Vierfeldertafel und Bayes - bonner
Werbung
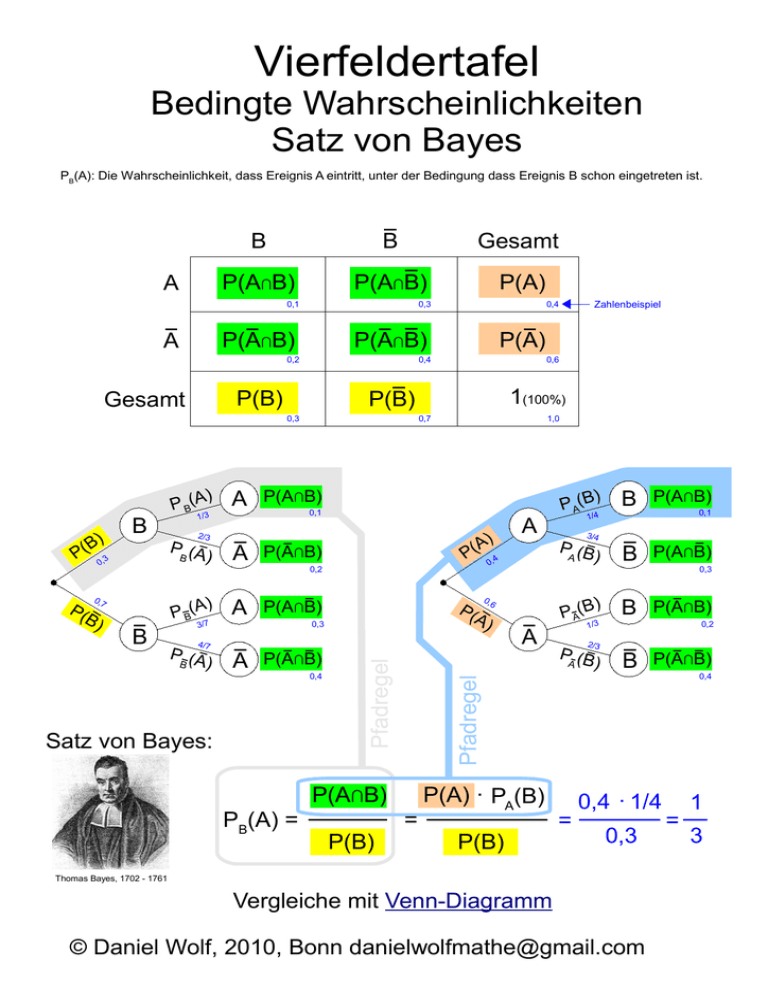
Vierfeldertafel Bedingte Wahrscheinlichkeiten Satz von Bayes PB(A): Die Wahrscheinlichkeit, dass Ereignis A eintritt, unter der Bedingung dass Ereignis B schon eingetreten ist. A B B Gesamt P(A∩B) P(A∩B) P(A) 0,1 0,3 P(A∩B) A P(A∩B) 0,2 0,7 B) B 0,1 ) A P(A∩B) ) P B(A A P(A∩B) 0,2 3/7 4/7 P (A B ) A) P( 0,4 P( 0,3 A P(A∩B) Satz von Bayes: 0,4 P(A∩B) PB(A) = P(B) A A B P(A∩B) B P(A∩B) B P(A∩B) 0,1 1/4 3/4 PA (B ) ) PA(B 0,6 A) ) PA(B 0,3 0,2 1/3 2/3 PA (B ) B P(A∩B) 0,4 Pfadregel P( 2/3 1,0 P(A∩B) 1/3 PB (A 1(100%) 0,7 Pfadregel B) P( 0,3 B A 0,6 P(B) 0,3 ) P B(A P(A) 0,4 P(B) Gesamt Zahlenbeispiel 0,4 = P(A) . PA(B) P(B) = 0,4 . 1/4 0,3 Thomas Bayes, 1702 - 1761 Vergleiche mit Venn-Diagramm © Daniel Wolf, 2010, Bonn [email protected] = 1 3











