x(E − + - füllenbach
Werbung
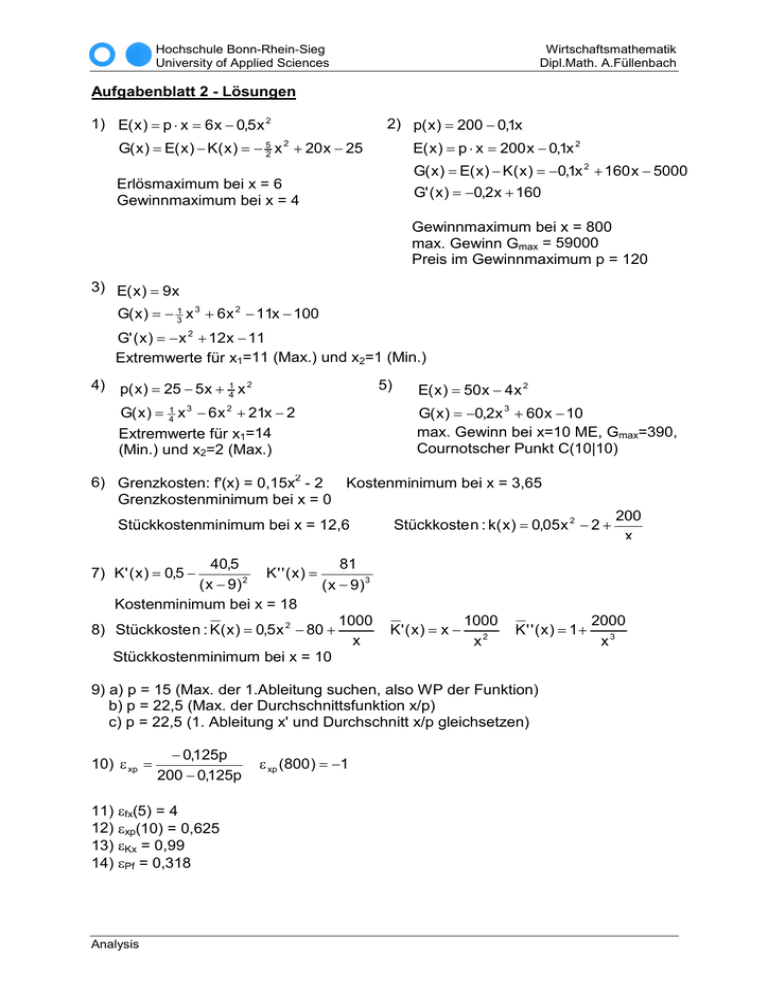
Hochschule Bonn-Rhein-Sieg University of Applied Sciences Wirtschaftsmathematik Dipl.Math. A.Füllenbach Aufgabenblatt 2 - Lösungen 1) E( x ) = p ⋅ x = 6 x − 0,5 x 2 2) p( x ) = 200 − 0,1x G( x ) = E( x ) − K( x ) = − 52 x 2 + 20 x − 25 E( x ) = p ⋅ x = 200 x − 0,1x 2 G( x ) = E( x ) − K( x ) = −0,1x 2 + 160 x − 5000 Erlösmaximum bei x = 6 Gewinnmaximum bei x = 4 Cournotscher Punkt C(4|4) G' ( x ) = −0,2x + 160 Gewinnmaximum bei x = 800 max. Gewinn Gmax = 59000 Preis im Gewinnmaximum p = 120 3) E( x ) = 9 x G( x ) = − 31 x 3 + 6 x 2 − 11x − 100 G' ( x ) = − x 2 + 12 x − 11 Extremwerte für x1=11 (Max.) und x2=1 (Min.) 4) p( x ) = 25 − 5 x + 1 x 2 4 5) G( x ) = 41 x 3 − 6 x 2 + 21x − 2 Extremwerte für x1=14 (Min.) und x2=2 (Max.) E( x ) = 50 x − 4 x 2 G( x ) = −0,2x 3 + 60 x − 10 max. Gewinn bei x=10 ME, Gmax=390, Cournotscher Punkt C(10|10) 6) Grenzkosten: f'(x) = 0,15x2 - 2 Kostenminimum bei x = 3,65 Grenzkostenminimum bei x = 0 Stückkostenminimum bei x = 12,6 40,5 81 K' ' ( x) = 2 ( x − 9) ( x − 9)3 Kostenminimum bei x = 18 1000 8) Stückkoste n : K( x ) = 0,5 x 2 − 80 + x Stückkostenminimum bei x = 10 Stückkoste n : k( x ) = 0,05 x 2 − 2 + 200 x 7) K ' ( x ) = 0,5 − K' ( x ) = x − 1000 x2 K' ' ( x) = 1+ 9) a) p = 15 (Max. der 1.Ableitung suchen, also WP der Funktion) b) p = 22,5 (Max. der Durchschnittsfunktion x/p) c) p = 22,5 (1. Ableitung x' und Durchschnitt x/p gleichsetzen) 10) ε xp = − 0,125p 200 − 0,125p 11) εfx(5) = 4 12) εxp(10) = 0,625 13) εKx = 0,99 14) εPf = 0,318 Analysis ε xp (800 ) = −1 2000 x3