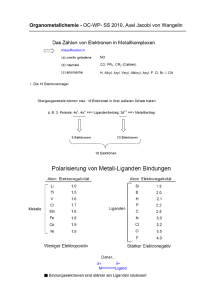
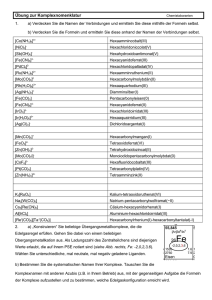
[Mo(CO)6], [Ru(CO)5] und [RhCl(CO)(PPh3)2]
Werbung
![[Mo(CO)6], [Ru(CO)5] und [RhCl(CO)(PPh3)2]](http://s1.studylibde.com/store/data/005606366_1-015cff068bd8932129b59ee7ad5cb2c5-768x994.png)
Anorganische Chemie I A. Mezzetti HCI H 235 Fragenkatalog II 1. [Mo(CO)6], [Ru(CO)5] und [RhCl(CO)(PPh3)2] sind alle diamagnetisch. – Bestimmen Sie ihre Strukturen anhand der Valenzstruktur-Theorie! – In bestimmten Fällen sind mehrere Strukturen möglich. Zeichnen Sie alle! – Benennen Sie die Komplexe! L L L L L L [Mo(CO)6]: Mo(0) d6, 6 Liganden: d2 s p3 oktaedrisch CO OC Mo CO CO OC CO Hexacarbonylmolybdän(0) L L (18-Elektronen) L L L Ru(0) d8, 5 Liganden: [Ru(CO)5]: d s p3 CO OC Ru CO OC CO Pentacarbonyleisen(0) (18-Elektronen) Die Struktur ist trigonal bipyramidal (Für eine Erklärung, siehe später, MO-LCAO). Im Prinzip wäre aber eine quadratisch-pyramidale Struktur möglich: CO OC Ru CO CO OC L L L L [RhCl(CO)(PPh3)2]: Rh(I) d8, 4 Liganden : Ph3P Rh CO PPh3 Cl d s p2 trans-Carbonylchlorobis(triphenylphosphin)rhodium(I) Der Komplex besitzt 16-Valenzelektronen, ist somit koordinativ ungesättigt! Der entsprechende cis-Komplex ist weniger stabil (siehe später …): Ph3P Rh Ph3P CO Cl 2. [NiBr2(PPh3)2] besitzt zwei ungepaarten Elektronen. Welche Struktur hat der Komplex? PPh3 L 8 Ni(II), d , 4 Liganden: L L L sp 3 tetraedrisch Cl Cl Ni PPh3 Obwohl der Komplex (nur) 16-Valenzelektronen besitzt, kann er nur durch Paarung von 2 Elektronen einen fünften Liganden binden! 5. Bestimmen Sie die Punktgruppe folgender Komplexe. Ermitteln Sie die Symmetrie mit und ohne Einbezug der Chelatringe! PPh3 Pd Ph3P PPh3 PPh3 + NH2 Co Cl Cl H2N Cl Co H2N + Cl NH2 Cl NC NH3 2– Mo PPh2 Ph2P Rh H Ph2P PPh2 C2 (C2v ohne Chelatringe) Cl Cl OC Cl H O H2H2N N Co N H2 H2N NH3 Co O Cl + OH2 PPh3 C2v D2h (D4h ohne Chelatringe) C2 (C2v ohne Chelatringe) Cl Rh Ph3P P Ph2 NH2 NH2 NC Ph3P D2h (D4h ohne Chelatringe) Td H2N H2N Ph2 + P Ph2 P Co P Ph2 OH2 PPh3 PPh3 PPh3 D4h C1 3+ CN NH2 NC NH2 Ni 3– CN CN NC D3 (Oh ohne Chelatringe) C1 Ru C4v 3. Formulieren und benennen Sie folgende Komplexe: a) Cl NH3 Cl Co NH3 Cl H3N NH3 b) Ph2 H H P Os PPh2 P Ph2 P Ph2 a) trans-[CoCl2(NH3)4]Cl trans-Tetraammindichlorocobalt(III)-chlorid b) cis-[OsH2(dppe)2] cis-Bis(1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethan)dihydridoosmium(II) (1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethan vor Hydrid) 4. Benennen Sie folgende Koordinationsverbindungen: a) [Ni(H2O)2(NH3)4]SO4 Tetraammindiaquanickel(II)-sulfat b) Na2[OsCl5N] Natrium-pentachloronitridoosmat(2–) c) [CoCl(NO2)(NH3)4]Cl Tetraamminchloronitritocobalt(III)-chlorid Im diesem Falle müsste eigentlich noch angegeben werden, über welches Ligandatom der NO2Ligand an das Metallzentrum gebunden ist. Hier handelt sich um einen sog. Nitrito-Komplex (Ngebunden). Alternativ existiert [CoCl(ONO)(NH3)4]Cl, Tetraamminchloronitrocobalt(III)-chlorid (O-gebunden). d) [CoCl(NH2)(en)2]NO3 Amidochlorobis(ethylendiammin)cobalt(III)-nitrat e) [FeH(CO)3(NO)] Tricarbonylhydridonitrosyleisen(0) Sieht man den Nitrosyl-Liganden als formal kationisch (NO+) an (siehe später), so hat Eisen hier die Oxidationszahl 0. In Fällen, in denen die Zuordnung einer formalen Oxidationszahl nicht eindeutig ist, verzichtet man am besten auf deren Angabe. f) [PtCl(NH2CH3)2(NH3)]Cl Amminchlorobis(methylammin)platin(II)-chlorid. Der Komplex existiert entweder als trans- oder als cis-Isomer!