File - Frau Holmquist
Werbung

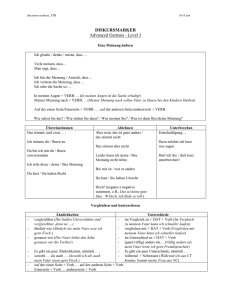
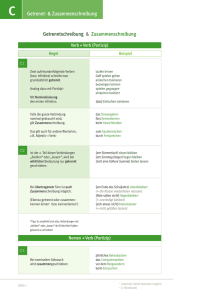
Das Perfekt German 3-4 Past Tense Verb Packet Name _____________________________________________________ Stunde: ________ The Present Perfect & U2’s: “I Still Haven’t Found What I’m Looking for” You know how to conjugate verbs in the present tense. Now we will move on to being able to describe events in the past. Luckily for us, English and German are very similar when writing or speaking in the past tense. We will be learning the Present Perfect Tense (das Perfekt). This is also called the “conversational past tense” because it is used most often when speaking. To help us recognize the building blocks of the tense, we wil be listening to U2’s song, “I Still Haven’t Found What I’m Looking for.” Below are the lyrics (auf Englisch!) with the past tense verbs missing. Fill in the blanks with the past tense verbs as you hear the song. VERSE 1 I _____________ ___________________ highest mountains I _____________ ___________________ through the fields Only to be with you Only to be with you. VERSE 2 I _____________ ___________________ I _____________ ___________________ I _____________ ___________________ these city walls These city walls Only to be with you. CHORUS But I still _____________ not ___________________ What I’m looking for. But I still _____________ not ___________________ What I’m looking for. VERSE 3 I _____________ ___________________ with the tongue of angels I _____________ ___________________ the hand of a devil It was warm in the night I was cold as a stone. After you’ve completed the song, circle the helping verbs and underline the past participle. Name the 2 parts of the present perfect verb: 1) 2) ***Weisst du was? German and English are very similar! English uses helping verbs in the present perfect tense and so does German! In English, you would say: I have (helping verb) spoken (past participle). In German, you would say: Ich habe (helping verb) gesprochen (past participle). 1 Das Perfekt German 3-4 Past Tense Verb Packet Now that you’ve done it in English, let’s see what you can do AUF DEUTSCH! Anleitungen: Circle the helping verbs and UNDERLINE the past participles in every sentence. Write what you think it is saying underneath the sentence! zum Beispiel: Du hast einen Bleistift gehabt. You have had a pencil. 1. Wir haben Abendessen gegessen. (essen) 2. Ihr habt eine Frage gefragt. (fragen) 3. Ich habe in Enumclaw gewohnt. (wohnen) 4. Ich bin nach Berlin geflogen. (fliegen) 5. Du hast ein Buch gelesen. (lesen) 6. Er hat zuviel gegessen. (essen) 7. Sie haben bei McDonalds gearbeitet. (arbeiten) 8. Sie hat viel in Deutsch Klasse gelernt. (lernen) 9. Er hat auf dem Tisch gesessen. (sitzen) 10. Wir haben sehr laut gesungen. (singen) 11. Ihr habt zu ruhig gesprochen. (sprechen) 12. Ich bin nach Tacoma gegangen. (gehen) 13. Er hat seinen Hund gesucht. (suchen) 14. Sie sind nach Kalifornien gefahren. (fahren) 15. Es hat nicht genug gegessen. (essen) 16. Sie hat keinen Bleistift gehabt. (haben) 17. Ich bin krank gewesen. (sein) 2 Das Perfekt German 3-4 Past Tense Verb Packet The Helping Verb When using the present perfect tense, all verbs need a helping verb. In English, the helping verb is “have.” For example: I have already had dinner. In German, there are 2 possible helping verbs: HABEN or SEIN. These are the two most important verbs in German. Below, write in the conjugations for each verb AUF DEUTSCH. SEIN HABEN Singular Plural wir ich ihr du er sie es sie Sie Singular ich du er sie es Plural wir ihr sie Sie Most german verbs use the helping verb “haben.” Verbs that use “sein” as a helping verb are verbs that denote a change of location or a change of condition. For example, the verb “gehen” is a verb of movement, changing location to “go” from one place to another. The verb “sterben” (to die) is a change of condition from living to dead, and thus uses “sein” as a helping verb. There are very few exceptions to this rule: ex. “bleiben” (to stay) uses “sein.” Below, fill in the english meaning of each german verb. After, determine if the verb is a change of location (helping verb “sein”) or uses the regular “haben” helping verb. Check either “haben” or “sein” box for each verb. You may need to use a dictionary. helping verb Deutsch Englisch sein haben haben sein fahren schreiben spielen essen kommen 3 Das Perfekt German 3-4 Past Tense Verb Packet The Past Participle As previously mentioned, the present perfect tesnse in German uses: helping verb + past participle. Like everything in German grammar, there are regular and irregular past participles, and each are built a bit differently. Regular: helping verb + ge (stem) t Irregular: helping verb + ge (stem form) en hat + gehabt hat + gelernt (haben) (lernen) hat + gelesen hat + gegessen ist + geflogen (lesen) (essen) (fliegen) In the chart below, you will see the the verb in english, the german infinitive (or the unconjugated original verb), the simple past verb, the present perfect past participle. We are concentrating on the present perfect form. The simple past verb is used mostly in writing, so we will not be concentrating on learning how to use it at this point, although it is important to recognize the form. REMEMBER: Germans use the Present Perfect in conversation! Fill in the chart below: you may use either a dictionary, German verb book, or www.leo.org. Meaning in English 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 BEISPIEL AUF ENGLISCH to go To drive, to travel Infinitive (unconjugated) to go gehen fahren sein haben machen tun werden geben antworten sitzen wohnen kaufen trinken stehen essen arbeiten suchen verkaufen fragen kommen studieren Simple Past went ging fuhr Present Perfect (past participle) has gone IST gegangen IST gefahren 4 Das Perfekt German 3-4 Past Tense Verb Packet Present Perfect Practice Helping verb: HABEN oder SEIN? Was ist das richtige Hilfsverb? Fülle die Lücken mit den richtigen Formen von „haben“ oder „sein“ ein. First, underline the past participle in each sentence. Is it a change in location or condition? Then use “sein.” If not, use “haben.” Once this is determined, fill in the blank with the correct form of “haben” or “sein” (conjugate the helping verb for the pronoun). zum Beispiel: Ihr habt das Buch gekauft. 1. ______________ ihr gestern Abend noch ins Kino gegangen? 2. Ich ______________ zu Hause gewesen. 3. Er ______________ einen Bleistift gehabt. 4. Wir ______________ nach dem Film nach Seattle gefahren. 5. Ich ______________ das Auto gestern gekauft. 6. Die Polizei (singular) ______________ gekommen. 7. ______________ du in dem Stuhl gesessen? 8. Wir ______________ ein Buch gehabt. 9. Er ______________ nach einer Bank gesucht. 10. Du ______________ ein schönes Mädchen geworden. 11. ______________ Sie in Enumclaw gewohnt? 12. Sie (formal) ______________ nach Sumner gefahren. 13. Ich ____________ nicht besonderes getan, und dann _____________ ich ins Bett gegangen. 14. Ihr ______________ den neuen James Bond Film gesehen, oder? What rule can you determine about the placement of the helping verb in each sentence? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 5 Das Perfekt German 3-4 Past Tense Verb Packet Which Past Participle? Was ist das richtige partizip? Fülle die Lücken mit dem richtigen Partizip. In this exercise, fill in the spaces with the correct past participle. Use the past participles in the box below to complete the sentences below – write the english translation next to the past participle first. Underline each helping verb. Again, you may need to use a dictionary. zum Beispiel: Ihr habt das Buch gekauft . gekommen gestorben studiert gefahren gesessen gelesen gegessen gegeben besucht gemacht gekostet geflogen 1. Hast du deine Hausaufgaben ______________________________? 2. Ich habe auf meinem Bett ______________________________. 3. Er ist mit dem Auto ______________________________. 4. Meine Mutter hat das Buch ______________________________. 5. Wieviel hat dein Fahrrad ______________________________? 6. Tom hat ein Party am Samstag ______________________________. 7. Hat Rudi die Eier ______________________________? 8. Herr Miller ist letztes Jahr nach Japan ______________________________. 9. Helga ist gestern nicht zur Schule ______________________________. 10. Ich habe meine Oma zu Hause ______________________________. 11. Meine Schwester hat Biologie an der Uni ______________________________. 12. Albert Einstein ist im Jahre 1955 ______________________________. 13. Hast du Harry Potter auf Deutsch ______________________________? What rule can you determine about the placement of the past participle in each sentence? __________________________________________________________________________________________ 6 Das Perfekt German 3-4 Past Tense Verb Packet Das Perfekt: Jetzt bist du dran! Now it’s your turn to write some sentences in the present perfect tense. First, decide the subject of the sentence(s). For each subject, you will write 2 sentences, one that takes “haben” as a helping verb and one that takes “sein” as a helping verb. Fill in the rectangles with extra information, such as: heute, gestern, ein Buch, usw. Finally, write the past participle of the verb you chose. Subject HELPING VERB Extra Information Partizip Extra Information Partizip Extra Information Partizip HABEN? SEIN? Subject HELPING VERB HABEN? SEIN? Subject HELPING VERB HABEN? SEIN? 7 Das Perfekt German 3-4 Past Tense Verb Packet The Past Participle: Weak or Strong? We know that in order to build the past tense in German, we need a helping verb (haben or sein) and a past participle. German verbs come in two varities: Weak (regular) or Strong (irregular). As you saw on page 4 of this packet: Weak verbs build their past participle using ge + stem + t. Strong verbs build their past participle using ge + stem form + en. Using previous pages, a dictionary, or www.leo.org, write the english translation next to the verb. Then put their past participles into the correct category. Strong verbs are divided into those with “sein” as a helping verb and those with “haben.” 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. sitzen wohnen machen sehen sein Schwache Verben regelmäßig (weak verbs) ge______________t 6. gehen 7. fahren 8. kommen 9. singen 10. tun 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. werden suchen haben bleiben sprechen Starke Verben unregelmäßig (strong & irregular) ist ge____________en 16. 17. 18. 19. denken verstehen kaufen stehen 20. warten Starke Verben unregelmäßig (strong & irregular) hat ge___________(e)n 8