Lösen von quadratischen Gleichungen in C C5
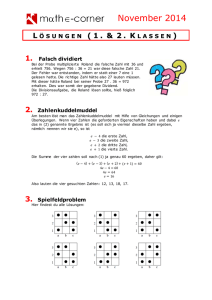
Werbung
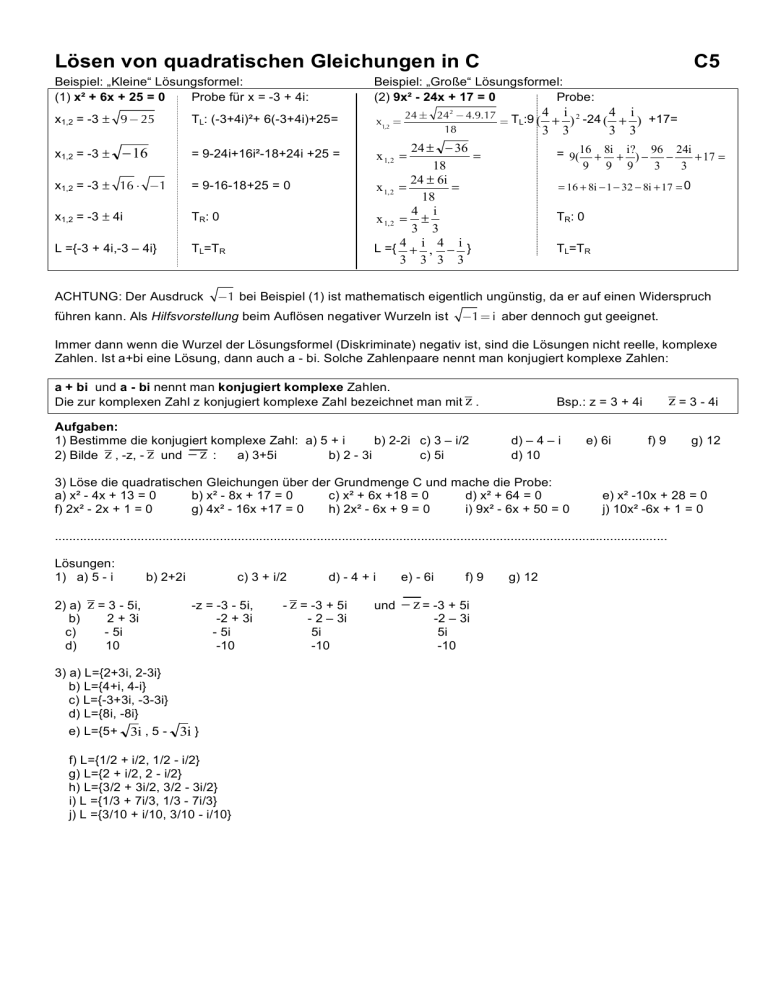
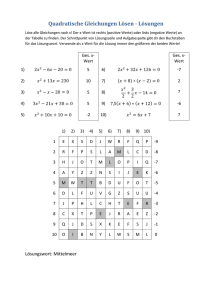
Lösen von quadratischen Gleichungen in C
C5
Beispiel: „Kleine“ Lösungsformel:
(1) x² + 6x + 25 = 0
Probe für x = -3 + 4i:
Beispiel: „Große“ Lösungsformel:
(2) 9x² - 24x + 17 = 0
Probe:
x1,2 = -3 ± 9 ! 25
x1,2 =
x1,2 = -3 ±
! 16
TL: (-3+4i)²+ 6(-3+4i)+25=
= 9-24i+16i²-18+24i +25 =
x1,2 = -3 ± 16 ! "1
= 9-16-18+25 = 0
x1,2 = -3 ± 4i
TR: 0
L ={-3 + 4i,-3 – 4i}
TL=TR
ACHTUNG: Der Ausdruck
24 ± 24 2 ! 4.9.17 T :9 4 i 2 -24 4 i +17=
( + )
= L ( + )
18
3 3
3 3
24 ± ! 36
=
18
24 ± 6i
x 1, 2 =
=
18
4 i
x 1, 2 = ±
3 3
4
L ={ + i , 4 ! i }
3 3 3 3
= 9(16 + 8i + i ?) ! 96 ! 24i + 17 =
9 9 9
3
3
x 1, 2 =
= 16 + 8i ! 1 ! 32 ! 8i + 17 = 0
TR: 0
TL=TR
!1 bei Beispiel (1) ist mathematisch eigentlich ungünstig, da er auf einen Widerspruch
führen kann. Als Hilfsvorstellung beim Auflösen negativer Wurzeln ist
!1= i aber dennoch gut geeignet.
Immer dann wenn die Wurzel der Lösungsformel (Diskriminate) negativ ist, sind die Lösungen nicht reelle, komplexe
Zahlen. Ist a+bi eine Lösung, dann auch a - bi. Solche Zahlenpaare nennt man konjugiert komplexe Zahlen:
a + bi und a - bi nennt man konjugiert komplexe Zahlen.
Die zur komplexen Zahl z konjugiert komplexe Zahl bezeichnet man mit z .
Aufgaben:
1) Bestimme die konjugiert komplexe Zahl: a) 5 + i
b) 2-2i c) 3 – i/2
2) Bilde z , -z, - z und ! z :
a) 3+5i
b) 2 - 3i
c) 5i
z = 3 - 4i
Bsp.: z = 3 + 4i
d) – 4 – i
d) 10
3) Löse die quadratischen Gleichungen über der Grundmenge C und mache die Probe:
a) x² - 4x + 13 = 0
b) x² - 8x + 17 = 0
c) x² + 6x +18 = 0
d) x² + 64 = 0
f) 2x² - 2x + 1 = 0
g) 4x² - 16x +17 = 0
h) 2x² - 6x + 9 = 0
i) 9x² - 6x + 50 = 0
e) 6i
f) 9
e) x² -10x + 28 = 0
j) 10x² -6x + 1 = 0
...........................................................................................................................................................................
Lösungen:
1) a) 5 - i
2) a)
b)
c)
d)
z = 3 - 5i,
2 + 3i
- 5i
10
b) 2+2i
c) 3 + i/2
-z = -3 - 5i,
-2 + 3i
- 5i
-10
3) a) L={2+3i, 2-3i}
b) L={4+i, 4-i}
c) L={-3+3i, -3-3i}
d) L={8i, -8i}
e) L={5+ 3i , 5 - 3i }
f) L={1/2 + i/2, 1/2 - i/2}
g) L={2 + i/2, 2 - i/2}
h) L={3/2 + 3i/2, 3/2 - 3i/2}
i) L ={1/3 + 7i/3, 1/3 - 7i/3}
j) L ={3/10 + i/10, 3/10 - i/10}
d) - 4 + i
- z = -3 + 5i
- 2 – 3i
5i
-10
und
e) - 6i
f) 9
! z = -3 + 5i
-2 – 3i
5i
-10
g) 12
g) 12