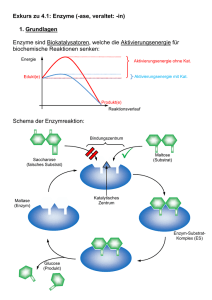
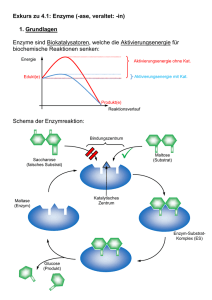
- Karl-Ziegler
Werbung

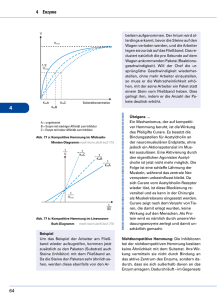
Fachbegriffe zur Zellbiologie/Genetik/ Enzymatik, Stoffwechsel für 10.1/10.2) Mikroskop (plus wesentliche Bestandteile) Elektronenmikroskop Prokaryoten/Eukaryoten Kompartimentierung Zellwand, Zellmembran Doppelmembran Membranprotein Plasmalemma Zytoplasma Vakuole, Tonoplast Plasmolyse, Deplasmolyse Nucleus, Nucleolus Mitochondrium, Chloroplast Ribosom, Dictyosom glattes/rauhes ER Lipid, Kohlenstoffhydrat hydrophil, hydrophob lipohil, lipophob Diffusion Osmose aktiver/passiver Transport Carrier, (Membranfluss) Endozytose/Exozytose Brownsche Molekularbewegung Osmotische Zustandsgleichung osmotischer Druck, hydrostatischer Druck semipermeable/selektiv permeable Membran Konzentrationsgradient/-gefälle hyperton, isoton, hypoton Zellzyklus Mitose Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase Interphase G0/G1/ S-Phase/G2-Phase, Zentromer, Kinetochor Zentrosom, Zentriolen Äquationsteilung, Reduktionsteilung Chromosom, Ein-/Zweichromatidchromosom Chromatide Telomer haploid, diploid DNS/DNA (int.) Purinbasen, Pyrimidinbasen Nucleotid, Nucleosid Aminosäure (Grundstruktur) Aminogruppe, organischer Rest, Carboxylgruppe Peptidbindung Primärstruktur, Sekundärstruktur Tertiärstruktur, Quartärstruktur Alpha-Helix, ß-Faltblatt Optimum (pH, Temp.) Michaelis-Menten Konstante (Keine Berechnung!) Sättigungskurve Protein, Enzym Aktives Zentrum Allosterisches Zentrum kompetitive/nichtkompetitive Hemmung allosterische Hemmung Inhibitor Co-Enzym/Co-Substrat prosthetische Gruppe Glucose, Fettsäuren Glycolyse, ß-Oxidation aerob, anaerob ATP, NAD, FAD, NADP Kreatinphosphat Atmungskette, Zitronensäurezyklus Gärung Phosphorylierung Oxidation/Reduktion Grundumsatz/Leistungsumsatz