PERSONAL PRONOMEN 1 Person singular 2 Person singular 3
Werbung

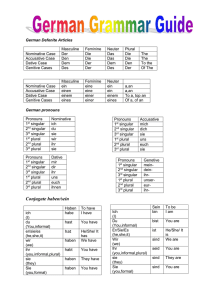
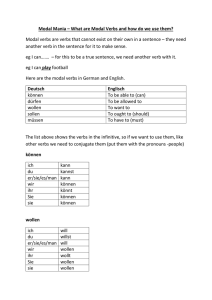
PERSONAL PRONOMEN Nominativ Akkusativ Dativ ENGLISH 1 Person singular 2 Person singular 3 person singular Male 3 person singular Female 3 person singular Neutral 1 person plural 2 person plural 3 person plural ICH MICH MIR I DU DICH DIR YOU ER IHN IHM HE SIE SIE IHR SHE ES ES IHM IT WIR UNS UNS WE IHR EUCH EUCH YOU SIE SIE IHNEN THEY 1 Person singular 2 Person singular 3 person singular Male 3 person singular Female 3 person singular Neutral 1 person plural 2 person plural 3 person plural MEIN MEINER MY DEIN DEINER YOUR SEIN SEINER HIS IHR IHRER HER SEIN SEINER ITS UNSER UNSERER OUR EUER EUERER YOUR IHR IHRER THEIR POSSESSIV PRONOMEN Adjektiv Pronomen ENGLISH ARTIKEL Nominativ Male DER Female DIE Neutral DAS Plural DIE English THE Akkusativ DEN DIE DAS DIE THE Dativ DEM DER DEM DEN THE Male Female Neutral Plural English Nominativ KEIN KEINE KEIN KEINE SOME Akkusativ KEINEN KEINE KEIN KEINE SOME Dativ KEINEM KEINER KEINEM KEINEN SOME Nominativ Male EIN Female EINE Neutral EIN English A/AN Akkusativ EINEN EINE EIN A/AN Dativ EINEM EINER EINEM A/AN HABEN Ich Du Er,sie,es Wir Ihr Sie/sie HABE HAST HAT HABEN HABT HABEN I You He,She,it We You They HAVE HAVE HAS HAVE HAVE HAVE & SEIN Ich Du Er,sie,es Wir Ihr Sie/sie BIN BIST IST SIND SEID SIND I You He,She,it We You They AM ARE IS ARE ARE ARE PAST PARTICIPLE In linguistics, the perfect tense is the past tense used to describe completed actions in the past In most languages the perfect is constructed by the use of an auxiliary verb (either to be or to have) in the present and the past participle. Weak verbs: Drop –en at the end, add ge-t Example: machen = gemacht Strong verbs: Add ge at the beginning of the word. Example: sprechen = gesprochen Exceptions: gehen= gegangen Etc. HOW TO DETERMINE THE GENDER OF GERMAN NOUNS: German nouns ending in –o are usually neuter: das Auto, Büro, Kasino, Konto, Radio. Some of the exceptions are very common: die Avocado, der Euro, die Limo, der Zoo. German nouns ending in -ik are usually feminine: die Grammatik, Grafik, Klinik, Mathematik Another German feminine noun suffix is the -in ending. An -er ending usually indicates a masculine noun. However, some common nouns ending in -er are not masculine: das Fenster, die Mutter, die Schwester, die Tochter, das Wetter. GRAMMATICAL EXPRESSIONS Adverbs: is an invariable part of the speech that serves to modify the meaning of nouns, adjective… Adjective: is the word that adds to the noun and deliver a quality. Noun: is the one who is doing the action or is receiving the action. Verb: is the action. EXAMPLE: Adverb Adjektive Noun Verb Die Pizza ist sehr gut. Das ist eine gute Pizza. Die Pizza ist gut. Die Pizza ist gut. PREPOSITIONS: DATIV, AKKUSATIV DEUTSCH An Auf Hinter In Neben Über Unter Vor Zwischen ENGLISH At, on, to At, to, on, upon Behind In, into Beside, near, next to About, above, across, over Under, among In front of, before, ago (time) between DIR. / INDIR. OBJECT – SUBJECT A direct object answers the question "What?". A indirect object answers the question "To whom?" or "For whom?". The subject of a sentence is any part of the speech of which the predicate tell us something: an action, a way of being, a condition, and a quality.