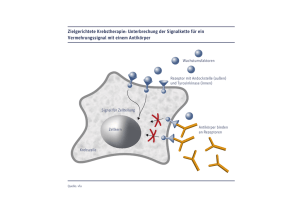
V2 - Studmed
Werbung

16.05.2012 Passive Immunisierung und Antikörpertherapien Konteptvorlesung 3 Themenblock 8 Beda M. Stadler Institut für Immunologie KV 8.3 Diese Folien stehen auch als PPT Files zum download bereit unter: http://www.iib.unibe.ch/wiki/?p=teaching/medical_students&l=de 1 Protein Pharmaceutika 2011 • 134 FDA-zugelassene biotechnologisch hergestellte (Proteine/Peptide) Medikamente • Protein Pharmaceutika kosten derzeit ca. $50 Milliarden/Jahr 2 1 16.05.2012 3 Top Ten Monoclonal Antibodies 2009/2010 Sales $ billion 2009 / 2010 Generic Name Brands® Indications Infliximab Remicade RA,UC,CD,Ps,PsA,AS 6.9 8.0 Bevacizumab Avastin Colon cancer 5.9 6.8 Rituximab Rituxan NHL,RA 5.8 6.7 Adalimumab Humira RA,Ps,JIA,PsA,AS,CD 5.4 6.5 Trastuzumab Herceptin Breast Cancer 5.0 5.5 Cetuximab Erbitux Colon, head and neck cancer 2.5 3.2 Ranibizumab Lucentis Wet macular degeneration 2.4 3.1 Natalizumab Tysabri Multiple sclerosis Omalizumab Xolair Allergic Asthma 0.9 1.1 Palivizumab Synagis RSV 1.1 1.0 1.0 1.7 Thearapeutische Antikörper auch zu teuer für uns? 2 16.05.2012 Übersicht / Lernziele • Antikörper Produktion einst • Passive Immuntherapie einst • Monoklonale / rekombinante Antikörper • Antikörper als Therapie für: • Immunsuppression • Krebs Therapie • Immunmodulation • Anti-Adhäsionstherapien Paul Ehrlich vor 100 Jahren • Rückblick und Zukunft KV 8.3 5 Passive Immuntherapie einst KV 8.3 6 3 16.05.2012 Passive Immuntherapie mit polyklonalen Antikörpern Krankheit Therapeutikum Schwarze Spinnenbiss Pferd Antivenin Botulismus Pferd Antitoxin Diphtherie Pferd Antitoxin Hepatitis A and B Multispender human Gammaglobulin Masern Multispender human Gammaglobulin Tollwut Multispender human Gammaglobulin Schlangenbiss Pferd Antivenin Tetanus Multispender human Gammaglobulin oder Pferd Antitoxin KV 8.3 7 Monoklonale Antikörper Hybridoma Technologie KV 8.3 8 4 16.05.2012 Therapeutische Maus Antikörper Probleme • Immunogenizität (humane anti-Maus AK, HAMA) • keine Effektor Mechanismen (Maus Fc) • Unerwartete Toxizität (Reaktivitiät mit normalem Gewebe, Kreuzreaktion mit anderen Antigenen) • Verlust von Tumorantigen (z.B. anti-idiotyp Behandlung von Lymphomen) KV 8.3 9 Immunogenicität von Infliximab (chimärer monokl. Ak gegen TNFα) • 61% of patients had detectable antibodies after the fifth infusion of Infliximab • Incidence of the formation of antibodies to Infliximab is reduced with immunosuppressive therapy Human anti-mouse Ab Human/mouse chimeric Ab (Infliximab) KV 8.3 10 5 16.05.2012 Diversity of Antibodies is Generated by Gene Rearrangement Dank Wissen um Grundlagen rekombinante Antikörper KV 8.3 11 Die Domänenstruktur hilft zum Umbau von Antikörpern scFv IgG (a) Immunoglobulin G Fab CL VL VH Hinge CH Fv VL KV 8.3 VH CH2 CH3 Fc 12 6 16.05.2012 Humanisierung von Maus Antikörpern Maus Chimäre Humanisiert KV 8.3 Human 13 Ezzell, Scientific American Therapeutische Antikörper Generic name Trade name Target Type Muromonab Orthoclone OKT3 CD3 Murine Abciximab ReoPro Platelet GP IIb/IIIa Murine Rituximab Rituxan CD20 Chimeric Daclizumab Zenapax IL2Ra Humanized Basiliximab Simulect IL2R Chimeric Palivizumab Synagis RSV Humanized Infliximab Remicade TNFa Chimeric Trastuzumab Herceptin Her2/neu/ErbB2 Humanized Gemtuzumab Mylotarg CD33 Humanized Alemtuzumab Campath-1H CD52 Humanized Endrecolomab Panorex 17A-1 Humanized Ibritumomab tiuxetan Zevalin CD20 Chimeric Adalimumab Humira TNFa Human Omalizumab Xolair IgE Humanized Centuximab Erbitux EGFR/ErbB1/Her1 Humanized Bevacisumab Avastin VEGF Humanized Efalizumab Raptiva CD11a Humanized KV 8.3 14 7 16.05.2012 Mono- & plurivalente Ak-Fragmente (a) Monovalent antibody fragments Fab Fab Fv Fv scFv scFv dsFv dsFv VL VH VL VH VL VH VH VL CL V VH H CH1 (b) Single chain two-domain constructs scFv scFv Ag Diabody Diabody Triabody Triabody Ag L Tetrabody Tetrabody or Ag Ag Ag Ag Ag Ag L L Ag Ag VH VL L VH VL VH VL L KV 8.3 15 Transgene Humanisation humane Antikörper in human Ig transgenenen Mäusen KV 8.3 16 8 16.05.2012 Der Wunsch nach humanen AK Humane Antikörper mittels Repertoire Klonierung mRNA von B Zellen Blut PCR of H&L chain genes mRNA cDNA Antikörper (Fab) Expression auf p3 des M13 Phagen Klonierung und Rekombination KV 8.3 17 Expression von Antikörpern Antikörper DNA Transfektion Antikörper Vektor Zellkultur Expression KV 8.3 18 9 16.05.2012 Industrielle Antikörper Produktion Flask Spinner Bioreaktor (Bench scale) Bio Reactor (Plant) 1mL → 100mL → 1L → 1Lx3 → 12L → 100L → 300L → 2’000L→ 10’000L Subkultur Produktion KV 8.3 19 Ersatz von passivem IgG durch rekombinante anti-RhD RhD+ Erythrozyten rekombinante Antikörper mittels phage display KV 8.3 20 10 16.05.2012 Neue Therapeutische Antikörper KV 8.3 21 Immunsuppressive Anikörper (anti-T Zell Antikörper) • Lymphocyte immune globulin (Atgam®) • lytic to human thymic lymphocytes; blocks T-cell responding • Anti-CD3: (OKT3®, muromonab-CD3) • binds CD3, blocks antigen binding; depletes T-cells • Anti-CD3: huOKT3 • Humanized version of OKT3 • Anti-CD4: OKT4 • less infusion-related reaction • Anti-Tac monoclonal antibody (Zenopax®) • binds IL-2 receptor of activated T-cells causing their inactivation KV 8.3 22 11 16.05.2012 Lymphocyte Depleting Antibody Therapies Polyclonal Anti-Thymocyte Globulin Campath-1H OKT3 CD52 CD3 KV 8.3 23 Immunsuppressive Anikörper (anti B-Zell Antikörper) • Anti-CD20: Rituxan® (Rituximab) • results in mature B-cell depletion and induces apoptosis (B-cell mediated vascular rejection) for Bcell Non Hodgkin’s Lymphoma CD19 DR slg CD20 CD22 • anti-CD52: Campath-1H (Alemtuzumab) • depletes T and B lymphocytes, NK cells, monocytes and macrophages KV 8.3 24 12 16.05.2012 Side effects • • • • • • • • • fever chills weakness headache nausea vomiting diarrhea low blood pressure rashes KV 8.3 25 Antikörper Krebs Therapie Strategien 2 ADCC NK Complement pathway Tumor cell 5 -Y-90 -Y-90 Anti Angiogenese -Y-90 1 TNF Anti-Idiotyp -Y-90 IL-1 -Y-90 Mac 3 -Drug -Tox -Tox 4 -Drug -Tox -Tox KV 8.3 Drug 26 13 16.05.2012 Strategie 1 Antikörper vermittelte Zytotoxizität NK Zelle Ziel Zelle Ziel Zelle Apoptosis via Induktion von intrazellulären Signal-Pathways Antikörper-abhängige Zytotoxizität (ADCC) Ziel Zelle Complement-abhängige Zytotoxizität (CDC) KV 8.3 27 z.B. Herceptin® (Trastuzumab) normal cell tumor cell treatment Binds HER-2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2), a growth factor receptor found on some tumor cells (some breast cancers, lymphomas). Over-expression of HER2 causes increased cell growth and reproduction. HER2 protein over-expression affects approximately 25% to 30% of breast cancer patients KV 8.3 28 14 16.05.2012 Strategie 1: maligne B-Zellen Stem cell ProB cell PreB cells Immature B cell Mature Activated B cell B cell Antigen independent Plasma cell Antigen dependent HLA-DR TDT CD19 CD10 CD20 CD22 CD21 CD38 Neoplasias: Leukemias from B-cell Precursors (B-ALL) B-cell Lymphomas (NHL, CLL) Multiple Myeloma KV 8.3 29 (B-Zell Lymphome) Strategie 1 anti idiotypische Antikörper KV 8.3 30 15 16.05.2012 Strategie 2: Verschiedene Isotope Nackter Antikörper Radiomarkierter Antikörper KV 8.3 31 Isotopen markierte Antikörper LymphoCide (anti CD22, found on some B-cell leukemias. Tositumomab (Anti-CD20) Lym-1 (Oncolym). AntiHLA-DR expressed at high levels on lymphoma cells. KV 8.3 32 16 16.05.2012 Strategie 3: Mylotarg® (anti CD-33) A conjugate of a monoclonal antibody that binds CD33 (cell-surface molecule expressed by the cancerous cells in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) but not found on the normal stem cells needed to repopulate the bone marrow) and calicheamicin, an oligosaccharide that blocks the binding of transcription factors (proteins) to DNA and thus inhibits transcription. KV 8.3 33 Strategie 4: Enzym markierte Antikörper Antibody directed enzyme prodrug therapy (ADEPT) 4 Antikörper 1 2 3 Prodrug Enzym Tumor antigen Zytotoxischer Wirkstoff Tumorzelle KV 8.3 34 17 16.05.2012 Strategie 5: Anti-Angiogenes KV 8.3 35 Anti-VEGF: Avastin ® • Recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody against VEGF; prevents binding with its receptor. • Blocks stimulation of angiogenesis stops tumor growth. KV 8.3 36 18 16.05.2012 Immunmodulatorische Antikörper • Anti-TNF Therapie • • • • Infliximab Etanercept Humira etc (Biosimilarika) • Anti-IgE Therapie • Xolair KV 8.3 37 Anti-TNF-a: Infliximab Chimeric monoclonal antibody • Binds specifically to TNF-a, neutralizing its activity • Used for Crohn’s disease and rheumatoid arthritis • Side-effect: can convert a latent case of tuberculosis into active disease KV 8.3 38 19 16.05.2012 Infliximab: Mechanism of Action Binds and neutralizes soluble and membrane bound TNFa TNFa TNFR2 Nucleus transcription No Signal NFB KV 8.3 39 Other Postulated Mechanisms of Action… Antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) Lysis of TNFa-expressing cells through complement (C’) activation Complement Activation C’ Complement Receptor Phagocyte T Cell KV 8.3 Phagocytosis 40 20 16.05.2012 TNF-a: Rezeptor oder Antikörper Infliximab Etanercept KV 8.3 41 Biosimilarika: z.B. anti-TNF Generic Name Brand name (source) Molecular Derivation Remicade® Human/mouse chimeric anti-human TNF monoclonal Ab Approved in US & Europe for CD & RA Etanercept Enbrel® Human recombinant p75 (TNF receptor fusion protein) Good for RA CDP-571 Humicade™ Humanised antihuman TNF mAb Trials ongoing for CD & ulcerative colitis CDP-870 N/A(Celltech) Humanised anti-TNF mAb fragment Phase III trials ongoing Adalimumab Humira® Human anti-human TNF mAb Approved for RA Infliximab KV 8.3 Development status 42 21 16.05.2012 Omalizumab Reduces IgE and FcεRI Levels Omalizumab (Xolair®) ↓ free IgE ↓ FcεRI ↓ Degranulation ↓ Inflammation ↓ Symptoms anti-IgE FcεRI B MC Mediator Release Allergic Inflammation IgE Holgate S. et al., J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005 vol. 115 (3) pp. 459-65 Anti-IgE: Omalizumab (Xolair®) KV 8.3 44 22 16.05.2012 Anti Adhäsionstherapie • Efalizumab (Raptiva®) • Anti-CD11a (subunit of LFA-1) inhibits activation of T cells • Alefacept (Amevive®) • binds to CD2 on memory effector T lymphocytes, inhibiting their activation • Abciximab (Reopro®) • Anti-Gp IIb/IIIa KV 8.3 45 Efalizumab (Raptiva) Interactions between leukocyte-function associated antigen type 1 (LFA-1) and intercellular adhesion molecules are important in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Efalizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody, binds to the subunit (CD11a) of LFA-1 and inhibits the activation of T cells KV 8.3 46 23 16.05.2012 Alefacept (Amevive®) Anti-CD2 CD2 KV 8.3 47 Abciximab (Reopro®) Anti-GpIIb/IIIa Inhibits the clumping of platelets by binding the receptors on their surface that normally are linked by fibrinogen. Helpful in preventing reclogging of the coronary arteries in patients who have undergone angioplasty. KV 8.3 48 24 16.05.2012 Ausblick: mehr Antikörper für… • Transplantation • Knochenmark, Niere, Leber und Pancreas Insel Zellen. • Krebs • Metastatic Brust Krebs, CLL, non-Hodgkin’s Lymphome. • Autoimmunkrankheiten • Rheumatoide Arthritis, Psoriasis, Multiple Sclerosis, Crohn’s Krankheit. • Infektionskrankheiten • Respiratory syncytial virus, Cytomegalovirus, Septikämien. • Allergien: • Mehr als 150 weitere Ak in der Pipeline… KV 8.3 49 25