Innovative Strategien bei Sepsis
Werbung

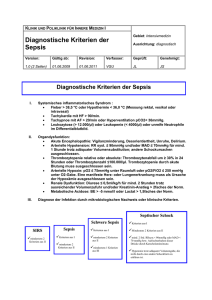
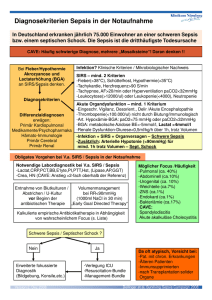
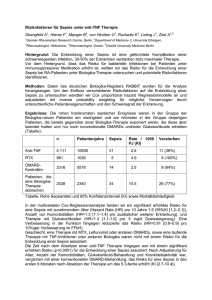
Innovative Strategien bei Sepsis Michael Bauer Klinikum der Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena Sepsis – „unmet medical needs“ Sepsis – Fakten Häufigkeit •300Sterblichkeit 54 % Schlaganfall 100 Herzinfarkt •200ca. 140-160 Menschen sterben täglich an den Folgen AIDS Brustkrebs Sepsis • Akutbehandlung: 1,72 Milliarden 50 Euro/Jahr („direkte Kosten“) Neuerkrankungen pro 100.000 Einwohner/Jahr in Deutschland Akute Phase / septischer Schock + 3 Wochen: Spätfolgen Encephalopathie/ Polyneuropathie 1914 Eine Sepsis liegt dann vor, wenn sich innerhalb des Körpers ein infektiöser Herd gebildet hat, von dem aus Erreger streuen und so in peripheren Organen eine systemische Wirkung verursachen. H. Schottmü Schottmüller, Verhandl. Verhandl. d. 31. Deutschen Kongresses fü für Innere Medizin 1914; XXXI:257XXXI:257-280 von Hugo Schottmüller zu Roger Bone 1895 „Coley‘s Cocktail“ - Sepsisinduktion als Tumortherapie Sepsis TBC TU William Coley TU 1975 Sepsis und Tumor-Reduktion - Synthese eines „Tumor Necrosis Factor“ bei Sepsis Infektion Infektion Sepsis Sepsis Serum i.v. Sepsis Lloyd Old, Sloan Kettering, New York 1985 Effekte von Tumor-Nekrose-Faktor (TNF) - TNF = Mediator des septischen Schocks TNF i.v. - Hypotension - Fieber - DIC - ARDS - ARF - MODS Bruce Beutler, Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, California, † Septischer Schock Trauma - Infektion - Sepsis - Schock: ein sterotypes Reaktionsmuster (SIRS) ? Infektion Sepsis Trauma / Ischämie Organversagen Host pattern recognition and sensing of the innate immune system to Gram-negative bacterial pathogens Host pattern recognition and sensing of the innate immune system to Gram-positive bacterial pathogens Host pattern recognition and sensing of the innate immune system to fungal pathogens Circulating Mitochondrial DAMPs Cause Inflammatory Responses to Injury Qin Zhang, Mustafa Raoof, Yu Chen, Yuka Sumi, Tolga Sursal, Wolfgang Junger, Karim Brohi, Kiyoshi Itagaki, and Carl J. Hauser Nature. 2010 March 4; 464(7285): 104–107. mitochondria tissue injury Formyl Peptides Mito-DNA FPR-1 TLR9 Trauma - Infektion - Sepsis - Schock: ein sterotypes Reaktionsmuster (SIRS) ? healthy post-op wound local infection SIRS local infection with SIRS blood stream infection Modulation der Wirtsantwort bei Sepsis: „The graveyard of pharmaceutical industry“ No. of patients 500 1000 Control 1500 2000 Odds Ratio intervention AT III Bay x 1351 TNF-MAb rhAPC Bay x 1351 TNF-MAb Antril IL-1RA Antril IL-1RA 95% Confidence Intervall BN52021 Anti-PAF Bay x 1351 TNF-MAb CPO-127 Anti-Bradykinin Odds Ratio P-55 sTNFR Ibuprofen Anti-Prostaglandin mod. : Zeni F. Crit Care Med 1997;25(7):10951997;25(7):10951100 MAK 195F TNF-MAb BN 5202 Anti-PAF CPO-127 Anti-Bradykinin Low-dose Hydrokortison P-80 sTNFR MAK 195F TNF-MAb Antril IL-1RA CB0006 TNF-MAb CDP57 TNF-MAb MAK 195F TNF-MAb Ibuprofen Anti-Prostaglandin Ibuprofen Anti-Prostaglandin Agent 0,125 0,25 0,5 0,67 1 1.5 Disadvantage No effect 2 4 8 Advantage Therapieprinzipien Einfluß auf Prognose Fokussanierung (operative Entlastung) Antibiotika (so breit wie nötig) Organunterstützende Therapie (Beatmung, Kreislaufunterstützung, Dialyse) Modulation der Wirtsantwort (Kortikosteroide, aktiviertes Protein C) von Hugo Schottmüller zu Roger Bone …und zurück Sepsis: the role of the pathogen Vol 351, October 28,2004 Sterblichkeit in Abhängigkeit von der Antibiose Appropriate therapy Rello et al Inappropriate therapy Alvarez-Lerma Ibrahim et al Luna et al Garnacho-Montero et al Vallés et al 0 20 40 60 mortality (%) 80 100 Rello et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997;156:196–200; Alvarez-Lerma. Intensive Care Med 1996;22:387–394 Ibrahim et al. Chest 2000;118:146–155; Luna et al. Chest 1997;111:676–685 Garnacho-Montero et al. Crit Care Med 2003;31:2742–2751; Vallés et al. Chest 2003;123:1615–1624 Schlüsseldefizit: Frühe Diagnose! Pathogen (Bakterien, Pilze) Resistenzen Fokus 100 % Probability for survival Share of patients receiving ABs 80 % 60 % 40 % 20 % 0% 0 0,5 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 12 24 >36 Hours after onset of shock Kumar et al. CCM 2006 Diagnostik der Infektion Potenzial und Limitationen FDG-PET Breitspektrum Antibiotiose resultiert in zunehmender Anzahl multiresistenter Keime XXL gegen bakterielle Infektionen •25.9 Vancomycin/enterococci •54.5 Methicillin/S. aureus • 86.7 Methicillin/CNS •3.2 3rd gen.ceph./E. coli • 8.9 3rd gen.ceph./K. pneumoniae •18.5 Imipenem/P. aeruginosa •23.0 Quinolone/P. aeruginosa • 20.0 3rd gen.ceph./P. aeruginosa •36.4 3rd gen.ceph./Enterobacter spp. 0 10 •January–May 1999 1994–1998 (+ standard deviation) 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 Resistance (%) Weinstein. Emerg Infect Dis 2001;7:188–192 We should be measuring genomic bacterial load and virulence factors Thiago Lisboa, MD; Grant Waterer, MD, PhD; Jordi Rello, MD, PhD Crit Care Med 38; 2010: S656-S662 Kulturbasierter Erregernachweis dauert… Hunfeld K-P. Anästhesist 2008 Anteil positive Befunde (%) 25 PCR Blutkultur 20 15 10 5 0 grampositiv gramnegativ Pilze PCR: Einfluß auf die Therapieentscheidung PCR negative 63.4 % 4.9 % new antifungal 9.8 % 22 % new antibiotic no change in antimicrobials Evaluation of a polymerase chain reaction assay for pathogen detection in septic patients under routine conditions: An observational study; Bloos et al. submitted Verknüpfung von Diagnostik & Therapie „Theragnostik“ Parallelen aus der Inneren Medizin ECG in AMI Troponin concentration Biomarkers in AMI Reperfusion=prognosis ↑ Occlusion=prognosis ↓ Time (hours) Sensitivity: 70% Specifity: 85% Sensitivity: 85% Specifity: 100% PCT – ‚cut off‘ oder ‚dynamic range‘ PCT (µg/L) 100 Diagnose Antibiose Sept. Schock Schwere Sepsis 10 Sepsis 1 Pneumonie Bronchitis kein Infekt 0.1 JA! ja nein NEIN! 0.01 Christ-Crain M et al. SWISS MED WKLY 2005;135:451–460 · Procalcitonin to Reduce Antibiotic Exposure in the Medical ICU – The ProRata-Trial Bouadma L et al. Lancet 2010 Procalcitonin to Reduce Antibiotic Exposure in the Medical ICU – The ProRata-Trial Antibiotic Therapy (%) 100 90 80 Control group Procalcitonin 70 23% less exposure to antibiotics p< 0.001 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 Bouadma L et al. Lancet 2010 10 20 Days 30 Sepsis – Kinetik von Biomarkern Aufnahme / DD Cut off Prognose ‚downdown-stream‘ stream‘Biomarker CRP, PCT, LBP Marker 1 Marker 2 Ansprechen auf Therapie TNF IL-1 IL-6 IL-8 ULN Pangenomische Analyse des Transkriptoms bei Infektion - Präklinische Daten (Pneumonie vs. Peritonitis bei Mäusen) RNA aus Vollblut RNA aus Milz Peritonitis 6h Peritonitis 24h PROGRESS Pneumonie 6h Pneumonie 24h M. Weber, U. Maus, M. Bauer, unpublished hyperim mun Gesunde Person mit MeningokokkenMeningokokken-Sepsis Alter Patient mit Malnutrition und Divertikulitis Patient mit Diabetes, chronischem Nierenversagen und Pneumonie hypoimm un normal hypoimmun Immunstatus „Sepsis“ - ein Krankheitsbild ? Erholung Tod 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Tage Hotchkiss R, Karl I. N Engl J Med. 2003 (mod.) The efficacy of anti-inflammatory treatment in sepsis is positively correlated with the severity of disease pooled data from APC trials prospective animal data Eichhacker et al, 2002, Am J Resp Crit Care Med, 166:1197-1205 Warum “Theragnostik” in der adjuvanten Sepsistherapie? AntiAnti-endotoxin Therapy 9 trials; 3057 Patients AntiAnti-TNF Antibodies 10 Trials; 6821 Patients ILIL-1ra 3 Trials; 1688 Patients Intravenous immune globulin 20 Trials; 2621 Patients Activated Protein C; All Patients 2 Trials 4303 Patients Activated Protein C; Patients with MOF 2 Trials; 2133 Patients 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 Experimental Agent Better 1.0 1.1 1.2 Placebo Better 1.3 Zusammenfassung - Entwicklungen Diagnostik und Monitoring der Sepsis Infektion Sepsis Markerkombinationen statt Einzelmarkern Schwere Sepsis Zusammenfassung - Entwicklungen Therapie der Sepsis Warum Theragnostik in adjuvanten Sepsistherapie AntiAnti-endotoxin Therapy 9 trials; 3057 Patients AntiAnti-TNF Antibodies 10 Trials; 6821 Patients ILIL-1ra 3 Trials; 1688 Patients Intravenous immune globulin 20 Trials; 2621 Patients Activated Protein C; All Patients 2 Trials 4303 Patients Erregerelimination !! Activated Protein C; Patients with MOF 2 Trials; 2133 Patients 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 Experimental Agent Better Adjuvante Therapie: Verknüpfung mit „Biomarkern“ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Placebo Better 1.3