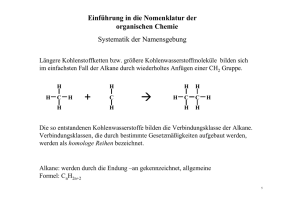
Organische Chemie
Werbung
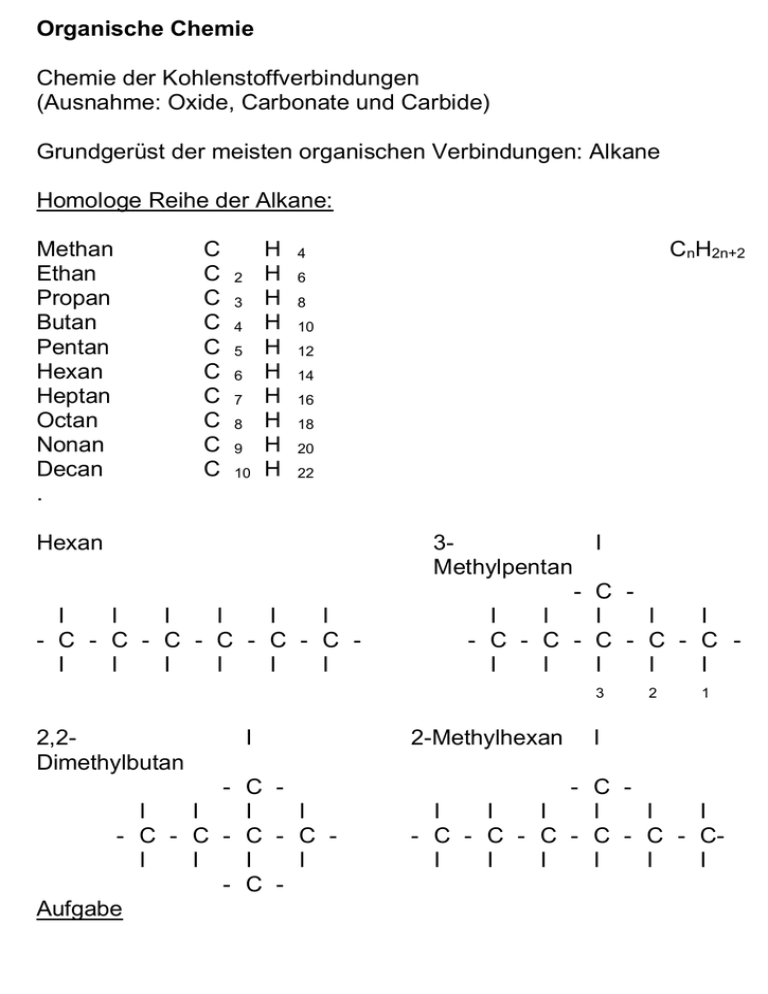
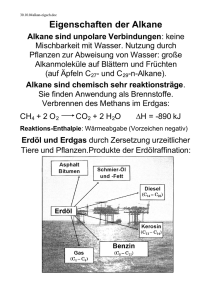
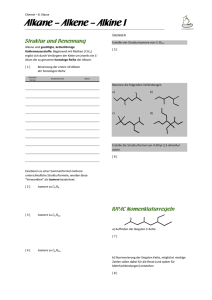
Organische Chemie Chemie der Kohlenstoffverbindungen (Ausnahme: Oxide, Carbonate und Carbide) Grundgerüst der meisten organischen Verbindungen: Alkane Homologe Reihe der Alkane: Methan Ethan Propan Butan Pentan Hexan Heptan Octan Nonan Decan . C C C C C C C C C C 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 H H H H H H H H H H CnH2n+2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 Hexan I I I I I I - C - C - C - C - C - C I I I I I I 3I Methylpentan - C I I I I I - C - C - C - C - C I I I I I 3 2,2Dimethylbutan I - C I I I I - C - C - C - C I I I I - C Aufgabe 2-Methylhexan 2 1 I - C I I I I I I - C - C - C - C - C - CI I I I I I 2,2,4 Trimethylpentan 4-Ethyl-2methylhexan propyloctan Stoffklasse Funktionelle Name Gruppe Alken Zweifachbindung Propen Alkin Dreifachbindung Propin Alkohol Hydroxyl-Gruppe 1-Propanol 3,4-Diethyl 5Strukturformel CH2=CH-CH3 CH=C-CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2OH Ether Methoxy-Gruppe Ethylmethylether CH3-CH2-OCH3 HalogenKW Halogen 1-Chlorpropan CH3-CH2-CH2Cl Amin Amino-Gruppe 1-Propylamin CH3-CH2-CH2NH2 Aldehyd Carbonyl-Gruppe 1-Propanal CH3-CH2-COH Keton Keto-Gruppe Propanon CH3-CO- CH3 Carbonsäure Carboxyl-Gruppe Propansäure CH3-CH2COOH Halogenalkane Werkstoffe: PVC (Polyvinylchlorid), Teflon (Polytetrafluorethen) Wirkstoffe: Insektizide (Lindan Hexachlorcyclohexan), DDT (Dichlordiphenyltrichlorethan) Narkosemittel (Halothan/2Brom2Chlor-1,1,1- trifluorethan) Chloroform (Trichlormethan) Lösungsmittel 1,1,1-Trichlorethan (Reinigung) Dichlormethan (Fette, Öle, Harze, Kunststoff, Lacke) Extraktionsmittel Lebensmittel: Entkoffeinierung) Trichlorfluormethan (Pelz- und Lederreinigung) Treibgase Chlorfluoralkane (Freon, Frigen) Giftigkeit: narkotisierend, Atemlähmend, Herzrhythmusstörungen Leber- und Nierenschäden durch Metaboliten (Membranzerstörung) auch reaktionsträge Halogene Anreicherung im Fettgewebe und Múttermilch Reaktion mit Aminen Veränderung der Zellinformation In Keimzellen mutagene Wirkung