Enzyme
Werbung

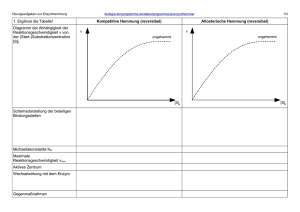
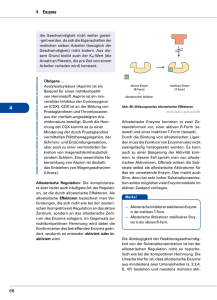
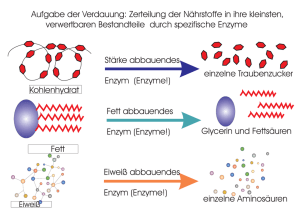
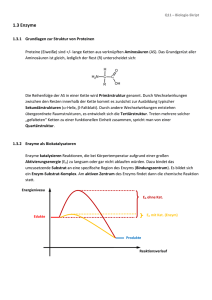
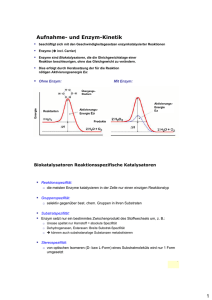
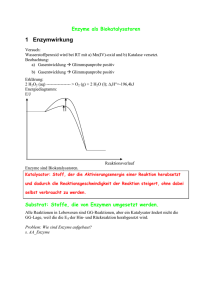
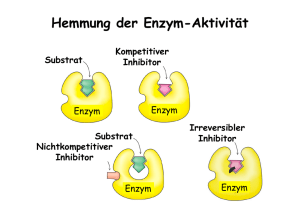
ENZYME Hauptsätze der Thermodynamik H=G+ST, H: Enthalpie, G: Freie Energie, S: Entropie, T: Temperatur, Kelvin Ex- und endergonische Reaktionen Aktivierungsenergie bringt Reaktionen in Gang Enzyme: Hochspezifische Biokatalysatoren E+S -> ES –> E+P; Katalisierte – nichtkatalysierte Reaktionen Enzyme: erniedrigen Aktivationsenergieschwelle, beeinflussen das Gleichgewicht nicht Änderungen im aktiven Zentrum des Enzyms Citrat-synthase Lysosim Chymotrypsin Enzyme selbst ändern ihre Konformation durch Substratbindung Cofaktoren: Anorganische Ionen; Coenzyme: Für die Aktivität des Enzyms sind benötigt; Prosthetische Gruppen: Dauerhaft an Enzym gebunden, wie Häm 9 Nicht-protein-Komponente Typ des Moleküls Cofaktoren Fe2+ vagy Fe3+ Cu+ vagy Cu2+ Zn2+ Chemische Rolle Oxidierung, Reduzierung Oxidierung, Reduzierung NAD-Bindung Coenzyme Biotin Coenzym A NAD FAD ATP -COOH-Transport -CO-CH3-Transport Elektron-Transport Elektron-Transport s Energiaquelle Prosthetische Gruppen Häm Flavin Retinal O2--Bindung Elektron-Bindung Lichtkonversion Metabolische Wege 10 Cofaktoren, Vitamine Nucleotid Metabolismus Saccharid Metabolismus Andere Aminosäure Metabolismus Lipid Metabolismus AminosaureMetabolismus ATP Synthese Metabolismus Anderer Stoffe Irreversible Enzymhemmung DFP: Diisopropylfluorophosphat Reversible Enzymhemmung Kompetitive- nichtkompetitive Hemmung Allosterische Enzymregulierung Allosterisches Zentrum: Positive Effektoren stabilisieren die aktive Form, Negative die inaktive Form des Enzyms 14 Allosterische Enzymhemmung INAKTÍV FORMA Inaktives Enzym Katabolische Untereinheit Aktives Enzym AKTÍVFORMA Aktive Stelle Aktív hely Inhibitionsstelle Regulatorische Untereiheit Aktivátor hely Aktivatorsbindungsstelle Aktivatorsbindungsstelle Gleichgewicht zwischen inaktives und aktives Enzym 15 Allosterische Enzymhemmung Inktives Enzym Das inaktive Enzym bindet kein Substrat 16 Allosterische Enzymhemmung Inaktive Form Allosterische Hemmung Inhibitorsbindung hemmt das Aufnehmen de aktiven Form 17 Allosterische Enzymhemmung Aktive Form Substrat Enzym-Substrat Wechselwirkung in aktiver Form 18 Allosterische Enzymhemmung AKTIVE FORM Substrat Allosterische Aktivator Allosterische Aktivator-Bindung ermöglicht Bildung der aktiven Form 19 Allosterische Enzymhemmung AKTIVE FORM Inaktive Form Kein Produkt Produktbildung Enzyme Paul D. Boyer John E. Walker Jens C. Skou Nobelpreisträger, 1997: Paul D. Boyer, John E. Walker (ATP-Synthese) und Jens C. Skou (IonTransporter Enzyme, Na+, K+ -ATPase)