. A. Samokhvalov, S. V. Naumov, G. K. Tatarinova, M. Demeter, S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann, A. Moewes, Phys. Rev. B62, 4922 – 4926 (2000) 90. Soft x-ray fluorescence spectra of the quasi-one-dimensional Heisenberg aniferromagnet tetraphenylverdazyl, E. Z. Kurmaev, V. R. Galakhov, S. Shimada, T. Otsuka, K. Endo, D. L. Ederer, A. Moewes, H. Schürmann, M. Neumann, S. Tomiyoshi, N. Azuma, M. Iwami, Phys. Rev. B62, 15660 - 15665 (2000) 91. Magnetic Properties of FeCr2S4:Cu,In Semiconductors, V.Tsurkan, D. Samusi, E. Burzo, V. Pop, M.Neumann, M. Demeter, M. Baran, R. Szymczak, H. Szymczak, Interface Controlled Materials 9, 50 - 53 (2000) 92. Weak ferromagnetism induced by atomic disorder in Fe2TiSn, A. Slebarski, M. B. Maple, E. J. Freeman, C. Sirvent, D. Tworuszka, M. Orzechowska, A. Wrona, A. Jezierski, S. Chiuzbaian, M. Neumann, Phys. Rev. B62, 3296 - 3299 (2000) 93. The electronic structure of the doped La-Mn-O perovskites M.Demeter, M. Neumann, V. R. Galakhov, N. A. Ovechkina, E. Z. Kurmaev, N. I. Laba- 80 chevskaya Acta Physica Polonica A98, 587 - 591 (2000) 94. Magnetic and Electronic Properties of GdNi5-xAlx Intermetallic Compounds M. Coldea, S. G. Chiuzbaian, M. Neumann, D. Todoran, M. Demeter, R. Tetean, V. Pop, Acta Physica Polonica A98, 629 - 636 (2000) 95. Photoelectron spectroscopy on iron containing CaO-SiO2-P2O5 glass ceramics, V.Simon, S.G.Chiuzbaian, M.Neumann, D.Eniu, E.Indrea, A.Török-Kiss, S.Simon, Modern Physics Letters B14, 767 – 772 (2000) 96. Angle Resolved Ultraviolet Photoelectron Spectroscopy (ARUPS) of Oriented Sexiphenyl H. Schürmann, N. Koch, A. Vollmer, S. Schrader, M. Neumann Synthetic Metals 111 – 112, 591 –594 (2000) 97. Magnetic Properties of Tb3Rh single crystals, E. Talik, W. Witas, J. Kusz, A. Winiarski, T. Mydlarz, M. Neumann, H. Böhm, Physica B293, 75 – 83 (2000) 98. Magnetic Circular dichroism in X-ray fluorescence of Heusler alloys at Threshold Excitation, M. V. Yablonskikh, V. I. Grebennikov, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, E. Z. Kurmaev, S. M. Butorin, L.-C. Duda, C. Såthe, T. Käämbre, M. Magnusson, J. Nordgren, S. Plogmann, M. Neumann, Solid State Commun. 117, 79 – 82 (2001) 99. Exchange splitting of photoemission lines in GdF3 and metallic Gd compounds J. Szade, M. Neumann, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13, 2717 – 2725 (2001) 100.Electronic structure of the mixed-valent system V2-xMoxO5 M. Demeter, M. Neumann, A. V. Postnikov, V. M. Cherkashenko, V. R. Galakhov, E. Z. Kurmaev, Surf. Science 482-485, 708 - 711 (2001) 101.Inelastic X-ray scattering measurements of iron organophoshate L. D. Finkelstein, A. V. Postnikov, E. Z. Kurmaev, M. Matteucci, G. Robert, B. Schneider, M. Neumann, C. Bellitto, Phys. Rev. B63, 075113(7) (2001) 102.X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study of a hexanuclear cluster S. G. Chiuzbaian, M. Neumann, O. Waldmann, B. Schneider, I. Bernt, R. W. Saalfrank, Surf. Sci. 482-485, 1272 – 1276 (2001) 103.Origin of magnetic circular dichroism in soft x-ray fluorescence of Heusler alloys at threshold excitation, M. V. Yablonskikh, V. I. Grebennikov, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, E. Z. Kurmaev, S. M. Butorin, L.-C. Duda, J. Nordgren, S. Plogmann, M. Neumann, Phys. Rev. B63, 235117(10) (2001) 104.Electronic structure and magnetic properties of HoMn2 single crystals E. Talik, M. Kulpa, A. Winiarski, T. Mydlarz, M. Neumann, J. Alloys and Compounds 316, 51 – 57 (2001) 105.Mixed valence state of Ce ions in CeNi2Al3, M. Coldea, M. Neumann, V. Pop, M. Demeter, J. Alloys and Compounds 323 – 324, 431 – 434 (2001) 81 106.Magnetic splitting in XPS Cr L-spectra of Fe2CrAl, Co2CrAl and Cu2CrAl, A. Slebarski, M. Neumann and B. Schneider, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13, 5515 - 5518 (2001) 107.Electronic structure of CoxTiSe2 and CrxTiSe2 A. N. Titov, A. V. Kuranov, V. G. Pleschev, Yu. M. Yarmoshenko, M. V. Yablonskikh, A. V. Postnikov, S. Plogmann, M. Neumann, , A. V. Ezhov, E. Z. Kurmaev, Phys. Rev. B63 , 035106(8) (2001) 108.Electronic structure of thiophenes and phtalocyanines, E. Z. Kurmaev, S. N. Shamin, and V. R. Galakhov, A. Moewes, T. Otsuka, S. Koizume, and K. Endo, H. E. Katz, M. Bach and M. Neumann, D. L. Ederer, M. Iwami, Phys. Rev. B64, 045211(7) (2001) 109.Magnetic properties and electronic structures of RCo2-xSix (R=Gd, Y) compounds E. Burzo, R. Tetean, Z. Sarkozi, L. Chioncel, M. Neumann, J. Alloys and compounds 323, 490 – 493 (2001) 82 3.2 Laserspektroskopie (Kapphan) 3.2.1 Drittmittelakquisition 1. DFG, SFB 225, Periode 95 – 98, C 7 320 TDM 2. DFG, SFB 225, Periode 98 – 00, C 7 193 TDM 3. VW-Stiftung, Ming Gao, 95 – 98 75 TDM 4. DFG, 1995 – 98, Feng Xiqi, 446/GHV-113/116 12 TDM 5. DFG, 1996 – 99, Vikhnin, 436 RUS 113/341 14 TDM 6. NATO, 96 – 98, HTECH-LG 960540 15 TDM 7. NATO, 96 – 98, CSN. 960998 5 TDM 8. Humboldt Stiftung, 98/99, Kaplyanskii,IV RUS IO 52206 GSA/Osn. 60 TDM 9. Humboldt Stiftung, 2000, Zusatz V-8151/K-DEU/1013155 55 TDM 10. MPI, 2000, Feng Xiqi 4 TDM 11. DAAD, 2000/2001, Vikhnin, Proj. VIK 147 TDM 12. NaTO-C.L.G., 2001, PST.CLG 977348 19 TDM 13. DFG-Graduiertenkolleg, Nd. opt. Mat., 2001, Proj. I. K. 115 TDM 14. DAAD, 2001, Pedko, A/01/06595 14 TDM 15. DAAD, 2001/2001, Trepakov 134 TDM 7 TDM 16. DFG, 2001,Kutsenko, 436 RUS 113/483/11-1 Gesamt 3.2.2 1188 TDM Publikationstätigkeit 1996 A. Gröne and S. Kapphan, Direct OH and OD Librational Absorption Bands in LiNbO3, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, Vol. 57, 325 (1996) V. Vikhnin, P. Voigt, S. Kapphan, Percolation in the System of Interacting Li+ Dipoles in KTaO3 studied by Second Harmonic Generation, EMF8, Nijmegen 1995 and Ferroelectrics, Vol. 185, 209 (1996) C. Auf der Horst, S. Magnien, S. Kapphan, Variation of Luminescence and Second Harmonic Generation of Defect Polarization Clusters Induced by Reduction in Pure KTaO3 and KTaO3:Fe, EMF8, Nijmegen 1995 and Ferroelectrics, Vol. 185, 265 (1996) A. Gröne, S. Kapphan, Direct OH Librational Mode in Proton Exchanged LiNbO3, EMF8, Nijmegen 1995 and Ferroelectrics, Vol. 186, 177 (1996) 83 G. Greten, S. Hunsche, U. Knüpffer, R. Pankrath, U. Siefker, N. Wittler, S. Kapphan, Defect and Light Induced Absorption, Luminescence and Dielectric Properties in SBN:Cerium, EMF8, Nijmegen 1995 and Ferroelectrics, Vol. 185, 289 (1996) 1997 S. Kapphan, G. Greten, R. Pankrath, Optical and Dielectric Investigations in SBN: Ce, Mat. Science Forum, Vol. 239, 321 (1997) S. A. Basun, V. E. Bursian, H. Hesse, S. Kapphan, L. S. Sochava, V. S. Vikhnin, Polarization Sensitive Photo Recharging and Optical Alignment of the tetragonal Fe3+ Center in KTaO3, Mat. Science Forum, Vol. 239, 345 (1997) M. F. Limonov, S. Kapphan, V. S. Vikhnin, L. V. Laisheva, H. Hesse, A. N. Krivospitskii and M. B. Smirnov, Effects of Vibronic Interactions in Polar Microdomain Formation in Incipient Ferroelectric KTaO3: Comparison Analysis of Raman Scattering and Second-Harmonic Generation, Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, Bd. 201, 215 (1997) K. Buse, S. Breer, K. Peithmann, S. Kapphan, M. Gao, and E. Krätzig, Origin of thermal fixing in photorefractive lithium niobate crystals, Physical Review B, Vol. 56, 1225 (1997) V. S. Vikhnin, S. Kapphan, Perovskite-Type Ferroelectrics with 3d-Impurities as Possible Illumination Induced Relaxor Systems: Optical Alignment of Tetragonal FeK3+ Centres in Incipient Ferroelectric Potassium Tantalate, Ferroelectrics, Vol. 199, 83 (1997) Xiqi Feng, Guanqin Hu, Ming Gao and S. Kapphan, OH Infrared Absorption Bands In PbWO4 Crystals, Prodeed. Int. Conf. on Inorganic Scintillators and their application, (CAA, Shanghai Branch Press, Shanghai), 271 (1997) 1998 V. S. Vikhnin and A. S. Polkovnikov, H.-J. Reyher, B. Faust and S. Kapphan, Dipole Fe3+-OI Center Reorientations in Incipient Ferroelectric KTaO3: Light-induced and Phonon-induced Effects, Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, 486 (1998) V. A. Trepakov, V. S. Vikhnin, V. V. Lemanov and P. P. Syrnikov, F. Smutný, M. E. Savinov and L. Jastrabík, S. Kapphan, Dielectric Properties and Phase Transitions of SrTiO3 – KTaO3 System, Journal of Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, 277 (1998) V. S. Vikhnin, S. Kapphan, J. Seglins, The Possible Role of Vibronic Charge Transfer Exciton States in Drastic Shift with Temperature of the UV-absorption Edge in Ferroelectric Oxide Crystals, Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, 621 (1998) 84 V. Trepakov and A. Skvortsov, S. Kapphan and C. Fischer, L. Jastrabik and I. Gregora, Chromium Optical Spectra and Stark Effect in LiNbO3, Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, 1140 (1998) S. Eden, C. auf der Horst and S. Kapphan, Luminescence and Second Harmonic Generation at Low Temperature in Reduced, Pure and Doped KTaO3, Journal of Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, 411 (1998) V. Trepakov and V. Vikhnin, S. Eden, S. Kapphan and H. Hesse, J. Seglins, L. Jastrabík, Optical Spectra of BaTiO3:Cr, Journal of Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, 1113 (1998) Ming Gao, S. Porcher, R. Pankrath and S. Kapphan, Light-induced VIS and NIR Absorption in SBN:Ce and SBN:Cr Crystals, Journal of Korean Physical Society, Vol. 32, 542 (1998) V. S. Vikhnin and S. Kapphan, Vibronic charge-transfer excitons: possible nature of the unusual properties of virtual perovskitelike ferroelectrics, Physics of the Solid State, Vol. 40, 834 (1998) H. Hünnefeld, U. Rütt, J.R. Schneider and S. Kapphan, The spontaneous strain in SrTiO3 in the quantum paraelectric regime: the dependence on sample preparation, J. Phys.: Condens, Matter, Vol. 10, 6453 (1998) V.S. Vikhnin, S. Kapphan, B.A. Melekh and E.B. Shadrin, Jahn-Teller Polarons and Peculiarities of their Absorption in LaMnO3 and La1-xSrxMnO3 Perovskite-Like Systems, Ferroelectrics (1998) in press S. Eden, S. Kapphan, and H. Hesse, V. Trepakov and V. Vikhnin, I. Gregora and L. Jastrabik, J. Seglins, Observations of the absorption, infra-red emission, and excitation spectra of Cr in BaTiO3, Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 10, 1077510786 (1998) 1999 D.V. Azamat, S.A. Basun, V.E. Bursian, A.G. Razdobarin, L.S. Sochava, H. Hesse, S. Kapphan, EPR of the non-Kramers ion Fe4+ in KTaO3, Fizika Tverdogo Tela, „Physics of the Solid State“, Vol. 41, 1303 (1999) P.G. Johannsen and V. Schäferjohann, S. Kapphan, Effect of pressure on OH and OD impurities in LiNbO3, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 11, 583 – 591 (1999) S.A. Prosandeyev, V.S. Vikhnin, and S. Kapphan, Alignment of Microscopic Impurities in Incipient Ferroelectrics, phys. stat. sol. (a), 172, 499 (1999) Ming Gao, S. Kapphan, S. Porcher and R. Pankrath, Experimental study of NIR absorption due to Nb4+ polarons in pure and Cr- or Ce-doped SBN crystals, J. Phys.:Condens. Matter, 11, 4913-4924 (1999) 85 Ming Gao, S. Kapphan, and Xuefeng Yue, Spectroscopic Study of Light-Induced Charge Transfer Processes in Pure KNSBN, KNSBN:Ce and KNSBN:Cu Crystals, phys. stat. sol. (b), 214, 187 (1999) M. Gao, R. Pankrath, S. Kapphan, V. Vikhnin, Light-induced charge transfer and kinetics of the NIR absorption of Nb4+ polarons in SBN crystals at low temperatures, Appl. Phys., B 68, 849-858 (1999) V.S. Vikhnin, V.A. Trepakov and S. Kapphan, Superparaelectric Phase Transition in KTaO3:Li with a Small Amount of a „Second Admixture“ , Ferroelectrics Letters, Vol. 25, 153-160 (1999) M. Wierschem, C. Bäumer, A. Jovanović, M. Wöhlecke, S. Kapphan and L. Kovács, Fundamental and Overtone spectra of the OH and OD Stretch Mode in Congruent and Stoichiometric LiTaO3, phys. stat. sol (b), 215, R7 (1999) V.A. Trepakov, S. Kapphan, V.S. Vikhnin, M. Gao, M.E. Savinov, L. Jastrabik, C.B. Azzoni and D. Di Martino, Properties of Ta-doped SrTiO3 Crystals, Radiation Effects & Defects in Solids, Vol. 151, 165-169 (1999) S. Eden, S. Kapphan, H. Hesse, V. Trepakov, V. Vikhnin, L. Jastrabik and I. Gregora, Near Infra-red Luminescence of BaTiO3:Cr, Radiation Effects & Defects in Solids, Vol. 149, 107-112 (1999) A.G. Deineka, V.A. Trepakov, I. Tupicyn, L. Jastrabik, S. Kapphan and P.P. Syrnikov, Optical Spectra and Li-Impurity Effect in Energy Structure of KTaO3 Quantum Paraelectric, Radiation Effects & Defects in Solids, Vol. 149, 113-117 (1999) V. Vikhnin, M. Aulich, S. Eden and S. Kapphan, Possible Nature of the Red Luminescence in Incipient Ferroelectric KTaO3, Radiation Effects & Defects in Solids, Vol. 149, 125-130 (1999) V.S. Vikhnin, S. Kapphan and J. Seglins, Temperature Induced Red Shift of the UV Fundamental Absorption Edge in Ferroelectric Oxide Crystals: Effect of Charge Transfer Vibronic Excitons, Radiation Effects & Defects in Solids, Vol. 150, 109-114 (1999) A. Skvortsov, V. Trepakov, S. Kapphan, V. Vorlicek and L. Jastrabik, Optical Spectra of VTE LiNbO3:Cr, Radiation Effects & Defects in Solids, Vol. 150, 293-297 (1999) Ming Gao, V. Vikhnin and S. Kapphan, Dynamics of Light-induced NIR-Absorption of Nb4+ Polarons in SBN : Cr Crystals at Low Temperature, Radiation Effects & Defects in Solids, Vol. 151, 51-55 (1999) V.A. Trepakov, M.E. Savinov, V.S. Vikhnin, L. Jastrabik, S. Kapphan and P.P. Syrnikov, Dielectric Constant and Ordering Effects of Pure and Doped KTaO3 Quantum Paraelectric; Cu-Codoping Enhancement Effect, Radiation Effects & Defects in Solids, Vol. 151, 97-102 (1999) 86 S.E. Kapphan, Spatially resolved second-harmonic generation in ABO3-type ferroelectric crystals, Journal of Luminescence, 83-84, 411-415 (1999) V. S. Vikhnin, S. Kapphan, ‘The models for polaron complexes in ferroelectric and ferroeleastic systems’, Ferroelectrics, Vol. 233, 77-91 (1999) G. M. Sally, B. A. Basun, G. F. Imbusch, A. A. Kaplyanskii, S. Kapphan, R. S. Meltzer, U. Happek, ‘Chromium centers in LiNbO3 revisited’, Journal of Luminescence, Vol. 83-84, 423-427 (1999) V. Trepakov, V. Vikhnin, M. Savinov, P. Syrnikov, S. Kapphan, V. Lemanov, H. Hesse, L. Jastrabik, ‘Dielectric Permittivity and Fe- and Cu-Doping Effect in KTaO3 and K1-xLixTaO3’, Ferroelectrics, Vol. 235, 59-75 (1999) V. S. Vikhnin, S. Kapphan, B. Melekh, E.Shadrin, ‘J-T Polarons and Pecularities of their Absorption in LaMnO3 and La1-xSrxMnO3 Perovskite-like Systems’, Ferroelectrics, Vol. 235, 211-220 (1999) Valentin S. Vikhnin, Huimin Liu, Weiyi Jia, S.E. Kapphan, Roberts Eglitis, Denis Usvyat, ‘Critical effects in optical response due to charge transfer vibronic excitons and their structure in perovskite-like systems’ Journal of Luminescence, 83-84, 109113 (1999) Valentin S. Vikhnin, Huimin Liu, Weiyi Jia, S. E. Kapphan, ‘Charge transfer vibronic excitons in ferroelectric oxides: experiment and theory’, Journal of Luminescence, 8384, 91–96 (1999) 2000 M. Gao, S. Kapphan, R. Pankrath, J. Zhao, ‘NIR-Absorption of Nb4+-Polarons in Reduced SBN-Crystals’, phys. stat. sol. (b), Vol. 217, 999 (2000) V. Vikhnin, S. Eden, M. Aulich, S. Kapphan, ‘The origin of the red luminescence in incipient ferroelectric KTaO3’, Solid state communications, Vol. 113, 455 (2000) S. A. Prosandeev, V. S. Vikhnin, S. Kapphan, ‘Percolation with constraints in the highly polarizable oxide KTaO3:Li’, Eur. Phys. J. B 15, 469-474 (2000) V. A. Trepakov, V. S. Vikhnin, S. Kapphan, L. Jastrabik, J. Licher, P. P. Syrnikov, ‘Zero-phonon optical lines of impurity centers in ABO3 perovskite-like ferroelectrics’, Journal of Luminescence, 87-89, 1126-1129 (2000) V. Vikhnin, S. Kapphan, H. Liu, W. Jia, V. Trepakov, L. Jastrabik, ‘Polaron and Charge Transfer Vibronic Exciton Phenomena in Ferroelectrics’, Ferroelectrics, 237, 81-88 (2000) V. Trepakov, M. Savinov, S. Kapphan,V. Vikhnin, L. Jastrabik, L. Boatner, ‘Dielectric Properties and Phase Transitions in K1-xLixTa1-yNbyO3:Cu’, Ferroelectrics, 239, 305312s (2000) 87 I. I. Tupitsyn, A. Deineka, V. Trepakov, L. Jastrabik and S. Kapphan, ‘Li-Doping Effect on the Energy Structure of KTaO3’, Ferroelectrics, Vol. 237, 9-16 (2000) V. A. Trepakov, M. E. Savinov, P. P. Syrnikov, S. Kapphan, A. Badalyan, V. Vikhnin and L. Jastrabik, ‘Cu- and Fe-Doping in Properties of KTaO3 and KTaO3:Li Crytals’, Ferroelectrics, 239, 289-296 (2000) V. Trepakov, A. Skvortsov, S. Kapphan, L. Jastrabik and V. Vorlíček, ‘Comparative Studies of Luminescence in Congruent and Stoichiometric VTE-Treated LiNbO3:Cr’, Ferroelectrics, Vol. 239, 297-304 (2000) Ming Gao, S. Kapphan, R. Pankrath, Xiqi Feng, Yuanfen Tang, V. Vikhnin, ‘Lightinduced VIS-absorption and light-induced charge transfer in pure and doped SBN crystals’, J. of Phys. Chem. Sol., 61, 1775-1787 (2000) M. Gao, S. Kapphan, R. Pankrath, ‘Photoluminescence and thermoluminescence in SBN:Cr crystals’, J. of Phys. Chem. Sol., 61, 1959-1971 (2000) M. Gao, S.Kapphan, R. Pankrath, J. Zhao, ‘NIR Absorption of Nb4+ Polarons in reduced SBN crystals’, Ferroelectrics, 239, 251-256 (2000) 2001 S. A. Prosandeyev, V. A. Trepakov, M. E. Savinov, S. E. Kapphan, ‘Coupling of Li+ relaxators to the soft mode in KTaO3:Li’, J. Phys.: Cond. Matter, 13, 719-725 (2001) V. A. Trepakov, M. E. Savinov, E. Giulotto, P. Galinetto, P. Camagni, G. Samoggia, L. A. Boatner, S. E. Kapphan, ‘Dipole ordering effects and reentrant dipolar glass state in KTaO3:Li,Nb’, Phys. Rev. B, Vol. 63, 172203 (2001) S. A. Basun, A. A. Kaplyanskii, A. B. Kutsenko, V. Dierolf, T. Tröster, S. E. Kapphan, and K. Polgar, ‚Dominat Cr3+ Centers in LiNbO3 under Hydrostatic Pressure’ Phys. of Sol. State, Vol. 43, No. 6, 1043-1051 (2001) S. A. Prosandeev, A. E. Maslennikov, V. S. Vikhnin and S. Kapphan, ‘Nanoscale Clusters in Solid Solutions of Ferroelectrics in the Framework of a Six-Well Model’, Ferroelectr., Vol. 32, 279-285 (2001) S. A. Prosandeev, V. S. Vikhnin, S. Kapphan, ‘Percolative Clusters in KTaO3:Li’, Ferroelectr., Vol. 32, 355-360 (2001) V. S. Vikhnin, R. I. Eglitis, E. A. Kotomin, S. Kapphan, G. Borstel, ‚New PolaronicType Excitons in Ferroelectric Oxides: INDO-Calculations and Experimental Manifestation’, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc., Vol. 677, AA 4.15.1 (2001) 88 3.3 Nichtlineare Optik (Betzler) 3.3.1 Publikationstätigkeit 3.3.1.1 Wissenschaftliche Zeitschriften mit “peer review” D.Xue, K. Betzler: Influence of optical-damage resistant dopants on the nonlinear optical properties of lithium niobate. Applied Physics B 72, 641 (2001). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse, D. Lammers: Linear and nonlinear optical susceptibilities of orthorhombic rare earth molybdates RE2(MoO4)3. J. Phys. Chem. Solids, in print (2001). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse: Induced Li-site vacancies and nonlinear optical behavior of doped lithium niobate crystals. Optical Materials 16, 381 (2001). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse: Second order nonlinear optical properties of In-doped lithium niobate. J. Appl. Phys. 89, 849 (2001). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse, D. Lammers: Temperature dependence of the dielectric response of lithium niobate. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 62, 973 (2001). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse: Dielectric properties of I-III-VI2 type chalcopyrite semiconductors. Physical Review B15, 62, 13546 (2000). D. Lammers, K. Betzler, D. Xue, J. Zhao: Optical Second-Harmonic Generation in Benzophenone. physica status solidi (a) 180/2, R5 (2000). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse: Chemical bond analysis of the second order nonlinear optical behavior of Zn-doped lithium niobate. Optics Communications, 182, 167 (2000). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse: Dielectric properties of lithium niobate-tantalate crystals Solid State Communications, 115, 581 (2000). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse: Chemical bond analysis of the second order nonlinear optical behavior of Mg-doped lithium niobate J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 12, 6245 (2000). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse, D. Lammers: Nonlinear optical properties of borate crystals. Solid State Communications 114, 21 (2000). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse: Dielectric constants of binary rare-earth compounds J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 3113 (2000). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse: Structural characteristics and second order nonlinear optical properties of borate crystals Trends in Optics and Photonics Series 34, 542 (2000). D.Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse, D. Lammers, S. Zhang: Theoretical studies of nonlinear optical properties of compounds K4Ln2(CO3)3F4 (Ln=Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd) J. Appl. Physics 87, 2849 (2000). K. Betzler, H. Hesse, R. Jaquet, D. Lammers: Optical second-harmonic generation in lead formate. J. Appl. Physics 87, 22 (2000). D. Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse, D. Lammers:http://www.physik.uni- osnabrueck.de/nonlinop/papers/abstracts.htm - XBHL99b Relationship between Dielectric Responses and Constituent Atoms in Crystal Materials. physica status solidi (b) 216/2, R7 (1999). D. Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse, D. Lammers: Origin of the Large Nonlinear Optical Coefficients in Bismuth Borate BiB3O6. physica status solidi (a) 176/2, R1 (1999). K.-U. Kasemir, K. Betzler: Characterization of photorefractive materials by spontaneous noncolinear frequency doubling. Applied Physics B 68, 763 (1999). Chr. a. d. Horst, K.-U. Kasemir, K. Betzler: Determination of Homogeneity of Pure and Doped Lithium Niobate by SHG Temperature Phase-Matching. J. Appl. Physics, 84, 5158 (1998). 89 K. Kasemir, K. Betzler, B. Matzas, B. Tiegel, T. Wahlbrink, M. Wöhlecke, B. Gather, N. Rubinina, T. Volk: Influence of Zn/In Codoping on the Optical Properties of Lithium Niobate. J. Appl. Physics, 84, 5191 (1998). K. Kasemir, K. Betzler, B. Matzas, B. Tiegel, M. Wöhlecke, N. Rubinina, T. Volk: Influence of In Doping on the Refractive Indices of Lithium Niobate. physica status solidi (a) 166/1, R7 (1998). K. Chah, M. Aillerie, M. D. Fontana, G. I. Malovichko, K. Betzler, E. Kokanyan: Influence of chromium doping on the electro-optic properties of lithium niobate. Optics Commun. 136, 231 (1997). A. Reichert, K. U. Kasemir, K. Betzler: Application of noncolinear frequency doubling for crystal characterization. Materials Science Forum 239-241, 329 (1997). M. Wöhlecke, G. Corradi, K. Betzler: Optical Methods to Characterise the Composition and Homogeneity of Lithium Niobate Single Crystals. Applied Physics B 63,323 (1996). A. Reichert, K. Betzler: Induced noncolinear frequency doubling: A new characterization technique for electrooptic crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 2209 (1996). U. Schlarb, B. Matzas, A. Reichert, K. Betzler, M. Wöhlecke, B. Gather, T. Volk: Refractive indices of Zn/In-co-doped lithium niobate. Ferroelectrics, 185, 269 (1996). A. Reichert, K. U. Kasemir, K. Betzler: Crystal characterization by noncolinear frequency doubling. Ferroelectrics, 184, 21 (1996). T. Volk, M. Wöhlecke, N. Rubinina, A. Reichert, and N. Razumovski: Optical-damage-resistant impurities (Mg, Zn, In, Sc) in lithium niobate. Ferroelectrics 183, 291 (1996). Dazu kommen zahlreiche Tagungs- und Konferenzbeiträge, die hier nicht im Einzelnen aufgeführt sind. 90 3.4 Magnetische Resonanzspektroskopie (Schirmer) 3.4.1 Publikationstätigkeit 3.4.1.1 Referierte Aufsätze 1. Rüdiger, O. F. Schirmer, A. Kadashchuk, A. Grabar Light-induced charge transfer in nominally pure and iron doped Sn2P2S6: a study by combined EPR and optical absorption spectroscopy Trends in Optics and Photonics Series 62, 561 (2001) 2. S. Bernhardt, L. Mize, P. Delaye, R. Pankrath, O. Schirmer, G. Roosen Orientation dependence of photorefractive gainin BCT: determination of electrooptic coefficients Trends in Optics and Photonics Series 6, 504 (2001) 3. T. Volk, L. Ivleva , P. Lykov, D. Isakov, V. Osiko, M. Wöhlecke Modification of the optical and photorefractive properties of Ce-doped strontium-barium niobate by co-doping with a nonphotorefractive La impurity Appl. Phys. Letters 79, 854 (2001) 4. Ruediger, O. Schirmer, S. Odoulov, A. Shumelyuk, A. Grabar Studies of light-induced charge transfer in Sn2P2S6 by combined EPR/optical absorption spectroscopy Optical Materials (in print) 5. O. F. Schirmer, M. Meyer, A. Ruediger, C. Veber Combined EPR/optical investigations of light-induced charge transfers in photorefractive materials Optical Materials (in print) 6. T. Volk, L. Ivleva, P. Lykov, N. Pollok, V. Salobutin, R. Pankrath, M. Wöhlecke Effects of rare-earth impurity doping on the ferroelectric and photorefractive properties of strontium-barium niobate crystals Optical Materials (in print) 7. Th. Woike, T. Granzow, U. Dörfler, Ch. Poetsch, M. Wöhlecke, R. Pankrath Refractive Indices of congruently melting Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 phys. stat. sol. (a) 186, R13 (2001) 8. M. Wöhlecke, L. Kovács OH- ions in Oxide Crystals Critical Reviews in Solid State and Materials Sciences, 26(1):1 - 86 (2001) 9. H.J. Reyher, M. Pape, N. Hausfeld Photoactive Pb 3+ host lattice ions in photorefractive Pb5Ge3O11 investigated by magnetic resonance techniques J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13, 3767 (2001) 10. T. Granzow, U. Dörfler, Th. Woike, M. Wöhlecke, R. Pankrath, M. Imlau, W. Kleemann Influence of pinning effects on the ferroelectric hysteresis in cerium-doped SrxBa1xNb2O6 Phys. Rev B 63, 174101 (2001) 11. T. Volk, B. Maximov, T. Chernaya, N. Rubinina, M. Wöhlecke, V. Simonov Photorefractive Properties of LiNbO3:Zn Crystals Related to the Defect Structure Appl. Phys. B 72, 647 (2001) 12. Th. Woike, U. Dörfler, L. Tsankov, G. Weckwerth, D. Wolf, M. Wöhlecke, T. Granzow, R. Pankrath, M. Imlau, W. Kleemann Photorefractive properties of Cr-doped Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 related to crystal purity and 91 doping concentration Appl. Phys. B 72, 661 (2001) 13. H.J. Reyher, N. Hausfeld, M. Pape A magnetic circular dichroism and optically detected magnetic resonance investigation of Fe2+ and Fe3+ centres in KTaO3 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 10599 (2000) 14. M. Meyer, M. Wöhlecke, O. F. Schirmer On the temperature dependence of the band edge of Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 phys. stat. sol. (b) 221, R1 (2000) 15. O. F. Schirmer EPR investigations of small electron and hole polarons in oxide perovskites in ‘Defects and surface-induced effects in advanced perovskites’, G. Borstel et al. (eds.), Kluwer 2000, p. 75 – 88 16. H. Donnerberg, A. Birkholz Ab initio study of oxygen vacancies in barium titanate J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 8239 (2000) 17. V. Grachev, G. I. Malovichko EPR, ENDOR and optical absorption study of Cr3+ centers substituting for niobium in Li-rich lithium niobate crystals Phys. Rev. B 62, 7779 (2000) 18. J. Wingbermühle, M. Meyer, O. F. Schirmer, R. Pankrath, R. K. Kremer Electron paramagnetic resonance of Ce3+ in strontium-barium niobate J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 4277 (2000) 19. S. Lenjer, R. Scharfschwerdt, Th. W. Kool, O. F. Schirmer An off-center ion near a Ba site in BaTiO3 as studied by EPR under uniaxial stress Solid State Commun. 116, 133 (2000) 20. R. Ratheesh, M. Wöhlecke, B. Berge, Th. Wahlbrink, H. Haeuseler, E. Rühl, R. Blachnik, P. Balan, N. Santha, M. T. Sebastian Raman study of the ordering in Sr(B'0.5Nb0.5)O3 compounds J. Appl. Phys. 88, 2813 (2000) 21. T. R. Volk, V. Yu. Salobutin, L. I. Ivleva, N. M. Polozkov, R. Pankrath, and M. Wöhlecke Ferroelectric Properties of Strontium Barium Niobate Crystals Doped with Rare-Earth Metals Physics of the Solid State 42, 2066 (2000) 22. K. Chah, M. Aillerie, M. D. Fontana, G. Malovichko Electro-optic properties in Fe-doped LiNbO3 crystals as a function of composition Opt. Commun. 176, 261 (2000) 23. G. Malovichko, V. Grachev, E. Kokanyan, O. Schirmer EPR, NMR and ENDOR study of intrinsic and extrinsic defects in disordered and regularly ordered lithium niobate crystals Ferroelectrics 239, 1227 (2000) 24. V. Grachev, G. Malovichko, O. Schirmer Models of axial and low-symmetry impurity centers in lithium niobate crystals derived from EPR and ENDOR data Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids 150, 277 (1999) 25. G. Malovichko, V. Grachev, E. Kokanyan, O. Schirmer Point imperfections and clusters of intrinsic and extrinsic defects in non-stoichiometric and stoichiometric Lithium Niobate: The Regularly ordered crystal Radiation Effects and Defects in Solids 150, 227 (1999) 92 26. Y. Lin, J.E. Eldridge, J. Sichelschmidt, S.W. Cheong, T. Wahlbrink Fröhlich-interaction induced one-phonon Raman scattering in La2CuO4 using an infrared laser Solid State Commun. 112, 315 (1999) 27. O.F. Schirmer, A. Mazur, C. Veber, A. Rüdiger Photoinduced charge transport in BaTiO3 and congruent Ba1-xCaxTiO3 doped with transition metal and alkali ions Trends in Optics and Photonics (TOPS) 27, 149 (1999) 28. T. Volk, T. Woike, U. Dörfler, H. Schmitz, R. Pankrath, M. Wöhlecke Ferroelectricity Driven Two-Beam Coupling Gain in Strontium-Barium Niobate Crystals Trends in Optics and Photonics (TOPS) 27, 86 (1999) 29. M. Pape, H.J. Reyher, N. Hausfeld, S. Mendricks Photoactive Pb3+ host lattice ions in photorefractive Pb5Ge3O11 characterized by ODMR and EPR Trends in Optics and Photonics (TOPS) 27, 42 (1999) 30. T. Volk, B. Maximov, S. Sulyanov, N. Rubinina, F. Abdi, M. Aillerie, M. Fontana, P. Bourson, M. Wöhlecke Optical and Photorefractive Properties of Optical-Damage Resistant LiNbO3:Zn Crystals Related to Structure Parameters Trends in Optics and Photonics (TOPS) 27, 144 (1999) 31. M. Wierschem, C. Bäumer, A. Jovanovic, M. Wöhlecke, S. Kapphan, L. Kovács Fundamental and overtone spectra of the OH and OD stretch mode in congruent and stoichiometric LiTaO3 phys. stat. sol. (b) 215, R7 (1999) 32. H.-J. Reyher, N. Hausfeld, M. Pape, J. Baur, J. Schneider Attribution of the Near-UV Absorption Bands of YAG: Ce to Ce3+-Ions by MCD and ODMR Solid State Commun. 110, 345 (1999) 33. R. Scharfschwerdt, O. F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, D. Rytz Fermi level engineering of BaTiO3 by alkali codoping: Increasing the near infrared absorption by rhodium, Appl. Phys. B 68, 807 (1999) 34. G. Malovichko, V. Grachev, O. Schirmer Interrelation of intrinsic and extrinsic defects. Congruent, stoichiometric and regularly ordered lithium niobate Appl. Phys. B 68, 785 (1999) 35. F. Abdi, M. Aillerie, M. Fontana, P. Boursons, T. Volk, B. Maximov, S. Sulyanov, N. Rubinina, and M. Wöhlecke Influence of Zn doping on electrooptical properties and structure parameters of lithium niobate crystals Appl. Phys. B 68, 795 (1999) 36. U. B. Dörfler, R. Piechatzek, Th. Woike, M. K. Imlau, V. Wirth, L. Bohaty, T. Volk, R. Pankrath, and M. Wöhlecke A holographic method for the determination of all linear electrooptic coefficients applied to Ce-doped Strontium-Barium-Niobate, Appl. Phys. B 68, 843 (1999) 37. O.F. Schirmer Light-induced charge transfer between defects in photorefractive materials Radiation effects and defects in solids, 149, 1 (1999) 93 38. Mazur, C. Veber, O.F. Schirmer, C. Kuper, H. Hesse Light-induced charge transport in photorefractive BaTiO3: Fe and Ba0,77 Ca0,23TiO3: Fe Radiation effects and defects in solids 150, 281 (1999) 39. Mazur, C. Veber, O.F. Schirmer, C. Kuper, H. Hesse Light-induced charge transport processes in photorefractive Ba0,77Ca0,23TiO3 doped with iron J. Appl. Phys. 85, 6751 (1999) 40. S. Köhne, O.F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, T.W. Kool, V. Vikhnin Ti3+ Jahn-Teller polarons and bipolarons in BaTiO3 J. Superconductivity 12, 193 (1999) 41. G.I. Malovichko, V. Grachev, E. Kokanyan, O. Schirmer Axial and low symmetry centers of trivalent impurities in lithum niobate. Chromium in congruent and stoichiometric crystals, Phys. Rev. B 59, 9113 (1999) 42. M. Aillerie, K. Chah, F. Abdi, P. Bourson, M. D. Fontana, K. Polgar, G. Malovichko Influence of the non-stoichiometry on the electro-optic properties of LiNbO3 Ferroelectrics 223, 365 (1999) 43. F. Lhomme, P. Bourson, G. Boulon, G. Malovichko New spectroscopic investigation of Cr3+ centres in LiNbO3 crystals J. Lumin. 83, 441 (1999) 44. T. R. Volk, M. Wöhlecke Optical Damage Resistance in Lithium Niobate Crystals, Ferroeelectrics Review 1, 195-262 (1998) 45. K. Kasemir, K. Betzler, B. Matzas, B. Tiegel, T. Wahlbrink, M. Wöhlecke, B. Gather, N. Rubinina, T. Volk Influence of Zn/In-codoping on the optical properties of Lithium Niobate J. Appl. Phys. 84, 5191 (1998) 46. H. Kröse, R. Scharfschwerdt, A. Mazur, O. F. Schirmer A multichannel spectrometer for correlated EPR-optical absorption analysis of photochromic processes in crystals; Appl. Phys. B-Lasers & Optics. 67, 79-86 (1998) 47. E. Ruza, H. J. Reyher, J. Trokss, M. Wöhlecke Optically detected magnetic resonance via the blue luminescence of Ti-doped Al2O3 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 10, 4297 (1998) 48. T. Woike, T. Volk, U. Dörfler, R. Pankrath, L. Ivleva, M. Wöhlecke Ferroelectric and optical hysteresis in SBN doped with rare-earth elements Ferroelectric Letters 23, 127 (1998) 49. K. Kasemir, K. Betzler, B. Matzas, B. Tiegel, M. Wöhlecke, N. Rubinina, T. Volk Influence of In Doping on the Refractive Indices of Lithium Niobate physica status solidi (a) 166/1, R7 (1998) 50. Leroux, G. Nihoul, G. Malovichko, V. Grachev, C. Boulesteix Investigation of correlated defects in non-stoichiometric lithium niobate by high resolution electron microscopy J. Phys. Chem. Solids 59, 311 (1998) 51. F. Lhomme, P. Bourson, M. D. Fontana, G. Malovichko Luminescence of Cr3+ in lithium niobate: influence of the chromium concentration and crystal composition J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10, 1137 (1998) 94 52. K. Chah, M. D. Fontana, M. Aillerie, P. Bourson, G. Malovichko Electro-optic properties in undoped and Cr-doped LiNbO3 crystals Appl. Phys. B 67, 65 (1998) 53. I. Kochelaev, J. Sichelschmidt, B. Elschner, W. Lemor (Univ. Osnbrück), A. Loidl Three-Spin Polaron in La2-xSrxCuO4: Experimental evidence by EPR measurements Phys. Rev. Lett. 79, 4274 (1997) 54. Th. Woike, U. Dörfler, M. Imlau, G. Schetter, T. Volk, M. Wöhlecke, R. Pankrath Die ferroelektrischen und photorefraktiven Eigenschaften von Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 dotiert mit Cr, Co, Ce, Tm Z. Krist. Suppl. 12, 96 (1997) 55. Mazur, U. van Stevendaal, K. Buse, M. Weber, O. F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig Light-Induced Charge Transport Processes in Photorefractive Barium Titanate Crystals Doped with Iron Appl. Phys. B 65, 481 (1997) 56. T. Volk, T. Woike, U. Dörfler, R. Pankrath, L. Ivleva, M. Wöhlecke Ferroelectric phenomena in holographic properties of strontium-barium niobate crystals doped with rare-earth elements Ferroelectrics 203, 457 (1997) 57. Mazur, O. F. Schirmer, S. Mendricks Optical absorption and light-induced charge transport of Fe2+ in BaTiO3 Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 2395 (1997) 58. M. Wöhlecke, T. Volk, H. Donnerberg On the Role of Intrinsic Clusters in Damage-Resistant LiNbO3 Ferroelectrics Letters 22, 53 (1997) 59. H. Donnerberg Computer Modeling of Trapped Holes in Barium Titanate (ICDIM conference, Winston-Salem, North Carolina 1996) Materials Science Forum 239-241, 341 (1997) 60. H.-J. Reyher, B. Faust, B. Sugg, R. Rupp, L. Ackermann Optically detected magnetic resonance via the magnetic circular dichroism of absorption of cerium impurities in bulk paramagnetic terbium gallium garnet J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9, 9065 (1997) 61. L. Kovács, G. Ruschhaupt, K. Polgár, G. Corradi, M. Wöhlecke Composition dependence of the ultraviolet absorption edge in lithium niobate Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 2801 (1997) 62. H. Donnerberg, S. Többen, A. Birkholz Formation of Localized Hole States in Complex Oxides J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9, 6359 (1997) 63. K. Chah, M. Aillerie, M. D. Fontana, G. Malovichko Influence of chromium doping on the electro-optic properties of LiNbO3 Opt. Commun. 136, 231 (1997) 64. Ridah, P. Bourson, M. D. Fontana, G. Malovichko The composition dependence of the Raman spectrum and new assignment of the phonons in LiNbO3 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 9, 9987 (1997) 65. K. Chah, M. Aillerie, M. D. Fontana, G. Malovichko Influence of intrinsic and extrinsic defects on the electro-optic properties of lithium niobate Ferroelectrics 202, 11 (1997) 95 66. V. G. Grachev, G. I. Malovichko, O. F. Schirmer Single, dimer and trimer chromium centers in LiNbO3 Ferroelectrics 185, 639 (1996) 67. R. Scharfschwerdt, O. F. Schirmer, H. Kröse, T. W. Kool Oxygen vacancy related defects in BaTiO3, Ferroelectrics 185, 643 (1996) 68. T. Varnhorst, O. F. Schirmer, H. Kröse, R. Scharfschwerdt, T. W. Kool O--holes associated with alkali acceptors in BaTiO3 Phys. Rev. B 53, 116 (1996) 69. Faust, H.-J. Reyher, O. F. Schirmer Optically detected magnetic resonance of Fe4+ - OI in KTaO3 Solid State Commun. 18, 445 (1996) 70. U. Schlarb, B. Matzas, A. Reichert, K. Betzler, M. Wöhlecke, B. Gather, T. Volk, N. Rubinina Refractive indices of Zn/In-Co-doped lithium niobate Ferroelectrics 185, 269 (1996) 71. T. Volk, M. Wöhlecke, N. Rubinina, A. Reichert, N. Razumovski Optical-damage-resistant impurities (Mg, Zn, In, Sc) in lithium niobate Ferroelectrics 183, 291 (1996) 72. R. Scharfschwerdt, A. Mazur, O. F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, S. Mendricks Oxygen Vacancies in BaTiO3 Phys. Rev. B 54, 15284 (1996) 73. G. Wübbeler, O. F. Schirmer, S. Köhne Phase separation in La2CuO4+d as probed by a paramagnetic surface defect Phys. Rev. B 54, 9054 (1996) 74. W. Lemor, G. Wübbeler, O. F. Schirmer Phase Separation in La2CuO4+d studied by electric transport measurements Journal of Superconductivity 9, 365 (1996) 75. H.-J. Reyher, B. Faust, M. Käding, H. Hesse, E. Ruza, M. Wöhlecke Optical alignment of axial Fe centers in KTaO3 Phys. Rev. B 51, 6707 (1995), Erratum: Phys. Rev. B 54, 3662 (1996) 76. H.-J. Reyher, B. Faust, M. Maiwald, H. Hesse ODMR and EPR investigations of Fe centers in KTaO3 Appl. Phys. B 63, 331 (1996) 77. M. Wöhlecke, G. Corradi. K. Betzler Optical methods to characterise the composition and homogeneity of lithium niobate single crystals Appl. Phys. B 63, 323 (1996) 78. H. Donnerberg, R. H. Bartram Embedded Cluster Calculations for Transition-Metal Impurities in BaTiO3 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 8, 1687 (1996) 79. H. Donnerberg Comments on the Defect Chemistry of Magnesium-doped Lithium Niobate J. Solid State Chem. 123, 208 (1996) 80. O. Cerclier, V. Grachev, J. Estienne, G. Malovichko Evolution of lattice constants of LiNbO3 doped with potassium and magnesium J. Phys. IV 6 (C4), 49 (1996) 96 3.4.1.2 Monographien H. Donnerberg Atomic Simulation of Electrooptic and Magnetooptic Oxide Materials Springer Tracts in Modern Physics, Vol. 151, Springer Verlag (Berlin, Heidelberg 1999) 3.4.1.3 Konferenzbeiträge, Vorträge und Poster 1. O. F. Schirmer, Lichtinduzierte Defektumladungen in photorefraktiven oxidischen Perovskiten (eingeladen), Seminar ETH Zürich, 11. 12. 97 2. Mazur, Light-induced charge transport in BaTiO3:Fe as detected by simultaneous EPRoptical absorption studies, Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, Chiba, Japan, 11. – 13.06.1997 3. K. Buse, U. van Stevendaal, M. Weber, A. Mazur, O.F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, Photorefractive Properties of barium titanate crystals doped with iron, Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, Chiba, Japan, 11. – 13.06.1997 4. O. F. Schirmer, Light-induced defect processes investigated by EPR/optical spectroscopy, Deutsch-Russisches Seminar “Punktdefekte in Isolatoren und Halbleitern”, Petersburg, 27. 9. – 4. 10. 1997 5. Mazur, Characterisation and optimisation of light-induced charge transport in photorefractive materials using simultaneous EPR and optical absorption studies, Seminar, Risoe Forschungszentrum, Risoe, 04.12.1997 6. O.F. Schirmer, Characterisation of defects in optical materials and photoinduced charge transfers between them using a combined EPR-optical spectrometer, VIth RussianGerman Seminar on Point Defects in Insulators and Deep-Level Centres in Semiconductors, St. Petersburg, 22.09. – 04.10.1997 7. H.-J. Reyher, Magnetic resonance detected via the blue luminescence of T-doped Al2O3 – first results, VIth Russian-German Seminar on Point Defects in Insulators and DeepLevel Centres in Semiconductors, St. Petersburg 1997 8. H.-J. Reyher, MCD-ODMR investigations of KTaO3:Fe and Tb3Ga5O12:Ce, VIth RussianGerman Seminar on Point Defects in Insulators and Deep-Level Centres in Semiconductors, St. Petersburg 1997 9. T. Volk, T. Woike, U. Dörfler, R. Pankrath, L. Ivleva, M. Wöhlecke, Ferroelectric hysteresis phenomena in two-beam coupling in SBN crystals doped with rare-earth elements, Top. Meet. on Photorefractive Effects and devices, PR'97, Japan, June 11-13, 1997 10. Th. Woike, U. Dörfler, T. Volk, A. Ivleva, M. Wöhlecke, R. Pankrath und M. Imlau, Photorefraktive und ferroelektrische Eigenschaften von dotiertem SrxBa1-xNb2O6 , DPGFrühjahrstagung 1997 11. R. Scharfschwerdt, O.F. Schirmer, M. Maiwald, H. Hesse, Fermi level positioning by Na acceptor doping in BaTiO3, 8th Europhysical Conference on Defects in Insulating Materials, Keele, 06. – 11.07.1998 12. A. Mazur, C. Veber, O.F. Schirmer, C. Kuper, H. Hesse, Light-induced charge transports of photorefractive BaTiO3:Fe and Ba0.77Ca0.23TiO3:Fe, 8th Europhysical Conference on Defects in Insulating Materials, Keele, 06. – 11.07.1998 97 13. V. Grachev, G.I. Malovichko, O.F. Schirmer, Models of axial and low-symmetry impurity centers in lithium niobate crystals, derived from EPR and ENDOR data, 8th Europhysical Conference on Defects in Insulating Materials, Keele, 06. – 11.07.1998 14. G.I. Malovichko, V. Grachev, O.F. Schirmer, Determination of the structure of Me3+ impurities in LiNbO3 crystals by means of EPR and ENDOR study, 29th AMPERE International Conference, Berlin, 02. – 07.08.1998 15. T. Volk, Th. Woike, U. Dörfler, R. Pankrath, M. Wöhlecke, L. Ivleva, Ferroelectricity Driven Holographic Properties of SrxBa1-xNb2O6 Crystals, ISAFXI'98, Switzerland, Montreux, Aug. 23-27, 1998 16. T. Volk, V. Salobutin, T. Woike, H. Schmitz, R. Pankrath, M. Wöhlecke, Ferroelectric Switching and Relaxor Properties of SrxBa1-xNb2O6 Crystals Doped with Rare-Earth Elements, ISAFXI'98, Switzerland, Montreux, Aug. 23-27, 1998 17. O. F. Schirmer, Light-induced charge transfers between defects in photorefractive materials (eingeladen), 8th Europhysical Conference on Defects in Insulating Crystals, Keele (UK), 6. – 11. 7. 1998 18. O. F. Schirmer, Ti3+ Jahn-Teller polarons in BaTiO3 (eingeladen), Seminar Universität Zürich, 13. 5. 1998 19. Mazur, Light-induced charge transport in photorefractive materials as detected by simultaneous EPR-optical absorption studies, Seminar, West Virginia University, 18.02.1998 20. O.F. Schirmer, Ti3+ Jahn-Teller polarons and bipolarons in BaTiO3, Euroconference on Polarons, Condensation, Pairing, Magnetism, Erice (Sizilien), 09. – 17. Juni 1998 21. N. Huot, G. Pauliat, J.M.C. Jonathan, G. Roosen, R. Scharfschwerdt, O.F. Schirmer, D. Rytz, Fourfold improvement of the photorefractive time constant of BaTiO3:Rh by oxidation, Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Glasgow, 14. – 18.09.1998 22. H.-J. Reyher, Was macht Bleigermanat (Pb5Ge3O11) photorefraktiv? Die Antwort durch ESR und MCD-ODMR, Seminar I. Physikalisches Institut der Universität Gießen, Gießen 1998 23. H.-J. Reyher, MCD and ODMR investigations of iron centers in potassium tantalate, 8th Europhysical Conference on Defects in Insulating Materials, Keele 1998 24. E. Ruza, Magnetic resonance detected via the blue luminescence of titanium-doped corundum, 8th Europhysical Conference on Defects in Insulating Materials, Keele, 06. – 11.07.1998 25. G.I. Malovichko, V. Grachev, E. Kokanyan, O.F. Schirmer, Point imperfections and dusters of intrinsic and extrinsic defects in regularly ordered and non-stoichiometric lithium niobate crystals, 8th Europhysical Conference on Defects in Insulating Materials, Keele, 06. – 11.07.1998 26. U. Dörfler, M. Imlau, Th. Woike, T. Volk, A. IvLeva, R. Pankrath und M. Wöhlecke, Bestimmung der elektrooptischen Koeffizienten von Cer - dotiertem Strontium-Barium-Niobat (Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce) mittels Reflexionsholographie, DPG-Frühjahrstagung 1998 27. O. F. Schirmer, Identifying light-induced charge transfer paths in photorefractive crystals by combined EPR/optical spectroscopy, International Symposium “Trends in Applied Optics”, Osnabrück, 25/26. 6. 1999 98 28. O. F. Schirmer, A. Mazur, C. Veber, A. Rüdiger, Photoinduced charge transport in BaTiO 3 and congruent Ba1-xCaxTiO3 doped with transition metal and alkali ions, 7th Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, Elsinore (Dänemark), 27.- 30. Juni 1999 29. O. F. Schirmer, EPR investigations of small electron and hole small polarons (eingeladen), NATO ARW on Defects and Surface Induced Effects in Advanced Perovskites, Riga, 23. – 25. 8. 1999 30. U. Dörfler, M. Imlau, R. Piechatzek, Th. Woike, T. Volk, R. Pankrath und M. Wöhlecke, Elektrisches Fixieren von Volumenphasenhologrammen in dotiertem Strontium-BariumNiobat, DPG-Frühjahrstagung 1999 31. R. Piechatzek, U. Dörfler, M. Imlau, Th. Woike, T. Volk, A. Ivleva, R. Pankrath und M. Wöhlecke, Temperaturabhängige Messungen der elektrooptischen Koeffizienten von Cer - dotiertem Strontium-Barium-Niobat Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce mittels Holographischer Streuung, DPG-Frühjahrstagung 1999 32. T. Granzow, U. Dörfler, M. Imlau, L. Bohaty, Th. Woike, R. Pankrath, M. Wöhlecke und W. Kleemann, Ferroelektrische Untersuchungen der elektrischen Eigenschaften im Relaxor-Ferroelektrikum Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 , DPG-Frühjahrstagung 1999 33. R. Piechatzek, U. Dörfler, M. Imlau, V. Wirth, L. Bohaty, Th. Woike, T. Volk, R. Pankrath, M. Wöhlecke, Temperaturabhängigkeit der Holographischen Streuung im RelaxorFerroelektrikum Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce, DGK-Tagung 1999 34. O. F. Schirmer, Elektronen- und Loch-Polaronen in photorefraktiven Perovskiten (eingeladen), Seminar Freiburger Materialforschungszentrum, Freiburg/Bg., 21. 1. 2000 35. S. Lenjer, O. F. Schirmer, T. W. Kool, Ti3+ Jahn-Teller polarons in BaTiO3, 15th International Symposium on the Jahn-Teller Effect, Boston, 16. – 22. 8. 2000 36. O. F. Schirmer, Combined EPR/optical investigations of light-induced charge transfers in photorefractive materials (eingeladen), EMRS-Frühjahrstagung, Straßburg, 30. 6. – 2. 7. 2000 37. Rüdiger, O. F. Schirmer, S. Odoulov, S. Shumelyuk, A. Grabar, Studies of light-induced charge transfer in Sn2P2S6 by combined EPR/optical spectroscopy, EMRS – Frühjahrstagung, Straßburg, 30. 6. – 2. 7. 2000 38. O. F. Schirmer, Defects in oxide materials and their light-induced charge conversions, Workshop “Microstructure of oxide materials”, Universität Osnabrück, 13. – 15. 6. 2000 39. O. F. Schirmer, EPR/optische Simultan-Spektroskopie zur Aufklärung des lichtinduzierten Ladungstransports in oxidischen Perovskiten (eingeladen), Frühjahrstagung der DPG, Regensburg, 27. – 31. 3. 2000-08-24 40. G. I. Malovichko, V. G. Grachev, O. F. Schirmer, Charge transfer processes and photosensitive paramagnetic centers in barium calcium titanate, 14th International Conference on Defects in Insulating Materials, Johannesburg, 3. – 7. April 2000 41. V. G. Grachev, G. I. Malovichko, R. Pankrath, O. F. Schirmer, Photosensitive centers in barium titanate and barium calcium titanate crystals, 2nd International Symposium “Laser, Scintillator and Nonlinear Optical Materials”, Lyon, 28. – 31. 5. 2000 99 42. G. I. Malovichko, V. G. Grachev, O. F. Schirmer, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse, Light-induced electron and hole centers in barium calcium titanate crystals, 12th International Symposium on Integrated Ferroelectrics, Aachen, 12. – 15. 3. 2000 43. H.-J. Reyher, Magnetic Circular Dichroism and g-Values of Small Bound Hole Polarons in KTaO3 and in MgO. A Comparative Study, 14th International Conference on Defects in Insulating Materials, Johannesburg 2000 44. M. Colakoglu, P. Herth, M. Imlau, Th. Woike, M. Fally, R.A. Rupp, R. Pankrath und M. Wöhlecke, Holographische Streuung im Relaxor-Ferroelektrikum Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 dotiert mit Cer, DPG-Frühjahrstagung 2000 45. U. Dörfler, M. Imlau, Th. Woike, W. Kleemann, R. Pankrath und M. Wöhlecke, Holographische Messungen als Sonde für Domänendynamik und - Umklappprozesse in RelaxorFerroelektrika am Beispiel von dotiertem Strontium-Barium-Niobat, DPG-Frühjahrstagung 2000 46. T. Granzow, M. Imlau, Th. Woike, R. Pankrath, M. Wöhlecke und W. Kleemann, Einfluß von Pinning-Effekten auf die Dynamik ferroelektrischer Domänen im RelaxorFerroelektrikum Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 , DPG-Frühjahrstagung 2000 47. M. Colakoglu, U. Dörfler, M. Imlau, Th. Woike, M. Fally, R.A. Rupp, R. Pankrath und M. Wöhlecke, Holographische Streuung im Relaxor-Ferroelektrikum Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce, DGK-Tagung 2000 48. T. Granzow, M. Imlau, Th. Woike, W. Kleemann,R. Pankrath, M. Wöhlecke, Untersuchungen der Domänendynamik und Pinning-Effekte im Relaxor-Ferroelektrikum Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce, DGK-Tagung 2000 49. U. Dörfler, M. Imlau, Th. Woike, W. Kleemann, R. Pankrath, M. Wöhlecke, Die holographische Messmethode als Sonde für Domänendynamik und - Umklappprozesse in Relaxor-Ferroelektrika am Beispiel von Strontium-BariumNiobat dotiert mit Cer, DGK-Tagung 2000 100 3.5 Oberflächenphysik und Nanostrukturen (Heiland, Schleberger) 3.5.1 Forschungskooperationen AEG-Forschungslabor, Frankfurt D Arifof Institute of Electronics, Tashkent Uzbekistan ETH-Zürich CH Universität Osnabrück: Graduiertenkolleg: “Molekulare Physiologie: Wechselwirkungen zwischen zellulären Nanostrukturen“ D HMI Berlin D Hong Kong University of Science and Technology HK Humbold-Universität Berlin D Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Leuven BE Manne Siegbahn Institut, Stockholm SE Max Planck Institut für Festkörperphysik, Stuttgart D Max Planck Institut für Plasmaphysik Garching D Universität Osnabrück: International Graduate School “Synthesis and Characterisation of Surfaces and Interfaces assembled from Clusters and Molecules” D Technion, Haifa Israel Technische Universität Eindhoven NL Technische Universität Wien A Universidad del Pais Vasco San Sebastian S Universita di Firenze I Universita di Genova I Universität Bern CH Universität Braunschweig D Universität Clausthal-Zellerfeld D Universität Groningen, KVI Groningen NL Universität Linz A Universität Oldenburg D Universität Utrecht NL Universität Wien A Université Paris-Sud F Universitet Odense DK 101 3.5.2 Drittmittelakquisition THEORETISCHE UND EXPERIMENTELLE UNTERSUCHUNGEN VON ENERGIEVERLUSTUND LADUNGSAUSTAUSCHPROZESSEN AN OBERFLÄCHEN (A. Närmann) Zusammenarbeit mit P. Sigmund, Odense, F. Flores, Madrid, P. M. Echenique, San Sebastian Förderung: DFG 1991 - 1996 PLASMAÄTZEN VON POLYMEREN (W. Heiland) Förderung: Deutsche Telekom 1991 - 1996 DER ORDNUNGS-UNORDNUNGSÜBERGANG DER Pt(110) OBERFLÄCHE (W. Heiland) Förderung: DFG 1992 - 1997 INTERACTION OF SLOW HIGHLY CHARGED IONS WITH SURFACES (W. Heiland zusammen mit HMI Berlin u. a.) Koordinator: N. Stolterfoht Förderung: EU (Human Capital and Mobility) ERBCHRXCT 93-0103: 1993 - 1997 WECHSELWIRKUNG HOCHGELADENER IONEN MIT Al, Cu und Pt OBERFLÄCHEN (W. Heiland) Förderung: DFG 1994 - 1999 DISSOZIATION VON SCHNELLEN MOLEKÜLEN AN OBERFLÄCHEN VARIABLER AUSTRITTSARBEIT (W. Heiland) Förderung: DFG 1994 - 2000 CHARGE EXCHANGE PROCESSES AT SURFACES (W. Heiland zusammen mit Univ. Clausthal-Zellerfeld u. a.) Koordinator: V. Kempter Förderung: EU (Human Capital and Mobility) ERBCHRXCT 94-0571: 1994 - 1997 QUANTIFICATION OF SURFACE ANALYSIS BY LOW ENERGY ION SCATTERING (W. Heiland zusammen mit T. U. Eindhoven u. a.) Koordinator: H. Brongersma Förderung: EU (Human Capital and Mobility) ERBCHRXCT 94-0154: 1994 - 1997 STRUKTURUNTERSUCHUNGEN AN kfz (110) METALLOBERFLÄCHEN MIT RASTERTUNNELMIKROSKOPIE UND IONENSTREUUNG (W. Heiland) Förderung: DFG 1994 - 1998 IONEN-OBERFLÄCHEN WECHSELWIRKUNG (W. Heiland zusammen mit Univ. Madrid und Univ. San Sebastian) Förderung: DAAD (Acciones Integradas) 1994 - 1997 STRUKTURUNTERSUCHUNGEN AN Pd (111) UND Pd (110) MIT S UND K ADSORBATEN Förderung: DFG 1995 - 1999 WECHSELWIRKUNG SUPERTHERMALER MOLEKÜLE MIT FESTKÖRPEROBER-FLÄCHEN mit V. Ferleger und I. Wojciechowski, Arifov Institute of Electronics, Tashkent, Uzbekistan Förderung: BMBF 1996 - 1999 OBERFLÄCHENZUSAMMENSETZUNG KATALYTISCH WICHTIGER OXIDE UND LEGIERUNGEN - UNTERSUCHUNGEN MIT IONENSTRAHLEN UND ANDEREN OBERFLÄCHENMETHODEN mit E. Taglauer, MPI für Plasmaphysik und U. Bardi, Universität Florenz, Italien Förderung: DAAD VIGONI-Programm: 1997 – 1999 102 STREUUNG NIEDERENERGETISCHER HE-IONEN ZUR UNTERSUCHUNG MAGNETISCHER DÜNNER FILME UND OBERFLÄCHEN (Projektleiterin: M. Schleberger) Förderung: DFG: 1997 - .... ENERGIEVERLUSTE LANGSAMER IONEN UND ELEKTRONISCHE STRUKTUR VON METALLOBERFLÄCHEN Förderung: DFG 1998 - 2002 BILDUNG NEGATIVER MOLEKÜLIONEN BEI DER STREUUNG AN ISOLATOROBERFLÄCHEN Förderung: DFG 1998 - 2002 DIE STRUKTUR DER Pt3Sn(100) OBERFLÄCHE (Projektleiterin: S. Speller) Förderung: DFG 1998 - 2002 DER EINFLUSS VON STUFEN AUF DIE ELEKTRONISCHE UND GEOMETRISCHE STRUKTUR VON REINEN KUPFEROBERFLÄCHEN MIT KOBALT- UND CHROM- FILMEN (Projektleiterin: S. Speller) Förderung: DFG 1998 - 2002 ALENET: ESF NETWORK ON ELEMENTARY STEPS OF LAYER GROWTH IN THE FABRICATION OF NOVEL MATERIALS BY ATOMIC LAYER EPITAXY (Coordinator: U. Bardi, Florenz) Förderung: ESF 1998 - 2001 MAGNETISMUS UND STRUKTUR DÜNNER EISENFILME AUF SILIZIUMSUBSTRATEN (Projektleiterin: M. Schleberger) Förderung: DFG: 1998 - …. Research Collaboration with the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Förderung: DAAD 2000 - 2001 Vigoni – Projekt mit Genua DYNAMISCHE EIGENSCHAFTEN DER AG(110)- UND DER AL(110)-OBERFLÄCHE: UNTERSUCHUNGEN MIT IONENSTREUUNG UND DER STREUUNG THERMISCHER ATOME (Projektleiter: Werner Heiland) Förderung: DAAD 2000 - 2002 RASTERKRAFTMIKROSKOPIE AN BIOLOGISCHEN MATERIALIEN (Projektleiterinnen: S. Speller, M. Schleberger) Förderung: DFG Graduiertenkolleg 2000 – 2003 LADUNGSAUSTAUSCH UND GITTERFÜHRUNG VON FULLERENEN BEI DER STREUUNG AN OBERFLÄCHEN (Zusammenarbeit mit E. Kolodney, Technion, Haifa, Israel) Förderung: MWK Niedersachsen 2000 - 2001 103 3.5.3 3.5.3.1 Publikationstätigkeit Zeitschriftenaufsätze mit review-Prozess Chr. Schröder, W. Heiland, R. Held, W. Loose Analysis of reverse current-voltage characteristics of Ti/6H-SiC Schottky diodes Appl. Phys. Lett. 68 (1996) 1957 - 1959 I. Paulini, W. Heiland, A. Arnau, F. Zarate, P. Bauer Stopping cross sections of protons and deuterons in Lithiumniobate near the stopping power maximum Nucl. Instr. Meth. B118 (1996) 39-42 Thomas Schlathölter, Thorsten Schlathölter, M. Vicanek, W. Heiland Interaction of fast N2 molecules with palladium surfaces Surf. Sci. 352-354 (1996) 195-200 J. Kuntze, M. Huck, T. Rauch, J. Bömermann, S. Speller, W. Heiland The Pt(110) surface studied by STM and RHEED Surf. Sci. Lett. 355 (1996) L300-304 D. Fujita, M. Schleberger, S. Tougaard Extraction of depth distributions of electron-excited Auger electrons in Fe, Ni, and Si using inelastic peak shape analysis Surf. Sci. 357/358, (1996) 180-185 D. Fujita, M. Schleberger, S. Tougaard Estimation of excitation depth distribution from electron-excited Auger spectra of iron using peak shape analysis Surf. Interface Anal. 24, (1996) 211-216 M. Vicanek, T. Schlathölter, W. Heiland Scattering of fast H2 molecules from Pd(110) surfaces: Classical trajectories simulations Nucl. lnstr. Meth. B115 (1996) 206-210 S. Hausmann, C. Höfner, T. Schlathölter, H. Franke, A. Närmann, W. Heiland Energy loss of light ions scattered of Al(110) single crystal surfaces at low energy Nucl. Instr. Meth. B115 (1996) 31-33 N. Hatke, S. Hustedt, J. Limburg, I. G. Hughes, R. Hoekstra, W. Heiland, R. Morgenstern Energy loss of highly charged ions on an Al surface Nucl. lnstr. Meth. B115 (1996) 165-167 T. Schlathölter, H. Franke, M. Vicanek, W. Heiland The interaction of small molecules with Pd and K covered Pd surfaces at energies from 200eV to 6keV Surf. Sci. 363 (1996)79-84 J. Bömermann, M. Huck, J. Kuntze, T. Rauch, S. Speller, W. Heiland An STM, AES and LEED study of segregated sulfur on Pd(111) Surf. Sci. 357-358(1996)849-854 104 S. Speller, J. Kuntze, T. Rauch, J. Bömermann, M. Huck, M. Aschoff, W. Heiland The (1x2) and (1x4) structure on clean Pt(110) studied by STM, AES and LEED Surf. Sci. 366 (1996) 251-259 C. Nagl, E. Platzgummer, M. Schmid, P. Varga, S. Speller, W. Heiland Subsurface islands and superstructures of Cu on Pb(111) Surf. Sci. 352-354 (1996) 540-545 M. Schleberger, D. Fujita, S. Tougaard The characteristic depth of the excitation function for Auger electrons in Cu, Au, and Ag determined by inelastic background analysis J. Elec. Spec. 82, (1996) 173-178 A. Närmann, M. Schleberger, M. Dirska, J. Manske, G. Lubinski, R. Hoekstra Surface magnetism investigated by low energy ion scattering in the grazing incidence mode Surf. Rev. Lett., 4 (1996) 1039-1042 M. Schleberger, A. Cohen Simonsen, S. Tougaard, J. L. Hansen, A. N. Nylandsted Ge growth on Si(001) studied by XPS peak shape analysis and AFM J. Vac. Sci. Techn. A 15 (1997) 3032 N. Hatke, M. Dirska, M. Grether, E. Luderer, A. Robin, A. Närmann, W. Heiland Surface channeling experiments at 20 MeV and resonant coherent excitation of N6+ ions Phys. Rev. Lett. 79 (1997) 3395-3398 S. Speller, M. Schleberger, W. Heiland Structural studies of the Pb(110) surface with ISS and RHEED Surf. Sci. 380 (1997) 1-8 S. Speller, S. Parascandola, W. Heiland Structural parameters of Pd(110) and Pt(110)(1x2) in the temperature range of 300 K to 900 K studied by low energy ion scattering Surf. Sci. 383 (1997) 131-136 Thomas Schlathölter, Thorsten Schlathölter, M. Vicanek, W. Heiland Scattering of fast N2 from Pd(111): A classical trajectory study Chem. Phys. 106 (1997) 4723-4733 M. Vicanek, T. Schlathölter, W. Heiland Molecule scattering from solid surfaces: Orientation and corrugation effects Nucl. Instr. Meth. B125 (1997) 194-200 H. H. Khemliche, J. Limburg, R. Hoekstra, R. Morgenstern, N. Hatke, E. Luderer, W. Heiland I. Energy loss and charge state distribution of N6,7+ ion Al(110) surface collisions Nucl. Instr. Meth. B125 (1997) 116-119 Thomas Schlathölter, Martin Vicanek, W. Heiland Scattering of fast N2 from Pd(111): Orientational influences on the interaction dynamics Rad. Eff. Def. in Solids 141 (1997) 175-184 105 J. Kuntze, J. Bömermann, T. Rauch, S. Speller, W. Heiland Surface reconstruction of the Ir(110) - surface Surf. Sci. 394 (1997) 150-158 R. Hoekstra, J. Manske, M. Dirska, G. Lubinski, M. Schleberger, A. Närmann Circular polarized photon emission spectroscopy of keV ion scattering off (un-) magnetized surfaces Nucl. Instr. Methods B 125 (1997) 53-58 J. Manske, M. Dirska, G. Lubinski, M. Schleberger, A. Närmann, R. Hoekstra Surface magnetism studied by polarized light emission after He+ scattering J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 168 (1997) 249-256 M. Schleberger, M. Dirska, J. Manske, A. Närmann Measuring hysteresis of magnetic surfaces by ion scattering Appl. Phys. Lett. 71 (1997) 3156-3158 M. Schleberger, A. Cohen Simonsen, S. Tougaard, J. L. Hansen, A. N. Nylandsted Ge growth on Si(001) studied by XPS peak shape analysis and AFM Vac. Sci. Tech. A 15 (1997) P. Walser, M. Schleberger, P. Fuchs, M. Landolt Heat Induced Antiferromagnetic coupling in Multilayers with Ge Spacers Phys. Rev. Letters 80 (1998) 2217-2220 N. Hatke, M. Dirska, E. Luderer, A. Robin, M. Grether, A. Närmann, W. Heiland Energy loss and resonant coherent excitation of fast highly charged ions on a Pt(110)-surface Nucl. Instr. Meth. B135 (1998) 307-313 A. Närmann, M. Dirska, J. Manske, G. Lubinski, M. Schleberger, R. Hoekstra Spin-elective electron capture into excited states as a probe to investigate magnetic surfaces Surf. Sci. 398 (1998) 84-90 G. Piaszenski, M. Aschoff, S. Speller, W. Heiland Structure evaluation of an alloy single crystal surface, Au3Pd(113), by low energy ion scattering Nucl. Instr. Meth. B135 (1998) 331-335 A. Närmann, M. Dirska, J. Manske, M. Schleberger Probing of magnetic surfaces with inherent monolayer sensitivity by ion scattering Nucl. Instr. Meth. B136-138 (1998) 1212-1217 M. Aschoff, G. Piaszenski. S. Speller, W. Heiland The structure of the Au3Pd(113)-surface studied by low energy ions scattering Surf. Sci. 402-404 (1998) 770-773 K. Brüning, J. Granow, M. Reiniger, W. Heiland, M. Vicanek, T. Schlathölter Dissociation of fast N2 – Molecules at a Pd(110) Surface Surf. Sci. 402-404 (1998) 215-218 106 J. Kuntze, S. Speller, W. Heiland The Ir(110)-Surface studied by STM Surf. Sci. 402-404 (1998) 764-769 H. H. Brongersma, M. Carrere-Fontaine, R. Cortenrad, A. W. Denier van der Gon, P. J. Scanlon, I. Spolveri, B. Cortigiani, U. Bardi, E. Taglauer, S. Reiter. S. Labich, P. Bertrand, L. Houssiau, S. Speller, S. Parascandola, H. Ünlü-Lachnitt, W. Heiland A round robin experiment of elemental sensitivity factors in low-energy ion scattering Nucl. Instr. Meth. B142 (1998) 377-386 I. A. Wojciechowski, V. Kh. Ferleger, M. V. Medvedeva, M. Vicanek, K. Brüning, W. Heiland Electronic processes in molecule-surface scattering Nucl. Instr. Meth. B140 (1998) 265-272 I. A. Wojciechowski, M. B. Medvedeva, V. Kh. Ferleger, K. Brüning, W. Heiland The broadening of energy spectra of atoms by a solid surface under molecular ion bombardment Nucl. Instr. Meth. B143 (1998) 473 (1998) 473-478 J. Limburg, C. Bos, T. Schlathölter, R. Hoekstra, R. Morgenstern, S. Hausmann, W. Heiland, A. Närmann Energy loss of keV He2+ scattered off an Al(110) surface Surf. Sci. 409 (1998) 541-552 M. Aschoff, S. Speller, J. Kuntze, W. Heiland, E. Platzgummer, M. Schmidt, P. Varga, B. Baretzky Unreconstructed Au(100) monolayers on a Au3Pd(100) surface Surf. Sci. Lett. 415 (1998) L1051-L1054 J. Kuntze, S. Speller, W. Heiland, A. Atrei, I. Spolveri, U. Bardi Reconstruction and dislocation network formation of the (111) surface of the ordered alloy Pt3Sn Phys. Rev. B 58 (1998) R16005-16008 C. Höfner, A. Närmann Stopping of low energy ions at metal surfaces Appl. of Accelerators in Res. and Ind., ed by J. L. Duggan and I. L. Morgan Academic Press, N. Y. (1998) 1381-1384 S. Speller, S. Degroote, J. Dekoster, G. Langouche, J. E. Ortega, A. Närmann Low temperature deposition of Co on Cu(111): effects on step etching Surf. Sci. Lett. 405 (1998) L542-L548 A. Cohen Simonsen, M. Schleberger, S. Tougaard, J. L. Hansen, A. Nylandsted Larsen Nanostructure of Ge deposited on Si (001): A Study by XPS peak shape analysis and AFM Thin solid films 338 (1999) 165-171 M. Hoheisel, J. Kuntze, S. Speller, A. Postnikov, W. Heiland, I. Spolveri, U. Bardi Metastable and equilibrium structures on Pt3Sn(100) studied by STM, RHEED, LEED and AES, Phys. Rev. B60 (1999) 2033-2039 107 S. Speller, M. Aschoff, J. Kuntze, A. Atrei, U. Bardi, E. Platzgummer, W. Heiland The Au3Pd(001) Surface Studied by Ion Scattering and LEED Surf. Rev. Letters 6 (1999) 829-833 J. Kuntze, S. Speller, W. Heiland, A. Atrei, G. Rovida, U. Bardi Surface structure and composition of the alloy Au3Pd(100) determined by LEED and ISS Phys. Rev. B 60 (1999) 1535-1538 J. Scheer, K. Brüning, T. Fröhlich, P. Wurz, W. Heiland Scattering of small molecules from a diamond surface Nucl. Instr. Meth. B157 (1999) 208-212 N. Hatke, A. Robin, M. Grether, A. Närmann, W. Heiland Scattering of multiply charged ions from surfaces Int. J. Mass Spectrometry 192 (1999), 393-405 J. Kuntze, S. Speller, W. Heiland, P. Deurinck, C. Creemers, A. Atrei, U. Bardi Surface structure and segregation profile of the alloy Au3 Pd(110): Experiment and theory Phys. Rev. B60 (1999) 9010-9018 S. Speller, T. Rauch, J. Bömermann, P. Borrmann, W. Heiland Surface structures of S on Pd(111) Surf. Sci. 441 (1999) 107-116 M. Schleberger, P. Walser, M. Hunziker, M. Landolt Amorphous Fe-Si and Fe-Ge nanostructures quantitatively analyzed by x-ray-photoelectron spectroscopy Phys. Rev. B 60 (1999) 14360-14365 M. Schleberger, P. Walser, M. Hunziker, M. Landolt Amorphous Te-Si and Te-Ge nanostructures quantitatively analyzed by x-ray- photoelectron spectroscopy Phys. Rev. B60 (1999) 14360-14365 M. Schleberger Quantitative Investigation of Amorphous Fe/Ge and Fe/Si by Inelastic Peak Shape Analysis Surf. Sci. 445 (2000) 71-79 R. Vollmer, S. van Dijken, M. Schleberger, and J. Kirschner Dependence of the Curie temperature on the Cu cover layer in x-Cu/Fe/Cu(001) sandwiches Phys. Rev. B 61 (2000) 1303-1310 S. Speller, T Rauch, A. Postnikov, W. Heiland Scanning tunneling microscopy and spectroscopy of S on Pd(111) Phys. Rev. B61 (2000) 7297-7300 A. Robin, N. Hatke, A. Närmann, M. Grether, D. Plachke, J. Jensen, W. Heiland Energy loss of fast Nq+ ions scattered off a Pt(110) surface Nucl. Instr. Meth. B164-165 (2000) 566-574 A. Wojciechowski, M. B. Medvedeva, K. Kh. Ferleger, K. Brüning, W. Heiland 108 Dissociative scattering of H2+ on metal surfaces: Analysis of the high-energy parts of the spectra of scattered molecule constituents Nucl. Meth. B164-165 (2000) 626-632 L. Pedemonte, M. Aschoff, K. Brüning, R. Tatarek, W. Heiland Surface structure and surface dynamics analysis of the Ag(110)-surface by low energy on ion scattering NucI. Instr. Meth. B164-165 (2000) 645-649 K. Sekar, B. Sundaravel, I. H. Wilson, W. Heiland Scanning tunneling microscopy and ion channeling studies on thin Co films on bromine treated Si(100) surfaces Appl. Surf. Sci. 156 (2000) 161-168 J. Kuntze, S. Speller, W. Heiland Adsorbate-induced reconstruction and overlayer structures of sulfur on Ir(110): An STM study Phys. Rev. B62 (2000) 4681-4685 K. Brüning, W. Heiland, T. Schlathölter, I. A. Wojciechowski. M. B. Medvedeva, V. Kh. Ferleger Dissociation of fast N2 - molecules scattered from different fcc(110) surfaces J. Chem. Phys. 113 (2000) 2456-2469 Bo-Rong Shi, N. Cue, Ke-Ming Wang, D. Fink, M. Müller, W. Heiland Three-dimensional range distributions of 400 keV Nd ions implanted into Si Radiation Effects & Defects in Solids,152 (2000) 295-305 T. Schlathölter, A. Närmann, A. Robin, D. F. A. Winters, S. Marini, R. Morgenstern, R. Hoekstra Sputtering of hollow atoms from carbon surfaces Phys. Rev. A 6204 (2000) 2901 I. A. Voitsekhovsky, M. V. Medvedeva, F. K. Ferleger, K. Brüning, W. Heiland Broadening of energy spectra of atoms scattered by the surface of solid at molecular bombardment Izv. Akad. Nauk Ser. Fiz. 64 (2000) 653-657 E. Ortega, S. Speller, A. R. Bachmann, A. Mascaraque, E. G. Michel, A. Närmann, A. Mugarza, A. Rubio, F. J. Himpsel The electron wave function at a vicinal surface: Switch from terrace to step modulationPhys. Rev. Letters, 84 (2000) 6110 K. Sekar, J. Scheer, K. Brüning, W. Heiland Interaction of molecular hydrogen with LiF(100) surface Phys. Rev. B 63, (2001) 045411-1-6 S. Jans, P. Wurz, R. Schletti, K. Brüning, K. Sekar, W. Heiland, J. Quinn, R. E. Leuchtner Scattering of Atoms and Molecules off a Barium Zirconate Surface Nucl. lnstr. Meth. B173 (2001) 503-515 109 L. Pedemonte, G. Bracco, R. Tatarek, M. Aschoff, K. Brüning, W. Heiland The Ag(110) thermal disordering mechanism studies by low-energy ion scattering Surf. Sci. (2001) in press M. Hoheisel, S. Speller, J. Kuntze, U. Bardi, W. Heiland The structure of Pt3Sn (110) studied by scanning tunneling microscopy Phys. Rev. B63 (2001) 245403-1-7 K. Brüning, T. Schlathölter, W. Heiland Molecule dissociation at low energies on Pt(110) Nucl. Instr. Meth. B in press J. E. Ortega, A. Mugarza, A. Närmann, A. Rubio, S. Speller, A. R. Bachmann, J. Lobo, E. G. Michel, F. J. Himpsel Transition from terrace to average-surface modulation of the surface state wave function at vicinal (Cu(111) Surf Sci., accepted A. R. Bachmann, A. Mugarza, J. E. Ortega, S. Speller One-dimensional Ag-Cvu superlattices on vicinal Cu(111) Phys. Rev B. accepted 3.5.3.2 Review-articles und invited papers A. Arnau, F. Aumayr, P. M. Echenique, M. Grether, W. Heiland, review J. Limburg, R. Morgenstern, P. Roncin, S. Schippers, R. Schuch, N. Stolterfoht, P. Varga, T. J. M. Zouros, H. P. Winter Interaction of slow multicharges ions with solid surfaces Surf. Sci. Reports 27 (1997) 113-239 W. Heiland, M. Aschoff, S. Speller invited Low energy ion scattering analysis of metal alloy surfaces, page 251-256 (1998) Proc. of the Int. Symp. on Atomic Level Characterization, Maui, Hawaii, U.S.A., Nov. 2328,1997, The Microbeam Analysis 141 Comm. of Japan Soc. for the Promotion of Science M. Schleberger, S. Speller, W. Heiland Surface Characteristion Methods in Experimental Physics, vol. 30 (1998) 291-327 review W. Heiland, K. Brüning, M. Aschoff invited Surface Analysis using Low Energy Ion Beams Proc. of the 8th Int. Workshop on Ion Beam Surface Diagnostics, Uzhgorod, Ukraine (1998) 5-8 A. R. Bachmann, S. Speller, J. Manske, M. Schleberger, A. Närmann, W. Heiland Structural and Magnetic Properties of Co-Cu Film Systems The Physics of Low Dimensional Systems, Ed.: J. L. Moran - Lopez (Kluiwer Academic/Plenum Press, New York, 2001) 265-272 invited S. Speller, W. Heiland and M. Schleberger review 110 Surface Characterisation: Composition, Structure and Topography Handbook of Surface Science, Ed.: S. Nalwa (Academic Press, New York 2001) 3.5.3.3 Zeitschriftenaufsätze und Beiträge ohne review-Prozess M. Dirska, J. Manske, G. Lubinski, M. Schleberger, R. Hoekstra, A. Närmann Ion scattering off magnetic surfaces AIP Conf. Proc. 392 (1997) 1381 C. Höfner, A. Närmann Stopping of Low energy ions at metal surfaces AIP Conf. Proc. 392 (1997) 269 P. Segovia, A. Mascaraque, E. G. Michel, A. Närmann, J. E Ortega Photoemission cross section effects in quantum well states of Cu thin films deposited on Co(100) Jahresbericht 1997, Hasylab (DESY), Hamburg (1998) P. Wurz, T. Fröhlich, K. Brüning, J. Scheer. W. Heiland, E. Hertzberg, S. Fuselier Formation of Negative ions by Scattering from a Diamond (111) Surface Proc. Week of Postdoc. Students (1998) (eds. J. Safrankov and A. Kanka), Charles University Prague, Czech Republick (1998) 257-272 A. Bachmann, S. Speller, T. Rauch, A. Masquaraque, A. Tejeda, E. Michel, H. Höchst, F. J. Himpsel, A. Närmann, J. Ortega Low-dimensional electronic states on vicinal Cu(111) Hasylab Annual Report 1998 http:/www-hasylab.desy.de/science/annual_reports/1998/index.html K. Brüning, J. Granow, T. Schlathölter, W. Heiland Surface channeling and dissociation of small molecules 3S’98 Park City, Utah, USA J. E. Ortega, A. Mugarza, A. R. Bachmann, S. Speller, A. Närmann, J. Lobo, E. G. Michel The electron wave function at a vicinal surface: mixed terrace/average-surface behaviour in Cu(10 10 13) Hasylab Annual Report 1999 http:/www-hasylab.desy.de/science/annual_reports/1999_report/ A. R. Bachmann, A. Mugarza, F. Ostendorf, S. Speller, J. Lobo, E. G. Michel, J. E. Ortega Ag on vicinal Cu(111) surface states and LEED Hasylab Annual Report 2000 http:/www-hasylab.desy.de/science/annual_reports/2000_report/ . 111 3.6 Umweltphysik-Prozessstudien (Rühl) 3.6.1 Forschungskooperationen 3.6.1.1 Hochschule Name Institution Thema Prof. Dr. M. Fachbereich Physik Untersuchungen zur RamanWöhlecke Spektroskopie Prof. Dr. W. Hei- Fachbereich Physik Deponierte Cluster land Prof. Dr. W. Ibel Fachbereich Physik Experimente zur Neutronenkleinwinkelstreuung Prof. Dr. H. Reu- Fachbereich Biolo- Charakterisierung von metallter gie/Chemie organischen Verbindungen Prof. Dr. R. Fachbereich Biolo- Untersuchungen zur RamanBlachnik gie/Chemie Spektroskopie Dr. A. Lipski Fachbereich Biolo- Charakterisierung von Baktegie/Chemie rien mit Lichtstreuung Prof. Dr. M. Institut für AngeAbbau von schwerflüchtigen Matthies wandte Systemwis- Umweltchemikalien senschaft 3.6.1.2 2001 1999 1999 1999 2000 2000 Regional Name Institution Thema Prof. Dr. C. Zetzsch Abbau Persistenter Umwelchemikalien (Forschungsverbund) Prof. Dr. H. Willner FraunhoferInstitut für Toxikologie und Aerosolforschung, Hannover Universität Duisburg Prof. Dr. J. Bleck-Neuhaus Universität Bremen 3.6.1.3 Zusammenarbeit seit 1999 Charakterisierung atmosphärischer Moleküle Entwicklung von Messverfahren zu UmweltProzessstudien Zusammenarbeit seit 2000 1988 2000 National Name Dr. Th. Möller Prof. Dr. K. Rademann Institution Thema Zusammenarbeit seit HASYLAB am Rumpfniveauanregung 1996 DESY von Clustern (Forschungsverbund) Humboldt UniÜbergangsmetall1996 versität zu Berlin Schwefel-Cluster (For- 112 schungsverbund) Prof. Dr. W. Humboldt UniÜbergangsmetallSauer versität zu Berlin Schwefel-Cluster (Forschungsverbund) Prof. Dr. H. Technische Uni- ÜbergangsmetallSchwarz versität Berlin Schwefel-Cluster (Forschungsverbund) Prof. Dr. H. Freie Universität Levitierte Baumgärtel Berlin Aerosole/Interstellare Moleküle Prof. Dr. L. Wös- Freie Universität Levitierte Aerosole te Berlin Prof. Dr. Th. TU Ilmenau Levitierte Aerosole Leisner Prof. Dr. K.-H. Universität Forschungsverbund Meiwes-Broer Rostock zur Nutzung des Freien-ElektronenLasers (TESLA) Prof. Dr. G. Gan- Universität Kon- Forschungsverbund teför stanz zur Nutzung des Freien-ElektronenLasers (TESLA) Prof. Dr. W. BESSY (Berlin) Forschungsverbund Eberhardt zur Nutzung des Freien-ElektronenLasers (TESLA) Prof. Dr. D. Ger- TU Chemnitz Forschungsverbund lich zur Nutzung von Synchrotronstrahlung Prof. Dr. U. Be- Fritz-HaberForschungsverbund cker Institut der MPG, zur Nutzung von SynBerlin chrotronstrahlung Prof. Dr. W. Max-BornForschungsverbund Widdra Institut, Berlin zur Nutzung von Synchrotronstrahlung Prof. Dr. S. Universität Entwicklung von Borrmann Mainz Feldmessverfahren für die Atmosphärenforschung Prof. Dr. E. IlFU Berlin Elektronenanlagerung lenberger an atmosphärische Moleküle 1996 1996 1983 1994 1994 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 2001 2000 1992 113 3.6.1.4 International Name Institution Prof. Dr. P.A. Dowben Prof. Dr. J.J. Neville University of Nebraska, U.S.A. University of New Brunswick, Kanada McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Kanada KVI Groningen, Niederlande Prof. Dr. A.P. Hitchcock Prof. Dr. R. Morgenstern Dr. C.-M. Teodorescu Prof. Dr. A.A. Pavlychev Prof. Dr. N. Kosugi Prof. Dr. I.T. Steinberger Prof. Dr. S. Leach Prof. Dr. D.N. McIlroy 3.6.2 Thema Oberflächenphysik, Clusterphysik RumpfniveauAnregung von Clustern Rumpfniveauanregung von Atomen, Molekülen, Clustern und Adsorbaten Ladungsaustausch von hochgeladenen Ionen mit Clustern LURE, Orsay, Innerschalenanregung Frankreich von Clustern St. Petersburg Innerschalenanregung State University, von Atomen, MoleküSt. Petersburg, len, Clustern, AdsorRußland baten Institute for Mo- Innerschalenanregung lecular Science, von Molekülen und Okazaki, Japan Clustern Hebrew Univer- Innerschalenanregung, sity, Jerusalem, Photoleitfähigkeit Israel Observatoire de Interstellare Moleküle Paris-Meudon, Frankreich University of Innerschalenanregung Idaho, Moscow von Clustern Zusammenarbeit seit 1990 1999 1988 1999 1996 1993 1996 1995 1987 1994 Drittmittelakquisition Thema Förderperiode Institution Photoprozesse atomsphärischer Radikale Metall/NichtmetallÜbergang Rumpfniveauanregung von Clustern Untersuchung der physikalischen und chemischen Eigenschaften von klimarelevanten Aerosolen in einerelektrodynamischen Falle Photoreaktionen stratosphärischer Moleküle und Radikale 1996-1997 Personal- akquirierte mittel* Mittel in DM 30.000,- 1993-1997 Zentrum für Umweltfor- schung Rheinland-Pfalz 1 NSF (USA) 2 - 1993-1997 NATO 3 - 28.000,- ** 1994-1996 Freie Universität Berlin 4 2 406.500,- 1997-2000 BMBF im Ozonforschungs- 1 programm 302.552,- 40.000,-** 114 Ramanspektrometer Lasersystem Physikalische und chemische Eigenschaften atmosphärischer Aerosole Größenabhängige Eigenschaften von freien Übergangsmetall-SchwefelClustern Experimentelle und theoretische Untersuchungen zur Innerschalenanregung von Atomen, Moleülen, Clustern und Adsorbaten Photoinduzierte Bildung atmosphärischer Radikale 1997/1998 1998 1998-2001 1996-2001 3.6.2.1 * 1 443.660,80 267.999,68 198.003,- 1 338.456,- 1996-2000 DFG (Az: 436/RUS/113/339/(R)) 17.000,- ** 1999-2002 Deutsche Bundesstiftung 1 Umwelt (DBU) im Stipendienprogramm 6 Studienmission der Arabi- 1 schen Republik Ägypten 7 Umweltbundesamt (UBA) 1 im UFOPLAN (Az:200 67 406/02) 159.000,- ** Graduiertenkolleg „Nichtli- 2 nearitäten optischer Materialien“ der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) Promotionsprogramm des 1 Landes Niedersachsen 230.000,- 2001-2004 BMBF im Rahmen der Ver- 1 bundforschung (Forschung mit Synchrotronstrahlung; Az: KAIS05014100) 393.900,- 2001-2004 BMBF im Rahmen der Ver- 1 bundforschung (Forschung mit Synchrotronstrahlung) 8 985.500,- 2001/2002 2001-2004 HBFG 5, 9 DFG: Hochaufgelöste Inner- 1 schalenanregung der Rumpfniveaus von Atomen, Molekülen, Clustern und Adsorbaten (Az: RU 420/51) 9 399.950,352.000,- ** Physical Properties of At- 2000-2003 mospheric Aerosols Aufbau eines Messverfah- 2000-2002 rens zum photooxidativen Abbau von semivolatilen Pflanzenschutzmitteln und POPs an levitierten Einzelpartikeln Nichtlinearitäten optischer 2001-2004 Materialien Synthesis and Characterization of Surfaces and Interfaces assembled from Clusters and Molecules Aufbau und Test eines Messstandes zur Untersuchung gespeicherter Nanopartikel mit Synchrotronstrahlung Aufbau und Charakterisierung eines Experimentes am Freien Elektronenlaser zur Untersuchung größenabhängiger Eigenschaften von selektierten Clusterionen Toroidgittermonochromator Untersuchungen zur hochaufgelösten Rumpfniveauanregung von Atomen, Molekülen, Clustern und Adsorbaten HBFG (MRS/64) 5 HBFG (LSR/64) 5 BMBF im Aerosolforschungsprogramm (Az: 07AF216/0) DFG (Az: RU420-4) 2001-2004 200.000,- ** 115.775,- 180.000,- ** Anmerkungen Anzahl der eingeworbenen Stellen. Geschätzte Gesamtmittel (bei ausländischen Projekten bei derzeitigem Wechselkurs, Ansatz enthält auch Personal- bzw. Reisemittel). 1 Mittelverwaltung durch die Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz. 2 Mittelverwaltung durch die University of Nebraska at Lincoln (U.S.A.). ** 115 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 3.6.3 Mittelverwaltung durch die McMaster University (Hamilton, Ont., Kanada). Mittelverwaltung durch die Freien Universität Berlin. Ausstattungsmittel des Bereichs Umweltphysik. Stipendiat: Jürgen Plenge. Stipendiatin: Mariam Hamza. Mittelverwaltung des Verbundes durch die Universität Rostock. Antrag ist zurzeit in der Begutachtung. Betrag bezieht sich auf die beantragten Mittel. Technologie- und Wissenstransfer Anzahl und Art der Beratungen, Gutachten, Diplom- und Doktorarbeiten für Wirtschaft, Verwaltung, Politik Jahr 1996/1997 Leistung Gutachter 1996 Gutachter Seit 1996 1997-2001 Gutachter Gutachter 1998 Beratung zur Meteorologie Gemeinsame Betreuung der Diplomarbeit von Herrn Olaf Müller Gutachter 1998/99 Seit 1999 2000 2000 2000 2000 2000 2001 2001 2001 Firma/Institution Arbeitsgruppe für innovative Projekte beim Ministerium für Wissenschaft und Kultur des Landes Niedersachsen (AGIP) BMBF (Ozonforschungsprogramm) BESSY GmbH (Strahlzeitkomitee) Forschungsprogramme der Deutschen Bundesstiftung Umwelt (DBU) im Rahmen des Stipendienprogramms und des Programms ‚Atmosphärische Diagnostik’ Neue Osnabrücker Zeitung Siemens AG - Regensburg LURE (Frankreich, Strahlzeitkomitee) Beitrag zur Hannover Hannover Messe Messe 2000 Gutachter BMBF (Atmosphärenforschungsprogramm 2000) Beratung zur UmCIBA Specialty Chemicals weltverträglichkeit von Chemikalien Gutachter BMBF (Verbundforschung mit Synchrotronstrahlung) Gutachter German-Israeli Foundation (GiF) Beratung und KonSchoeller, Osnabrück taktvermittlung Optimierung von Harting, Espelkamp Steckkontakten Gutachter INFM Research Management, Genova, Italien 116 117 3.6.4 Publikationstätigkeit 3.6.4.1 Zeitschriftenaufsätze mit Peer Review-Prozeß 1. M. Schwell, H.-W. Jochims, B. Wassermann, U. Rockland, R. Flesch und E. Rühl "Ionization Energies of ClO and Cl2O2" J. Phys. Chem. 100, 10070 (1996). 2. E. Rühl und H.-W. Jochims "Core Excitation in Molecules: Formation of Cations and Anions" Z. Phys. Chem. 195, 137 (1996). 3. E. Rühl, A. Knop, A.P. Hitchcock, P.A. Dowben und D.N. McIlroy "Core Excitation in Free Clusters: Ionization, Relaxation and Fragmentation" Surf. Rev. Lett. 3, 557 (1996). 4. P.A. Dowben, D.N. McIlroy, J. Zhang und E. Rühl "When are Thin Films of Metals Metallic? Part III" Materials Science and Engineering B 217/218, 258 (1996). 5. B. Krämer, M. Schwell, O. Hübner, H. Vortisch, T. Leisner, E. Rühl, H. Baumgärtel und L. Wöste "Homogeneous Ice Nucleation Observed in Single Levitated Micro Droplets" Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 100, 1911 (1996). 6. S. Kakar, O. Björneholm, J. Weigelt, A.R.B. de Castro, L. Tröger, R. Frahm, T. Möller, A. Knop und E. Rühl "Size-Dependent K-Edge EXAFS Study of the Structure of Free Ar Clusters" Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1675 (1997). 7. A.P. Hitchcock, S.G. Urquhart, A.T. Wen, A.L.D. Kilcoyne, T. Tyliszczak, E. Rühl, N. Kosugi, J.D. Bozek, J.T. Spencer, D.N. McIlroy und P.A. Dowben "Inner-Shell Excitation Spectroscopy of Closo-Carboranes" J. Phys. Chem. B 101, 3483 (1997). 8. H.W. Jochims, E. Rühl, H. Baumgärtel, S. Tobita und S. Leach "VUV Peaks in Absorption Spectra and Photoion Yield Curves of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Compounds" Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Proc. 167/168, 35 (1997). 9. A. Knop, B. Wassermann und E. Rühl "Site-Specific Excitation in Free Krypton Clusters" Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 2302 (1998). 10. C.-M. Teodorescu, D. Gravel, E. Rühl, T.J. McAvoy, J. Choi, D. Pugmire, P. Pribil, J. Coos und P.A. Dowben "Retractable Miniature Double Pass Cylindrical Mirror Analyzers" Rev. Sci. Instrum. 69, 3805 (1998). 11. A.A. Pavlychev, N.G. Fominykh, I.T. Steinberger, S. Rabe, B. Wassermann, D. Gravel, C.M. Teodorescu und E. Rühl "Effect of Cluster Size on Inner Valence-Shell Excitations in Free Atomic Clusters" Surface, Russ. Akad. Nauk 8/9, 97 (1998). 12. C.M. Teodorescu, D. Gravel und E. Rühl "S 2p Excitation and Fragmentation of Sulfur Aggregates" J. Chem. Phys. 109, 9280 (1998). 13. B. Steiner, B. Berge, R. Gausmann, J. Rohmann und E. Rühl 118 "A Fast in-situ Sizing Technique for Single Levitated Liquid Aerosols" Appl. Opt. 38, 1523 (1999). 14. E. Rühl, U. Rockland, H. Baumgärtel, O. Lösking, M. Binnewies und H. Willner "Photoionization Mass Spectrometry of Chlorine Oxides" Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 185-187, 545 (1999). 15. C.-M. Teodorescu, D. Gavel, J. Choi, D. Pugmire, P.A. Dowben, N. Fominykh, A.A. Pavlychev und E. Rühl "Inner-Shell Excitation and Fragmentation of Sulfur Aggregates" J. El. Spectroscop. Relat. Phenom. 101-103, 193 (1999). 16. I.T. Steinberger, B. Wassermann, C.-M. Teodorescu, D. Gravel, R. Flesch, G. Reichardt, C.W. Hutchings, A.P. Hitchcock und E. Rühl "Resonant Excitation Series at the Kr 3p and Xe 4p Thresholds" Phys. Rev. B 60, 3995 (1999). 17. G. Senn, H. Drexel, G. Marston, N.J. Mason, T.D. Märk, M. Meinke, C. Schmale, E. Rühl und E. Illenberger "Low Energy Dissociation of OClO Following Electron Capture" J. Phys. B 32, 3615 (1999). 18. B. Krämer, M. Schwell, O. Hübner, H. Vortisch, E. Rühl, H. Baumgärtel, L. Wöste und T. Leisner "Homogeneous Nucleation Rates of Supercooled Water Measured in Single Levitated Microdroplets" J. Chem. Phys. 111, 6521 (1999). 19. P.M. Pachomov, B. Steiner, S.D. Chijnyak, E.W. Kruglova und E. Rühl "Application of Raman Spectroscopy to Studies of Nodes in Physical Networks of Polyethylene Gels" Fiziko-Khimija Polimerov (Russ.), Special Issue on Physical Chemistry of Polymers, Twer State University, 1999, S. 10. 20. R. Flesch, M.C. Schürmann, J. Plenge, M. Hunnekuhl, H. Meiss, M. Bischof und E. Rühl "Absolute Photoionization Cross Sections of the Primary Photofragments of Chlorine Dioxide and Dichlorine Monoxide" Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1, 5423 (1999). 21. B. Berge, K. Sudholz, B. Steiner, J. Rohmann und E. Rühl "In Situ Size Determination of Single Levitated Solid Aerosols" Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1, 5485 (1999). 22. A.A. Pavlychev und E. Rühl "Dynamic Localization of Inner-Shell Excitations in Free Atomic and Molecular Clusters" J. Electron Spectroscop. Relat. Phenom. 106, 207 (2000). 23. R. Flesch, M.C. Schürmann, M. Hunnekuhl, H. Meiss, J. Plenge und E. Rühl "A Pump-Probe Photoionization Mass Spectrometer Utilizing Tunable XUV-LaserProduced-Plasma-Radiation" Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71, 1319 (2000). 24. H. Vortisch, B. Krämer, M. Schwell, I. Weidinger, H. Baumgärtel, L. Wöste , T. Leisner, M. Schwell, H. Baumgärtel und E. Rühl "Homogeneous Freezing Nucleation Rates and Crystallization Dynamics of Single Levitated Sulfuric Acid Aerosols" Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2, 1407 (2000). 119 25. R. Flesch, H.-W. Jochims, J. Plenge und E. Rühl "Time-Resolved UV/VIS-Fluorescence of 2p-Excited Argon" Phys. Rev. A 62, 62504 (2000). 26. M. Schwell, H. Baumgärtel, I. Weidinger, B. Krämer, H. Vortisch, L. Wöste und T. Leisner und E. Rühl "Uptake Dynamics and Diffusion of HCl in Sulfuric Acid Solution Measured in Single Levitated Microdroplets" J. Phys. Chem. 104, 6726 (2000). 27. R. Ratheesh, M. Wöhlecke, B. Berge, Th. Wahlbrink, H. Haeusler, E. Rühl, R. Blachnik, P. Balan, N. Santha und M.T. Sebastian "Comparative Raman Study of the Tilting and Ordering in Sr(B0.5Nb0.5)O3 Compounds" J. Appl. Phys. 88, 2813 (2000). 28. R. Flesch, M-.C. Schürmann, H. Meiss, J. Plenge, M. Hunnekuhl und E. Rühl "Autoionization and Photoionization of O(1D)" Phys. Rev. A 62, 52723 (2000). 29. E. Rühl, R. Flesch, W. Tappe und A.A. Pavlychev "Progress on Inner-Shell Excitations of Molecular Van der Waals Clusters" J., Synchrotron Radiat. 8, 154 (2001). 30. R. Flesch, A.A. Pavlychev, J.J. Neville, J. Blumberg, M. Kuhlmann, W. Tappe, F. Senf, O. Schwarzkopf, A.P. Hitchcock und E. Rühl "Dynamic Stabilization in 1u1g-Excited Nitrogen Clusters" Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 3767 (2001). 31. J. Plenge, R. Flesch, M.-C. Schürmann und E. Rühl "Photofragmentation of Nitryl Chloride in the Ultraviolet- and Vacuum UltravioletRegime" J. Phys. Chem. A 105, 4844 (2001). 32. R. Flesch, J. Plenge, M.-C. Schürmann, S. Kühl, M. Klusmann, und E. Rühl „Single-Photon Ionization of the Primary Photofragments of Chlorine Monoxide“ Surf. Rev. Lett., zur Veröffentlichung eingereicht (2001). 33. R. Flesch, W. Tappe, A.A. Pavlychev, und E. Rühl “High-Resolution Near-Edge Spectroscopy of Molecules and Molecular Van der Waals Clusters“ Surf. Rev. Lett., zur Veröffentlichung eingereicht (2001). 34. M. Meyer, R. Flesch, A. Marquette, E. Rühl, A. Grum-Grzhimailo „Aligment of Ar+-Ions Produced After the Resonant Auger Decay of Ar* 2p5 3d Resonances“ Surf. Rev. Lett., zur Veröffentlichung eingereicht (2001). 3.6.4.2 Aufsätze in Monographien 35. J. Berkowitz, E. Rühl und H. Baumgärtel "Valence Ionization Processes in the VUV Region" in: ‘VUV and Soft X-Ray Photoionization Studies’, Hg.: U. Becker und D.A. Shirley, in:"Physics of Atoms and Molecules", Hg.: P.G. Burke u. H. Kleinpoppen, Plenum Press, New York (1996), S. 221. 36. E. Rühl und R. Zellner "Chemie an Aerosolen und in der Gasphase" 120 in: "Deutsche Ozonforschung", Hg.: R. Zellner, T. Peter, K. Dämmer, L. Quintern, Verlag für Marketing und Kommunikation, Worms (1999), S. 72. 37. E. Rühl "Core Level Excitation of Clusters" in: 'Theory and Experiments on Clusters', Hg.: T. Kondow, F. Mafune, World Scientific, Singapore, im Druck (2001). 3.6.4.3 Tagungsbeiträge (mit Peer Review-System) 38. E. Rühl und A. Knop “Kr(3d) Spectroscopy of Free Krypton Clusters“ in: "Structures and Dynamics of Clusters", Hg: T. Kondow, K. Kaya u. A. Terasaki, Universal Academy Press, Tokyo (1996), S. 235. 39. A. Knop, D.N. McIlroy, P.A. Dowben und E. Rühl "Auger Electron Spectroscopy of Free Argon Clusters" in: "Two Center Effects in Ion-Atom Collisions", AIP Conf. Proc. 362, Hg.: T.J. Gay u. A.F. Starace, American Institute of Physics, Woodbury, New York (1996), S. 274. 3.6.4.4 Sonstige Aufsätze 40. E. Rühl Buchbesprechung "Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Vacuum Ultraviolet Radiation Physics", Hg.: T. Miyahara, Y. Azuma, M. Watanabe, T. Ishii, Elsevier, Amsterdam (1996) Z. Phys. Chem. 205, 132 (1998). 41. E. Rühl "Levitierte Aerosole" Nachr. Chem. Techn. Lab. 46, 1114 (1998). 42. R. Flesch Discuss. Faraday Soc. 115, 203 (2000). 43. R. Flesch Discuss. Faraday Soc. 115, 316 (2000). 44. E. Rühl "Helmut Baumgärtel zum 65. Geburtstag" Bunsen-Magazin 3, 98 (2001) 121 3.7 Umweltphysik-Feldmessungen (Kallenrode) 3.7.1 Publikationstätigkeit 3.7.1.1 Zeitschriftenaufsätze a. b. c. d. e. f. 3.7.1.2 Heber, B., Modulation of galactic and anomalous cosmic rays in the inner heliosphere, Adv. Space Res. 27, (3)451-460, 2001 Heber, B., P. Ferrando, A. Raviart, C. Paizis, R. Müller-Mellin, and H. Kunow, Propagation of 3-10 MeV electrons in the inner heliosphere: Ulysses observations, Adv. Space Res. 27, (3)547-552, 2001 Kallenrode, M.-B., 2001: Shock as a black box II: effects of adiabatic deceleration and convection included, J. Geophys. Res., im Druck Kallenrode, M.-B., 2001: Charged particles, neutrals, and neutrons, ESA-SP, im Druck Kallenrode, M.-B., 2001: Magnetic clouds and interplanetary transport, submitted to J. Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics Zhang, M., R.B. McKibben, C. Lopate, J.R. Jokipii, J. Giacalone, and M.-B. Kallenrode, Ulysses observations of energetic particles from the July 14, 2000 event at high heliographic latitudes, submitted to J. Geophys. Res. Aufsätze g. 3.7.1.3 Kallenrode, M.-B., 2001: Space physics: the Sun, the Earth and everything?, Science NW, http://nextwave.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2001/07/09/01 Sammelwerke h. Kallenrode, M.-B., 2000: Galactic cosmic rays, in The outer heliosphere: beyond the planets (eds. K. Scherrer, H. Fichtner, and E. Marsch), p. 165-190, Copernicus, Lindau i. Kallenrode, M.-B., 2000: Klimavariabilität: interne und externe Ursachen, in Perspektiven der Umweltwissenschaften (Hrsg. E. Brandt), S. 141-161, Nomos, Baden-Baden j. Landwehr, B., M.-B. Kallenrode, R. Pacena, und W. Engelhardt, 2001: Konzeption einer verbesserten physikalischen Ausbildung von SachunterrichtslehrerInnen auf der Grundlage einer empirischen Untersuchung mit dem Ziel einer besseren naturwissenschaftlichen Frühförderung von Jungen und Mädchen, in Niedersächsischer Forschungsverbund für Frauen- und Geschlechterforschung in Naturwissenschaft, Technik und Medizin (NFFG): Tagungsbeiträge und Forschungsergebnisse 1997-2000 (Hrsg. U. Paravicini und C. Riedel), Wiss. Reihe, Hannover k. Matzner, R.A. (ed), 2001: Dictionary of Geophysics, Astrophysics and Astronomy, CRC Press, Boca Raton 3.7.1.4 Lehrbücher l. m. Kallenrode, M.-B., 2001: Space Physics, Springer, Berlin Kallenrode, M.-B., 2001: Wind, Wasser, Wellen: Umweltphysik exemplarisch, in Studium der Umweltwissenschaften, Bd. 5, Naturwissenschaften (Hrsg. W. Härdtle), Springer, Berlin, im Druck 122 3.7.1.5 Tagungsbeiträge n. Belov, A.,V., E.A. Eroshenko, B. Heber, V.G. Yanke, A. Raviart, R. MüllerMellin, H. Kunow, K. Röhrs, G. Wibberenz, and C. Paizis, 2001: Latitudinal and radial variation of >2 GeV/n protons and alpha particles in the southern heliosphere at solar maximum: Ulysses COSPIN/KET and neutron monitor network observations, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray. Conf. 10, 3996-3999 o. Blake, J.B., M. Fraenz, and B. Heber, 2001: Time history of low energy GCR modulation at Earth and Ulysses, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 9, 3766 p. Blake, J.B., R. Selesnick, M. Fraenz, and B. Heber, 2001: Solar cycle variations of GCR anisotropies at Ulysses, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 10, 3947 q. Cliver, E.W., A. Falcone, J. Ryan, H. Aurass, L.C. Gentile, M.-B. Kallenrode, A.G. Ling, M.J. Rainer, C St. Cyr, and M. Yoshimori, 2001: Particle injection in the relativistic SEP event of 6 November 1997, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 8, 3277-3280 r. Dalla, S., A. Balogh, B. Heber, C. Lopate, and R.B. McKibben, 2001: Solar energetic proton intensity profiles at 5 AU from the Sun, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 8, 3289-3292 s. Ferreira, S.E.S., M.S. Potgieter, R.A. Burger, H. Fichtner, and B. Heber, 2001: Latitudinal transport of 7 MeV Jovian and galactic electrons in the inner heliosphere, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 9, 3702-3705 t. Fichtner, H., M.S. Potgieter, S.E.S. Ferreira, B. Heber, and R.A. Burger, 2001: Time-dependent 3-D modelling of the heliospheric propagation of few-MeV electrons, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 9, 3666-3669 u. Heber, B., P. Ferrando, A. Raviart, C. Paizis, R. Müller-Mellin, H, Kunow, M.S. Potgieter, S.E.S. Ferreira, and H, Fichtner, 2001: Om the determinateion of the gamma-ray contribution in the 3-10 MeV KET electron channel along the Ulysses trajectory, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 6, 2255-2258 v. Heber, B., P. Ferrando, A. Raviart, C. Paizis, R. Müller-Mellin, H. Kunow, G. Wibberenz, M.S. Potgieter, S.E.S. Ferreira, and R.A. Burger, 2001: latitudinal gradients and charge sign dependent modulation of galactic cosmic rays, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 10, 3897-3900 w. Kallenrode, M.-B., 2001: The influence of magnetic clouds on the propagation of energetic charged particles in interplanetary space, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 8, 3273-3276 x. Kallenrode, M.-B., and E.W. Cliver, 2001: Rogue SEP events: Observational aspects, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 8, 3314-3317 y. Kallenrode, M.-B., and E.W. Cliver, 2001: Rogue SEP events: Modeling, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 8, 3318-3321 z. McDonald, F., Z. Fujii, P. Ferrando, B. Heber, A. Raviart, H. Kunow, R. Müller-Mellin, G. Wibberenz, R.E. McGuire, and C. Paizis, 2001: The cosmic ray radial and latitudinal intensity gradients in the inner and outer heliosphere 19962001.3, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 10, 3906-3909 aa. McKibben, R.B., J.J. Connell, C. Lopate, M. Zhang, A. Balogh, S. Dalla, R.G. Marsden, T.R. Sanderson, C. Tranquille, J.D. Anglin, H. Kunow, R. MüllerMellin, B. Heber, A. Raviart, and C. Paizis, 2001: Ulysses Cospin observations of the energy and charge dependence of the propagation of solar energetic particles to the Sun’s south polar regions. Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 8, 3281-3264 bb. Quack, M., M.-B. Kallenrode, M. Von König, K. Künzi, J. Burrows, B. Heber and E. Wolff, 2001: Ground level events and its consequences for stratospheric chemistry, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 10, 4023-4026 123 cc. Sarri, G., C. Paizis, B. Falconi, B. Heber, P. Ferrando, A. Raviart, R. MüllerMellin, and H. Kunow, 2001: Recurrent cosmic ray decreases during the second Ulysses orbit. COSPIN/KET results, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 9, 3575 dd. Thomson, D.J., L.J. Lanzerotti, C.G. MacLennan, B. Heber, H. Kunow, and R.E. Gold, 2001: Coherence of charged particle oscillations in the heliosphere f~5µHz: implications for a solar modulation source, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 9, 3822-3825 ee. Zhang, M., R.-B. McKibben, C. Lopate, R. Jokipii, J. Giacalone, and M.-B. Kallenrode, 2001: Ulysses observations of solar energetic particles from the July 14, 2000 event at high heliographic latitudes, Proc. 27th Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 8, 3302-3305 124 4 Kristallzucht 4.1 Kristallzucht (Hesse) 4.1.1 Publikationstätigkeit 4.1.1.1 Zeitschriftenaufsätze M. Simon, F. Mersch, Ch. Kuper, S. Mendricks, S. Wevering and E. Krätzig, „Refractive indices of photorefractive Bismuth Titanate, Barium-Calcium Titanate“, Bismuth Germanium Oxide and Lead Germanate“, phys. stat. sol. 159, 559 (1997) X. Yue, F. Mersch, R. A. Rupp, E. Krätzig, „Absorption gratings in ferroelectric Bi4Ti3O12“, Appl. Phys. B 65, 505 (1997) Xuefeng Yue, Jingjun Xu, F. Mersch, R. A. Rupp, E. Krätzig, „Photorefractive properties of Bi4Ti3O12“, Phys. Rev. B 55, 9495 (1997) M. F. Limonov, S. Kapphan, V. S. Vikhnin, L. V. Laisheva, H. Hesse, A. N. Krivospitskii, M. B. Smirnov, „Effects of Vibronic Interactions in Polar Microdomain Formation in Incipient Ferroelectric KTaO3 Comparison Analysis of Raman Scattering and Second-Harmonic-Generation“, Z. Phys. Chem. 201, 215 (1997) Th. Woike, U. Dörfler, M. Imlau, G. Schetter, T. Volk, M. Wöhlecke, R. Pankrath, „Die ferroelektrischen und photorefraktiven Eigenschaften von Sr 0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 dotiert mit Cr, Co, Ce, Tm“, Z. Krist. Suppl. 12, 96 (1997) D. Kip, B. Kemper, I. Nee, R. Pankrath und P. Moretti, „Photorefractive Properties of Ion-Implanted Waveguides in Strontium-Barium Niobate Crystals“, Appl. Phys. B 65, 511 (1997) Th. Woike, G. Weckwerth, H. Palme, R. Pankrath, „Instrumental Neutron Activation Analysis and Absorption Spectroscopy of Photorefractive Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 Crystals Doped with Cerium“, Sol. Stat. Comm. 102, 743 (1997) T. Volk, Th. Woike, U. Dörfler, R. Pankrath, L. Ivleva, M. Wöhlecke, „Ferroelectric Phenomena in Holographic Properties of Strontium-Barium Niobate Crystals Doped with Rare-Earth Elements“, Ferroelectrics 203, 457 (1997) Ch. Kuper, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse, „Growth and dielectric properties of congruently melting Ba1-x CaxTiO3 crystals“, Appl. Phys. A 65, 301 (1997) V. E. Bursian, V. S. Vikhnin, L. S. Sochova, S. Kapphan, H. Hesse, „Observation of superfine structure in the ESR spectra of two tetragonal Fe centers in KTaO 3 and a new model for the center“, Phys. Sol. Stat. 39 (4), 547 (1997) A. Mazur, U. van Stevendaal, K. Buse, M. Weber, O. F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, „Light-induced charge transport processes in photorefractive barium titanate crystals doped with iron“, Appl. Phys. B 65, 481 (1997) A. Mazur, O. F. Schirmer and S. Mendricks, „Optical absorption and light-induced charge transport of Fe2+ in BaTiO3“, Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 2395 (1997) 125 M. Gao, S. Porcher, R. Pankrath, S. Kapphan, „Light-induced VIS and NIR Absorption in SBN:Ce and SBN:Cr Crystals“, J. Kor. Phys. Soc. Vol. 32, 542 (1998) T. Woike, T. Volk, U. Dörfler, R. Pankrath, L. Ivleva, M. Wöhlecke, „Ferroelectric and optical hysteresis in SBN doped with rare-earth elements“, Ferroelectric Lett. 23, 127 (1998) J. Neumann, S. Mendricks, E. Krätzig, M. Goulkov, S. Odoulov, „Photorefractive light amplification by forward four-wave mixing in BaTiO3“, Opt. Comm. 146, 220 (1998) S. Wevering, K. Buse, M. Simon, R. Pankrath und E. Krätzig, „Time-resolved Measurements of Photoconductivity in Cerium-Doped Photorefractive Strontium-Barium Niobate using Nanosecond Light Pulses“, Opt. Comm. 148, 85 (1998) S. Mendricks, X. Yue, T. Nikolajsen, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse und D. Kip, „Growth and photorefractive properties of doped Pb5Ge3O11 and (Pb1-xBax)5Ge3O11 solid solutions“, Proc. SPIE 3554, 205 (1998) Xuefeng Yue, S. Mendricks, Yi Hu, H. Hesse und D. Kip, „Photorefractive effect in doped Pb5Ge3O11 and in (Pb1-xBax)5Ge3O11 solid solutions“, J. Appl. Phys. 83, 3473 (1998) D. Kip, S. Mendricks and P.Moretti, „Optical waveguides in lead germanate formed by MeV proton and helium ion implantation“, phys. stat. sol. 166, R3 (1998) Xuefeng Yue, K. Buse, F. Mersch, E. Krätzig, R. A. Rupp, „Diffraction-efficiency enhancement of photorefractive gratings in Bi4Ti3O12 at low temperatures“, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 142 (1998) Ch. Kuper, K. Buse, U. van Stevendaal, M. Weber, T. Leidlo, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, „Electrooptic and Photorefractive Properties of Ferroelectric Barium- Calcium Titanate Crystals“, Ferroelectrics 208, 213 (1998) S. Wevering, K. Buse, M. Simon, R. Pankrath, E. Krätzig, „Time-resolved measurements of photoconductivity in cerium-doped photorefractive strontium-barium niobate using nanosecond light pulses“, Opt. Comm. 148, 85 (1998) S. Eden, S. Kapphan, H. Hesse, V. Trepakov, V. S. Vikhnin, I. Gregora, L. Jastrabik, J. Seglins, „Observations of the absorption, infra-red emission, and excitation spectra of Cr in BaTiO3“, J. Phys.: Cond. Matt. 10, 10775 (1998) V. Trepakov, V. S. Vikhnin, S. Eden, S. Kapphan, H. Hesse, J. Seglins, L. Jastrabik, „Optical Spectra of BaTiO3:Cr“, J. Kor. Phys. Soc. Vol. 32, 1113 (1998) D. Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse und D. Lammers, „Origin of the Large Nonlinear Optical Coefficients in Bismuth Borate BiB3O6“, phys. stat. sol. (a) 176/2, R1 (1999) J. Neumann, M. Röwe, H. Veenhuis, R. Pankrath und E. Krätzig, „Linear Electrooptic Coefficient r42 of Tetragonal Potassium-Tantalate-Niobate and Barium-CalciumTitanate“, phys. stat. sol. (b) 215/2, 9 (1999) 126 D. Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse und D. Lammers, „Relationship between dielectric responses and constituent atoms in crystal materials“, phys. stat. sol. (b) 216/2, R7 (1999) M. Wierschem, C. Bäumer, A. Jovanovic, M. Wöhlecke, S. Kapphan, L. Kovacs, „Fundamental and Overtone Spectra of the OH and OD Stretch Mode in Congruent and Stoichiometric LiTaO3“, phys. stat. sol. (b), 215, R7 (1999) M. Pape, H.J. Reyher, N. Hausfeld, S. Mendricks, „Photoactive Pb 3+ host lattice ions in photorefractive Pb5Ge3O11 characterized by ODMR and EPR“, OSA TOPS 27, (1999) T. Volk, T. Woike, U. Dörfler, H. Schmitz, R. Pankrath, M. Wöhlecke, „Ferroelectricity Driven Two-Beam Coupling Gain in Strontium-Barium Niobate Crystals“, OSA TOPS 27, 86 (1999) U. B. Dörfler, R. Piechatzek, Th. Woike, M. K. Imlau, V. Wirth, L. Bohaty, T. Volk, R. Pankrath, M. Wöhlecke, „A holographic method for the determination of all linear electrooptic coefficients applied to Ce-doped strontium-barium-niobate“, Appl. Phys. B 68, 843 (1999) M. Gao, R. Pankrath, S. Kapphan, V. Vikhnin, „Light-induced charge transfer and kinetics of the NIR absorption of Nb4+ polarons in SBN crystals at low temperatures“, Appl. Phys. B 68, 849 (1999) Xuefeng Yue, S. Mendricks, T. Nikolajsen, H. Hesse, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, „Multiple phase gratings in pure, Yb- and P-doped Pb5Ge3O11 after different thermal treatments“, J. Appl. Phys. 86, 1186 (1999) A.Moewes, A. V. Postnikov, B. Schneider, E. Z. Kurmaev, M. Matteucci, V.M.Cherkashenko, D. Hartmann, H. Hesse und M. Neumann, „Electronic structure of KNbO3:Nb M4,5 x-ray fluorescence measurements“, Phys. Rev. B 60, 4422 (1999) R. Scharfschwerdt, O. F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, D. Rytz, „Fermi-level engineering of BaTiO3 by alkali codoping: increasing the near-infrared absorption by rhodium“, Appl. Phys. B 68, 807 (1999) N. Korneev, D. Mayorga, S. Stepanov, H. Veenhuis, K. Buse, Ch. Kuper und E. Krätzig, „Holographic and Non-Steady-State Characterization of Photorefractive Barium-Calcium-Titanate", Opt. Comm. 160, 98 (1999) S. Mendricks, X. Yue, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse, D. Kip, „Dynamic properties of multiple grating formation in doped and thermally treated lead germanate“, Appl. Phys. B 68, 887 (1999) Xuefeng Yue, S. Mendricks, T. Nikolajsen, H. Hesse, D. Kip und E. Krätzig, „Transient enhancement of photorefractive gratings in lead germanate by homogenous pyroelectric fields“, J. Opt. Soc. Am. 16, 359 (1999) 127 M. Gao, S. Kapphan, S. Porcher, R. Pankrath, „Experimental study of NIR absorption due to Nb4+ polarons in pure and Cr- or Ce-doped SBN crystals“, J. Phys.: Cond. Matt. 11, 4913 (1999) S. Köhne, O.F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, T.W. Kool, V. Vikhnin „Ti3+ Jahn-Teller polarons and bipolarons in BaTiO3“, J. Supercond. 12, 193 (1999) A. Mazur, C. Veber, O. F. Schirmer, C. Kuper, H. Hesse, „Light-induced charge transport processes in photorefractive Ba0.77Ca0.23TiO3 doped with iron“, J. Appl. Phys. 85, 6751 (1999) H. Veenhuis, T. Börger, K. Buse, C. Kuper, H. Hesse und E. Krätzig, „Light-Induced Charge Transport Properties of Photorefractive Barium-Calcium-Titanate Crystals Doped with Iron“, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 1042 (2000) H. Veenhuis, T. Börger, K. Peithmann, M. Flaspöhler, K. Buse, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse und E. Krätzig, „Light-Induced Charge Transport Properties of Photorefractive Barium-Calcium-Titanate Crystals Doped with Rhodium“, Appl. Phys. B 70, 797, (2000) K. Betzler, H. Hesse, R. Jaquet, D. Lammers, „Optical second-harmonic generation in lead formate“, J. Appl. Phys. 87, 22 (2000) D. Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse, D. Lammers, „Nonlinear optical properties of borate crystals“, Sol. Stat. Comm. 114, 21 (2000) K. Szot, W. Speier, M. Pawelczyk, J. Kwapulinski, J. Hulliger, H. Hesse, U. Breuer and W. Quadakkers, „Chemical inhomogenity in the near-surface region of KTaO3 evolving at elevated temperatures“, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 4687 (2000) A.V. Postnikov, B. Schneider, M. Neumann, D. Hartmann, H. Hesse, A. Moeves, E. Z. Kurmaev, M. Matteucci, „Combined study of KNbO 3 and KTaO3 by different techniquesof photoelectron and X-ray emission spectroscopy“, J. Phys. and Chem. of Sol. 61, 265 (2000) P. Lehnen, J. Dec, W. Kleemann, Th. Woike and R. Pankrath, „Relaxor Properties of SBN:Ce“, Ferroelectrics 240, 281 (2000) J. Wingbermühle, M. Meyer, O. F. Schirmer, R. Pankrath and R. K. Kremer, „Electron paramagnetic resonance of Ce3+ in strontium-barium niobate“, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 4277 (2000) J. Dec, W. Kleemann, Th. Woike and R. Pankrath, „Phase transitions in Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce3+: I. Susceptibility of clusters and domains“, Eur. Phys. J. B 14, 627 (2000) Y. G. Wang, W. Kleemann, Th. Woike and R. Pankrath, „Atomic force microscopy of domains and volume holograms in Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce3+“, Phys. Rev. B, 61, 3333 (2000) 128 D. Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse, „Chemical bond analysis of the second-order nonlinear optical behaviour of Mg-doped lithium niobate“, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, 6245 (2000) P. Lehnen, W. Kleemann, Th. Woike, R. Pankrath, „Phase transitions in Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6:Ce3+: II. Linear birefrigence studies of spontaneous and precursor polarisation“, Eur. Phys. J. B14, 633 (2000) T. Woike, U. Dörfler, L. Tsankov, G. Weckwerth, D. Wolf, M. Wöhlecke, T. Granzow, R. Pankrath, M. Imlau, W. Kleemann, „Photorefractive Properties of Cr-doped Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6 related to crystal purity and doping concentration“, Appl. Phys. B 72, 661 (2001) D. Xue, K. Betzler, H. Hesse, D. Lammers, „Temperature dependence of the dielectric response of lithium niobate“, J. of Phys. and Chem. of Solids 62, 973 (2001) T. Granzow, U. Dörfler, Th. Woike, M. Wöhlecke, R. Pankrath, M. Imlau, W. Kleemann, „Influence of pinning effects on the ferroelectric hysteresis in cerium-doped Sr0.61Ba0.39Nb2O6“, Phys. Rev. B, Vol. 63, 174101 (2001) 4.1.1.2 Tagungsbeiträge G. Schetter, Ch. Kuper, H. Hesse, P. Held, L. Bohaty, „Züchtung und Eigenschaften der kongruent schmelzenden Mischkristalle Ba1-xCaxTiO3 (x=0.227)“, DGKJahrestagung, Hamburg, Deutschland (1997) K. Buse, U. v. Stevendaal, M. Weber, A. Mazur, O.F. Schirmer, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig,„Photorefractive Properties of Barium Titanate Crystals Doped with Iron“, Topical Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, Chiba, Japan (1997) S. Mendricks, R. Pankrath, X. Yue and H. Hesse, „Züchtung dotierter Bleigermanat Kristalle“, DGKK-Jahrestagung, Karlsruhe, Deutschland (1998) S. Eden, S. Kapphan, H. Hesse, V. Trepakov, „Lumineszenz von Cr in BaTiO3“ 62. Physikertagung, Regungsburg, Deutschland (1998) J. Seglins, S. Mendricks, R. Pankrath, V. Vikhnin and S. Kapphan, „Chromium doping effects in SBN crystals“ 62. Physikertagung, Regensburg, Deutschland (1998) S. Mendricks, X. Yue, T. Nikolajsen, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse and D. Kip, „Growth and photorefractive properties of doped Pb5Ge3O11 and (Pb1-xBax)5Ge3O11 solid solutions“, SPIE-Meeting on Photorefractive Materials, Peking, China (1998) S. Mendricks, X. Yue, T. Nikolajsen, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse and D. Kip, „Growth and photorefractive properties of doped Pb5Ge3O11 and (Pb1-xBax)5Ge3O11 solid solutions“, Nankai University, Tianjin, China (1998) 129 S. Mendricks, X. Yue, T. Nikolajsen, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse and D. Kip, „Growth and photorefractive properties of doped Pb5Ge3O11 and (Pb1-xBax)5Ge3O11 solid solutions“, Shandong Institute of Crystal Materials, Jinan, China (1998) R. Pankrath, ,,Kristallzüchtung von Sr1-xBaxNb2O6 (SBN) und Ba1-xCaxTiO3 (BCT)“, Institut für Kristallographie der Universität zu Köln (1998) S. Mendricks, X. Yue, T. Nikolajsen, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse and D. Kip, „Growth and photorefractive properties of doped and thermally treated lead germanate“, California Institute of Technology, Los Angeles, USA (1999) S. Mendricks, R. Pankrath, X. Yue and H. Hesse, „Growth and photorefractive properties of doped and thermally treated lead germanate“, BriGDe-Meeting on Crystal Growth, Zeist, Niederlande (1999) H. Veenhuis, K. Buse, C. Kuper, H. Hesse, E. Krätzig, N. Korneev, D. Mayorga, S. Stepanov, „Charakterisierung eines eisendotierten Barium-Calcium-Titanat-Kristalls mit Hilfe nichtstationärer Photoströme und holographischer Methoden“, Frühjahrstagung, Münster, Deutschland (1999) G. I. Malovichko, V. G. Grachev, O. F. Schirmer, R. Pankrath, H. Hesse, ,,LightInduced Electron and Hole Centers in Barium Calcium Titanate Crystals“, 12th International Symposium on Integrated Ferroelectrics, RWTH Aachen, Deutschland (2000) V. G. Grachev, G. I. Malovichko, R. Pankrath, O. F. Schirmer, ,,Photosensitive centers in barium titanate and barium calcium titanate crystals“, The 2nd International Symposium on Laser, Scintillator and Nonlinear Optical Materials, Chambre de Commerce et d`Industrie de Lyon, Lyon, Frankreich (2000) C. Bäumer, ,,Züchtung von LiTaO3- Kristallen in einer widerstandsbeheizten Anlage“, DGKK-Arbeitskreis `Kristalle für Laser und nichtlineare Optik`, Institut für Mineralogie, Universität Bonn, Deutschland (2000) H. Vogt, ,,Phasenbreite bei Kristallen mit Sillenitstruktur“, DGKK-Arbeitskreis `Kristalle für Laser und nichtlineare Optik`, Institut für Mineralogie, Universität Bonn, Deutschland (2000) R. Pankrath, H. Hesse, ,,Growth of photorefractive crystals“, French-German Crystal Growth Meeting, Seeheim-Jugenheim, Deutschland, 2001 130 5 Theoretische Physik 5.1 Festkörperphysik (Borstel) 5.1.1 Publikationstätigkeit 5.1.1.1 Publikationen in wissenschaftlichen Zeitschriften 1. B. Willerding, J. Braun and K. Wandelt, Relativistic calculations of photoemission spectra from ordered alloys: Applications to Cu3Au(001), Surf. Sci. 352-354, 665, 1996. 2. M. Getzlaff, J. Bansmann, J. Braun and G. Schönhense, J. Magn. Magn. Mater 161, 70, 1996. 3. J. Braun, The theory of angle-resolved ultraviolet photoemission and its applications to ordered materials, Rep. Progr. Phys. 59, 1267, 1996. 4. R. Paniago, R. Matzdorf, G. Meister, A. Goldmann, J. Braun and G. Borstel, Electron diffraction in angle-resolved UV-photoemission spectra from Au(111), Surf. Sci. 347, 46, 1996. 5. G. Chelkowska, H. Ufer, G. Borstel and M. Neumann, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 157/158, 719, 1996. 6. R. Matzdorf, R. Paniago, G. Meister, A. Goldmann, Ch. Zubrägel, J. Braun and G. Borstel, Surf. Sci. 352-354, 670, 1996. 7. Slebarski, A. Jezierski, A. Zygmunt, S. Mähl, M. Neumann and G. Borstel, Phys. Rev. B 54, 13551, 1996. 8. M. Grass, J. Braun, A.V. Postnikov, G. Borstel, H. Ünlü, M. Neumann, Full-potential photoemission calculations for KTaO3, Surf. Sci. 352-354, 760, 1996. 9. D. Fuks, S. Dorfman, J. Felsteiner, A. Gordon, A.V. Postnikov, and G. Borstel, Dynamics of the perovskite interphase boundary under pressure, Surf. Sci. 352-354, 879, 1996. 10. Grigorjeva L.G., Millers D.K., Kotomin E.A., Eglitis R.I., Lerman L.I., Optical properties of Silver Halide Fibers: Extrusion and Aging Effects, - J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 29, p. 578 - 583, 1996. 11. E.A.Kotomin, M.M.Kuklja, R.I.Eglitis, and A.I.Popov, Quantum Chemical Simulations of the Optical Properties and Diffusion of Electron Centers in MgO Crystals, - Materials Science & Engineering B 37, p. 212-214, 1996 12. R.I.Eglitis, M.M.Kuklja, E.A.Kotomin, A.Stashans, and A.I.Popov, Semi - empirical simulations of the electron centers in MgO crystal, - Computational Materials Science, 5, p. 298-306, 1996 13. R.I.Eglitis, A.V.Postnikov, and G.Borstel, Semiempirical Hartree - Fock calculations for KNbO3, - Phys. Rev. B, 54, p. 2421 - 2427, 1996 14. D.L. Novikov, M.I. Katsnelson, Yu. Jaejun, A.V. Postnikov, and A.J. Freeman, Pressureinduced phonon softening and electronic topological transition in HgBa2CuO4, Phys. Rev. B 54, 1313, 1996. 15. R.I.Eglitis, A.V.Postnikov, and G.Borstel, Semiempirical Hartree - Fock calculations for pure and Li – doped KTaO3, - Phys. Rev. B, 55, p. 12976 - 12981, 1997 16. R.I.Eglitis, N.E.Christensen, E.A.Kotomin, A.V.Postnikov, and G.Borstel, First-principles and semi- empirical calculations for F centers in KNbO3 crystal, - Phys. Rev. B, 56, p. 8599 - 8604, 1997 17. E.A.Kotomin, R.I.Eglitis, and A.I.Popov, Charge distribution and optical properties of F+ and F centers in KNbO3 crystal, - J. Phys. Cond. Matter, 9, L315-L321, 1997 18. Szajek, A. Jezierski, A. Kowalczyk, J. Baszynski, S. Bartkowski, M. Neumann and G. Borstel, X-ray photoemission spectra of the Dy(Co1-xAlx)2 systems, Acta Phys. Polon. A91, 439, 1997. 19. J. Lachnitt, H. Ufer, I. Karla, M. Neumann, J. Braun and G. Borstel, Photoemission investigation for GdCu, Surf. Sci. 377-379, 238, 1997. 131 20. A.V. Postnikov, G. Borstel, Refined geometry and frozen phonons in KNbO3, Ferroelectrics 194, 69, 1997. 21. M. Pothoff, J. Lachnitt, W. Nolting and J. Braun, One-step model of photoemission for nonlocal potentials, Phys. Stat. sol. (b) 203, 441, 1997. 22. M. Getzlaff, J. Bansmann, J. Braun and G. Schönhense, Spin resolved photoemission study of Fe(110) films, Z. Phys. B 104, 11, 1997. 23. J. Kutzner, R. Paucksch, C. Jabs, J. Braun, and H. Zacharias, Dispersion behaviour of surface states on Ni(111), Phys. Rev. B 56, 16003, 1997. 24. E.A.Kotomin, N.E.Christensen, R.I.Eglitis, and G. Borstel, A comparative study of the atomic and electronic structure of F centers in ferroelectric KNbO3: ab initio and semiempirical calculations, - Computational Materials Science 10, pp. 339-345, 1998 25. R.I.Eglitis, E.A.Kotomin, and G.Borstel, Semi-Empirical Calculations of Hole Polarons in MgO and KNbO3 Crystals,- Phys. Status Solidi (b), 208, 15-20, 1998 26. R.I.Eglitis, E.A.Kotomin, G.Borstel, S. Dorfman, Semi-empirical calculations of the Nbion positions in doped KTaO3 crystals, - J. Phys. Condens. Matter 10, 6271-6276, 1998. 27. R.I.Eglitis, A.V. Postnikov, G.Borstel, Semiempirical Hartree-Fock simulations of lattice relaxation and effective interactions in Li-doped KTaO3,- Phys. Status Solidi (b), 209, 187-193, 1998. 28. R.I. Eglitis, E.A. Kotomin, and G. Borstel, Quantum chemical calculations of KTN solid solutions, - Solid State Communications, 108, pp. 333-336, 1998. 29. R.I. Eglitis and E.A. Kotomin, Calculations of hole polaron properties in oxide crystals, Computer Modeling & New Technologies 2, pp. 21-24, 1998. 30. Y.M. Yarmoshenko, M.I. Katsnelson, E.I. Schreder, E.Z. Kurmaev, A. Slebarski, S. Plogmann, T. Sclathölter, J. Braun and M. Neumann, Observation of magnetic splitting in XPS MnL-spectra of Co2MnSn and Pd2MnSn, Eur. Phys. J. B 2, 1, 1998. 31. A.V. Postnikov, A.I. Poteryaev and G. Borstel, First principles calculations for Fe impurities in KNbO3, Ferroelectrics 206-207, 69, 1998. 32. E.Z. Kurmaev, V.M. Cherkasenko, Yu.M. Yarmashenko, St. Bartkowski, A.V. Postnikov, M. Neumann, L.-C. Duda, J.H. Guo, J. Nordgren, V.A. Parelyaev, W. Reichelt, Electronic structure of VO2 studied by x-ray photoelectron and x-ray emission spectroscopies, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 10, 4081, 1998. 33. J. Bansmann, M. Getzlaff, G. Schönhense, M. Fluchtmann and J. Braun, Valence band photoemission from thin iron films, a comparison of experimental and theoretical results, Surf. Sci. 402-404, 365, 1998. 34. Willerding, K. Oster, J. Radnik, J. Braun and K. Wandelt, Electronic properties of epitaxial Cu films on Pt(100), J. Elect. Spec. Rel. Phenom. 93, 215, 1998. 35. J. Bansmann, L.Lu, M. Getzlaff, M. Fluchtmann, J. Braun and K.H. Meiwes-Broer, Magnetic Linear Dichroism in valence band photoemission – a novel technique to study electronic and magnetic properties, J. Magn. Mater. 185, 94, 1998. 36. Mayer, J. Braun, B. Willerding and K. Wandelt, Relativistic photoemission Calculations applied to CoAl(110), J. Phys. Condens. Matter 48, 10839, 1998. 37. V.S.Vikhnin, R.I.Eglitis, P.A.Markovin, G.Borstel, Self-ordered second-component Nb clusters in KNbxTa1-xO3 solid solution and their physical properties,- Phys. Status Solidi (b), 212, pp. 53-63, 1999. 38. V.S. Vikhnin, R.I. Eglitis, P.A. Markovin, G. Borstel, Self-ordered clusters of secondcomponent in solid solutions on the basis of ferroelectric perovskites: Nb clusters and single Nb ion in KTaO3, Inorganic Materials, 35, pp. 823-827, 1999. 39. P.W.Jacobs, E.A.Kotomin, and R.I.Eglitis, Semi-empirical INDO and shell-model calculations for perovskites, Radiation Effects & Defects in Solids, 151, pp. 243-247, 1999. 132 40. R.I.Eglitis, E.A.Kotomin, A.V.Postnikov, N.E.Christensen, M.A. Korotin, G.Borstel, Computer simulations of defects in perovskite KNbO3 crystals, Ferroelectrics, 229, pp. 69-75, 1999. 41. R.I.Eglitis, A.V.Postnikov, G.Borstel, Semiempirical Hartree-Fock calculations for single and interacting Li impurities in KTaO3, Ferroelectrics, 229, pp. 63-67, 1999. 42. E.A. Kotomin, R.I. Eglitis, A.V. Postnikov, G. Borstel, and N.E. Christensen, Firstprinciples and semi-empirical calculations for bound hole polarons in KNbO3, Phys. Rev. B, 60, pp. 1-5, 1999. 43. V.S. Vikhnin, H. Liu, W. Jin, S. Kapphan, R. Eglitis, and D. Usvyat, Critical effects in optical response due to charge transfer vibronic excitons and their structure in perovskitelike systems, Journal of Luminescence, 83-84, pp. 109-113, 1999. 44. Y.M. Yarmoshenko, E.Z. Kurmaev, S. Plogmann, T. Schlathölter, J. Braun and M. Neumann, Local magnetic moments in Mn-based Heussler alloys, Phys. Rev. B 60, 6428, 1999. 45. M. Fluchtmann, S. Bei der Kellen, J. Braun and G. Borstel, Relativistic full-potential photoemission calculations applied to GaAs, surf. Sci. 432, 291, 1999. 46. G.H. Fecher, J. Braun, N.A. Cherepkov, L.V. Chernysheva, Th. Jentzsch, J. Morais, A. Oelsner, Ch. Ostertag, J. Paul, H. Ufer and G. Schönhense, Dichroism in Angular Resolved VUV-photoemission from the (0001)-surfaces of thin Gd and Nd films epitaxially grown on W(110), Eur. Phys. J. B 11, 161, 1999. 47. M. Potthoff, W. Nolting and J. Braun, relativistic photoemission theory for nonlocal potentials, Phys. Stat. sol. (b) 216, 1023, 1999. 48. Willerding, M. Grüne, R.J. Linden, G. Boishin, K. Wandelt, A.V. Postnikov and J. Braun, Photoelectron spectra of thin alloy films: measurements and relativistic calculations for the system C(2x2)CuMn on Cu(100), Surf. Sci. 433-435, 886, 1999. 49. S.W. Wu, T. Lischke, R. David, N. Müller, U. Heinzmann, C. Pettenkofer, A.Klein, A.Ya. Perlov, E.E. Krasovskii, W. Schattke and J. Braun, Spin resolved photoemission spectroscopy on WSe2, J. Elect. Spec. Rel. Phenom. 101-103, 449, 1999. 50. N.I. Kulikov, A.V. Postnikov, G. Borstel and J. Braun, Onset of magnetism in B2 transition metals aluminides, Phys. Rev. B 59, 6824, 1999. 51. R. Matzdorf, A. Gerlach, A. Goldmann, M. Fluchtmann and J. Braun, A comparison of photoemission matrix elements in one-step calculations with experiment, Surf. Sci. 421, 167, 1999. 52. S.W. Wu, T. Lischke, N. Miller, U. Heinzmann, C. Pettenkofer, A.Klein, P.Blaha and J. Braun, Spin resolved photoemission spectroscopy using circulary polarized radiation from InSe (0001), J. Phys. Condens. Matter 11, 6715, 1999. 53. P.W. M. Jacobs, E.A. Kotomin, and R.I. Eglitis, Semi-empirical defect calculations for the perovskite KNbO3, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, pp. 569-574, 2000. 54. E.A. Kotomin, R.I. Eglitis, G. Borstel, Quantum Chemical Modelling of point defects in KNbO3 perovskite crystals, Computational Materials Science 17, pp. 290-298, 2000. 55. E.A. Kotomin, R.I. Eglitis, G. Borstel, L.G. Grigorjeva, D.K. Millers, and V. Pankratov, Theoretical and experimental study of radiation defects in KNbO3 perovskite crystals, Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 166-167, pp. 299-304, 2000. 56. A.V. Postnikov, R.I. Eglitis, V. Caciuc, and G. Borstel, First-Principles Simulations of Ferroelectric Oxides, Ferroelectrics, 236, pp. 47-58, 2000. 57. R.I. Eglitis, E.A. Kotomin, and G. Borstel, Quantum chemical modelling of perovskite solid solutions, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, L431-L434, 2000. 58. E.A. Kotomin, R.I. Eglitis, and G. Borstel, Quantum chemical modelling of electron polarons and excitons in ABO3 perovskites, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 12, L557-L562, 2000. 133 59. G. Borstel, E.A. Kotomin, R.I. Eglitis and E. Heifets, Computer modeling of defects and surfaces in advanced perovskite ferroelectrics, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Vol. 39, S39-1, 24-28, 2000. 60. A.V. Postnikov, V. Caciuc and G. Borstel, Structure Optimization and Frozen Phonons in LiNbO3, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 61, 295, 2000. 61. V. Caciuc, A.V. Postnikov and G. Borstel, Ab initio and zone-center phonons in LiNbO3, Phys. Rev. B 61, 8806, 2000. 62. G. Zvejnieks and V.N. Kuzovkov, Monte Carlo simulations of the periodically forced autocatalytic A+B 2B reaction, Phys. Rev. E 61, 4593, 2000. 63. S. Piskunovs, Yu.F. Zhukovskii, E.A. Kotomin and Yu.N. Shunin, Hartree-Fock calculations for a cubic SrTiO3 crystal, Computer Modeling & New technologies 4, 7, 2000. 64. J.T. Devreese, V.M. Fomin, E.P. Pokatilov, E.A. Kotomin, R. Eglitis, and Yu.F. Zhukovskii, Theory of bound polarons in oxide compounds, Phys. Rev. B 63, 184304(p.1-6), 2001. 65. Zvejnieks and V.N. Kuzovkov, Monte Carlo simulations for a Lotka-type model with reactant surface diffusion and interactions, Phys. Rev. E 63, 051104, 2001. 66. Fuks, K. Mundim, V.Liubich, S. Dorfman, J. Felsteiner and G. Borstel, Modeling of the sliding resistance of Sigma (3)111 tungsten grain boundary: influence of boron additive, Composites Part A-Applied Science and Manufacturing 32, 591, 2001. 67. U.C. Mundim, V. Liubich, S.Dorfman, J. Felsteiner, D. Fuks and G. Borstel, Relaxation of atoms in the tugsten sigma (3) (111) grain boundary with and without boron interstitials, Solid State Communications 118, 301, 2001. 68. G. Borstel, R.I. Eglitis, E.A. Kotomin and E.Heifets, Modeling of Defects and Surfaces in Perovskite Ferroelectrics, Journal of Crystal Growth, 2001, submitted. 69. R.I. Eglitis, E.A. Kotomin and G. Borstel, Quantum Chemical Modelling of Polarons and Perovskite Solid Solutions, Computational Materials Science, 2001, in press. 70. Heifets, R.I. Eglitis, E.A. Kotomin, J. Maier and G. Borstel, Ab initio modelling of surface structure for SrTiO3 perovskite crystals, Physical Review B, 2001, submitted. 71. V.S. Vikhnin, R.I. Eglitis, E.A. Kotomin, S.E. Kapphan, and G. Borstel, New PolaronicType Charge Transfer Excitons in Ferroelectric Oxides, Chem. Phys. Lett. 2001, submitted. 72. V.S. Vikhnin, R.I. Eglitis, S.E. Kapphan, E.A. Kotomin and G. Borstel, A new phase of charge transfer vibronic excitons in perovskite ferroelectrics, Europhysics Letters, 2001, submitted. 5.1.1.2 Publikationen in wissenschaftlichen Sammelwerken 73. Karla, J. Braun, H. Schürmann, J. Lachnitt, J. Szade, D. Gravel and M. Neumann, Antiresonance in GdCu, BESSY Jahresbericht, 1996. 74. Willerding, K. Wandelt and J. Braun, Relativistic calculations of photoemission and LEED-intensities for ordered and disordered alloys application to Cu3Pt and Cu5Pt3, Properties of inorganic solids, 245, Plenum Publishing Corporation (New York, 1997). 75. J. Bansmann, L.Lu, M. Getzlaff, M. Fluchtmann, J. Braun, and K.H. Meiwes-Broer, Magnetic Linear Dichroism in valence band photoemission from thin cobalt films, BESSY Jahresbericht, 1997. 76. Karla, J. Braun, H. Schürmann, M. Neumann and J. Brügmann, Investigations of the Fano-Profiles of GdCu, HASYLAB Jahresbericht, 1997. 77. M. Fluchtmann, T. Schlathölter and J. Braun, UPS and XPS investigation to ferroemagnetic Gd, World Scientific Publishing Co. 439, 1998. 78. N.E. Christensen, E.A. Kotomin, R.I. Eglitis, A.V. Postnikov, G. Borstel, D.L. Novikov, S.Tinte, M.G. Stachiotti, and C.O. Rodriguez, Quantum mechanical modelling of pure and 134 defective KNbO3 perovskites, In: Defects and Surface-Induced Effects in Advanced Perovskites, ed. G. Borstel, NATO Science Series, High Technology, 77, pp. 3-16, 2000. 79. A.V. Postnikov, G. Borstel, A.I. Poteryaev, and R.I. Eglitis, First-principles simulations of substitutional defects in perovskites, In: Defects and Surface-Induced Effects in Advanced Perovskites, ed. G. Borstel, NATO Science Series, High Technology, 77, pp. 17-26, 2000. 80. G. Borstel and J. Inglesfield, Electronic States on Metal Surfaces, in: Handbook of Surface Science, Vol. 2, K. Horn and M. Scheffler, eds., North Holland, pp. 209-245, 2000 5.1.1.3 Publikationen in Tagungsbeiträgen 81. R.I.Eglitis, A.V.Postnikov, and G.Borstel, Semiempirical Hartree - Fock calculations for KNbO3 and KTaO3,- Proc. SPIE (Proc. of AOMD - 96 Conf., Riga, 1996), 2967, p.144149, 1997 82. R.I.Eglitis, and E.A.Kotomin, Calculations of F centers in KNbO3 ferroelectric crystals, Proc. SPIE (Proc. of AOMD-96 Conf., Riga, 1996), 2967, p.150-152, 1997 83. R.I.Eglitis, E.A.Kotomin, A.V.Postnikov, N.E.Christensen, and G.Borstel, First-principles and semi-empirical Hartree-Fock calculations for F centers in KNbO3 and Li impurities in KTaO3, - Proc. AIP (Proceedings of 5th Williamsburg Meeting of Ferroelectric Materials, Williamsburg, USA, 1998), 436, 207, 1998. 84. R.I.Eglitis, V.S.Vikhnin, P.A.Markovin, G.Borstel, Self-ordered second-component clusters in solid solutions on the basis of ferroelectric perovskites: Nb clusters in KTaO3,Proc. AIP (Proceedings of 5th Williamsburg Meeting of Ferroelectric Materials, Williamsburg, USA, 1998), 436, 87, 1998. 85. A.V. Postnikov and G. Borstel, LAPW vs LMTO full-potential simulations and anharmonic dynamics of KNbO3, First-Principles Calculations for Ferroelectrics: Fifth Williamsburg Workshop, ed. By R.E. Cohen, AIP Conference Proceedings 436, 217, 1998 86. S. Izvekov, M.R. Philpott, and R.I. Eglitis, Ab Initio Simulation of Metal Cluster Surrounded by Electrolyte, Journal of The Electrochemical Society 147, pp. 2273-2278, 2000. 87. R.I. Eglitis, S.V. Izvekov, and M.R. Philpott, Metal Dissolution in Aqueous Electrolyte. Semi-empirical Hartree-Fock and ab initio MD Calculations, Computational Materials Science 17, pp. 275- 278, 2000. 88. G. Borstel, E.A. Kotomin, R.I. Eglitis and E. Heifets, Computer modelling of point defects, impurity self-ordering effects and surfaces in advanced perovskite ferroelectrics, Acta Physica Polonica A 98, pp. 469-481, 2000. 89. G. Borstel, R.I. Eglitis, and E.A. Kotomin, Computer modelling of KTN solid solutions, In: Proceedings of the 2000 12th IEEE International Symposium on Applications of Ferroelectrics, (edited by S.K. Streiffer, B.J. Gibbons, and T.Tsurami), The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control Society (IEEE Catalog Number 00CH37076) 2, 671-674, 2001. 90. V.S. Vikhnin, R.I. Eglitis, E.A. Kotomin, S. Kapphan and G. Borstel, New PolaronicType Excitons in Ferroelectric Oxides: INDO-Calculations and Experimental Manifestation, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 677, AA4.15.1-AA4.15.6, 2001. 91. E. Heifets, E.A. Kotomin, R.I. Eglitis and R.E. Cohen, Calculations of Perovskite Surface Relaxation, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 654, AA5.3.1-AA5.3.6, 2001. 92. R.I. Eglitis, E.A. Kotomin and G. Borstel, Computer Modelling of Luminescence in ABO3 perovskites, MRS Symposium Proceedings, 2001, in press. 93. E.Heifets, R.I. Eglitis, E.A. Kotomin, and G. Borstel, First-principles and Semi-Empirical Calculations of Atomic and Electronic Structure for (100) and (110) Perovskite Surfaces, APS Conf. Proc. 2001, in press. 135 94. V.S. Vikhnin, R.I. Eglitis, E.A. Kotomin, S. Kapphan and G. Borstel, New-Polaronic Type Excitons in Ferroelectric Oxides: Nature and Experimental Manifestation, APS Conf. Proc., 2001, in press. 95. Heifets, R.I. Eglitis, E.A. Kotomin and G. Borstel, Calculations of Surface Structure for SrTiO3 Perovskite, MRS Conf. Proc. 2001, in press. 136 5.2 Magnetismus (Blügel) 5.2.1 Publikationstätigkeit S. Heinze, Ph. Kurz, D. Wortmann, G. Bihlmayer, and S. Blügel, Complex Magnetism in Ultra-Thin Films: Atomic-Scale Spin Structures and Resolution by the Spin-Polarized Scanning Tunneling Microscope, accepted by Appl. Phys. A (2001). D. Wortmann, S. Heinze, G. Bihlmayer and S. Blügel, Quantum-well states mediated STM images of buried two-dimensional transition-metal alloys, submitted to Phys. Rev. B. K. Schroeder, A. Antons, R. Berger, and S. Blügel, Surfactant mediated heteroepitaxy versus homoepitaxy: Kinetics for group-IV adatoms on As-passivated Si(111), submitted to Phys. Rev. Lett. Galanakis, G. Bihlmayer, V. Bellini, N. Papanikolaou, R. Zeller, S. Blügel and P. H. Dederichs, Broken bond counting rule for the surface energies of noble metals, submitted to Phys. Rev. Lett. K. Schroeder, A. Antons, R. Berger, and S. Blügel, Comment to ``Ge adatom adsorption, diffusion, and exchange on surfactant-coverd Si(111) surfaces'' , submitted to Phys. Rev. B. D. Wortmann, Ph. Kurz, S. Heinze, K. Hirai, G. Bihlmayer and S. Blügel, Resolving noncollinear magnetism by spin-polarized scanning tunneling microscopy, accepted by J. Magn. Magn. Mater., (2001). S. Heinze, G. Bihlmayer, and S. Blügel, First-Principles Interpretation of Scanning Tunneling Microscopy applied to Transition-Metal Surfaces: Buried CuIr/Cu(100) Surface Alloys, accepted by Phys. Stat. Sol. (2001). Ph. Kurz, G. Bihlmayer, S. Blügel, K. Hirai, T. Asada, Comment on ``Ultrathin Mn films on Cu(111) substrates: Frustrated antiferromagnetic order'', Phys. Rev. B 63, 096401 (2001). D. Wortmann, S. Heinze, Ph. Kurz, G. Bihlmayer, S. Blügel, Resolving Complex Atomic-Scale Spin-Structures by SP-STM, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 4132 (2001). 137 S. Clarke, G. Bihlmayer, S. Blügel, Chemical Effects in Rare Gas Adsorption, Phys. Rev. B 63, 085416 (2001). S. Link, H.A. Dürr, G. Bihlmayer, S. Blügel, W. Eberhardt, E.V. Chulkov, V.M. Silkin, P.M. Echenique, Elektron dynamics of image potential states on the clean and oxygem covered Pt(111) surface, Phys. Rev. B 63, 115420 (2001). H.-J. Kim, E. Vescovo, S. Heinze, S. Blügel, Surface electronic structure of Fe(110): the importance of surface reconances, Surf. Sci. 478, 193 (2001). Stefan Heinze und Stefan Blügel, Magnetische Ordnung wird sichtbar, Physik in unserer Zeit 32 (4), 154 (2001). 138 5.3 Makroskopische Systeme und Quantentheorie (Bärwinkel, Schmidt) 5.3.1 Publikationstätigkeit 5.3.1.1 Zeitschriftenaufsätze H.-J. Schmidt, J. Schnack, Partition functions and symmetric polynomials, Am. J. Phys., accepted Müller, M. Luban, C. Schröder, R. Modler, P. Kögerler, M. Axenovich, J. Schnack, P.C. Canfield, S. Bud'ko, and Neil Harrison, Classical and Quantum Magnetism in Giant Keplerate Magnetic Molecules, Chem. Phys. Chem. 2 (2001) 517 D. Mentrup, J. Schnack, Nose-Hoover dynamics for coherent states, Physica A 297 (2001) 337-347 H.-J. Schmidt, J. Schnack, M. Luban, Bounding and approximating parabolas for the spectrum of Heisenberg spin systems, Europhysics Letters 55 (2001) 105-111 Pop, A. Andronic, I. Berceanu, M. Duma, D. Mois, M. Petrovici, V. Simion, A. Bonasera, G. Immé, G. Lanzanò, A. Pagano, G. Raciti, N. Colonna, G. d'Erasmo, A. Pantaleo, H. Feldmeier, and J. Schnack, Global features of dissipative processes in light heavy-ion collisions, Nucl. Phys. A 679 (2001) 793-823 H.-J. Schmidt, M. Luban, Continuous families of isospectral Heisenberg spin systems and the limits of inference from measurements, J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 34 (2001) 2839-2858 Schnack, M. Luban, Rotational modes in molecular magnets with antiferromagnetic Heisenberg exchange, Phys. Rev. B 63 (2001) 014418 Schnack, Properties of the first excited state of nonbipartite Heisenberg spin rings, Phys. Rev. B 62 (2000) 14855-14859 H.-J. Schmidt, F. Homann, Photon Stars, General Relativity and Gravitation (GRG) Vol. 32, No. 5 (May 2000) 919 - 931 H. Feldmeier, J. Schnack, Molecular Dynamics for Fermions, Rev. Mod. Phys. 72 (2000) 655-688 Bärwinkel, H.-J. Schmidt, J. Schnack, Ground state properties of antiferromagnetic Heisenberg spin rings, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 220 (2000) 227 D. Mentrup, H.-J. Schmidt, J. Schnack, M. Luban, Transition from quantum to classical Heisenberg trimers: Thermodynamics and time correlation functions, Physica A 278 (2000) 214-221 Y. Furukawa, M. Luban, F. Borsa, D.C. Johnston, A.V. Mahajan, L.L. Miller, D. Mentrup, J. Schnack, A. Bino, Spin dynamics of the magnetic cluster [Cr_4S(O_2CCH_3)_8(H_2O)_4](NO_3)_2H_2O, Phys. Rev. B 61 (2000) 8635 Bärwinkel, H.-J. Schmidt, J. Schnack, Structure and relevant dimension of the Heisenberg model and applications to spin rings, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 212 (2000) 240-250 D. Mentrup, J. Schnack, M. Luban, Spin dynamics of quantum and classical Heisenberg dimers, Physica A 272 (1999) 153-161 139 5.3.1.2 Schnack, Thermodynamics of the harmonic oscillator using coherent states, Europhysics Letters 45 (1999) 647-652 H.-J. Schmidt, J. Schnack, Thermodynamic fermion-boson symmetry in harmonic oscillator potentials, Physica A 265 (1999) 584-589 Bärwinkel, J. Schnack, U. Thelker, Quasi-Particle Picture for Monatomic Gases, Physica A 262 (1999) 496-504 J. Gerling, H.-J. Schmidt, Three-Term Asymptotics of the Spectrum of Self-Similar Fractal Drums, Journal of Mathematical Sciences Vol. 6, No. 1, University of Tokyo (1999) 101 H.-J. Schmidt, J. Schnack, Investigations on finite ideal quantum gases, Physica A 260 (1998) 479-489 J. Schnack, Molecular dynamics investigations on a quantum system in a thermostat, Physica A 259 (1998) 49-58 H. Feldmeier, T. Neff, R. Roth, J. Schnack, A unitary correlation operator method, Nucl. Phys. A632 (1998) 61-95 Monographien Andreas Danckert, Entwicklung und Anpassung von Streukernmodellen der MolekülOberflächenwechselwirkung und ihre Anwendung in der numerischen Simulation verdünnter Hyperschallströmungen, Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V., DLR-FB 96-29 (1996) Susanne Richter, Construction of states on two-dimensional quantum lattices and quantum cellular automata, Shaker-Verlag, Aachen (1996), ISBN 3-8265-0610-3 Uwe Thelker, Eine verallgemeinerte BGK-Theorie für Gase mit inneren Freiheitsgraden, Shaker-Verlag, Aachen (1996), ISBN 3-8265-1397-5 5.3.1.3 Konferenzbeiträge D. Mentrup, J. Schnack, Isothermal quantum dynamics: Nosé-Hoover method for coherent states, in Advances in Quantum Many-Body Theory, Proceedings of "The 11th International Conferences on Recent Progress in Many-Body Theories", Manchester, edited by Raymond F. Bishop, Tobias Brandes, Klaus A. Gernoth, Niels R. Walet, and Yang Xian (UMIST, Manchester, UK), World Scientific Schnack, M. Luban, R. Modler, Rotational band structure of low-lying excitations in small Heisenberg systems, in Advances in Quantum Many-Body Theory, Proceedings of "The 11th International Conferences on Recent Progress in Many-Body Theories", Manchester, edited by Raymond F. Bishop, Tobias Brandes, Klaus A. Gernoth, Niels R. Walet, and Yang Xian (UMIST, Manchester, UK), World Scientific H.-J. Schmidt, On a synthetic formulation of general relativistic spacetime geometry, in "Recent Advances in Relativity Theory", ed. by M.C. Duffy and M.Wegener, Hadronic Press, Palm Harboour (2001), Vol. 2, 267-278 H.-J. Schmidt, Is there a gravitational collaps of the wave-packet?, in "Trends in Quantum Mechanics", ed. by H.-D. Doebner, S.T. Ali, M. Keyl and R.F. Werner, World Scientific, Singapore (2000) 122-129 T. Neff, H. Feldmeier, R. Roth, J. Schnack, Realistic interactions and configuration mixing in Fermionic Molecular Dynamics, Multifragmentation, Proc. Int. Workshop XXXVII, Hirschegg (1999) 283--292, ISSN 0720-8715 140 H. Feldmeier, T. Neff, R. Roth, J. Schnack, Fermionic Molecular Dynamics and short range correlations, Proceedings of the "XVII RCNP International Symposium on Innovative Computational Methods in Nuclear Many-Body Problems", Osaka, World Scientific (1998) H. Feldmeier, J. Schnack, Liquid-gas phase transition in finite nuclei within Fermionic Molecular Dynamics, Proceedings of the "Workshop on Nuclear Matter in Different Phases and Transitions", Les Houches, France, Kluwer Academic Publ. in Fundamental Theories of Physics (1998) 141 5.4 Numerische Physik (Hertel) 5.4.1 Publikationstätigkeit M. Lohmeyer, R. Stoffer, L. Wilkens, H. Dötsch Integrated optical cross strip interferometer Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 4277, Integrated Optics Devices V, 230-241 (2001) M. Lohmeyer, L. Wilkens, O. Zhuromskyy, H.Dötsch, P. Hertel Integrated magnetooptic cross strip isolator Optics Communications 189 (4-6), 251-259 (2001) O. Zhuromskyy, H. Dötsch, M. Lohmeyer, L. Wilkens, P. Hertel Magnetooptical waveguides with polarization-independent nonreciprocal phase shift IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology 19 (2), 214-221 O. Zhuromskyy, M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, P. Hertel, H. Dötsch, A. F. Popkov Analysis of nonreciprocal light propagation in multimode imaging devices Optical and Quantum Electronics 32 (6/8), 885-897 (2000) M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, O. Zhuromskyy, P. Hertel Wave-matching-simulations of integrated optical coupler structures Fiber and Integrated Optics (submitted, 1999) M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, O. Zhuromskyy, H. Dötsch, P. Hertel Unidirectional magnetooptic polarization converters IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology 17 (12), 2605-2611 (1999) N. Bahlmann, M. Wallenhorst, L. Wilkens, V. Backherms, A. Josef, P. Hertel, H. Dötsch Reduction of the temperature dependence of the nonreciprocal effect of magneto-optic channel-waveguides Applied Optics 38 (27), 5747--5751 (1999) M. Fehndrich, A. Josef, L. Wilkens, J. Kleine-Börger, N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel, H. Dötsch Experimental Investigation of the Nonreciprocal Phase Shift of a TE-mode in a Magnetooptic Rib Waveguide Applied Physics Letters 74 (20), 2918-2920 (1999) M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, O. Zhuromskyy, P. Hertel Wave-matching-simulations of integrated optical coupler structures Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 3620, Integrated Optics Devices III, 68-78 (1999) M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, O. Zhuromskyy, P. Hertel Perturbational estimation of geometry tolerances for rectangular integrated optics devices Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 3620, Integrated Optics Devices III, 311-319 (1999) N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, O. Zhuromskyy, H. Dötsch, P. Hertel Nonreciprocal coupled waveguides for integrated optical isolators and circulators for TMmodes Optics Communications 161 (4-6), 330-337 (1999) 142 M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, O. Zhuromskyy, P. Hertel Radiatively coupled waveguide polarization splitter simulated by wave-matching based coupled mode theory Optical and Quantum Electronics 31, 877-891 (1999) O. Zhuromskyy, M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, H. Dötsch, P. Hertel, A.F. Popkov Analysis of polarization independent Mach-Zehnder type integrated optical isolator IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology 17 (7), 1200-1205 (1999) N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, H. Dötsch, P. Hertel Integrated magneto-optic Mach-Zehnder interferometer isolator for TE-modes Electronics Letters 34 (22), 2122-2123 (1998) N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, H. Dötsch, P. Hertel Finite element analysis of nonreciprocal phase shift for TE-modes in magneto-optic ribwaveguides with a compensation wall IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics 32 (2), 250-253 (1999) M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, O. Zhuromskyy, H. Dötsch, P. Hertel Phase-matched rectangular magnetooptic waveguides for applications in nonreciprocal integrated optics devices: Numerical assessment Optics Communications 158 (1-6), 189-200 (1998) M. Lohmeyer, N. Bahlmann, P. Hertel Geometry tolerance estimation for rectangular dielectric waveguide devices by means of perturbation theory Optics Communications 163 (1-3), 86-94 (1999) A. F. Popkov, M. Fehndrich, M. Lohmeyer, H. Dötsch Nonreciprocal TE-mode phase shift by domain walls in magnetooptic rib waveguides Applied Physics Letters 72 (20), 2508-2510 (1998) M. Lohmeyer, M. Shamonin, N. Bahlmann, P. Hertel, H. Dötsch Radiatively coupled waveguide concept for an integrated magnetooptic circulator MRS Symposium Proceedings: Vol. 517, High-Density Magnetic Recording and Integrated Magneto-Optics: Materials and Devices, 519-524 (1998) N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, M. Wallenhorst, H. Dötsch, P. Hertel A comparison of an improved design for two integrated optical isolators based on Optical nonreciprocal Mach-Zehnder interferometry MRS Symposium Proceedings: Vol. 517, High-Density Magnetic Recording and Integrated Magneto-Optics: Materials and Devices, 513-518 (1998) M. Wallenhorst, V. Backherms, A. Josef, N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel, H. Dötsch Optimized nonreciprocal rib waveguides for integrated magneto-optic isolators MRS Symposium Proceedings: Vol. 517, High-Density Magnetic Recording and Integrated Magneto-Optics: Materials and Devices, 463-468 (1998) M. Lohmeyer Vectorial wave-matching-method mode analysis of integrated optical waveguides and Quantum Electronics 30 (5/6), 385-396 (1998) 143 N. Bahlmann, M. Lohmeyer, M. Wallenhorst, H. Dötsch P. Hertel An improved design of an integrated optical isolator based on nonreciprocal Mach-Zehnder interferometry Optical and Quantum Electronics 30 (5/6), 323-334 (1998) N. Bahlmann, V. Chandrasekhara, A. Erdmann, R. Gerhardt, P. Hertel, R. Lehmann, D. Salz, F. Schröteler, M. Wallenhorst, H. Dötsch Improved Design of Magnetooptic Rib Waveguides for Optical Isolators IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology 16 (5), 818-823 (1998) M. Lohmeyer Wave-matching-method for mode analysis of dielectric waveguides Optical and Quantum Electronics 29 (9), 907-922 (1997) M. Shamonin, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel Analysis of power-dependent switching between radiatively coupled planar waveguides IEEE Journal of Lightwave Technology 15, 983-989 (1997) M. Lohmeyer, M. Shamonin, P. Hertel Integrated optical circulator based on radiatively coupled magnetooptic waveguides Optical Engineering 36, 889-895 (1997) M. Shamonin, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel Directional coupler based on radiatively coupled waveguides Applied Optics 36, 635-641 (1997) M. Lohmeyer, M. Shamonin, P. Hertel Boundary conditions for the finite difference beam propagation method based on plane wave solutions of the Fresnel equation IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics 33, 279-285 (1997) H. Dötsch, A. Erdmann, M. Fehndrich, R. Gerhardt, P. Hertel, B. Lührmann, M. Shamonin, M. Wallenhorst Application of magnetic garnet films in optical communication, in R. Marcelli (ed.), Microwave Nonlinear Effects and Signal Processing Applications in Magnetic Films, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1996) N. Bahlmann, R. Gerhardt, M. Wallenhorst, H. Dötsch Determination of the ferrimagnetic precission cone of in-plane magnetized garnet films using optical modulation technique Journal of Applied Physics 80 (7), 3977-3981 (1996) N. Bahlmann, R. Gerhardt, H. Dötsch Optical investigation of domain resonances in magnetic garnet films Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 161, 22-30 (1996) H. Dötsch, N. Bahlmann, M. Fehndrich, R. Gerhardt, B. Lührmann and H.P. Winkler High Frequency Light Modulation by Excitations of Domain Lattices in Magnetic Garnet Films IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 32 (5), 4162-4167 (1996) 144 M. Shamonin, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel, H. Dötsch Optimization of a nonreciprocal phase shifter comprising a magneto-optic slab waveguide Optics Communcations 131, 37-40 (1996) M. Shamonin, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel, H. Dötsch Radiatively coupled magneto-optic waveguides Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 2695, Functional photonic and fiber devices, 344-354 (1996) M. Shamonin, M. Lohmeyer, P. Hertel, H. Dötsch Magneto-optic waveguides: modeling and applications Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 2695, Functional photonic and fiber devices, 355-361 (1996) 145 5.5 Theoretische Optik (Ringhofer) 5.5.1 Publikationstätigkeit 1. M. Mann, E. Shamonina, and K. H. Ringhofer, Modelling of two wave mixing experiments in sillenite crystals, Computer Phys. Commun., vol 96, pp 61-86, (1996) 2. Kießling, R. Kowarschik, and K. H. Ringhofer, Experimental verification of a model for two-wave mixing with nonplanar waves in sillenites, SPIE, vol. 2778, (1996). Optics for Science and New Technology, 17. Congress of the International Commission for Optics August 19-23, 1996 TAEJON Korea. 3. T. E. McClelland, D. J. Webb, B. I. Sturman, E. Shamonina, M. Mann, and K. H. Ringhofer, Excitation of higher spatial harmonics by a moving light pattern in sillenites, Opt. Commun., vol. 131, pp. 315-321, (1996). 4. S. G. Odoulov, B. I. Sturmann, E. Shamonina, and K. H. Ringhofer, Stochastic photorefractive backscattering from LiNbO3 crystals, Opt. Lett., vol. 21, pp. 854-856, (1996). 5. K. H. Ringhofer, Space-charge waves in photorefractive crystals, in Proceedings of the XIX-th National Conference on Physics and Condensed Materials, (Águas de Lindóa, SP, Brazil), pp. 385-388, (1996). 6. E. Shamonina, M. Mann, K. H. Ringhofer, A. Kießling, and R. K. Warschik, Dynamic holography with nonplane waves in sillenites, Opt. and Quantum Electron., vol 28, pp. 25-42, (1996). 7. E. Shamonina, B. I. Sturman, S. G. Odoulov, and K. H. Ringhofer, Investigation of stochastic photorefractive backscattering, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, vol. 13, pp. 2242-2251, (1996). 8. E. Shamonina, G. Cedilnik, M. Mann, A. Kießling, D. J. Webb, R. Kowarschik, K. H. Ringhofer, Investigation of two-wave mixing in arbitrary oriented sillenite crystals, Appl. Phys. B 64, 49-56, (1997). 9. E. Shamonina, K. H. Ringhofer, P. M. Garcia, J. Frejlich, Shape-asymmetry of the diffraction efficiency in Bi12TiO20: the simultaneous influence of absorption and higher harmonics, Opt. Commun. 141, 132--136, (1997). 10. J. Frejlich, P. M. Garcia, K. H. Ringhofer, E. Shamonina, Phase modulation in two-wave mixing for dynamically recorded gratings in photorefractive materials, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 14, 1741-1749, (1997). 146 11. V. P. Kamenov, K. H. Ringhofer, B. I. Sturman, J. Frejlich, Feedbackcontrolled photorefractive two-beam coupling, Phys. Rev. A 56, R2541-R2544, (1997). 12. K. H. Ringhofer, V. P. Kamenov, B. I. Sturmann, and J. Frejlich, Feedbackcontrolled two-beam coupling: New Dynamics, in Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, PR ´97, (Chiba, Japan), pp. 387-390, June 11-13, (1997). 13. S. Bian, J. Frejlich, K. H. Ringhofer, Photorefractive Saturable Kerr-Type Nonlinearity in Photovoltaic Crystals, Phys. Rev. Lett., 18, 4035-4038, (1997). 14. B. I. Sturman, M. Aguilar, F. Agulló-López, K. H. Ringhofer, Fundamentals of the nonlinear theory of photorefractive subharmonics, Phys. Rev. E 55, 60726083, (1997). 15. B. I. Sturmann, E. Shamonina, and K. H. Ringhofer, Explanation of the transverse subharmonic split in sillenites, in Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, PR´97, (Chiba, Japan), pp. 145-148, June 11-13, (1997). 16. S. Bian, J. Frejlich, and K. H. Ringhofer, Photorefractive Saturable Kerr-Type Nonlinearity in Photovoltaic Crystals, Phys. Rev. Lett., vol. 18, pp. 4035-4038, (1997). 17. K. H. Ringhofer, V. Kamenov, J. Frejlich, A. Freschi, P. M. Garcia, and B. I. Sturman, Phase modulation and periodic states, PROCEEDING OF SPIE, vol. 3488, pp. 182-188, (1997). Proceedings of the International Conference on `Nonlinear Optics of Liquid and Photorefractive Crystals II´, 5-10 October 1997, Partenit, Crimea, Ukraine. 18. E. Shamonina, V. Kamenov, K. H. Ringhofer, G. Cedilnik, A. Kießling, R. Kowarschik, D. J. Webb, Optical activity in photorefractive Bi12TiO20, Opt. Commun. 146, 62-68, (1998) 19. E. Shamonina, V. Kamenov, K. H. Ringhofer, G. Cedilnik, A. Kießling, R. Kowarschik, The optimum orientation of phase volume gratings in photorefractive sillenites: is it always [111]?, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 15, 2552-2559, (1998) 20. E. Shamonina, K. H. Ringhofer, B. I. Sturman, V. Kamenov, G. Cedilnik, M. Esselbach, A. Kiessling, R. Kowarschik, A. A. Kamshilin, V. V. Prokofiev, T. Jaaskelainen, Giant momentary readout by switching electric fields during twowave mixing in sillenites, Opt. Lett. 23, 1435-1437, (1998) 21. B. I. Sturmann, E. Podivilov, A. E. Chernykh, K. H. Ringhofer, V. P. Kamenov, H. C. Pedersen, and P. M. Johansen, Instability of the resonance excitation of space-charge waves in sillenite crystals, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, vol. 16, (1999). 147 22. E. Shamonina, V. Kamenov, K. H. Ringhofer, G. Cedilnik, A. Kiessling, and R. Kowarschik, Thickness dependence of the optimum orientation of volume phase gratings in optically active piezoelectric sillenite crystals, in CLEO/Europe-EQEC 1998, 13-18 September 1998. ISBN: 0-903748-73-8. 23. V. P. Kamenov, K. H. Ringhofer, B. I. Sturman, and J. Frejlich, A model for feedback-stabilization in sillenites, in CLEO/Europe-EQEC 1998, 13-18 September 1998. ISBN: 0-903748-73-8. 24. G. Cedilnik, M. Esselbach, A. Kiessling, R. Kowarschik, A. A. Kamshilin, E. Shamonina, K. H. Ringhofer, Measurement of the electric screening field in Bi12TiO20, J. Appl. Phys. 85, 1317-1321, (1999). 25. Y. Hu, K. H. Ringhofer, B. I. Sturman, Two regimes of two-beam coupling in cubic 43m crystals, Appl. Phys. 68, 931-936, (1999). Feature edition. 26. B. I. Sturman, A. I. Chernykh, E. Shamonina, V. P. Kamenov, K. H. Ringhofer, Rigorous 3d-theory of the subharmonic instability in sillenites, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 16, 1099-1103, (1999). 27. B. I. Sturman, E. V. Podivilov, K. H. Ringhofer, E. Shamonina, V. P. Kamenov, E. Nippolainen, V. V. Prokofiev, A. A. Kamshilin, Theory of photorefractive vectorial wave coupling in cubic crystals, Phys. Rev. E 60, 3332-3352, (1999). 28. B. I. Sturman, E. V. Podivilov, K. H. Ringhofer, E. Shamonina, V. P. Kamenov, E. Nippolainen, V. V. Prokofiev, and A. A. Kamshilin, Theory and applications of vectorial beam coupling in sillenites, in Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, PR´99 (P. E. Andersen, ed.), pp. 207-213, OSA, (1999). 29. V. V. Shepelevich, Y. Hu, A. Firsov, E. Shamonina, K. H. Ringhofer, Gain optimization with respect to the thickness of a sillenite crystal, Appl. Phys. B 68, 923-929, (1999). feature edition. 30. V. V. Shepelevich, S. F. Nichiporko, A. E. Zagorskiy, N. N. Egorov, Y. Hu, K. H. Ringhofer, and E. Shamonina, Gain optimization at two-wave mixing in cubic photorefractive piezocrystals of (111)-cut, in Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, PR´99 (P. E. Andersen, ed.), pp. 353-360, OSA (1999). 31. K. H. Ringhofer, V. P. Kamenov, B. I. Sturman, A. I. Chernykh, and V. Y. Gayvoronsky, Two-wave coupling under fast phase modulation, in Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, PR´99 (P. E. Andersen, ed.), pp. 267-272, OSA, (1999). 32. B. I. Sturman, A. I. Chernykh. K. H. Ringhofer, and E. Shamonina, Effect of spatial inhomogeneity on the resonant photrefractive phenomena in sillenites, in 148 Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, PR´99 (P. E. Andersen, ed.), pp. 416-422, OSA, (1999). 33. K. H. Ringhofer, E. Shamonina, V. P. Kamenov, B. I. Sturman, Elastic contributions to electro-optics, SPIE Proc. 3904, 166-177, (1999) 34. Y. Hu, K. H. Ringhofer, E. Shamonina, V. P. Kamenov, and B. I. Sturman, Oscillatory regime of two-beam coupling in cubic 43m crystals, in Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, PR´99 (P. E. Andersen, ed.), pp. 330-346, OSA, (1999). 35. K. Shcherbin, S. Pavlyuk, O. Shumelyuk, S. G. Odoulov, B. I. Sturman, and K. H. Ringhofer, Active stabilization technique at high and low fringe modulation, in Photorefractive Materials, Effects and Devices, PR´99 (P. E. Andersen, ed.), pp. 35-38, OSA, (1999). Post deadline paper. 36. B. I. Sturman, A. I. Chernykh, V. P. Kamenov, E. Shamonina, K. H. Ringhofer, Resonant vectorial wave coupling in cubic photorefractive crystals, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 17, 985-996, (1999) 37. E. Shamonina, Y. Hu, V. P. Kamenov, K. H. Ringhofer, V. Y. Gayvoronsky, S. F. Nichiporko, A. E. Zagorskiy, N. N. Egorov, V. V. Shepelevich, Diffusion recording in photorefractive sillenite crystals: an analytical approach for engineering purposes, Opt. Commun. 180, 183-190, (2000) 38. V. P. Kamenov, Y. Hu, E. Shamonina, K. H. Ringhofer, V. Y. Gayvoronsky, Two-wave mixing in (111)-cut Bi12SiO20 and Bi12TiO20 crystals: characterization and comparison with the general orientation, Phys. Rev. E 62, 2863-2870, (2000) 39. V. P. Kamenov, E. Shamonina, K. H. Ringhofer, E. Nippolainen, V. V. Prokofiev, A. A. Kamshilin, Photorefractive light scattering families in (111)-cut Bi12TO20 crystals under ac recording, Phys. Rev. E 2000. Accepted 40. J. Frejlich, A. A. Freschi, P. M. Garcia, E. Shamonina, V. Y. Gayvoronsky, K. H. Ringhofer, Feed-back controlled running holograms in strongly absorbing photorefractive materials, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 17, 1517-1521, (2000) 41. K. H. Ringhofer, Y. Hu, E. Shamonina, A. A. Freschi, V. Y. Gayvoronsky, The effect of bulk light absorption on running photorefractive holograms, J. Opt. A: Pure and Applied Optics 2, 34-38, (2000) 42. K. H. Ringhofer, V. P. Kamenov, B. I. Sturman, and A. Chernykh, Shaping of photorefractive two-wave coupling by fast phase modulation, Phys. Rev. E 61, 2029-2037, (2000) 149 43. S. F. Nichiporko, A. E. Zagorskiy, V. V. Shepelevich, Y. Hu, K. H. Ringhofer, E. Shamonina, Orientation dependence of the diffraction efficiency of holograms in cubic photorefractive (111)-cut piezocrystals, Techn. Phys. Lett. 26, 44-49, (2000) 44. Y. Hu, K. H. Ringhofer, E. Shamonina, A. A. Firsov, and V. V. Shepelevich, Optimization of diffraction efficiency of transmission hologram in cubic photorefractive piezocrystal of (110)-cut in dc electric field, in Optics of Crystals. International Scientific Conference OC - 2000, Mozyr, Belarus, 26-30 September 2000, (2000). Poster-Session. 45. S. F. Nichiporko, A. E. Zagorskiy, V. V. Shepelevich, N. N. Egorov, K. H. Ringhofer, Y. Hu, and E. Shamonina, The effect of ac electric field on polarizatio dependence of holograms energy characteristics in Bi12TiO20 crystal, in Optics of Crystals. International Scientific Conference OC - 2000, Mozyr, Belarus, 26-30 September 2000, (2000). Poster-Session. 46. V. V. Shepelevich, S. F. Nichiporko, A. E. Zagorskiy, N. N. Egorov, Y. Hu, K. H. Ringhofer, E. Shamonina, V. Y. Gaivoronsky, Optimization of diffraction efficiency and gain for two-wave mixing in cubic (111)-cut photorefractive piezocrystals, Ferroelectrics, 2000. Submitted. 47. V. V. Shepelevich, S. F. Nichiporko, A. E. Zagorskiy, N. N. Egorov, Y. Hu, K. H. Ringhofer, E. Shamonina, Polarization and orientation dependence of diffraction efficiency and gain in cubic (111)-cut photorefractive piezocrystals, Optical Materials, 2000. Submitted. 48. Y. Hu, K. H. Ringhofer, and E. Shamonina, The parallel subsystem: an almost precise solution for wave-mixing in sillenites, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, 2000. Submitted. 49. E. V. Podivilov, B. I. Sturman, S. G. Odoulov, S. Pavlyuk, K. V. Shcherbin, V. Y. Gayvoronsky, K. H. Ringhofer, V. P. Kamenov, Attractors and autooscillations for feedback controlled photorefractive beams, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000. Submitted. 150 IV 1 Anhang Grunddaten Stellen und Personal der Lehreinheit Tabelle 1: Stellen der Lehreinheit nach Stellenart und Art der Finanzierung Stellenart Haushaltsmittel Sonderprogramme Drittmittel Professur C4 7 Professur C3 6 Professur C2 auf Zeit 1 Hochschuldozent/in C2 2 Wissenschaftliches Personal auf Dauer (A13-A15, IIa) 14 Oberassist./Obering. (C2) 1 Wiss. Assistent/in (C1) 4 FwN (IIa) 4 12 10,75 3 Wissenschaftliche Stellen insgesamt 39 1 10,75 Verwaltung (einschl. Bibliotheksdienst) 6 Technischer Dienst (einschl. EDV) 27 Nichtwissenschaftliche Stellen insgesamt 33 LfbA (einschließlich Lektor/in) Stichtag: 1. Januar 2001 Lehreinheit: Fachlich abgegrenzte Einheit gemäß der Kapazitätsberechnung Haushaltsmittel: Planstellen gem. Stellenbeilage (ehemalige Beilage) zum Haushaltsplan. „Drittmittel“: Aus Mitteln Dritter finanzierte Beschäftigungsverhältnisse (auch zeitlich befristet). Aus von Bund und Land gemeinsam finanzierten Sonderprogrammen – HSP, LÜP u.ä.- bestehende Stellen; auch zeitlich befristete Beschäftigungsverhältnisse. (Zentralkapitel 0608 und 0609 jedoch ohne nichtstellenbezogene Personalmittel) Sonderprogramme: 2 3 Forschungspoolstelle in Vollzeitbeschäftigte 15 Beschäftigten 151 Tabelle 2: Auflistung der unbesetzten Professuren im Studienjahr 2001 Wissenschaftliche Einrichtung Lehreinheit Physik 4 Denomination Grund Theoretische Physik Ausscheiden des Stelleninhabers Wissenschaftliche Einrichtung: Angabe des Instituts, Seminars oder der Abteilung. Denomination: Genaue Bezeichnung der Professur. 4 ab 1.04. besetzt mit Prof. Blügel 152 Tabelle 3: Planmäßig freiwerdende Stellen C4 bis C2 Planmäßig freiwerdende Stellen Professur C2 C2-Stellen auf Dauer Professur C4 Professur C3 Vermerke 2 12 13 Verbleib C4 bzw. C3 14 19 Verbleib 2001 2002 2003 2004 15 2005 2006 16 Verbleib 2007 2 78 Verbleib 2008 Summe 6 2 Prof. C2: Lebenszeitstellen. C2-Stellen: Hochschuldozenten/innen und Oberassist./-ing. der Besoldungsgruppe C2 auf Lebenszeitstellen. Vermerke: kw-Vermerke bzw. ku-Vermerke und deren Ausrichtung. (1) Makromolekülstruktur (2) Advanced Materials (Lokale Sonden) (3) Advanced Material (Dünne Schichten) (4) Umweltphysik /Sensorik (5) Molekulare Architektur (6) Advanced Materials (Mesoskopische Systeme) (7) Advanced Materials (Computational Physics) (8) Didaktik der Physik (9) Umweltphysik/Modellierung, möglich: Verwendung für Informatik ________________________________________________ 153 Tabelle 4: Wissenschaftliches Personal der Lehreinheit insgesamt nach Stellen und beschäftigten Personen davon Stellen insgesamt Stellen Beschäftigte Professur C4 7 7 Professur C3 6 55 Professur C2 auf Zeit 1 1 1 Hochschuldozent/in C2 2 2 2 Wissenschaftliches Personal auf Dauer (A13-A15, IIa) 14 8 8 Oberassist./Obering. (C2) 1 Wiss. Assistent/in (C1) 4 4 4 15,75 20,756 4,75 16 50,75 47,75 5,75 42 FwN (IIa) Frauen Männer 7 1 4 LfbA (einschließlich Lektor/in) Wissenschaftliches Personal insgesamt Stichtag: 1. Januar 2001 Lehreinheit: Fachlich abgegrenzte Einheit gemäss der Kapazitätsberechnung. Stellen insgesamt: Planstellen, aus Mitteln Dritter und aus Sonderprogrammen finanzierte Beschäftigungsverhältnisse (siehe Tab. 1). Bei der Angabe der Stellen sind Teilzeitarbeitsplätze oder Arbeitsplätze, die nur teilzeitbesetzt sind, als Vollzeitäquivalente umzurechnen. Beispiel: drei Beschäftigte mit 50% der regulären Arbeitszeit entsprechen 1,5 Stellen. 5 6 zusätzlich 1 C3 besetzt ab 1.04.2001 20,75 Vollzeitäquivalente entspricht 29 Beschäftigten, davon 15 im Drittmittelbereich 154 2 Mittel für Lehre und Forschung Tabelle 5: Jahr Mittel für Lehre der Lehreinheit Physik in DM Hauptgruppe 4 Hauptgruppe 5 Hauptgruppe 8 Gesamt 1996 203.191,51 DM 690.134,91 DM 156.152,75 DM 1.049.479,17 DM 1997 147.427,06 DM 589.044,61 DM 210.403,21 DM 946.874,88 DM 1998 153.190,20 DM 665.106,07 DM 71.437,90 DM 889.734,17 DM 1999 156.336,42 DM Keine Angabe 588.441,37 DM 95.923,76 DM 840.701,55 DM 2000 2001 Keine Angabe Angaben in Haushaltsjahren Bibliotheksmittel (Ausgaben): 1996: 310.900 DM 1997:366.200 DM 1998: 432.500 DM 1999: 406.100 DM 2000: 421.700 DM 2001: 395.500 DM (Zuweisung) Lehrmittel: Ansatz gem. Haushaltsplan (TG 71/81) bzw. Ist-Ausgaben gem. der Hauptgruppen 4, 5 und 8. Bibliotheksmittel – wenn möglich – bitte gesondert ausweisen. Tabelle 5: Mittel für Physik SFB 04 Jahr Hauptgruppe 4 Hauptgruppe 5 Hauptgruppe 8 Gesamt 1996 54.983,87 DM 83.509,88 DM 14.500,01 DM 152.993,76 DM 1997 52.805,04 DM 94.345,04 DM 0,00 DM 147.150,08 DM 1998 53.559,39 DM 92.181,14 DM 12.000,01 DM 157.740,54 DM 1999 47.555,40 DM 76.195,50 DM 23.484,38 DM 147.235,28 DM 155 Tabelle 6: Drittmittel SFB, TFB und Graduiertenkollegs 1996-2001 der Lehreinheit Physik kDM SFB 225 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 1.432,00 1.347,18 1.216,11 1.031,00 842,63 Summe 5.868,92 Transferbereich 1998 1999 2000 2001 16,4 326,6 420 36,39 Summe 799,39 Graduiertenkolleg 15 1998 1999 2000 2001 310,58 310,58 363,33 45,3 Summe 1029,79 Graduiertenkolleg 695 2001 497,84 Gesamtsumme 8.195,94 156 „Drittmittel“ der Organisationseinheiten in DM Tabelle 6.1: Drittmittel Einzelvorhaben (Zeitpunkt der Einwerbung 1996 - 2001) Arbeitsgruppe Beträge/kDM Elektrooptik 3.394,80 Magnetooptik 38,00 Didaktik der Physik 94,00 Elektronenspektroskopie 2.511,05 Laserspektroskopie 1.090,00 Magnetische Resonanzspektroskopie 274,00 Nichtlineare Optik Oberflächenphysik und Nanostrukturen 1.861,00 Umweltphysik-Prozessstudien 4.203,73 Umweltphysik-Feldmessungen 550,00 Kristallzüchtung Festkörperphysik 1.940,00 Magnetismus (nur 2001) 670,05 Makroskopische Systeme, Quantentheorie 72,50 Numerische Physik Theoretische Optik 8,00 16.994,63 Summe 3 Studierende Tabelle 7: Studierendendaten Studienjahr 1996 Studienjahr 2001 (WS 95/96 + SS 96) (WS 00/01 + SS 01) Zulassungszahl bzw. Aufnahmekapazität 135 121 Studienanfänger/innen (1. FS) 72 25 WS 1995/96 WS 2000/01 Studiengang: Diplom Physik Studierende gesamt Insges. weibl. Insges. weibl. 347 41 163 20 157 Studienjahr 1996 Studienjahr 2001 (WS 95/96 + SS 96) (WS 00/01 + SS 01) Zulassungszahl bzw. Aufnahmekapazität — 25 Studienanfänger/innen (1. FS) — 14 WS 1995/96 WS 2000/01 Studiengang: Bachelor Physik mit Informatik Studierende gesamt Insges. weibl. Insges. weibl. — — 14 2 Studienjahr 1996 Studienjahr 2001 (WS 95/96 + SS 96) (WS 00/01 + SS 01) Zulassungszahl bzw. Aufnahmekapazität 8 8 Studienanfänger/innen (1. FS) 3 2 WS 1995/96 WS 2000/01 Studiengang: Magister-Hauptfach Physik Studierende gesamt Insges. weibl. Insges. weibl. 7 2 8 2 Studienjahr 1996 Studienjahr 2001 (WS 95/96 + SS 96) (WS 00/01 + SS 01) Zulassungszahl bzw. Aufnahmekapazität 6 3 Studienanfänger/innen (1. FS) 1 2 WS 1995/96 WS 2000/01 Studiengang: LA berufsbild. Schulen Physik 1) Studierende gesamt 1) Insges. weibl. Insges. weibl. 4 3 4 2 Inklusive Erweiterungsprüfungen. Studienjahr 1996 Studienjahr 2001 (WS 95/96 + SS 96) (WS 00/01 + SS 01) Zulassungszahl bzw. Aufnahmekapazität 20 30 Studienanfänger/innen (1. FS) 10 5 WS 1995/96 WS 2000/01 Studiengang: LA Gymnasiun Physik 1) Studierende gesamt 1) Insges. weibl. Insges. weibl. 102 26 56 19 Inklusive Erweiterungsprüfungen. Studienjahr 1996 Studienjahr 2001 (WS 95/96 + SS 96) (WS 00/01 + SS 01) Zulassungszahl bzw. Aufnahmekapazität — 48 Studienanfänger/innen (1. FS) — 4 WS 1995/96 WS 2000/01 Studiengang: LA GHR Langfach Physik Studierende gesamt Insges. weibl. Insges. weibl. — — 9 5 158 Studienjahr 1996 Studienjahr 2001 (WS 95/96 + SS 96) (WS 00/01 + SS 01) Zulassungszahl bzw. Aufnahmekapazität 5 — 2) Studienanfänger/innen (1. FS) 4 — 2) WS 1995/96 WS 2000/01 Studiengang: LA Realschule Physik (alt) 1) Studierende gesamt 1) 2) Insges. weibl. Insges. weibl. 29 5 8 3 Inklusive Erweiterungsprüfungen. Eingestellt zum Wintersemester 1998/99. Studienjahr 1996 Studienjahr 2001 (WS 95/96 + SS 96) (WS 00/01 + SS 01) Zulassungszahl bzw. Aufnahmekapazität 19 — 2) Studienanfänger/innen (1. FS) 10 — 2) WS 1995/96 WS 2000/01 Studiengang: LA Realschule Physik 3. Fach (alt) 1) Studierende gesamt 1) 2) Insges. weibl. Insges. weibl. 56 40 19 13 Inklusive Erweiterungsprüfungen. Eingestellt zum Wintersemester 1998/99. Studienjahr 1996 Studienjahr 2001 (WS 95/96 + SS 96) (WS 00/01 + SS 01) Zulassungszahl bzw. Aufnahmekapazität 1 — 1) Studienanfänger/innen (1. FS) 1 — 1) WS 1995/96 WS 2000/01 Studiengang: LA GH (H) Physik 3. Fach (alt) Studierende gesamt 1) Insges. weibl. Insges. weibl. 7 4 5 1 Eingestellt zum Wintersemester 1998/99. Studiengänge: Nur der Lehreinheit zugeordnete Studiengänge. Zulassungszahl: Die auf Grund der Kapazitätsberechnung nach KapVO ermittelte Höchstzahl an zu vergebenden Studienplätzen im ersten Fachsemester bei Studiengängen mit Zulassungsbeschränkung nach Schwund. Aufnahmekapazität: Studienanfängerplätze bei Studiengängen ohne Zulassungsbeschränkung. Studierende: Angaben in Fachfällen. Hinweis: Bitte die Tabelle entsprechend der Anzahl der Studiengänge vervielfältigen. 159 Tabelle 8: Absolventen/innen nach Abschlussart 1996 Studiengänge / Abschlussart 1997 1998 1999 2000 insg. weibl. insg. weibl. insg. weibl. insg. weibl. insg. weibl. Diplom Physik 34 2 37 3 21 0 31 2 14 0 LA Realschule Physik 3 0 2 1 1 0 3 0 k.A. k.A. LA Gymnasium Physik 1 0 4 0 3 0 1 1 k.A. k.A. Angaben in Studienjahren Studiengänge: Nur grundständige Studiengänge sowie ggf. Lehramt an Gymnasien. Absolventen/innen: Studierende, die im Erststudium eine Abschlussprüfung bestanden haben. Bei Studiengängen mit Haupt- und Nebenfächern (Magister, LA) erfolgt die Zuordnung anhand des Faches der schriftlichen Arbeit. 4 Post-Graduierte Tabelle 9: Promotionen und Habilitationen 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 insg. weibl. insg. weibl. insg. weibl. insg. weibl. insg. weibl. Promotionen 10 2 7 0 12 0 22 4 8 0 Habilitationen 0 — 3 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 Promotionen: Angaben in Studienjahren. Habilitationen: Angaben in Kalenderjahren. 160 161 V Anhang Entwicklungsplan Beschluss des Fachbereichsrates vom 16. März 1999