Englisch als 1. Fremdsprache
Werbung

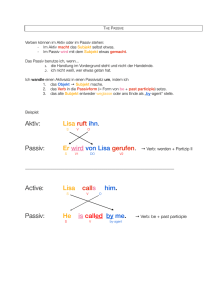
conditional clauses type 2 (Bedingungssätze Typ 2) if-clause main clause If I won a million, I would travel around the world. simple past infinitive) conditional (would/could/might + condition cannot be fulfilled or is unlikely to be fulfilled !!! If I were you, I … !!! indirect/reported speech I (Indirekte Rede I) 1. Change personal pronouns and possessive determiners according to the context. “I´m ill.” She says she is ill. 2. Change tenses (backshift) if the introductory verb (=einleitendes Verb) is in the past: simple present simple past present perfect simple past past perfect past perfect will may can would might could indirect/reported speech II (Indirekte Rede II) 3. Change expressions of time according to the context. “I was ill yesterday.” today tomorrow yesterday next year 4. 5. She said she had been ill the day before. (one week later) that day the next/following day the day before the next/following year tonight this evening three days ago last week that night that evening three days before/earlier the week before Questions in reported speech direct speech question with question word “What´s the problem?” indirect speech same question word She asked me what the problem was. question without question word “Do you like maths?” if/ whether She asked me if/whether I liked maths. Commands (Aufforderungen), requests (Bitten), advice (Ratshläge) in reported speech subject verb object She told me (not) + to + infinitive to close to tell, to ask, to want, to order, to warn, to advise, to expect the window. past perfect (simple) When I arrived, the others had eaten all the food. Verwendung: - drückt Vorzeitigkeit aus ! Handlung/ Zustand vor einer anderen Handlung/ einem anderen Zustand in der Vergangenheit ! Bezugspunkt liegt in der Vergangenheit Bildung: had + past participle Frage: The others had eaten all the food. X Had the others eaten all the food? Verneinung: The others hadn´t eaten all the food. !!! I had (already) had dinner when my parents came home. Dinner had already been prepared when I came home (passive!). Signalwörter ähnlich wie bei present perfect! The passive voice I (Das Passiv I) S V O Aktiv (A) He kisses her. Passiv (P) She is kissed by him. S V im Passiv by-agent A: Das Subjekt ”tut” etwas. unterschiedliche P: Mit dem Subjekt „“geschieht“ etwas. Handlungsträger: by-agent Perspektiven Der by-agent kann weggelassen werden, wenn er unwichtig, offensichtlich oder unbekannt ist oder wir ihn nicht nennen wollen: Somebody stole my bike. ! My bike was stolen. Bildung: Form von ‘to be’ in der richtigen Zeit + past participle The passive voive II (Das Passiv II) Verben + Präpositionen: They looked after the injured boy. The injured boy was looked after. ! Mit dem Verb eng verbundene Präpositionen stehen auch im Passiv direkt nach dem Verb (vgl. auch to operate on, to look for etc.) Infinitiv des Passiv: The parents must be informed. They should be told everything. ! be + past participle wird ohne ‘to’ direkt an Hilfsverben angehängt (Ausnahme: ought to) progressive form: The injured boy is being looked after. ! Form von ‘to be’ + being + past participle (nur im present und past üblich) ! Eine bestimmte Handlung ist zu einem Zeitpunkt/in einem Zeitraum noch nicht abgeschlossen