Modal verbs - Light Bulb Languages
Werbung
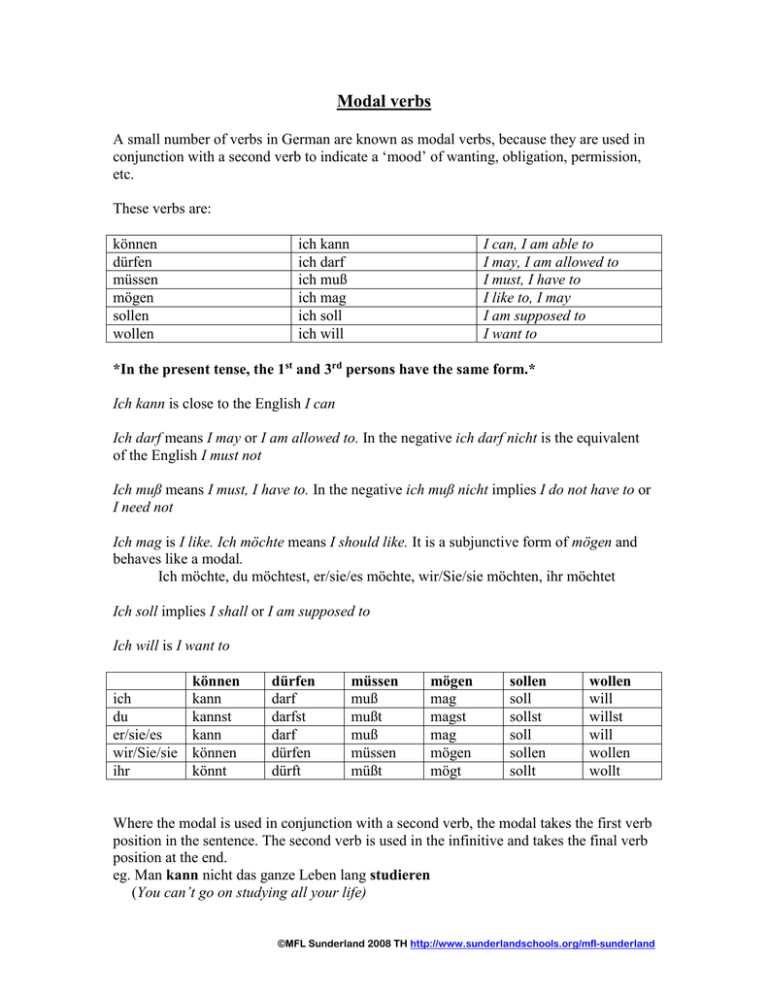
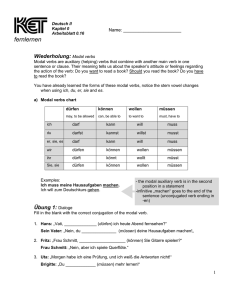
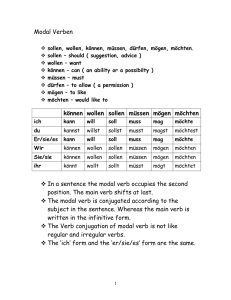
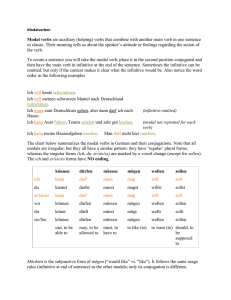
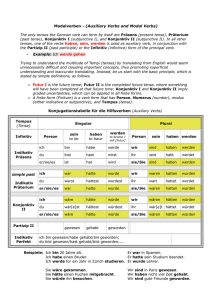
Modal verbs A small number of verbs in German are known as modal verbs, because they are used in conjunction with a second verb to indicate a ‘mood’ of wanting, obligation, permission, etc. These verbs are: können dürfen müssen mögen sollen wollen ich kann ich darf ich muß ich mag ich soll ich will I can, I am able to I may, I am allowed to I must, I have to I like to, I may I am supposed to I want to *In the present tense, the 1st and 3rd persons have the same form.* Ich kann is close to the English I can Ich darf means I may or I am allowed to. In the negative ich darf nicht is the equivalent of the English I must not Ich muß means I must, I have to. In the negative ich muß nicht implies I do not have to or I need not Ich mag is I like. Ich möchte means I should like. It is a subjunctive form of mögen and behaves like a modal. Ich möchte, du möchtest, er/sie/es möchte, wir/Sie/sie möchten, ihr möchtet Ich soll implies I shall or I am supposed to Ich will is I want to können ich kann du kannst er/sie/es kann wir/Sie/sie können ihr könnt dürfen darf darfst darf dürfen dürft müssen muß mußt muß müssen müßt mögen mag magst mag mögen mögt sollen soll sollst soll sollen sollt wollen will willst will wollen wollt Where the modal is used in conjunction with a second verb, the modal takes the first verb position in the sentence. The second verb is used in the infinitive and takes the final verb position at the end. eg. Man kann nicht das ganze Leben lang studieren (You can’t go on studying all your life) ©MFL Sunderland 2008 TH http://www.sunderlandschools.org/mfl-sunderland A Put the correct form of the verb in the following sentences 1. „Nein, Kinder, ihr (dürfen) nicht draußen spielen“ 2. Hans (können) gut Fußball spielen 3. Petra und Monika (sollen) sofort zum Direktor kommen 4. Vater (müssen) zur Arbeit gehen 5. Ich (wollen) ein Eis essen B Choose the correct modal verb part for each sentence 1. Mein Bruder ist sportlich und (muß/will/kann) immer Fußball spielen 2. Kinder (wollen/dürfen/sollen) immer Bonbons essen 3. Man (soll/will/darf) eine Strafe gleich bezahlen 4. Die Dame kommt zu spat ins Theater und sie (möchte/kann/muß) draußen warten 5. In einem Nichtraucher (kann/darf/muß) man nicht rauchen C Future plans. Clarify the meaning in each case by using the modal verb shown in brackets. eg. Ich lerne in der Schule sehr viel (müssen) Ich muß in der Schule sehr viel lernen 1. Ich gehe nach York (wollen) 2. Dort studiert man auch Linguistik (können) 3. Ich arbeite auch mit Computern (sollen) 4. Das ist sehr interessant (sollen) 5. Ich komme nächstes Jahr wieder nach Deutschland (möchten) 6. Ich arbeite für eine große Firma (möchten) 7. Ich werde vielleicht Übersetzerin (können) ©MFL Sunderland 2008 TH http://www.sunderlandschools.org/mfl-sunderland