Hepatitis C Virus
Werbung
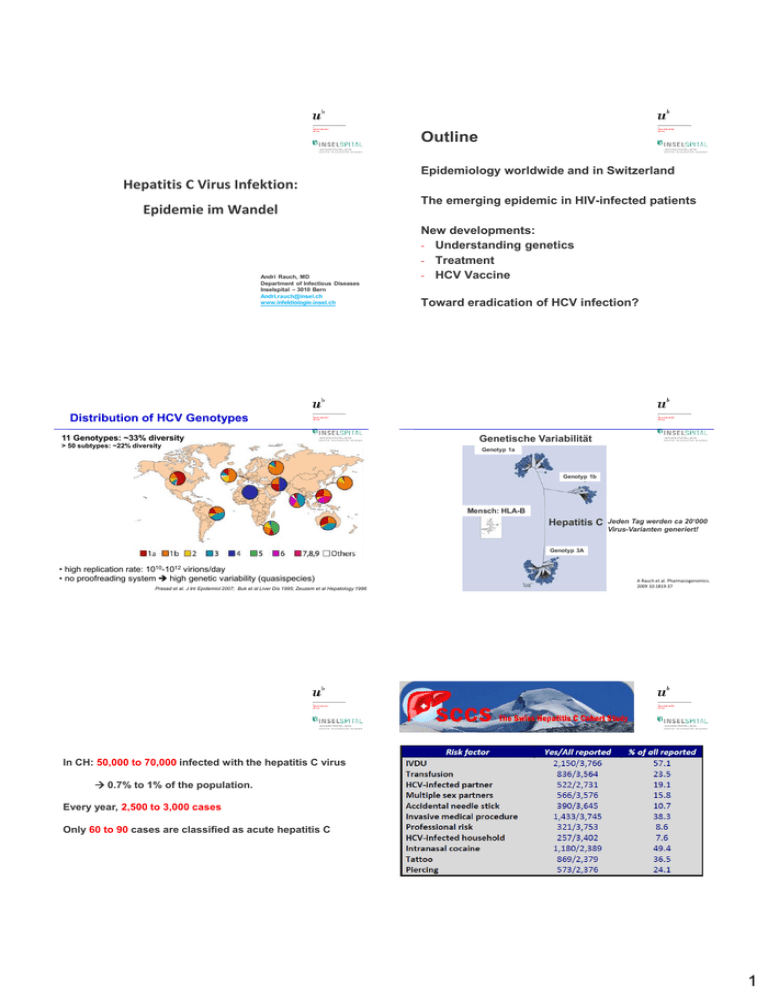
Outline Epidemiology worldwide and in Switzerland Hepatitis C Virus Infektion: Epidemie im Wandel Andri Rauch, MD Department of Infectious Diseases Inselspital – 3010 Bern [email protected] www.infektiologie.insel.ch The emerging epidemic in HIV-infected patients New developments: - Understanding genetics - Treatment - HCV Vaccine Toward eradication of HCV infection? BACKGROUND Distribution of HCV Genotypes 11 Genotypes: ~33% diversity > 50 subtypes: ~22% diversity Genetische Variabilität Genotyp 1a Genotyp 1b Mensch: HLA-B Hepatitis C Jeden Tag werden ca 20‘000 Virus-Varianten generiert! Genotyp 3A • high replication rate: virions/day • no proofreading system high genetic variability (quasispecies) 1010-1012 Prasad et al. J Int Epidemiol 2007; Buk et al Liver Dis 1995; Zeuzem et al Hepatology 1996 A Rauch et al. Pharmacogenomics. 2009 10:1819-37 In CH: 50,000 to 70,000 infected with the hepatitis C virus 0.7% to 1% of the population. Every year, 2,500 to 3,000 cases Only 60 to 90 cases are classified as acute hepatitis C 1 The HCV epidemic in HIV-infected MSM: An emerging epidemic HCV serology at study entry HCV incidence Risk factors for incident HCV infections in MSM Condom use Always Inconsistently/never Past history of syphilis No Yes HBV infection No Yes Univariable analysis HR (95%CI) p-value 0.001 Ref. 2.03 (1.33-3.10) <0.001 Ref. 2.20 (1.48-3.27) 0.12 Ref. 1.39 (0.92-2.09) Multivariable analysis aHR (95%CI) p-value 0.002 Ref. 2.09 (1.33-3.29) <0.001 Ref. 2.11 (1.39-3.20) 0.08 Ref. 1.48 (0.95-2.28) New developments in understanding genetics in HCV infection 2 Verlauf der Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Infektion Genetische Prädiktoren und Hepatitis C: Candidate gene studies Akute HCV Infektion ~30% ~70% CTLA4 Immunantwort effektiv: Spontane Ausheilung Genetische Faktoren Immunantwort ineffektiv Chronische Hepatitis C Progression Leberfibrose 1a hydr. (ViD) Gene mit Polymorphismen, welche mit der spontanen Ausheilung der Hepatitis C assoziiert wurden. Rauch et al, Pharmacogenomics Rauch et al. Pharmacogenomics. 2009 2009 (in 10:1819-37 press) Rauch et al. Tissue Antigens: Tissue Antigens 2006;69 Suppl 1:237-40. Candidate gene studies: Beschränkt auf einzelne Varianten z.B. HLA-Allele Genom-weite Studien: Erfassen Varianten im gesamten menschlichen Genom Bestimmung von ~500‘000 genetischen Varianten Repräsentativ für >95% der genetischen Variabilität Analysen betreffen: <<1% der Gene nur bekannte Gene Einfluss menschlicher genetischer Polymorphismen auf die spontane Ausheilung der HCV Infektion Unabhängig von a priori Hypothesen Typisierung mit DNA chips Mechanismus: IL28B beeinflusst Interferon-Stimulierte Gene (ISGs) P-Wert (-log10 Skala) IL28B IL28B kodiert interferon-l3, ein potenter Induktor von interferon-stimulierten Genen mit Genomweite Signifikanz antiviraler Aktivität. Assoziation sowohl mit spontaner als auch mit therapie-induzierter Ausheilung. Beispiel für den Nutzen von GWAS zur Entdeckung von neuen prognostischen und therapeutischen Ansätzen. Chromosomen A. Rauch et al., Gastroenterology. 138, 1338 (2010). A. Rauch et al., Eur. J Clin. Invest 40, 950(2010) A. Rauch et al., Eur. J Clin. Invest 40, 950(2010) 3 HIV und HCV: Unterschiedliche Gene entscheiden über den Verlauf der Infektion HIV Chr. 6 (‘adaptive Immunantwort’) Verbesserung der Voraussage einer SVR Stratified by viral genotype Overall SVR rate Stratified by viral and host genotype 100% 80% 60% 40% HCV Chr. 19 (‘angeborene Immunantwort’) 20% 0% Rauch et al, Gastroenterology 2010 GT1/4 GT2/3 non-TT TT Non-TT TT GT1/4 GT2/3 …and IP10 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% IL28B-CC 0% <150 pg/ml Lagging et al, Plos One 2011 IL28B-non CC 150-600 pg/ml >600 pg/ml IP-10 (plasma) Einschluss von spezifischen Risikogruppen in Studien IL28B und virale Kinetik Without knowledge on predictors of SVR SVR ???? % SVR Including demographic, host/viral genetic and ISG information „Improve efficacy“: New drugs, longer duration „Improve tolerability“: Lower dosage, shorter therapy Bochud et al, J Hepatol 2011 HCV Life Cycle and DAA Targets Receptor binding and endocytosis Transport and release Fusion and uncoating ER lumen (+) RNA LD LD Translation and NS3/4 protease polyprotein inhibitors processing Membranous web Virion assembly LD ER lumen NS5BRNA polymerase inhibitors replication Nucleoside/nucleotide Nonnucleoside NS5A* inhibitors CyclophillinInhibitor *Role in HCV life cycle not well defined Adapted from Manns MP, et al. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:991-1000. 4 P. Klenerman: Promising T cell vaccine Acute HCV infection „Host wins“ (~20%) „Virus wins“(~80%) T cell response T cell response Adapted from P. Klenerman, Nat.Immunol. 6, 873-879 (2005). P. Klenerman: HCV T cell vaccine Most responses are polyfunctional Vaccine-vector: rare human/chimp adenovirus without previous Immunization Immunogen: NS3-5B peptides 3 cytokine 2 cytokine Eradication of HCV infection? 5 Wrap-up Epidemiology worldwide and in Switzerland The emerging epidemic in HIV-infected patients New developments: - Understanding genetics - Treatment - HCV Vaccine Thomas DL, Lancet 2011 Toward eradication of HCV infection? 6