Zahlenbefunde "Neoplastische BB
Werbung
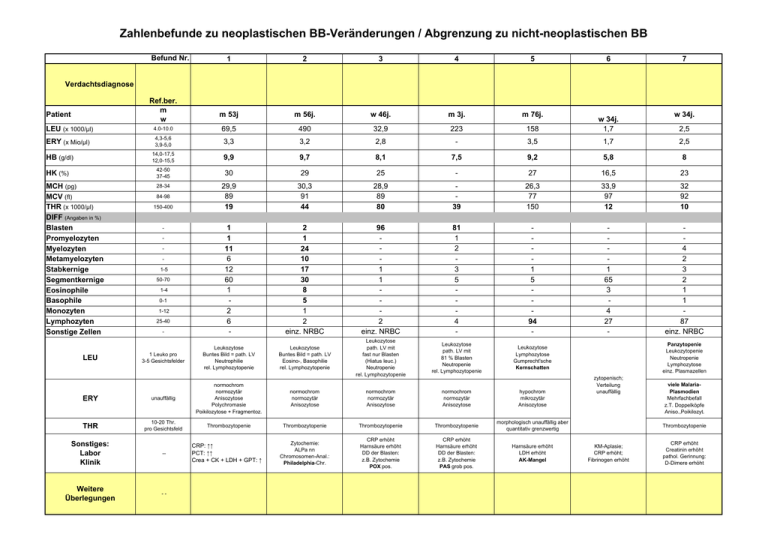
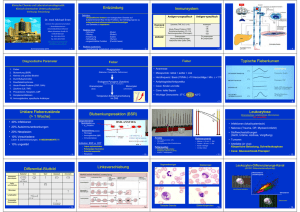
Zahlenbefunde zu neoplastischen BB-Veränderungen / Abgrenzung zu nicht-neoplastischen BB Befund Nr. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Verdachtsdiagnose Ref.ber. m w w 34j. m 53j m 56j. w 46j. m 3j. m 76j. LEU (x 1000/µl) 4.0-10.0 69,5 490 32,9 223 158 w 34j. 1,7 ERY (x Mio/µl) 4,3-5,6 3,9-5,0 3,3 3,2 2,8 - 3,5 1,7 2,5 14,0-17,5 12,0-15,5 9,9 9,7 8,1 7,5 9,2 5,8 8 Patient HB (g/dl) 2,5 42-50 37-45 30 29 25 - 27 16,5 23 28-34 29,9 89 19 30,3 91 44 28,9 89 80 39 26,3 77 150 33,9 97 12 32 92 10 1 1 11 6 12 60 1 2 6 - 2 1 24 10 17 30 8 5 1 2 einz. NRBC 96 1 1 2 einz. NRBC 81 1 2 3 5 4 - 1 5 94 - 1 65 3 4 27 - 4 2 3 2 1 1 87 einz. NRBC 1 Leuko pro 3-5 Gesichtsfelder Leukozytose Buntes Bild = path. LV Neutrophilie rel. Lymphozytopenie Leukozytose Buntes Bild = path. LV Eosino-, Basophilie rel. Lymphozytopenie Leukozytose path. LV mit fast nur Blasten (Hiatus leuc.) Neutropenie rel. Lymphozytopenie Leukozytose path. LV mit 81 % Blasten Neutropenie rel. Lymphozytopenie Leukozytose Lymphozytose Gumprecht'sche Kernschatten ERY unauffällig normochrom normozytär Anisozytose Polychromasie Poikilozytose + Fragmentoz. normochrom normozytär Anisozytose normochrom normozytär Anisozytose normochrom normozytär Anisozytose hypochrom mikrozytär Anisozytose THR 10-20 Thr. pro Gesichtsfeld Thrombozytopenie Thrombozytopenie Thrombozytopenie Thrombozytopenie morphologisch unauffällig aber quantitativ grenzwertig Sonstiges: Labor Klinik -- Zytochemie: ALPa nn Chromosomen-Anal.: Philadelphia-Chr. CRP erhöht Harnsäure erhöht DD der Blasten: z.B. Zytochemie POX pos. CRP erhöht Harnsäure erhöht DD der Blasten: z.B. Zytochemie PAS grob pos. Harnsäure erhöht LDH erhöht AK-Mangel Weitere Überlegungen -- HK (%) MCH (pg) MCV (fl) THR (x 1000/µl) DIFF (Angaben in %) Blasten Promyelozyten Myelozyten Metamyelozyten Stabkernige Segmentkernige Eosinophile Basophile Monozyten Lymphozyten Sonstige Zellen LEU 84-98 150-400 1-5 50-70 1-4 0-1 1-12 25-40 - CRP: ↑↑ PCT: ↑↑ Crea + CK + LDH + GPT: ↑ Panzytopenie Leukozytopenie Neutropenie Lymphozytose einz. Plasmazellen zytopenisch; Verteilung unauffällig viele MalariaPlasmodien Mehrfachbefall z.T. Doppelköpfe Aniso.,Poikilozyt. Thrombozytopenie KM-Aplasie; CRP erhöht; Fibrinogen erhöht CRP erhöht Creatinin erhöht pathol. Gerinnung: D-Dimere erhöht Zahlenbefunde zu neoplastischen BB-Veränderungen / Abgrenzung zu nicht-neoplastischen BB Befund Nr. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Sepsis + Verdachtsdiagnose Ref.ber. m w 7 Malaria tropica + Anämie durch toxische Hämolyse + DIC bei Verbrauchskoagulopathie CML + AML + ALL + Verdrängungssituat., Anämie+Thromb.penie Verdrängungsmyelopathie Verdrängungsmyelopathie Fe-Mangel-Anämie CLL + Aplast. Syndrom hier: trilineäre Bildungsstörung Anämie durch intravasale Hämolyse + DIC bei Verbrauchskoagulopathie w 34j. m 53j m 56j. w 46j. m 3j. m 76j. LEU (x 1000/µl) 4.0-10.0 69,5 490 32,9 223 158 w 34j. 1,7 ERY (x Mio/µl) 4,3-5,6 3,9-5,0 3,3 3,2 2,8 - 3,1 1,7 2,5 14,0-17,5 12,0-15,5 9,9 9,7 8,1 7,5 9,2 5,8 8 Patient HB (g/dl) 2,5 42-50 37-45 30 29 25 - 27 16,5 23 28-34 29,9 89 19 30,3 91 44 28,9 89 80 39 26,3 77 150 33,9 97 12 32 92 10 1 1 11 6 12 60 1 2 6 - 2 1 24 10 17 30 8 5 1 2 einz. NRBC 96 1 1 2 einz. NRBC 81 1 2 3 5 4 - 1 5 94 - 1 65 3 4 27 - 4 2 3 2 1 1 87 einz. NRBC 1 Leuko pro 3-5 Gesichtsfelder Leukozytose Buntes Bild = path. LV Neutrophilie rel. Lymphozytopenie Leukozytose Buntes Bild = path. LV Eosino-, Basophilie rel. Lymphozytopenie Leukozytose path. LV mit fast nur Blasten (Hiatus leuc.) Neutropenie rel. Lymphozytopenie Leukozytose path. LV mit 81 % Blasten Neutropenie rel. Lymphozytopenie Leukozytose Lymphozytose Gumprecht'sche Kernschatten ERY unauffällig normochrom normozytär Anisozytose Polychromasie Poikilozytose + Fragmentoz. normochrom normozytär Anisozytose normochrom normozytär Anisozytose normochrom normozytär Anisozytose hypochrom mikrozytär Anisozytose THR 10-20 Thr. pro Gesichtsfeld Thrombozytopenie Thrombozytopenie Thrombozytopenie Thrombozytopenie morphologisch unauffällig aber quantitativ grenzwertig Sonstiges: Labor Klinik -- CRP: ↑↑ PCT: ↑↑ Crea + CK + LDH + GPT: ↑ Zytochemie: ALPa nn Chromosomen-Anal.: Philadelphia-Chr. CRP erhöht Harnsäure erhöht DD der Blasten: z.B. Zytochemie POX pos. CRP erhöht Harnsäure erhöht DD der Blasten: z.B. Zytochemie PAS grob pos. Harnsäure erhöht LDH erhöht AK-Mangel KM-Aplasie; CRP erhöht; Fibrinogen erhöht CRP erhöht Creatinin erhöht pathol. Gerinnung: D-Dimere erhöht -- schwere akute Infektion? Fieber? Organversagen? Zerstörte Blut-KM-Schranke? tox. Hämolyse: Erreger? Bilirubin? Haptoglobin? D-Dimere? Leukostase? Hepato-/Splenomegalie? Anämie-Symptomatik? Blutungsneigung? Abwehrschwäche? Anämie-Symptomatik? Blutungsneigung? Leukostase? Abwehrschwäche? Anämie-Symptomatik? Blutungsneigung? rezidivierende Infekte? DD Fe-Mangel abs./rel.? THR: Verlauf beobachten Ausgeprägte Symptome: Abwehrschwäche? Anämiezeichen? Blutungsneigung? akute intravas. Hämolyse: Haptoglobin? HK (%) MCH (pg) MCV (fl) THR (x 1000/µl) DIFF (Angaben in %) Blasten Promyelozyten Myelozyten Metamyelozyten Stabkernige Segmentkernige Eosinophile Basophile Monozyten Lymphozyten Sonstige Zellen LEU Weitere Überlegungen 84-98 150-400 1-5 50-70 1-4 0-1 1-12 25-40 - Panzytopenie Leukozytopenie Neutropenie Lymphozytose einz. Plasmazellen zytopenisch; Verteilung unauffällig viele MalariaPlasmodien Mehrfachbefall z.T. Doppelköpfe Aniso.,Poikilozyt. Thrombozytopenie