Das simple present und das present progressive
Werbung

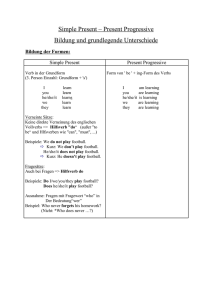
Das simple present und das present progressive Das kann ich hier üben! Das kann ich jetzt! Wie du beide Zeitformen bildest Wann du welche Zeitform verwendest Mit welchen Verben du in der Regel nur die einfache Form, nicht aber die Verlaufsform verwendest Bildung Das ist wichtig! Diese Formen musst du gut beherrschen: simple present: present progressive: Aussage: I do/he does am/are/is doing Verneinung: I don’t do/he doesn’t do ’m not/aren’t/isn’t doing Frage: do/does … do? am/are/is … doing? Verwendung beider Zeitformen Das ist wichtig! Mit dem simple present und dem present progressive berichtest du über Handlungen, die du gewöhnlich oder gerade tust� Das simple present (I do) verwendest du für Das present progressive (I am doing) verwendest du für allgemeine Tatsachen oder Dauerzustände: Tom lives in a big house� Handlungen, die jetzt gerade stattfinden: Tom is watching TV at the moment� Handlungen, die regelmäßig stattfinden, z� B� immer, oft, manchmal usw�: Tom usually cycles to school� His mother never drives him� einmalige Handlungen, die in oder um diese Zeit stattfinden: I’m meeting my friends after school today� Signalwörter: always, sometimes, often, never, usually, every day usw� Signalwörter: at the moment, now, just, today, this morning, this afternoon, this evening, tonight usw� 6 Verwendung beider Zeitformen ! Merke 1 Regelmäßige/dauerhafte Handlungen simple present� 2 Gerade ablaufende/einmalige Handlungen present progressive� 3 always, sometimes, never, often usw� stehen im englischen Satz meist - direkt vor dem Vollverb: We never have lunch before one o’clock� They don’t always watch TV in the evenings� - aber immer hinter einer Form des Verbs to be (am/are/is): Tom is often at Jack’s house� Übung 1 Put the verb into the correct form, simple present or present progressive� 1 Lisa (usually / to walk) ______________________________ to the sports club, but today it (to rain) ______________________________, so her mother (to take) ______________________________ her there in the car� 2 It’s half past seven� Jack (to sit) ______________________________ at his computer but he (not / to do) ______________________________ his homework� He (to chat) ______________________________ to his friends on the Internet� He (often / to chat) ______________________________ to them in the evenings� 3 On Tuesdays Tom (usually / not / to get home) ____________________________ before 5�30 because he (to go) ______________________________ to Drama Club after school� Every year the school Drama Club (to put on) ______________________________ a different play� This year they (to do) ______________________________ a musical and Tom (to have) ______________________________ the main role� He (to be) ______________________________ the star of the show� 7 Das simple present und das present progressive 4 Sophie (to live) ______________________________ in a small village near York. Every morning she (to catch) ______________________________ the bus to school. The bus (usually/to leave) ______________________________ at 8 o’clock, but there (often/to be) ______________________________ a lot of traffic in the mornings, so it (sometimes/to be) ______________________________ late. The bus ride (usually/to take) ______________________________ about twenty minutes, so Sophie (often/to finish) ______________________________ her homework on her way to school. Sophie (to sit) _____________________________ on the bus now but she (not / to go) ______________________________ to school today. Today is Saturday, and Sophie (to be) ______________________________ on her way to the swimming pool. She (always/to meet) ______________________________ her friends there on Saturdays. Besonderheiten bei der Verwendung der Verlaufsform Das ist wichtig! Es gibt eine Reihe von Verben, die in der Regel keine Verlaufsform bilden. Sie stehen grundsätzlich in der einfachen Form. Das sind Verben wie: 1 das Verb to be (sein); 2 V erben des Denkens: to know (kennen, wissen), to think (glauben, meinen), to agree (zustimmen), to remember (sich erinnern), to understand (verstehen), to mean (bedeuten); 3 V erben der Gefühle: to like (mögen), to love (lieben), to hate (hassen), to seem (scheinen), to want (wollen), to prefer (bevorzugen), to need (brauchen); 4 V erben der Sinneswahrnehmung: to see (sehen), to hear (hören), to look (aussehen), to sound (sich anhören, klingen); 8 Besonderheiten bei der Verwendung der Verlaufsform 5 Verben, die Besitzverhältnisse bezeichnen: to have (haben im Sinne von a) besitzen oder b) Zeit/Geld haben), to belong (gehören)� Vergleiche: Wir haben heute Zeit� We have time today� (= Zustand) ! Wir haben heute viel Spaß� We are having a good time today� (= Tätigkeit) Merke 1 Nur Verben, die eine Tätigkeit bezeichnen, können in der ing-Form stehen� 2 Verben, die einen Zustand darstellen, stehen in der Regel in der einfachen Form� Übung 2 Put in the verb into the correct form, simple present or present progressive� 1 Amy (to love) ____________________ sports but she (not / to belong to) ____________________ a sports club� 2 I’m afraid I (not / to know) ____________________ the answer to your question right now� 3 I (to look) __________________ for the twins� Do you know where they are? 4 Are Andrea and Marianne really twins? They (not / to look) ____________________ like each other� 5 You can borrow my rubber� I (not / to need) ____________________ it at the moment� 6 You can borrow my rubber� I (not / to use) ____________________ it at the moment� 7 The Simpsons (to have) ____________________ a flat in town and a house in the country� 8 Julia is on holiday in France at the moment� She (to have) ___________________ a great time� 9 Das simple present und das present progressive 9 I’m sorry I can’t help you at the moment� I (not / to have) ____________________ any time right now� 10 Lisa (to get on) ____________________ well at her new school� She (to seem) ____________________ to be very happy there� Übung 3 Make questions� Use the simple present or present progressive� 1 I’m going to the shops� (you/to want) _Do you want____________ anything? 2 I’m going to the shops� (you/to need) _________________________ anything? 3 (you/to believe) _________________________ everything you read in the newspapers? 4 What (Tom/usually/to do) _________________________ at the weekends? 5 What (Tom/to do) _________________________ this weekend? 6 How (you/usually/to get to) _______________________ school in the mornings? 7 How (you/to get to) _________________________ Tom’s party on Friday? 8 What (you/to think of) ________________________ Spielberg’s latest film? 9 You look worried� What (you/to think about) _________________________? 10 What (BFF/to mean) _______________________? – It means Best Friend Forever� Übung 4 Put in the verb into the correct form, simple present or present progressive� 1 Ben: Oh, look at that dog� He (to chase) _________________________ the cat again� Tom: Oh yes� He (not / to like) _________________________ that cat� Ben: He (always/to chase) ________________________ it when he (to see) _________________________ it� 10 Besonderheiten bei der Verwendung der Verlaufsform 2 Mark: (you/to hear) _________________________ that noise? Alex: Yes� Where (it/to come) _________________________ from? Mark: I (not / to know) _________________________� (you/to think) _________________________ that someone (to try) _________________________ to break in? 3 Alex: I hope not� Mum: Poor Tim must be worried about something� He (not / to sleep) _________________________ well at the moment� Dad: (you/to think) _________________________ that he (to worry about) _________________________ school? Mum: I (not/to think) _________________________ so� He (usually/to enjoy) ______________________ school� Maybe he (to worry about) _____________________ his appointment with the dentist on Friday� Das kann ich hier üben! Das kann ich jetzt! Ich kann beide Zeitformen bilden� Ich weiß, wann ich welche Zeitform verwenden muss� Ich weiß, mit welchen Verben in der Regel nur die einfache Form, nicht aber die Verlaufsform verwendet wird� 11