Nominativ • The subject is the acting person / thing in a sentence
Werbung
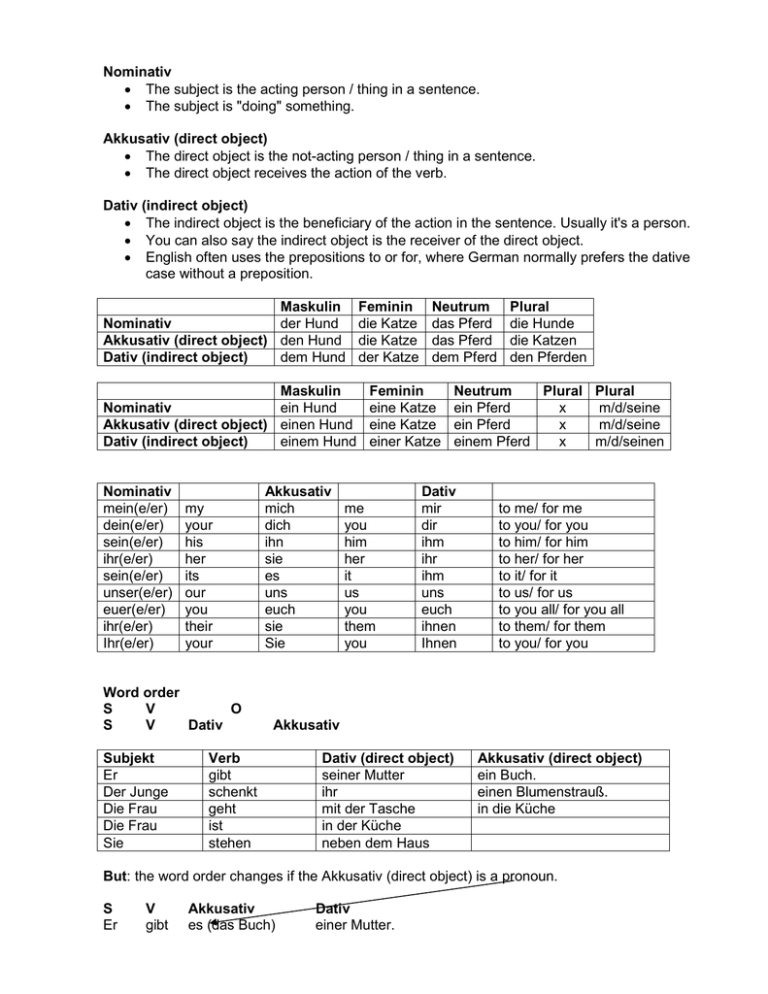
Nominativ • The subject is the acting person / thing in a sentence. • The subject is "doing" something. Akkusativ (direct object) • The direct object is the not-acting person / thing in a sentence. • The direct object receives the action of the verb. Dativ (indirect object) • The indirect object is the beneficiary of the action in the sentence. Usually it's a person. • You can also say the indirect object is the receiver of the direct object. • English often uses the prepositions to or for, where German normally prefers the dative case without a preposition. Maskulin Nominativ der Hund Akkusativ (direct object) den Hund Dativ (indirect object) dem Hund Maskulin Nominativ ein Hund Akkusativ (direct object) einen Hund Dativ (indirect object) einem Hund Nominativ mein(e/er) dein(e/er) sein(e/er) ihr(e/er) sein(e/er) unser(e/er) euer(e/er) ihr(e/er) Ihr(e/er) my your his her its our you their your Word order S V O S V Dativ Subjekt Er Der Junge Die Frau Die Frau Sie Akkusativ mich dich ihn sie es uns euch sie Sie Feminin die Katze die Katze der Katze Neutrum das Pferd das Pferd dem Pferd Feminin eine Katze eine Katze einer Katze me you him her it us you them you Plural die Hunde die Katzen den Pferden Neutrum Plural Plural ein Pferd x m/d/seine ein Pferd x m/d/seine einem Pferd x m/d/seinen Dativ mir dir ihm ihr ihm uns euch ihnen Ihnen to me/ for me to you/ for you to him/ for him to her/ for her to it/ for it to us/ for us to you all/ for you all to them/ for them to you/ for you Akkusativ Verb gibt schenkt geht ist stehen Dativ (direct object) seiner Mutter ihr mit der Tasche in der Küche neben dem Haus Akkusativ (direct object) ein Buch. einen Blumenstrauß. in die Küche But: the word order changes if the Akkusativ (direct object) is a pronoun. S Er V gibt Akkusativ es (das Buch) Dativ einer Mutter.