Hormonanalytik bei Schilddrüsenerkrankungen
Werbung

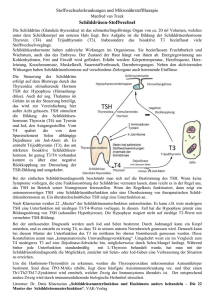
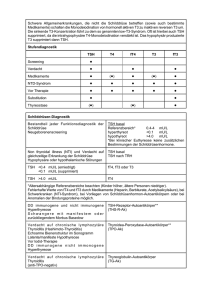
Hormonanalytik bei Schilddrüsenerkrankungen Potsdam 24. Juni 2011 Prof. Dr. med. B.L. Herrmann Endokrinologie /// Diabetologie Facharztpraxis und Labor Bochum PubMed U.S. National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health Search: Results: Thyroid 2009 n=4.913 Thyroid 2010 n=5.239 any date 150.131 Schilddrüsenerkrankungen Struma nodosa Knoten Karzinom Hashimoto DeQuervain-Thyreoiditis Zysten Morbus Basedow PD Dr. Herrmann - Bochum Hirnanhangsdrüse Jod TSH Schilddrüsenhormone T4/T3 Schilddrüse 73-jähriger Patient LABOR TSH fT4 TT4 TT3 Normalbereich 0,4 - 4,0 U/ml 10 - 25 pM 58 - 154 nM 1,2 - 3,1 nM 26.03.2001 0,15 ↓ 5↓ 41 ↓ 0,8 ↓ 30.03.2001 LH < 0,6 ↓ Prol 6,2 ↓ T < 1,8 ↓ GH < 0,5 ↓ FSH < 0,6 ↓ Cs 34 ↓ ACTH < 5 ↓ IGF1 26 ↓ Beispiel: TSH-Bestimmung als Routineuntersuchung Gibt es unterschiedliche TSH-Bereiche unter verschiedenen Völkern und bezogen auf das Alter? National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) Age- and Race-Based Serum Thyrotropin Reference Limits TSH higher in eldery people Shift in TSH distribution to higher concentrations with age. Data from NHANES III (NH3) and NHANES 1999–2002 (NH 99_02) populations Martin I. Surks and Laura Boucai , JCEM. 2010 Feb;95(2):496-502. Age- and Race-Based Serum Thyrotropin Reference Limits TSH in Blacks is lower than in Caucasians Shift in TSH distribution with race using NHANES III disease-free population and urban outpatient population. Data for disease-free Blacks and disease-free Caucasians are from NHANES III (1 ); data for urban Blacks and urban Caucasians are adapted from Boucai L and Surks MI (33 ). Martin I. Surks and Laura Boucai , JCEM. 2010 Feb;95(2):496-502. Framingham Heart Study 2007 males and females > 60 years; normal peripheral hormones Follow up: 10 years Relative Risk: 3.1 Sawin et al. 1994, New Engl J Med 331:1249-1252 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)-Thyroperoxidase Antibody Relationships Demonstrate That TSH Upper Reference Limits May Be Skewed by Occult Thyroid Dysfunction Most studies report that the lower TSH limit (2.5th percentile) lies between 0.2 and 0.4 mIU/liter, but upper limits (97.5th percentile) vary between 2.4 and 4.2 mIU/liter as related to ethnicity or geographic location (3, 4). Some variability is methodological (5, 6), but even when using the same assay, TSH upper limits vary between 3.1 and 3.7 mIU/liter for European Caucasians (4). Spencer CA, at al., The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism Vol. 92, No. 11 4236-4240, 2010 0,3 – 4,0 mU/l Daten der Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP) Wie suffizient ist die Einnahme von T4? Thyroid function tests in patients taking thyroid medication in Germany: Results from the population-based Study of Health in Pomerania (SHIP). Proportion of decreased, normal and increased serum thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels according to the local reference range ( < 50 years: 0.27-2.15 mIU/L; ≥ 50 years: 0.19-2.19 mIU/L) by type of thyroid medication. Hannemann A et al., BMC Res Notes, 2010 Schilddrüsen-Szintigraphie weder warm noch kalt Punktion warmer Knoten kalter Knoten <5% bösartig Überfunktion Schilddrüsen-Ultraschall-Screening PAPILLON (N=91.681) Diagnostisches Vorgehen bei Schilddrüsenknoten Anamnese, Palpation der Schilddrüse Hals-/Schilddrüsensonographie TSH, FT3, FT4, (TG,-TPO-AK), Calcitonin Cave: Sampling error Kalte(r) Knoten technisch inadäquat Negativ Repunktion Mann, Reiners, Schmid, Sektion Schilddrüse 2008 Symptom Struma – pathogenetische Einteilung Bei Jodmangel Bei Immunthyreopathien Bei Autonomie Bei Zystenbildung, nach Blutung, nach Trauma Bei Entzündungen Bei Schilddrüsentumoren Bei neoplastischer Produktion von TSH und TSH-ähnlichen Substanzen Bei Akromegalie Bei Enzymdefekten Bei Hormonresistenz Bei Befall der Schilddrüse durch extrathyr. bzw. systemische Erkrankungen Mediane Jodidurie (µg I-/l) gesunder 18- bis 70-Jähriger in definierten Regionen Deutschlands 2005 (n=1.538) 64% had no iodine deficiency (>100µg/l) Hampel et al. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2009, Dec, Epub Läßt sich das Knotenvolumen medikamentös beeinflussen ? Sdano M.T. et al., Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery 133, 2005, 391-396 „LISA-Studie“ (Levothyroxin und Iodid in der Strumatherapie als Mono- oder Kombinationstherapie – LISA) Plazebo Jodid L-Thyroxin* L-Thyroxin + Jodid 150* Knotenvolumen Schilddrüsenvolumen -5,2% -9,0% -12,1% -21,6% -1,9% -4,5% -7,1% -10,0% *TSH-adaptierte Dosis Multizentrische, randomisierte doppelblinde Studie N=1013, 62 Zentren Grußendorf M et al. Schilddrüse, Heidelberg 2009 Das diagnostische Problem 40% haben Knoten Papillär Follikulär Medullär Anaplastisch 75% 20% 3% 2% <0.01% davon sind bösartig Schilddrüsenkarzinome / Epidemiologie papillär 50 - 80 % C-Zell 4 - 10 % anaplastisch 2 - 3 % 10-Jahres-Überlebensraten: • papillär 85 – 90 % • follikulär 60 – 70 % follikulär 20 - 40 % onkozytär 4 - 6 % • onkozytär 50 – 60 % • anaplastisch 0 – 9 % Diagnostisches Vorgehen bei Schilddrüsenknoten Cave: Sampling error Mann, Reiners, Schmid, Sektion Schilddrüse 2008 Calcitonin-Screening Struma nodosa (alle Patienten) Calcitonin (CT) <10 pg/ml individuelle Behandlung (nach klin. Indikation) >10 pg/ml Pentagastrintest (0,5 g/kg i.v. 0,2,5 min) stim CT >100 pg/ml stim CT 30-100 pg/ml Totale Thyreoidektomie (+ LK-Dissektion, wenn stim. CT >200 pg/ml) Reevaluation nach 4-6 Mon. histologisch gesichertes MTC Karges W. et al., , Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes . Jan. 112 :52-8 (2004) RET-Mutationsnachweis Tumormarker Calcitonin für Medulläre SD-Carzinome Calcitonin-Messung im Blut (Screening) 4.400 calcitonin [pg/ml] 60 50 40 medullary carcinoma c-cell hyperplasia 30 20 10 0 0 25 50 75 100 age [years] Herrmann BL et al., Eur J Endocrinol. 2010 Mar 23. M. Basedow- Langzeitergebnisse Zusammenstellung aus 26 Studien (1953-1991): Von 4602 behandelten Patienten wurden 2279 Rezidive beobachtet Rezidivrate bei Erwachsenen: 50% Bei Kindern und Jugendlichen: 60% Hyperthyreose-Rezidiv in Abhängigkeit der TRAK-Spiegel n = 93 Patienten 50 Median: 2.2 IU/l 8.6 IU/l 40 Mittlere Dauer der thyreostatische Therapie insgesamt: 5,1 Mon - Rez.: 5,4 Mon - Rem: 4,6 Mon follow-up: 21,7 Mon TRAb IU/L Dauer der Rem: 17,0 Mon 30 TRAb (IU/l) Wahrscheinlichkeit einer Remission > 10 3,4% (1/29) 20 Spez. für Rezidiv 97% PPV für Rez. 96,4% 10 >7 >4 0 Remission Remission 13,9% (5/36) 15,6% (7/45) Relapse Rezidiv Schott M et al., Horm Metab Res 2004;36:92-96 TRAK-Verlauf unter Therapie Laurberg P et al. Eur J Endocrinol 2008;158(1):69-75 Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy after Treatment for Graves’ Hyperthyroidism with Antithyroid Drugs or Iodine-131 Conclusions: Radioiodine treatment is a significant risk factor for development of TAO in Graves’ hyperthyroidism. Smokers run the highest risk for worsening or development of TAO irrespective of treatment modality. Träisk F et al., J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Oct;94(10):3700-7 Selenoprotein P / Selen E.O. P<0.0001 P<0.0001 Die Patienten wiesen schon im Frühstadium der EO signifikant niedrigere SEPP-Spiegel (2.2 +/- 0.7 versus 3.0 +/0.6 mg/l, p<0.0001) und Selen-Spiegel (35.1 +/- 13.6 versus 62.8 +/- 11.0 mg/l, p<0.0001) im Vergleich zu den gesunden Kontrollen auf. Es zeigte sich kein Unterschied zwischen Patienten mit milder und schwerer EO. Weiterhin bestand kein Unterschied in Bezug auf die Prognose der Hyperthyreose – Patienten mit Remission unterschieden sich nicht von denen, die rezidivierten. Dehina N et al., ETA, Lisboa 2009 Selenium and the Course of Mild Graves' Orbitopathy The patients were given selenium (100 μg twice daily), pentoxifylline (600 mg twice daily), or placebo (twice daily) orally for 6 months and were then followed for 6 months after treatment was withdrawn. At the 6-month evaluation, treatment with selenium, but not with pentoxifylline, was associated with an improved quality of life (P<0.001) and less eye involvement (P=0.01) and slowed the progression of Graves' orbitopathy (P=0.01), as compared with placebo. Selenium administration significantly improved quality of life, reduced ocular involvement, and slowed progression of the disease in patients with mild Graves' orbitopathy. N Engl J Med. 2011 May 19;364(20):1920-31 „physiologische“ Schwangerschaftshyperthyreose 20% der Schwangeren haben ein erniedrigtes TSH (hCG- Stimulation der Schilddrüse) fast alle haben erhöhte TT4 und TT3 Spiegel ca. 5% haben zusätzlich ein passager erhöhtes fT4 Klinik ist variabel (oft Hyperemesis) Behandlung nur sehr selten erforderlich: symptomatisch Glinoer et al., Endocr Rev 1997, 18(3):404-33 Glinoer et al., JCEM 1990,71(2):276-87 Diaplazentarer Austausch Mutter Jodid TSH T3,T4 SD-AK Thyreostatika Plazenta Fetus TSH 1. Der Fetus ist während der gesamten Schwangerschaft auf die Versorgung mit Jodid durch die Mutter angewiesen. 2. Die Reifung des thyreoidalen Regelkreises dauert bis in die ersten Lebensmonate, Beginn der Hormonsynthese ab ~10. SSW Nieder-T3-Syndrom R. Gärtner Hormonanalytik bei Schilddrüsenerkrankungen Potsdam 24. Juni 2011 Prof. Dr. med. B.L. Herrmann Endokrinologie /// Diabetologie Facharztpraxis und Labor Bochum