Folie 1
Werbung

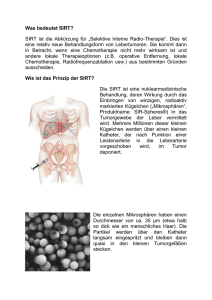
21.10.2013 Interventionelle Radiologie: SIRT, TACE Leo Pallwein-Prettner Peter Waldenberger Inst. für diagnostische & interventionelle Radiologie Embolisationstechniken arterielle Chemo-Perfusion Lipiodol-Installation unkalibrierte Partikel (PVA) kalibrierte Partikel (Mikrosphären) Medikamenten-beladene Partikel (TACE) Aktivitäts-beladene Partikel (SIRT) Prinzip Embolisation Transarterielle (Chemo-/Radio-)Embolisation Normales Lebergewebe Tumor > 75% aus Pfortader > 90% aus Leberarterien Neoangiogenese (Arterialisation 3:1 normales Par.) 1 21.10.2013 Prinzipien vor TACE nach TACE Geeignet nur für hypervaskularisierte TU z.B. HCC, NCC-Meta … VORAUSSETZUNG: Gefässanatomie Warum beladene Partikel? Rationale: • • • • 1. maximale Anreicherung des CTx 2. konsistente Daten (wiss. reproduzierbar) 3. anhaltender Effekt dr. langs. Freisetzg. d. CTx 4. Effekt am Tumor >>> system. NW 2 21.10.2013 Optimierung der CTx-Abgabe im Gewebe Grenzwert zw. intra- und extra-tumoralen Gefäßen: 310 Mikrometer (P < .0001) Kalibrierte Partikel PVA Embozene 500 µm class Date of Measurement: August 28, 2005; Median: 595 µm Target Bandwidth [µm]: 100; Oversized particles: 1,1%; Undersized particles: 0,55% 25,0% 20,0% 15,0% 10,0% 5,0% 0,0% 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 Diameter Drug-eluting-Beads-Irinotecan-DEBIRI unilobäre Metastasierung bilobäre Metastasierung • • • • • 4 Sessions (2 pro Lappen) • 100-300 µm Beads • 100 mg Irinotecan • 2 Wochen Intervall 2 Sessions 100-300 µm Beads 100 mg Irinotecan 3-4 Wochen Intervall 3 21.10.2013 DEBIRI: CRCmeta Embo (40µm Partikel) Progress unter polyCTx prae 1 d post TACE mCRC Zn neoadj. Chemotherapie vor TACE nach TACE vor TACE nach TACE CCC Zn pall. Chemotherapie nach 12 mo vor 1. TACE vor 2. TACE nach 2. TACE nach 6 mo 4 21.10.2013 Embolisations-Syndrom • • • • • • • Morphinen intra-arteriell Lidocain Hydrierung Dexamethason Zofran Cefazolin Zantac Chemotherapie assoziierte Steatohepatitis ● Response rate 66% (6m) / 75% (12m) ● OS 19m ● PFS 11m 5 21.10.2013 DEBIRI versus Intravenous Therapy (FOLFIRI) for hepatic mCRC: Final Results of a Phase III Study Fiorentini G et al. CIRSE 2012 Selective Internal Radiation Therapy: SIRT Y90 r ~ 2 mm • 32 µm DM • HWZ: 64 hours • Beta (0.93 MeV) • 100–1,000 Gy Verwendbare / verfügbare Isotopen HWZ Energie Iod131 Yttrium90 Rhenium 188 Lutetium 177 Holmium166 26.8 h 1.81 MeV Handelsname Größe Spezifisches Gewicht Aktivität/Partikel # Mikrosphären/ 3 GBq (70 mCi) per E Material Zulassung 193.4 h 0.606 MeV 64.2 h 0.937 MeV 16.9 h 2.12 MeV 159.6 h 0.50 MeV SIRSpheres ® (SIRTEX) TheraSpheres® (MSD Nordion) 22 ± 10 µm 32 ± 10 µm 1.6 g/dl 3.6 g/dl 50 Bq 2500 Bq 40-80 Mio ~1.2 Mio Y90 + Harz Y90 in Glasmatrix EU, USA, Asien USA/Canada 6 21.10.2013 Selective Internal Radiation Therapy: SIRT Morgan B, Kennedy AS, Lewington V et al. Intra-arterial brachytherapy of hepatic malignancies: watch the flow. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology 2011; 8: 115–120. Selective Internal Radiation Therapy: SIRT • Staging: • PET-CT >> Auschluß extrahepatischer TU • CT/MRT >> TU-Last/Verteilung • Vorbereitung: • Angio >> vaskuläre Vorbereitung, Shunts • TC-MAA >> Y-90 Simulation, Shunts • SIRT (+ 7-14d) • Angio-Kontrolle • Gamma-Kamera: Aktivitätsbeurteilung • 2-4 d Überwachung • Follow-up (6-12 W post SIRT): • PET-CT, MRT 7 21.10.2013 Selective Internal Radiation Therapy: SIRT Staging: PET-CT >> Auschluß extrahepatischer TU CT/MRT >> TU-Last/Verteilung Vorbereitung: Angio >> vaskuläre Vorbereitung, Shunts TC-MAA >> Y-90 Simulation, Shunts SIRT (+ 7-14d) Angio-Kontrolle Gamma-Kamera: Aktivitätsbeurteilung 2-4 d Überwachung Follow-up (6-12 W post SIRT): PET-CT, MRT VORAUSSETZUNG: Gefässanatomie • A gastroduodenalis • A cystica • A gastrica dextra • A lig. Falciforme • A hep. sin. >> A phren. inf. • A hep. sin >> A gastr. sin. • Supraduodenale Äste, Truncus hepatogastricus Tc-99m MAA – Angiographie & Scan 99mTc-MAA scan: to calculate the degree of hepato-pulmonary shunting, to further identify unnoticed collateral vessels, and to calculate differential distribution of particles between tumor and normal liver tissue (T/N or tumor to normal ratio). CI: Lung shunt volume >20%; 30 Gray one session, 50 Gray two or more sessions 8 21.10.2013 Selective Internal Radiation Therapy: SIRT Staging: PET-CT >> Auschluß extrahepatischer TU CT/MRT >> TU-Last/Verteilung Vorbereitung: Angio >> vaskuläre Vorbereitung, Shunts TC-MAA >> Y-90 Simulation, Shunts SIRT (+ 7-14d) Angio-Kontrolle Gamma-Kamera: Aktivitätsbeurteilung 2-4 d Überwachung Follow-up (6-12 W post SIRT): PET-CT, MRT A. gastroduodenalis und cystica Selective Internal Radiation Therapy: SIRT Selektive interne Radiotherapie Transarterielle Embolisation mit radioaktiven Y90-Partikeln 9 21.10.2013 Selective Internal Radiation Therapy: SIRT • • • Staging: • PET-CT >> Auschluß extrahepatischer TU • CT/MRT >> TU-Last/Verteilung Vorbereitung: • Angio >> vaskuläre Vorbereitung, Shunts • TC-MAA >> Y-90 Simulation, Shunts SIRT (+ 7-14d) • Angio-Kontrolle • Gamma-Kamera: Aktivitätsbeurteilung • • 2-4 d Überwachung Follow-up (6-12 W post SIRT): • PET-CT, MRT MammaCAMetsZ.n. PolyCTx 18.5.2009 NET – VK mittels DOPA PET-CT • ♀, 76a • hochdifferenziertes neuroendokrines Ca des LL • kein Primum • typ. Symptomatik 10 21.10.2013 Cholangiozelluläres Carcinom non op. SIRT PR Ulcera im Magen und Duodenum vor SIRT nach SIRT N. Recti Z.n. neoadj. RCT; limitierte Lebermetastasierung Liver-responder aber LR im Becken nach SIRT vor SIRT N. Recti Z.n. pall. CT; limitierte Lebermetastasierung Liver-responder 11 21.10.2013 ● EBM Level II-2 ● 792 Pat in 19 Studien, 195 1.-line ● Medianes Überleben 10.8 – 29.4 M Liver Tolerance & Tumour Sensitivity to Radiation SIRT RILD – Radiation-Induced Liver Disease Gy: 20 30 40 Effective Dose: Testicular Ca Lymphoma Myeloma 50 60 70 80 90 100 Curative Doses: Adenocarcinoma Preoperative Radiation: Rectal Ca Kennedy A, Coldwell D, Nutting C et al. Pathology and microdosimetry in human livers after 90Y-microspheres. Int J Rad Oncol Biol Phys 2004; 60(5): 1520–1533. Komplikationen Sangro et al. CIRSE 12 21.10.2013 Stratifizierte Therapie CRCMets local ablation + TACE, SIRT A Stang et al. 2009, Eur J Cancer 45(10): 1748-56 Kombinierte Therapie: CTx, SIRT, TACE, RFA vor SIRT nach RFA nach SIRT nach TACE + RFA TACE + Ablation ● Kombinationstherapie >>> Monotherapie ● Einfluß von nicht Komorbiditäten nicht ausreichend abgebildet ● Kurative Intention ● Differenzierte Studien erforderlich?! W Wang et al. 2010, Liver International, online first 13 21.10.2013 Zusammenfassung Minimal-invasiv einfach, sicher niedrige Komplikationsrate niedrige Nebenwirkungsrate kombinierbar, wiederholbar effektiv zunehmende konzeptionelle Akzeptanz Zusammenfassung Aktuelle Diskussion ● Indikationserweiterung ● Kombinationstherapie ● Multidisziplinäres Konzept kurative Intention ZUKUNFT: multifunktionale Nanopartikel Nanopartikel mit einem therapeutischen Agens umhüllt von tumorspezifischen Liganden specific for cancer cells wandern ins TumorInterstitium durch Permeation >> Retentionseffekt tumorspezifische Liganden binden selektiv an die Tumorzellen und entfalten ihre cytotoxische Wirkung From: Leary: Neurosurgery, Volume 58(6).June 2006.1009-1026 14