1.2.7. Logarithmusfunktionen DEF: Funktionen mit Gleichungen der
Werbung
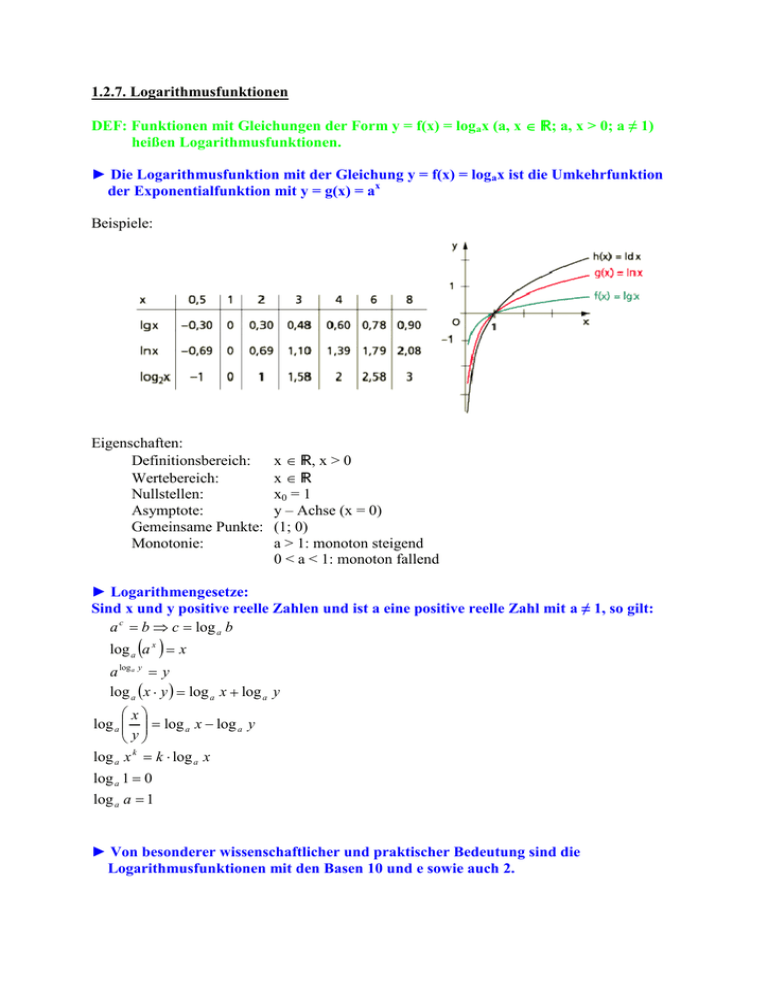
1.2.7. Logarithmusfunktionen DEF: Funktionen mit Gleichungen der Form y = f(x) = logax (a, x ∈ 3; a, x > 0; a heißen Logarithmusfunktionen. Die Logarithmusfunktion mit der Gleichung y = f(x) = logax ist die Umkehrfunktion der Exponentialfunktion mit y = g(x) = ax Beispiele: Eigenschaften: Definitionsbereich: Wertebereich: Nullstellen: Asymptote: Gemeinsame Punkte: Monotonie: x ∈ 3, x > 0 x∈3 x0 = 1 y – Achse (x = 0) (1; 0) a > 1: monoton steigend 0 < a < 1: monoton fallend Logarithmengesetze: Sind x und y positive reelle Zahlen und ist a eine positive reelle Zahl mit a a c = b ⇒ c = log a b log a (a x ) = x a log a y = y log a (x ⋅ y ) = log a x + log a y x log a = log a x − log a y y log a x k = k ⋅ log a x log a 1 = 0 log a a = 1 Logarithmusfunktionen mit den Basen 10 und e sowie auch 2. , so gilt: Man schreibt verkürzend: log10 x = lg x log e x = ln x log 2 x = ldx