Conjugation of Modals (Including möchten)
Werbung
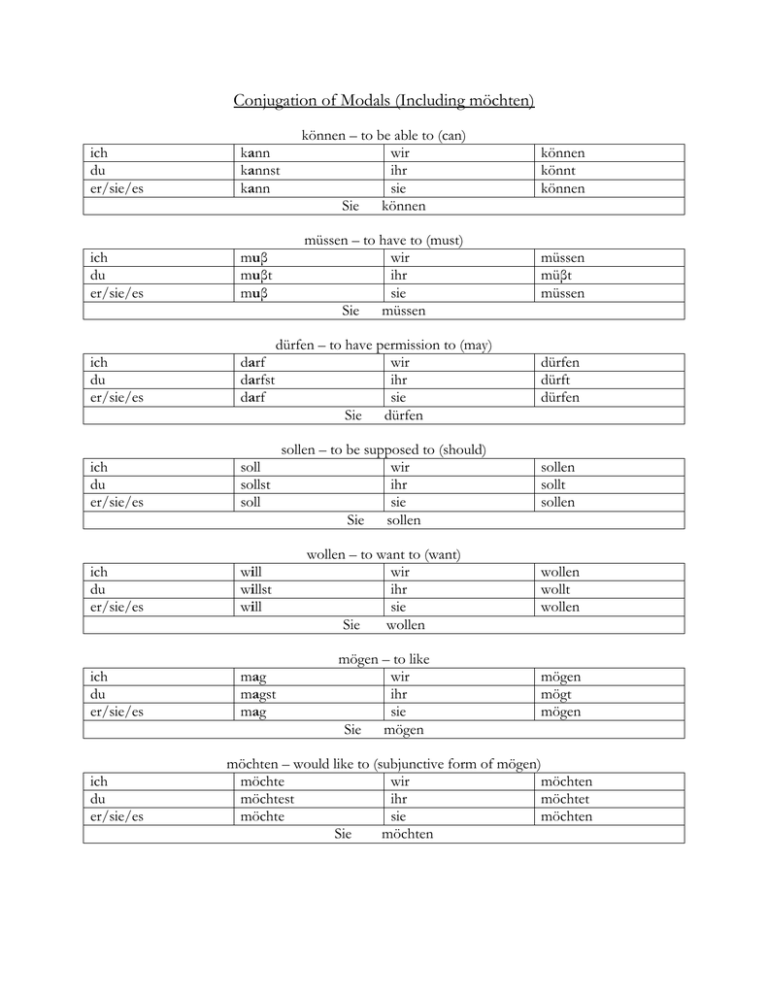
Conjugation of Modals (Including möchten) kann kannst kann können – to be able to (can) wir ihr sie Sie können können könnt können ich du er/sie/es muβ muβt muβ müssen – to have to (must) wir ihr sie Sie müssen müssen müβt müssen ich du er/sie/es dürfen – to have permission to (may) darf wir darfst ihr darf sie Sie dürfen dürfen dürft dürfen ich du er/sie/es sollen – to be supposed to (should) soll wir sollst ihr soll sie Sie sollen sollen sollt sollen ich du er/sie/es will willst will wollen – to want to (want) wir ihr sie Sie wollen wollen wollt wollen ich du er/sie/es mag magst mag mögen – to like wir ihr sie Sie mögen mögen mögt mögen ich du er/sie/es ich du er/sie/es möchten – would like to (subjunctive form of mögen) möchte wir möchten möchtest ihr möchtet möchte sie möchten Sie möchten Review of Modals German has 6 modal verbs: dürfen, können, mögen, müssen, sollen and wollen. Also often included in this group is möchten (the subjunctive form of mögen). These verbs indicate the subject’s attitude toward the action, condition or state expressed by the main verb. Modals are usually used with a main verb, but that verb can be omitted when: a verb of motion is implied .......................... Wann wollt ihr nach Deutschland (fahren)? the idea of to do or to make is understood Was wollt ihr dort (tun)? the meaning is clear from context ............... Könnt ihr deutsch (sprechen)? Examples of uses: Ich muβ Heiko finden. ......................................... I must find Heiko. Ich soll Heiko finden............................................ I am supposed to find Heiko. Erika kann Auto fahren. ...................................... Erika can (knows how to) drive a car. Erika darf Auto fahren. ........................................ Erika may (is allowed to) drive a car. Thomas will dieses Buch. .................................... Thomas wants this book. Thomas mag dieses Buch. ................................... Thomas likes this book. Thomas möchte dieses Buch................................. Thomas would like this book. Extra notes: Modals are always irregular in that the first and third person singular have no personal endings Müssen, können, dürfen and mögen have no umlauts in the singular form Only sollen and möchten do not have a stem vowel change The negative form nicht müssen means ‘not to have to’. Frau Schmidt muβ nicht anrufen. ............... Frau Schmidt does not have to call. To translate ‘must not’, use either nicht dürfen or nicht söllen Frau Schmidt darf/soll nicht anrufen ........ Mrs. Schmidt must not call Mögen can be used to express probability Wer mag das sein? ........................................ Who can that be? Wollen can be used by a speaker to imply that he/she does not believe what another speaker has said. Sie will ihr Buch haben. ................................ She claims to have her book.