MINT-VorKurs Physik - Rechenmethoden
Werbung

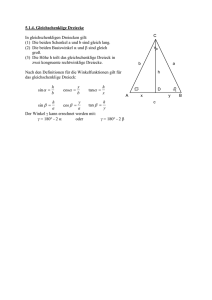
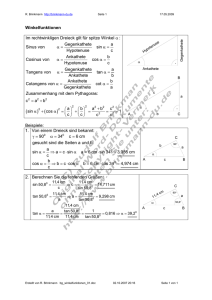
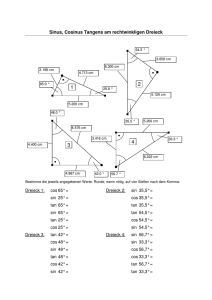
MINT-VorKurs Physik Rechenmethoden 0 Grundlagen 0.1 Zahlen und math. Zeichen Zahlenbereiche Natürliche Zahlen (mit Null) Ganze Zahlen Rationale Zahlen Irrationale Zahlen Reelle Zahlen Komplexe Zahlen Zeichen und Symbole Konstanten (π, e) Variable (x, y, v, T, α, δ, λ, ϕ, ω, ζ) (x1, yk, v3, T12, αik ........) Operatoren (+, -, <, =, lim, Vektoren Matrizen Σ, !,Π) 0.2 Ebener Winkel Winkeldefinition (physikalisch) Winkelvorzeichen Winkelmaße Bogen Grad (Minuten, Sekunden) Umrechnung Bogen - Grad Winkelbereiche Ausblick -> Raumwinkel 0.3 Trigonometrische Funktionen Definition von Sinus, Kosinus, Tangens ....... im rechtwinkligen Dreieck am Einheitskreis Funktionsgraphen (Plotter) Periodizität – Symmetrie Reduktion auf spitze Winkel Wenn: f (x) = sin x dann gilt: cos x tan x cot x f (-x) f (90°-x) = f (π/2 - x) - sin x cos x - tan x - cot x cos x sin x cot x tan x f (90° + x) = f (π/2 + x) cos x - sin x - cot x - tan x f (180° - x) = f (π - x) sin x - cos x - tan x - cot x f (180° + x) = f (π + x) - sin x - cos x tan x cot x f (270° - x) = f (3π/2 - x) - cos x - sin x cot x tan x f (270° + x) = f (3π/2 + x) - cos x sin x - cot x - tan x Additionstheoreme Typ 1: Additionstheoreme für die Summe, Differenz oder Vielfachen von Winkeln, Typ 2: Additionstheoreme für die Summe oder Differenz von Winkelfunktionen. Typ 3: Additionstheoreme für das Produkt von Winkelfunktionen. 0.4 Grundvorrat Funktionen (auch e, ln) Funktionen-Zoo Lineare Funktion (spez. dir. Prop.) Quadratfunktion Potenzfunktion – Potenzreihe Wurzelfunktion Gebrochen rationale Funktionen Trigonometrische Funktionen Exponentialfunktion Logarithmusfunktion Rechenregeln Potenzgesetze (Mehrfachexponenten – Klammersetzung) Logarithmusregeln 0.5 Lösung von Gleichungen/ Gleichungssystemen